Humans largely learn language through speech. In contrast, most LLMs learn from pre-tokenized text.
In our #Interspeech2025 paper, we introduce AuriStream: a simple, causal model that learns phoneme, word & semantic information from speech.
Poster P6, tomorrow (Aug 19) at 1:30 pm, Foyer 2.2!
19.08.2025 01:12 — 👍 52 🔁 10 💬 1 📌 1

1/7 If you're at CogSci 2025, I'd love to see you at my talk on Friday 1pm PDT in Nob Hill A! I'll be talking about our work towards an implemented computational model of noisy-channel comprehension (with @postylem.bsky.social, Ted Gibson, and @rplevy.bsky.social).
31.07.2025 17:55 — 👍 18 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 0
Great question! We have not directly compared. SMC offers a test-time approach to steer off-the-shelf models without additional training, whereas diffusion forcing trains autoregressive models to more effectively sample from the global target. These strategies can actually likely be combined.
13.05.2025 17:28 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
And check out the following papers, which set the technical landscape for this work to build on:
Lew et al (2023): arxiv.org/abs/2306.03081
Loula et al (2025): arxiv.org/abs/2504.13139
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Thanks to Ben LeBrun, @vigly.bsky.social bsky.social, @joaoloula.bsky.social sky.social, @drmaciver.bsky.social aciver.bsky.social, Li Du, Jason Eisner, Ryan Cotterell, Vikash Mansinghka, Tim O'Donnell, @alexlew.bsky.social ky.social, @xtimv.bsky.social
Paper Link: arxiv.org/abs/2504.05410
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Want to use AWRS SMC?
Check out the GenLM control library: github.com/genlm/genlm-...
GenLM supports not only grammars, but arbitrary programmable constraints from type systems to simulators.
If you can write a Python function, you can control your language model!
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

Why does AWRS work?
Formal and empirical runtime analyses tell a fascinating story.
AWRS scales adaptively with the KL divergence between the conditional and base token-level models.
As your LM better understands the constraint, AWRS gets faster.
As the LM struggles, AWRS closes the gap.
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We tested AWRS SMC on several controlled generation tasks, from text-to-SQL to PDDL goal inference to molecular synthesis.
AWRS SMC outperforms baselines by large margins, e.g., see the jump from 3% -> 53% in the goal inference domain with only ~2.5x clock time overhead.
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Next, SMC uses the proposed extensions and corresponding weights from AWRS to update importance weights associated with partial sequences (particles).
These particles are resampled proportional to their weights, re-allocating computation towards the most promising sequences.
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

First, AWRS reformulates the token-level inference problem from exact enumeration to adaptive rejection sampling.
This process yields equivalently distributed samples at a fraction of the cost.
AWRS then estimates and propagates an importance weight alongside these samples.
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

So, what can we do?
AWRS SMC is a hierarchical inference framework based on sequential Monte Carlo using a novel stochastic proposal algorithm.
By jointly considering local and global signals, AWRS SMC is both probabilistically sound and sample efficient.
How does it work?
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Problem B: LCD distorts the distribution.
Consider this simple LM over the tokens `a` and `b` with the constraint that “strings must end with `a`”.
While the distribution on complete strings favors `ba`, autoregressive sampling will favor `ab`.
We don’t want this.
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Problem A: Token masking is often slow.
Must classify all 100,000+ tokens in the vocab at each step.
While regular and context-free grammars support low-overhead solutions using tools like Outlines (dottxtai.bsky.social), open-ended constraint enforcement has been harder.
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Approach 2: Locally constrained decoding (LCD).
At each step, mask the next-token distribution to prevent violations.
Pros: All samples are constraint-satisfying.
Cons: A) Masking a large vocabulary is slow. B) LCD distorts the sampled distribution.
Example:
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Approach 1: Sample-verify/Best-of-N.
Draw 𝑁 strings from the LM and use the constraint to rank/filter.
Pros: Samples 𝑥 ∝ 𝑃 as 𝑁 grows.
Cons: 𝑁 required to get a target sample scales exp(KL[𝑃||𝑄]). For difficult constraints, this becomes infeasible.
Example:
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Consider a prompted language model 𝑄 (a prior) and a constraint function 𝐶 (a likelihood).
Our goal is to sample a string 𝑥 from the conditional distribution 𝑃 = 𝑄(·|𝐶(𝑥)=1) (the target posterior).
How do people do this now, and why do current approaches fall short?
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Many LM applications may be formulated as text generation conditional on some (Boolean) constraint.
Generate a…
- Python program that passes a test suite.
- PDDL plan that satisfies a goal.
- CoT trajectory that yields a positive reward.
The list goes on…
How can we efficiently satisfy these? 🧵👇
13.05.2025 14:22 — 👍 12 🔁 6 💬 2 📌 0
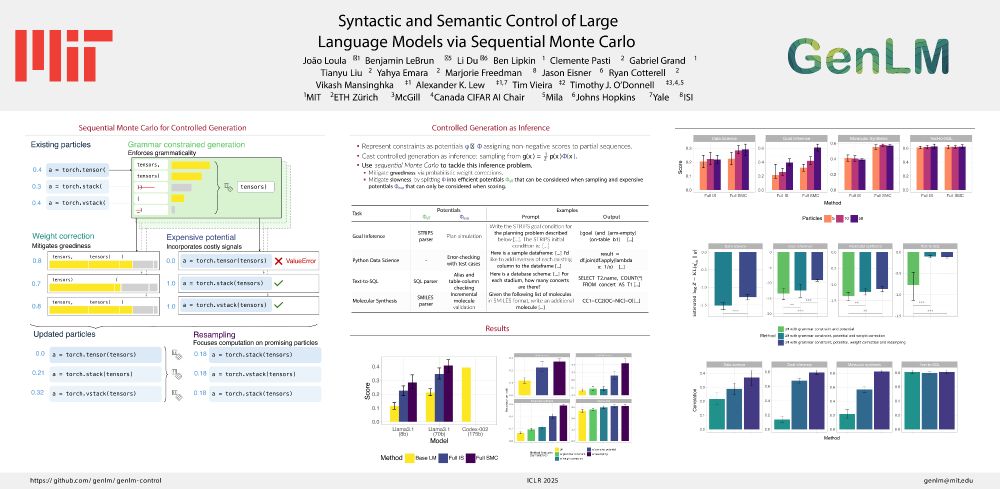
#ICLR2025 Oral
How can we control LMs using diverse signals such as static analyses, test cases, and simulations?
In our paper “Syntactic and Semantic Control of Large Language Models via Sequential Monte Carlo” (w/ @benlipkin.bsky.social,
@alexlew.bsky.social, @xtimv.bsky.social) we:
25.04.2025 19:33 — 👍 7 🔁 6 💬 1 📌 0
I might be able to hire a postdoc for this fall in computational linguistics at UT Austin. Topics in the general LLM + cognitive space (particularly reasoning, chain of thought, LLMs + code) and LLM + linguistic space. If this could be of interest, feel free to get in touch!
21.04.2025 15:56 — 👍 60 🔁 31 💬 0 📌 1

Syntactic and Semantic Control of Large Language Models via...
A wide range of LM applications require generating text that conforms to syntactic or semantic constraints. Imposing such constraints can be naturally framed as _probabilistic conditioning_, but...
Jason Eisner & Li Du’s “Syntactic and semantic control of large language models via sequential Monte Carlo” with @joaoloula.bsky.social, @benlipkin.bsky.social, @yahyaemara.bsky.social, @alexlew.bsky.social, @xtimv.bsky.social, & more presents an architecture for controlled LM generation: (11/12)
21.04.2025 16:44 — 👍 5 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0

The cerebellar components of the human language network
The cerebellum's capacity for neural computation is arguably unmatched. Yet despite evidence of cerebellar contributions to cognition, including language, its precise role remains debated. Here, we sy...
New paper! 🧠 **The cerebellar components of the human language network**
with: @hsmall.bsky.social @moshepoliak.bsky.social @gretatuckute.bsky.social @benlipkin.bsky.social @awolna.bsky.social @aniladmello.bsky.social and @evfedorenko.bsky.social
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
1/n 🧵
21.04.2025 15:19 — 👍 50 🔁 20 💬 2 📌 3
Big thanks to this awesome team: Ben LeBrun, @postylem.bsky.social, @joaoloula.bsky.social, @drmaciver.bsky.social, Li Du, Jason Eisner, Ryan Cotterell, Vikash Mansinghka, Tim O'Donnell, @alexlew.bsky.social, @xtimv.bsky.social
10.04.2025 19:19 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
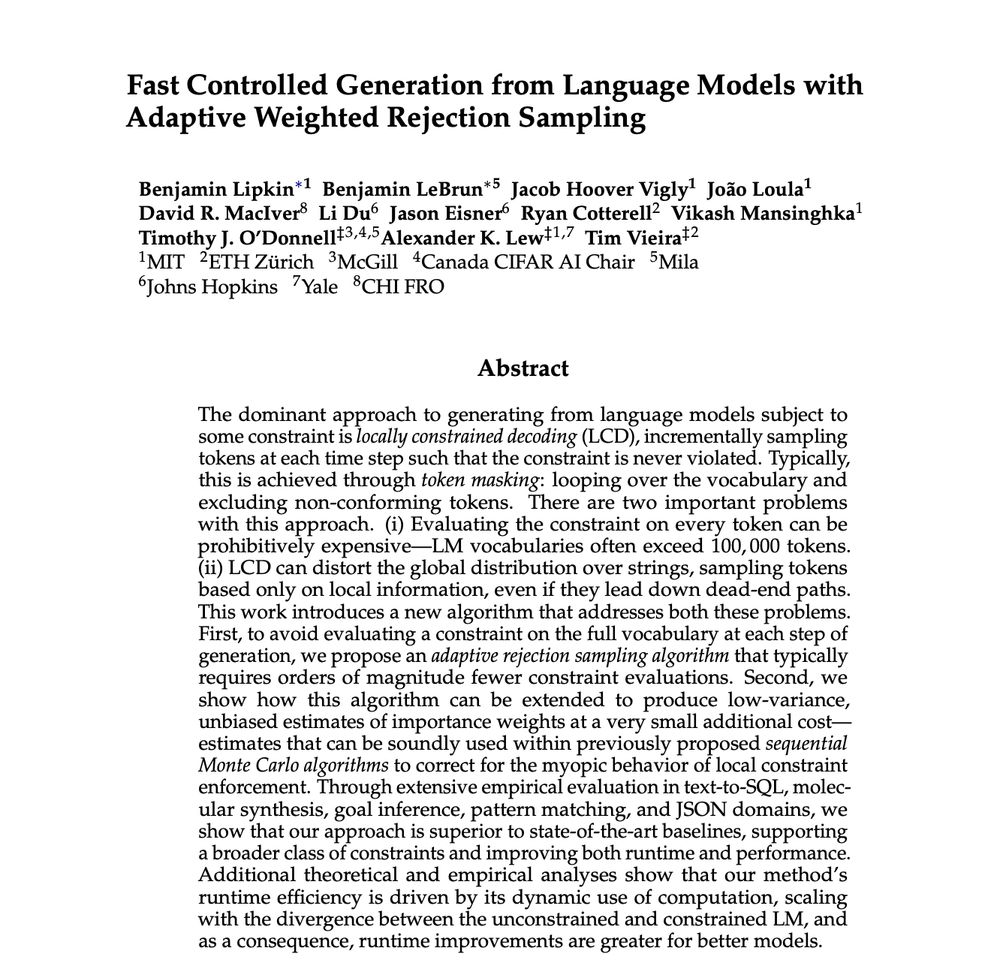
New preprint on controlled generation from LMs!
I'll be presenting at NENLP tomorrow 12:50-2:00pm
Longer thread coming soon :)
10.04.2025 19:19 — 👍 20 🔁 9 💬 1 📌 0

I defended my PhD at MIT Brain&Cog last week--so much gratitude to my advisor @evfedorenko.bsky.social, as well as my committee @nancykanwisher.bsky.social, @joshhmcdermott.bsky.social and Yoon Kim. Thank you to all my brilliant collaborators and the MIT community. I have loved this journey so much.
15.12.2024 15:13 — 👍 99 🔁 6 💬 5 📌 0

Probabilistic and differentiable programming at Yale — fully funded PhD positions starting Fall 2025! Apply by Dec. 15.
Do a PhD at the rich intersection of programming languages and machine learning.
If you're interested in a PhD at the intersection of machine learning and programming languages, consider applying to Yale CS!
We're exploring new approaches to building software that draws inferences and makes predictions. See alexlew.net for details & apply at gsas.yale.edu/admissions/ by Dec. 15
08.12.2024 16:27 — 👍 72 🔁 22 💬 1 📌 2
If this sounds useful for your work, feel free to reach out, and I’m happy to explore with you how `decoding` can best support your use cases
The goal is for this library to be generally useful for researchers across the LLM landscape
7/7
25.11.2024 16:19 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Check out the tutorial to see some examples in action: github.com/benlipkin/de...
The library is fully documented: benlipkin.github.io/decoding/dec...
And available for installation on PyPi: pypi.org/project/deco...
6/7
25.11.2024 16:19 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Researchers write arbitrary Python code and focus on expressing the core of their algorithms while deferring engineering details to the library
With access to the right set of primitives, it becomes simple to express the ideas of many papers in a few dozen lines of code
5/7
25.11.2024 16:19 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Machine learning & statistics researcher @ Flatiron Institute. Posts on probabilistic ML, Bayesian statistics, decision making, and AI/ML for science.
www.dianacai.com
PhD student @csail.mit.edu 🤖 & 🧠
Building Astral: Ruff, uv, and other high-performance Python tools, written in Rust.
CS PhD student at UT Austin in #NLP
Interested in language, reasoning, semantics and cognitive science. One day we'll have more efficient, interpretable and robust models!
Other interests: math, philosophy, cinema
https://www.juandiego-rodriguez.com/
I read a lot of research.
Currently reading: https://dmarx.github.io/papers-feed/
Statistical Learning
Information Theory
Ontic Structural Realism
Morality As Cooperation
Epistemic Justice
YIMBY, UBI
Research MLE, CRWV
Frmr FireFighter
Asst Prof. @ UCSD | PI of LeM🍋N Lab | Former Postdoc at ETH Zürich, PhD @ NYU | computational linguistics, NLProc, CogSci, pragmatics | he/him 🏳️🌈
alexwarstadt.github.io
CS PhD @utaustin.bsky.social
vision lab @ harvard
[i am] unbearably naive
MIT Brain and Cognitive Sciences
Post-doc @ University of Trento. I did my PhD @ University of Trento and the University of Pisa. I like #concepts, #symbols, and #representations, but I still don't know what they are.
📍 Trento, Italy
🧵 #identifiability, #shortcuts, #interpretability
Incoming assistant professor at TTIC, current faculty fellow at NYU, and previous PhD student at Berkeley. Natural language processing. He/him.
🌐 nickatomlin.github.io
Explainability, Computer Vision, Neuro-AI.🪴 Kempner Fellow @Harvard.
Prev. PhD @Brown, @Google, @GoPro. Crêpe lover.
📍 Boston | 🔗 thomasfel.me
http://timvieira.github.io/blog
PhD student @probcompproj and @MITCoCoSci, working on scaling data science using probabilistic programming.
PhD student at Harvard/MIT working with @evfedorenko.bsky.social @nancykanwisher.bsky.social | interested in neuroscience, language, AI | @kempnerinstitute.bsky.social @mitbcs.bsky.social | coltoncasto.github.io
Postdoc at MIT BCS, interested in language(s) in humans and LMs
https://andrea-de-varda.github.io/


















