@stefaniehoehl.bsky.social @trinhnguyen.bsky.social @dimitrisbolis.bsky.social @ateshkoul.bsky.social ... Please RT!
04.10.2025 11:47 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Could be of interest to: @introspection.bsky.social @annapzamm.bsky.social @antoniahamilton.bsky.social @yuliagolland.bsky.social @annaciaunica.bsky.social @leoschilbach.bsky.social @yfpan.bsky.social @micahgallen.com @jameskilner.bsky.social @manuelvarlet.bsky.social @alexgalvezpol.bsky.social
04.10.2025 11:47 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
However, the consequences that out-of-phase cardiorespiratory coupling has on the self, and whether it is related to self-regulation, remain unexplored.
04.10.2025 11:47 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
This paper took countless iterations of analysis, presentations, etc., before I dared to write it up (and am still skeptical). Hoping that this will open new conversations regarding effects of interpersonal synchronization on the self.
04.10.2025 11:47 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Amazing, congrats! And so well deserved!
29.09.2025 17:31 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Exciting new paper in Emotion led by @ndersen.bsky.social, showing that heart rate synchrony is enhanced by social closeness and associated with increased subjective arousal during a haunted house experience 🧟🧟♀️!
See 🧵👇:
08.08.2025 10:37 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0

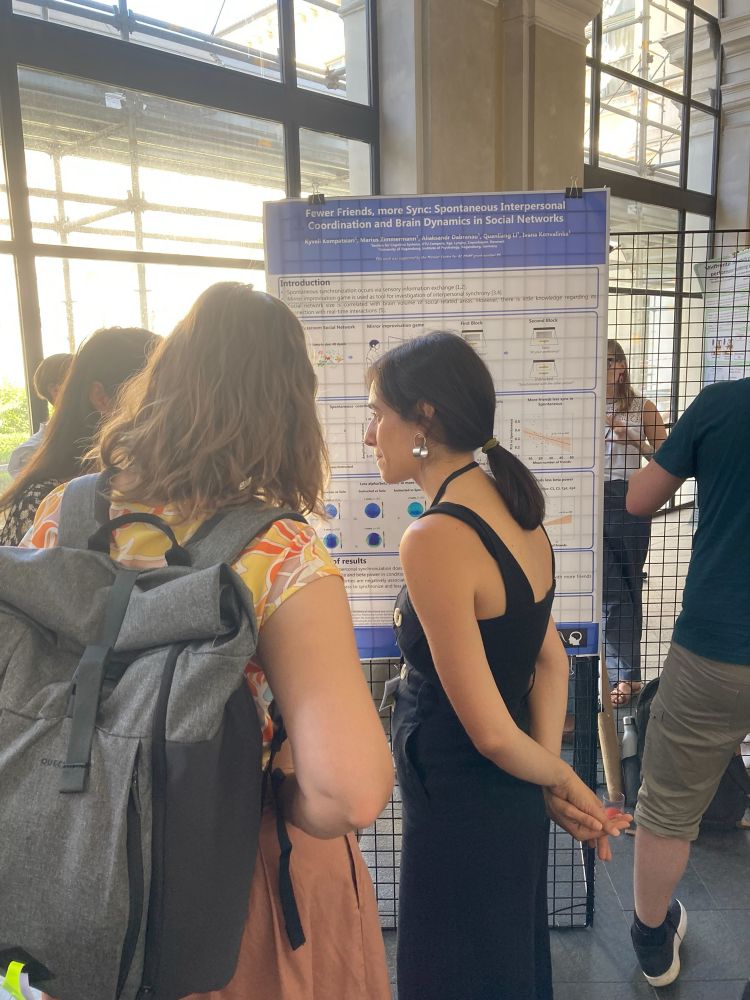
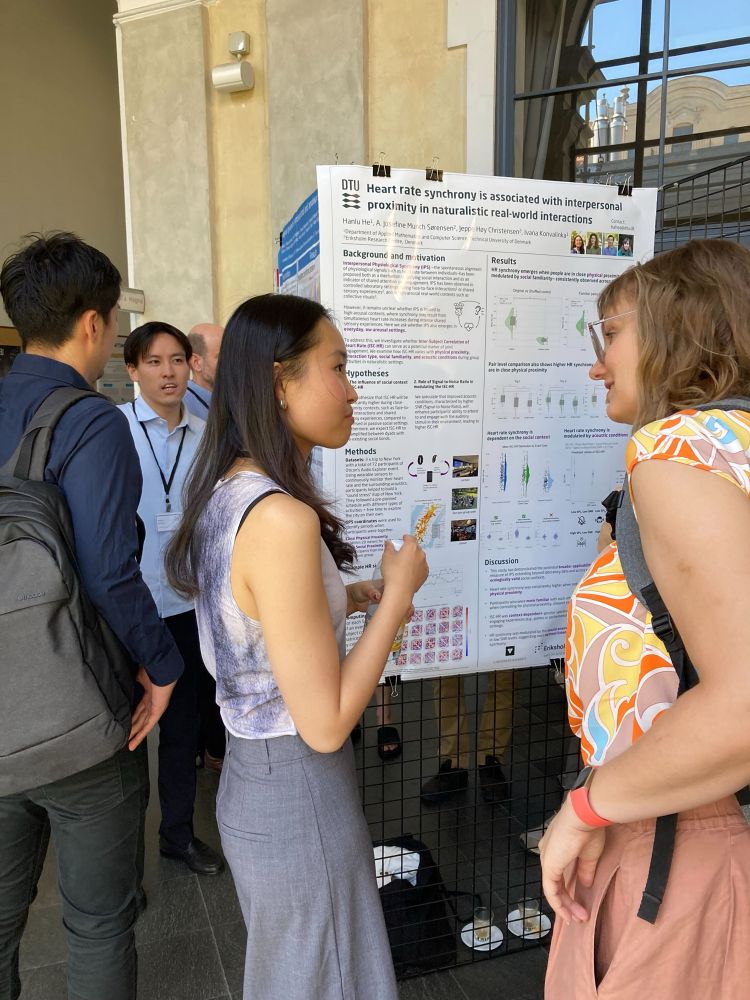
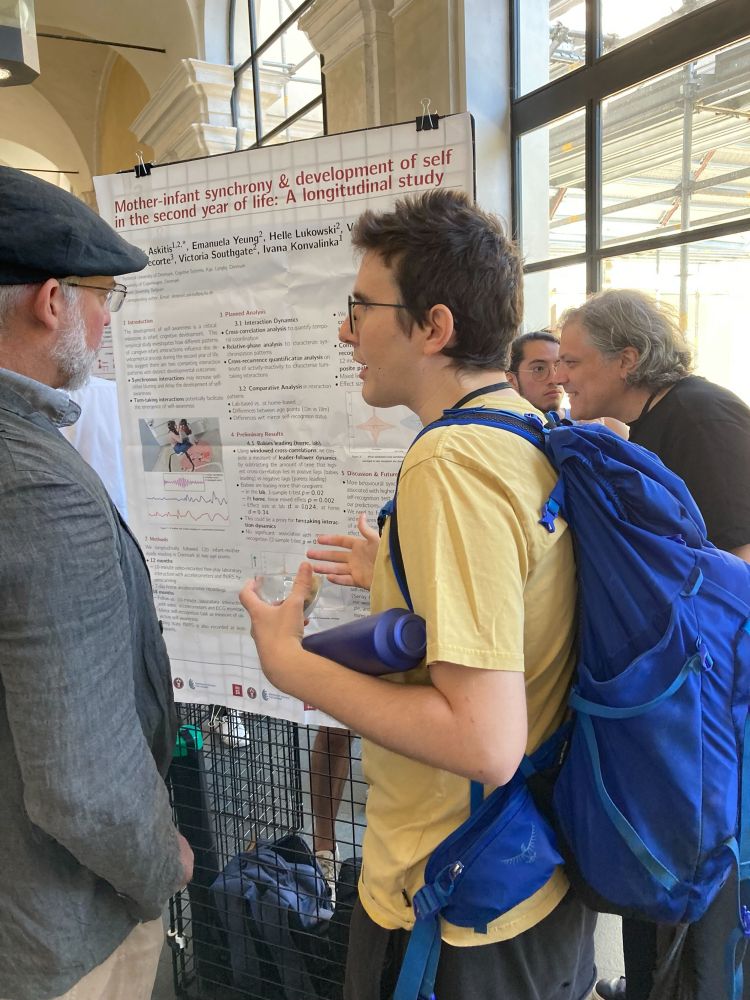 11.07.2025 19:06 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
11.07.2025 19:06 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Only a few days left to apply for a postdoc in social dynamics and complex systems!
Deadline: May 28th. Details 👇
23.05.2025 20:17 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
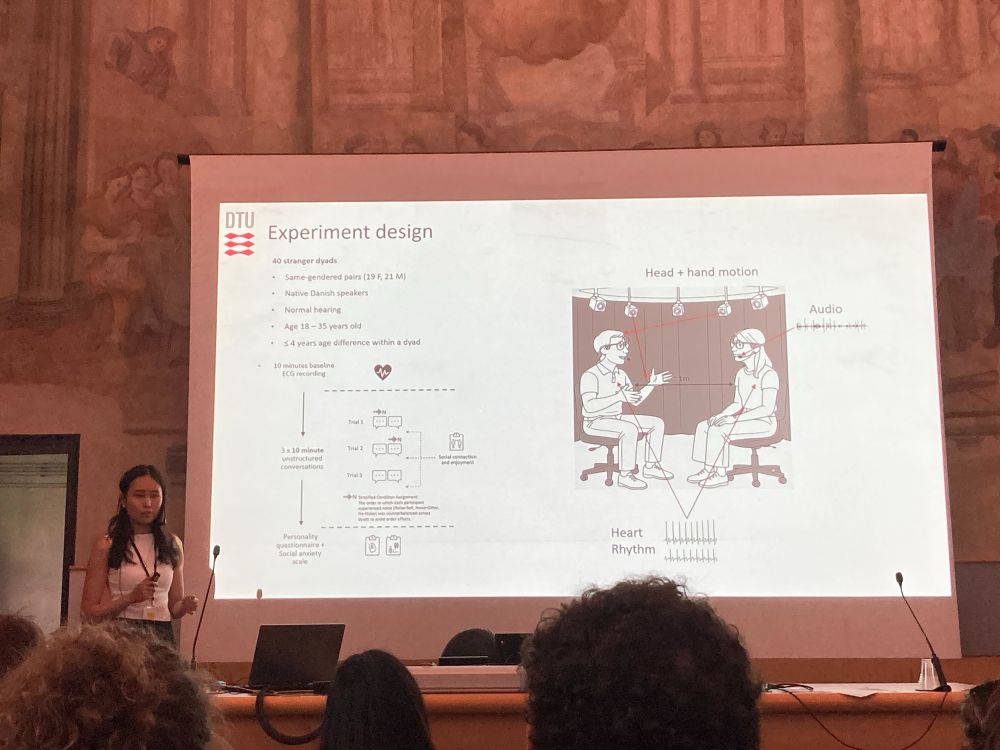
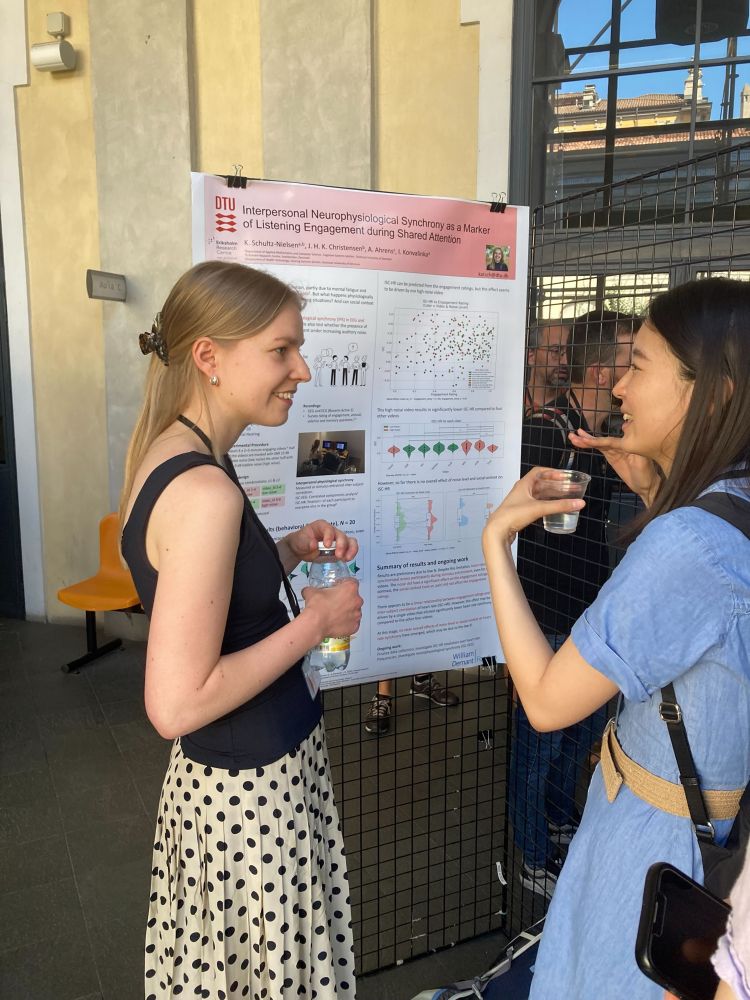
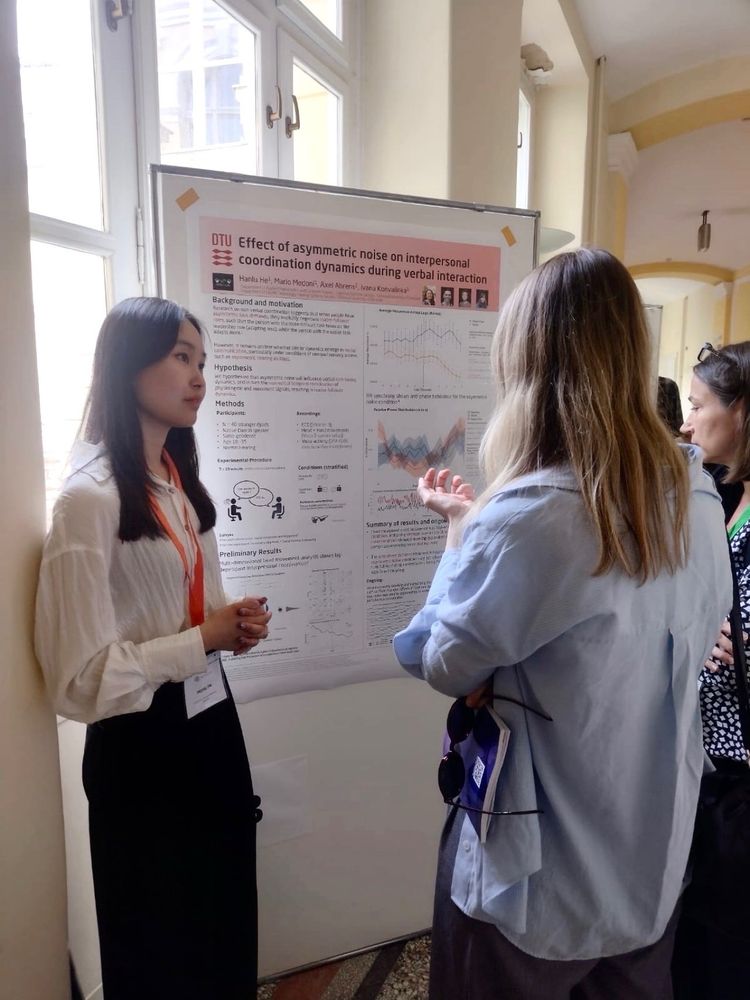
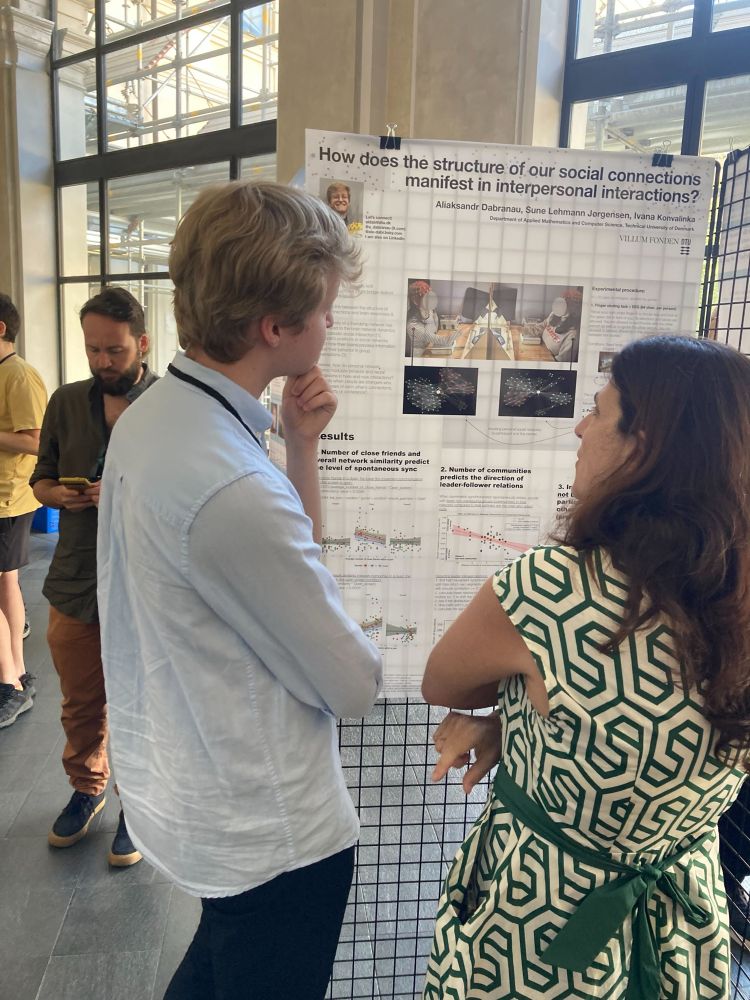
Check out exciting new work from our amazing PhD students @hanluhe.bsky.social and @ale-dabr.bsky.social!
28.04.2025 13:54 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
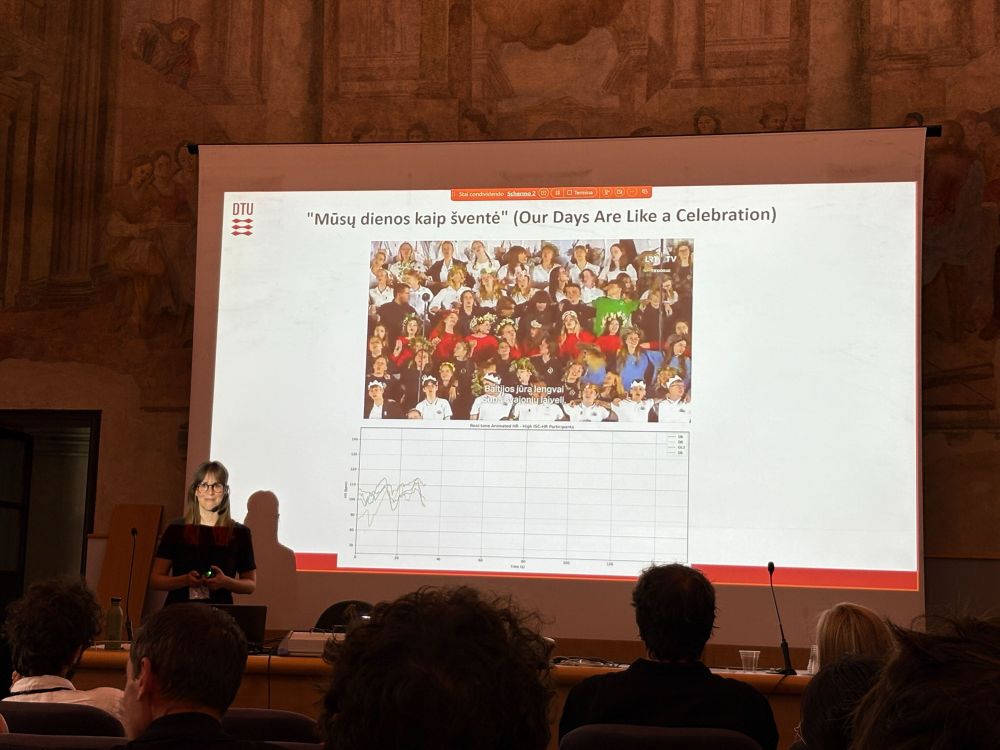
Huge thanks to Hanlu for representing our lab's work and my poster at #SANS2025 🚀
28.04.2025 07:11 — 👍 9 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
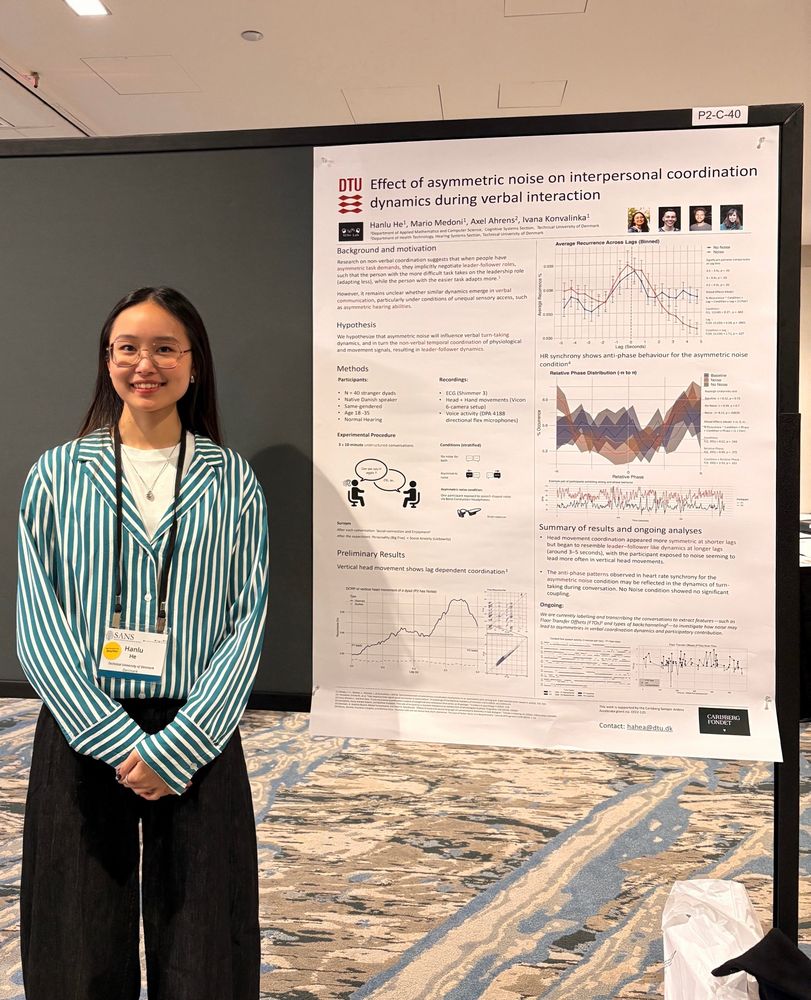
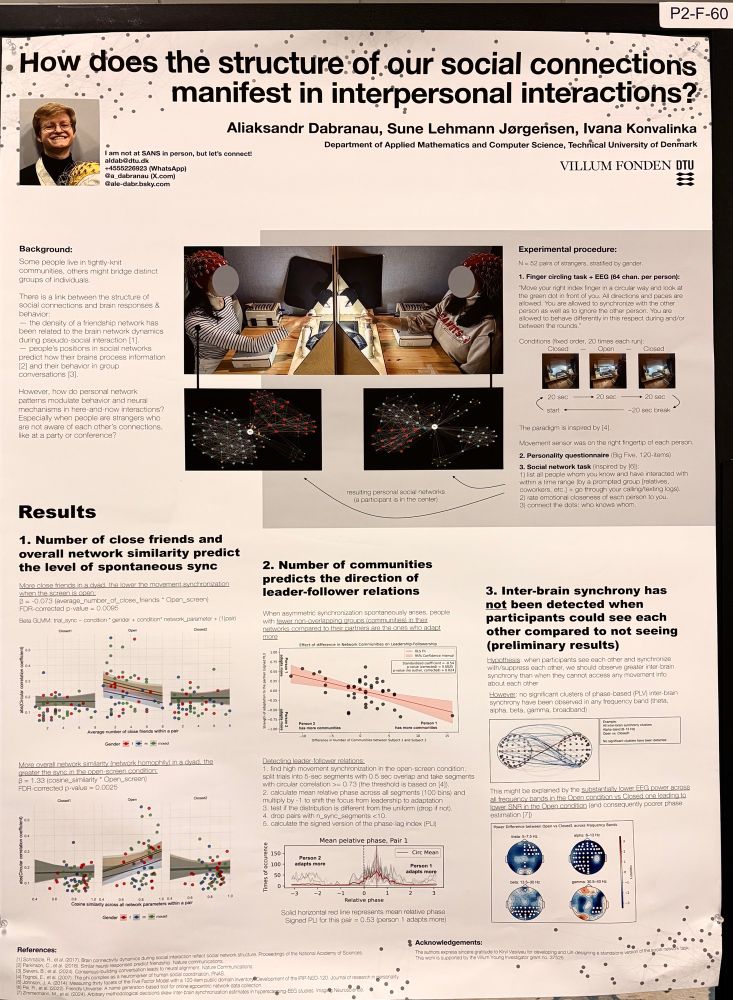
First time at #SANS2025!
Thrilled to hear about all the fascinating work and to present our own from @sinelabdtu.bsky.social
@ale-dabr.bsky.social!
28.04.2025 02:26 — 👍 12 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 2
New job opening in our department, in AI with applications in e.g., the social sciences, neuroscience, etc. Come join us!
01.04.2025 07:16 — 👍 2 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Frontiers | The ConNECT approach: toward a comprehensive understanding of meaningful interpersonal moments in psychotherapy and beyond
🚀 New Paper Alert! 🧠
Excited to share our new perspective paper with Niclas Kaiser
📝 “The ConNECT approach: toward a comprehensive understanding of meaningful interpersonal moments in psychotherapy and beyond”
🔗 Read it here: doi.org/10.3389/fnhu...
19.03.2025 16:45 — 👍 9 🔁 3 💬 1 📌 0

🏆 Embracing #Complexity: Principled and Practical Approaches to #Emergence 🏆
We are delighted to announce a first-of-its-kind workshop on emergence across scientific domains.
Hosted on 23-27 June, 2025, @ #IFISC, Mallorca, Spain
AND, WE WANT YOU TO COME! 🫵
🪧 ABSTRACT SUBMISSIONS OPEN 🪧
Link 👇
13.02.2025 18:38 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
We believe our new hyperscanning-EEG method is well suited for identifying asymmetric neural mechanisms during real-time social interaction. The methodology has an added benefit of being expandable to multi-brain microstates for investigating group interactions.
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
While we acknowledge that two-brain microstates were unable to pick up on interaction-related differences, possibly due to the low-level task, or IBS - probably because microstates focus on global neuronal brain states, overlooking smaller spatially focal synchronised processes....
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
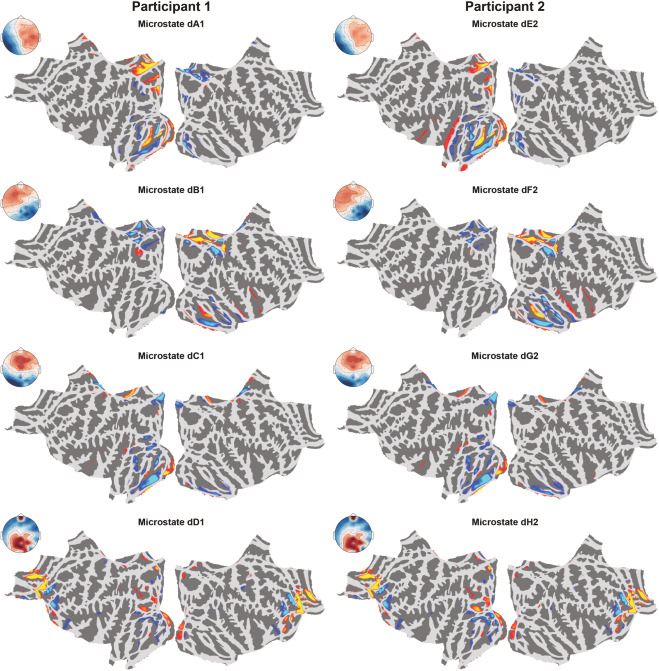
Source localisation indicated that the difference in microstate dynamics between symmetric and asymmetric conditions was likely modulated by a difference in default mode network related activity between the two participants when they took on different interactive roles.
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Pseudo-pairs also showed a significant difference in two-brain microstate dynamics for the asymmetric tasks, and there was no difference in dynamics between the real pairs and the pseudo-pairs, suggesting that the changes were not specific to the interaction, but rather the asymmetric tasks.
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
In order to discern whether the changes in two-brain microstate dynamics were specific to the interaction itself, as opposed to the asymmetric behavioural task, we computed the microstate features for pseudo-pairs (i.e. pairs that did not interact with each other).
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Interestingly, some of the two-brain microstates were similar to the conventionally determined single-brain resting state microstates, e.g. with dA1, dB1, dC1 and dD1 resembling our single-brain microstates A, B, C and E; and dE2, dF2, dG2, and dH2 also resembling A, B, C, and E, respectively.
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
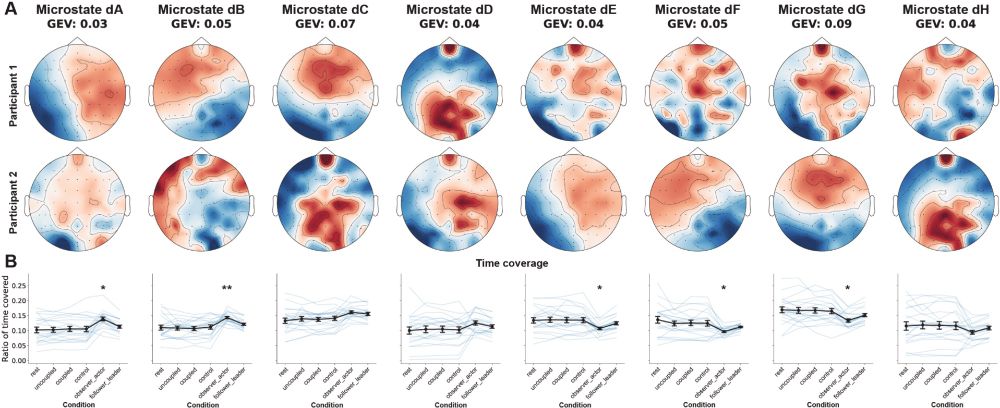
Our key finding: We show that traditional single-brain microstates don’t distinguish interaction conditions—but two-brain microstates do! Asymmetry in brain states emerges in asymmetric social roles (i.e., observer-actor, leader-follower).
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
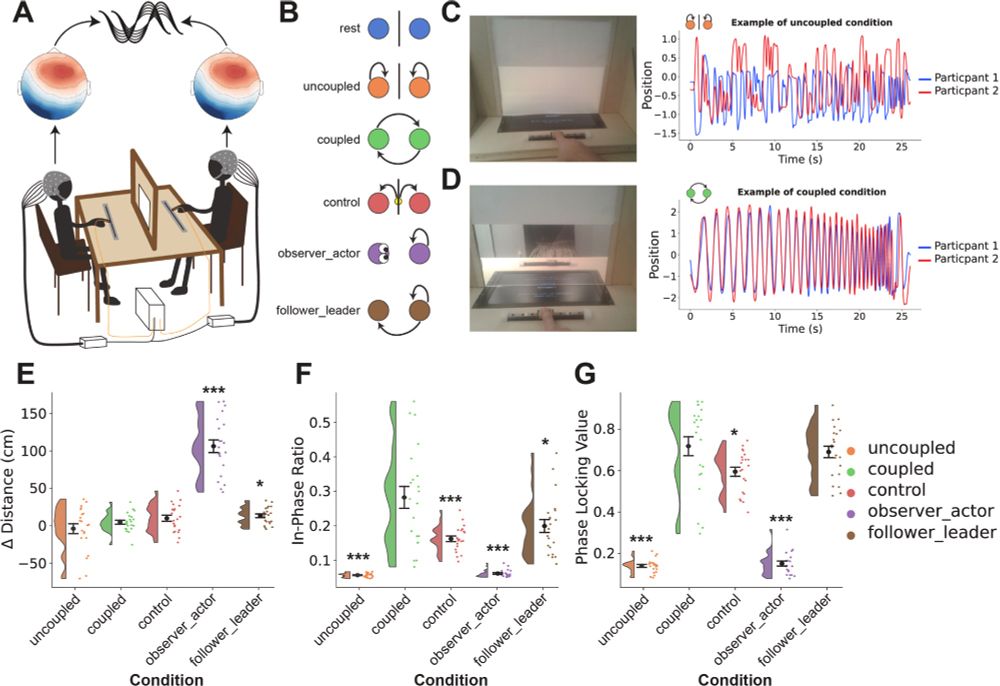
The participants produced movements across a number of interactive (when they could see each other) and non-interactive conditions. They also engaged in two conditions where they had asymmetric tasks (actor/observer) and roles (leader/follower). Data from: royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10....
09.02.2025 16:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Led by @suttonprofessor.bsky.social and Deputy Director Professor Paula Reavey, the Centre is a dynamic, collaborative, interdisciplinary research project advancing knowledge in relations between place and memory - placememory.net
Philosopher at Aarhus University #philsky #philsci https://mariongodman.wordpress.com/
Researching currently: latent variables and kinds in psychology; methods of normative political theory; European perspectives on philosophy of race & ethnicity
Philosopher at the University of Wollongong interested in temporality, technology, and neurodevelopment
VP for Research, T.H. Smoot Professor
Depts Chemical and Biomolecular Engn, Pathology, Oncology, INBT
Johns Hopkins University
3D multi-omic, CAR T therapy, cell migration and mechanics
Lab: https://wirtzlab.johnshopkins.edu
Postdoc in cognitive neuroscience 🧠 at the University of Jyväskylä 🇫🇮 . Previously Ecole Normale Superiéure 🇫🇷 & Maastricht University 🇳🇱
Interested in brain-body interactions, interoception, emotions
Website: www.tahneeengelen.com
Clinical Psychology @ UNC-Chapel Hill | interoception | self-other representation
PhD candidate at the Heart and Brain Center Göttingen.
Trying to understand the influence of the heart on visual perception.
Neuroscientist at EPFL - Swiss Federal Technology Institute of Lausanne
https://fbernasconi.netlify.app/
Assistant Professor of Clinical Couple and Family Psychology at Phillips-Universität Marburg | Psychotherapist | #firstgen | she/her/hers | views are my own
@coupleandfamilylab.bsky.social
PI @bodybrainbehaviour.bsky.social at IBB Muenster (GER) | Here for brain rhythms, body rhythms, and predictive processing in health and disease | ERC StG: 'DYNABODY' (2025)
Life Lover and Scientist. Lecturer and Researcher at the Reichman University: Synchrony. Compassion. Social Playfulness.
Fascinated by the way our biology leads us through life and into each other.
Mathematics Sorceror (sensory alchemist) at the Arctangent Transpetroglyphics Algra Laboratory (ATAL), I transflarnx mathematics into living rainbows. http://owen.maresh.info https://github.com/graveolensa
Psoeppe-Tlaxtlal, (an undreamt splendour?)
Director, Centre for the Sciences of Place & Memory, Stirling Uni, Scotland. Skill, memory, embodied cognition, philosophy, cognitive history, cricket, music, collaborating, wayfinding. Leverhulme International Prof: johnsutton.net & placememory.net
PhD candidate in Cognitive Psychology with @haslagter.bsky.social | Attention, Action, Learning, Memory
PhD researcher in Cognitive Science at Central European University
Social Psych PhD student @ USC studying social learning and interactions
Social Neuroscience | University of Leeds | #Neuroscience #Robotics #HTLab | https://mastodon.social/@letstido
Assistant Professor at the IT University of Copenhagen. Interested in networks, spreading processes, and data science.
Assistant Professor of Psychology
University of Houston
Integrative Program in Developmental, Cognitive, & Behavioral Neuroscience | Texas Institute for Measurement, Evaluation, and Statistics |Texas Center for Learning Disorders
@borjonlab.com
At Heartbond we study heart rate variability synchronisation in pairs and groups, particularly in the performing arts. We have developed technology to study this fascinating phenomenon in real time. www.heartbond.co.uk






 11.07.2025 19:06 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
11.07.2025 19:06 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0