Pathways to Neurosciences
The Pathways to Neurosciences program fosters belonging, excellence, and leadership in the next
We’re excited to share that Maylin Fu, Ph.D. student in the Qi Lab, has been accepted into the NIH-funded Pathways to Neurosciences program at Stanford, supported by the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute. #Neuroscience #QiLab #WuTsaiNeuroscienceInstitute
neuroscience.stanford.edu/programs/pro...
02.09.2025 22:24 — 👍 4 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
Beyond maps to mechanisms, this new list of comprehensive aging signatures offers biomarkers of aging status and targets to engineer for better anti-aging therapies without altering core cell identity. #CellTherapy #Aging
06.08.2025 17:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

We integrated 405 GWAS datasets and found that CRISPRi-defined inflammaging genes are significantly enriched for heritability of aging traits across diverse organ systems. #GWAS #Aging
06.08.2025 17:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We discovered and validated inflammaging-specific drivers including EIF2AK2, SERPING1, HMGCS2, CMKLR1. Inhibiting them blunts IL-6-associated senescence while maintaining cell identity.
06.08.2025 17:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Mitochondrial pathway emerges as top hits: SAMM50 and AK2 act as pro-aging genes and CRISPRi knockdown reduces aging biomarkers on stem cells while preserving cell identity (CD29/CD44/CD73/CD90).
06.08.2025 17:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0


Two screens for two aging states: replicative senescence (RSS) and IL-6–driven inflammaging (ISS). Positive-selection CRISPRi reveals novel regulators you can modulate without breaking MSC identity to alter their aging state.
06.08.2025 17:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We’re happy to share our new paper in Genome Biology led by Lingling Wu and Xiang Wu, in collaboration with Xueqiu Lin lab at Fred Hutch. Parallel whole-genome CRISPRi screens in primary human MSCs map distinct regulators of aging processes across organs. #Aging #CRISPRi #Senescence
06.08.2025 17:54 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
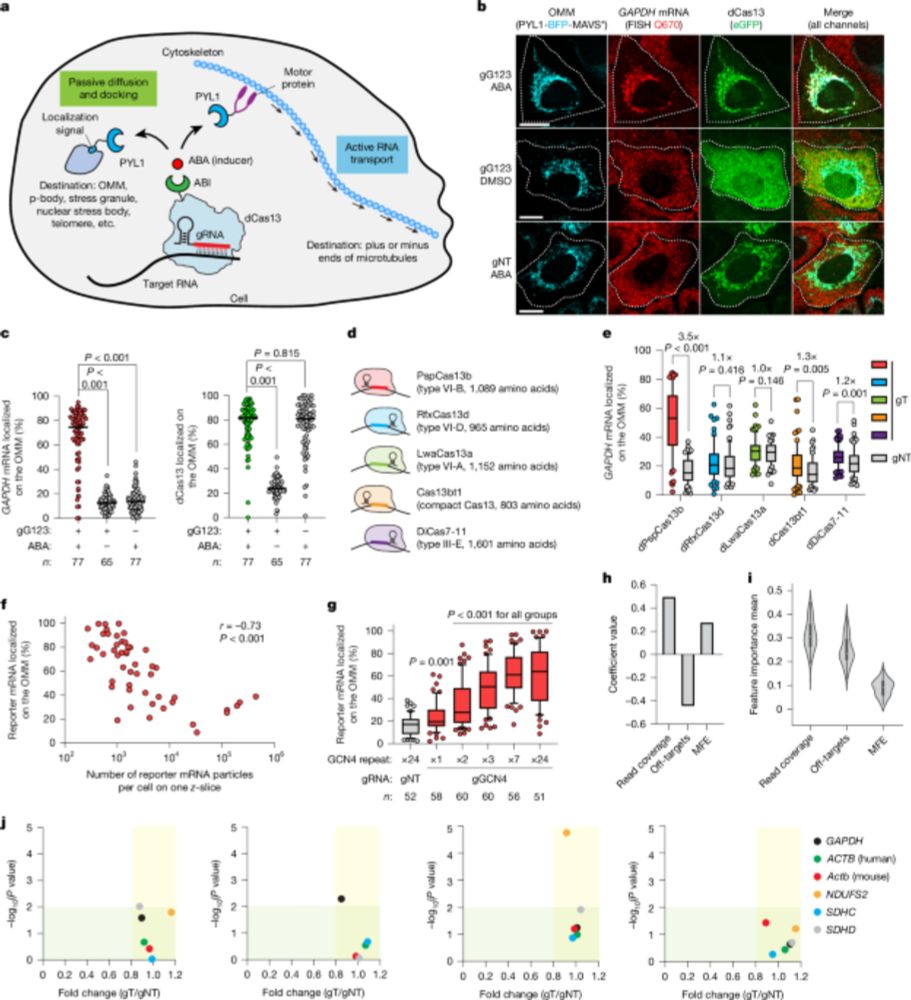
CRISPR-TO bridges a critical gap left by sequencing and imaging technologies and will greatly accelerate the functional study of spatial transcriptome in the future.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
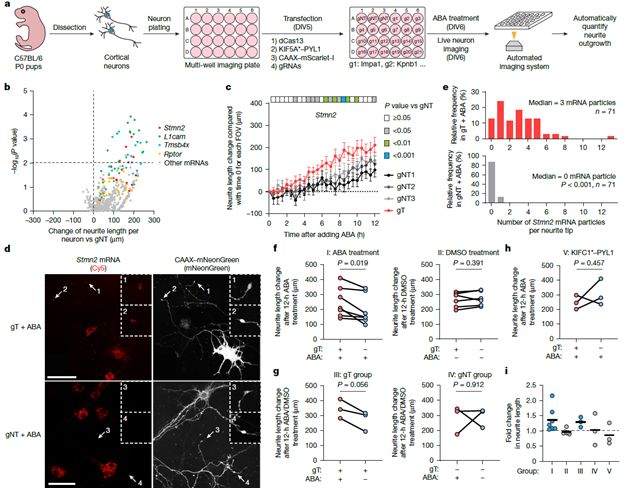
CRISPR-TO-enabled screening in primary neurons identifies Stmn2 mRNA localization as a driver of neurite outgrowth.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
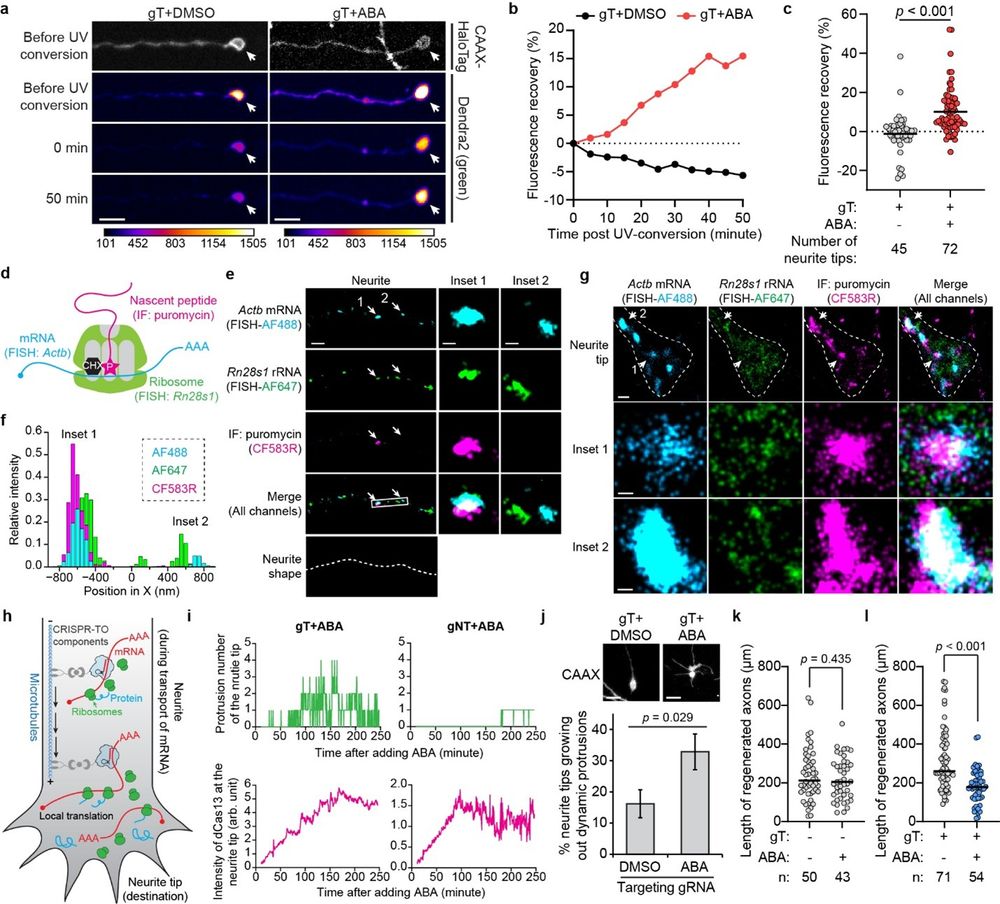
In primary cortical neurons, we demonstrate that repositioned mRNAs undergo local translation, which regulates neuronal morphology and axonal regeneration.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
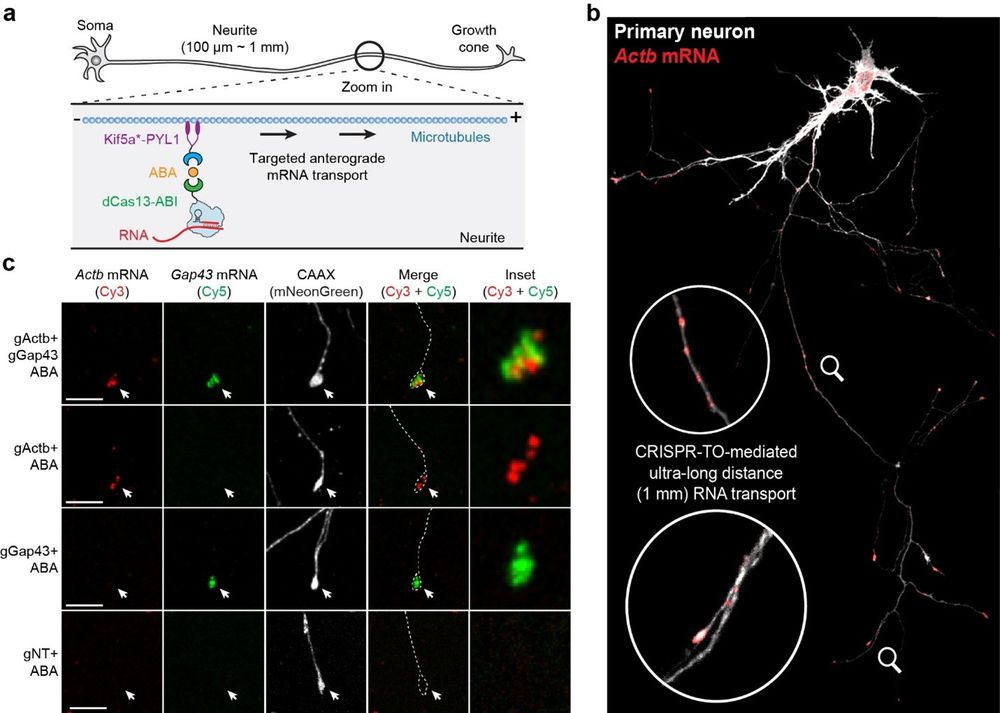
CRISPR-TO effectively functions in primary neurons for ultra-long distance RNA transport, in which spatial transcriptomes are crucially linked to pathological processes.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
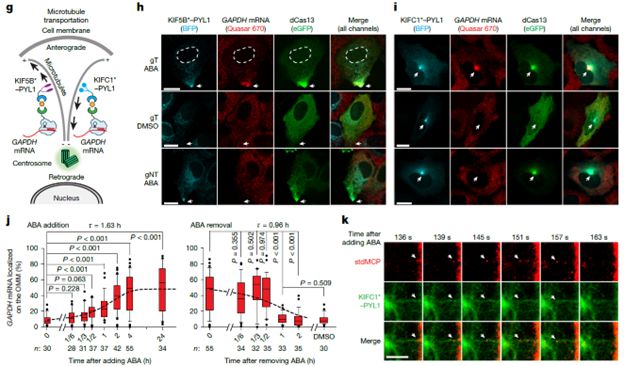
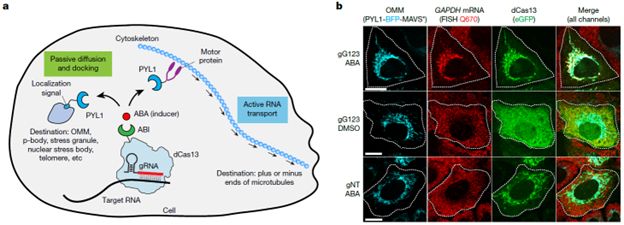
It allows for inducible and reversible bidirectional RNA transport along microtubules via motor proteins.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
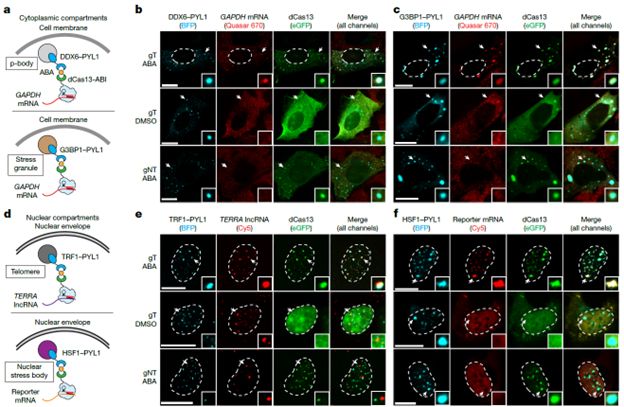
CRISPR-TO enables targeted localization of endogenous RNAs to diverse subcellular compartments.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Spatial RNA organization has a pivotal role in diverse cellular processes and diseases. However, its functional implications remain largely unexplored due to limited technologies for perturbing endogenous RNA localization.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Spatial RNA organization has a pivotal role in diverse cellular processes and diseases. However, its functional implications remain largely unexplored due to limited technologies for perturbing endogenous RNA localization.
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Thrilled to share our paper in
@nature.com led by @MengtingHan123
on CRISPR-TO technology, which paves the way for treatments for neurodegenerative diseases by precisely delivering therapeutic RNA to the damaged sites. A 🧵@Stanford_ChEMH, @bioe_stanford, @Stanford
26.05.2025 01:02 — 👍 0 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
We look forward to seeing further applications enabled by the technology! 🔬
16.04.2025 23:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
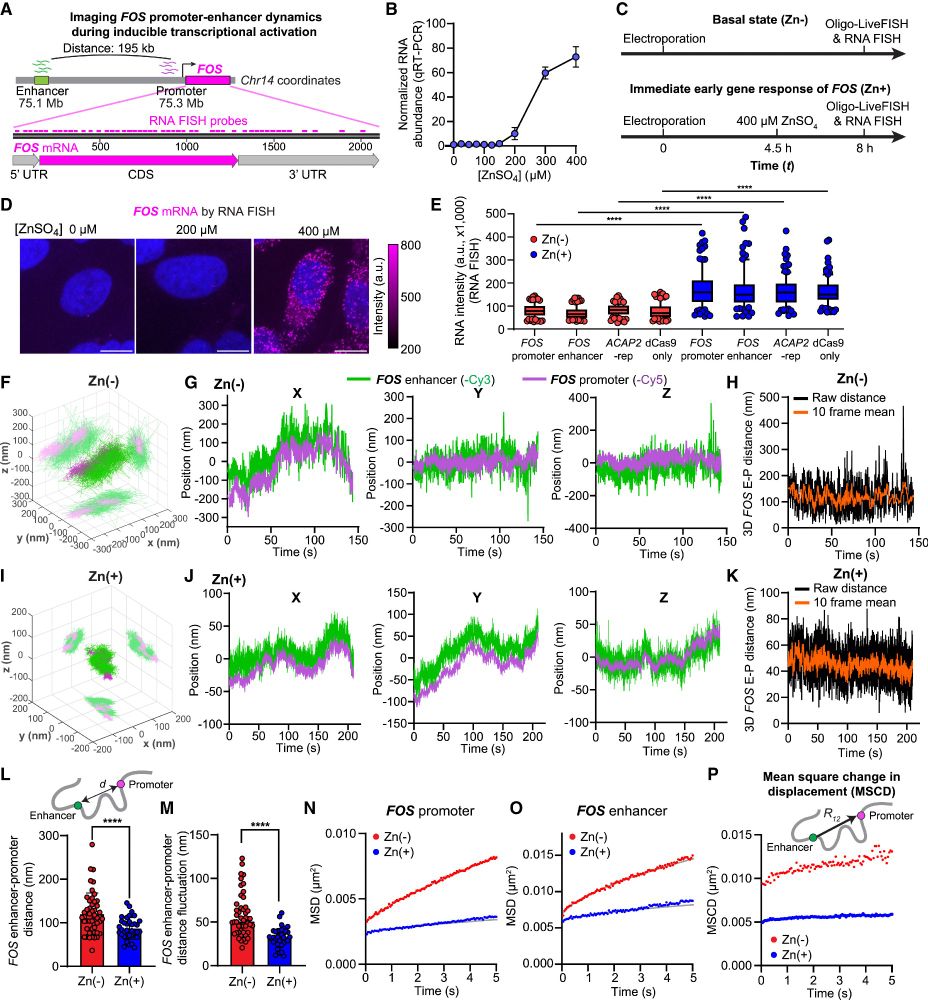
Applying Oligo-LiveFISH to study enhancer-promoter interaction, we found that stimulating FOS transcription led to reduced 3D distance, increased confinement, and slower dynamics between the FOS enhancer and promoter.
16.04.2025 23:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
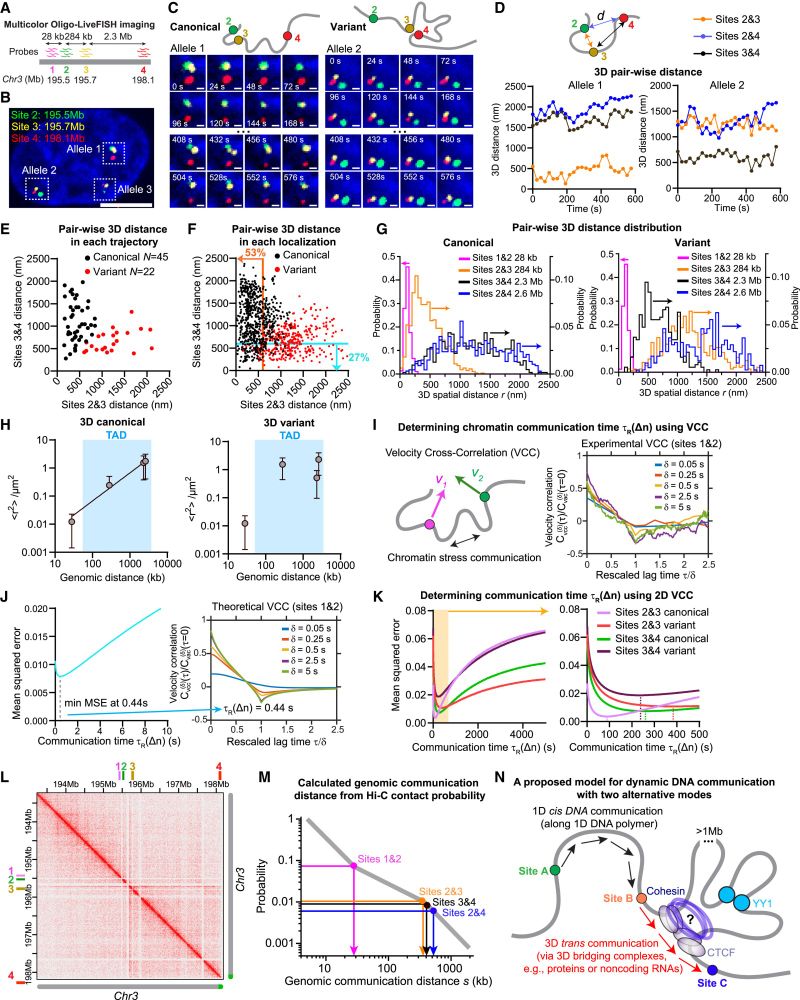
Combined with polymer-based dynamic modeling, Oligo-LiveFISH revealed two distinct modes of chromatin communication: 1D cis-communication, predominated at short distances (up to 300 kb), and 3D trans-communication, which is significant over long distances (> 1 Mb).
16.04.2025 23:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
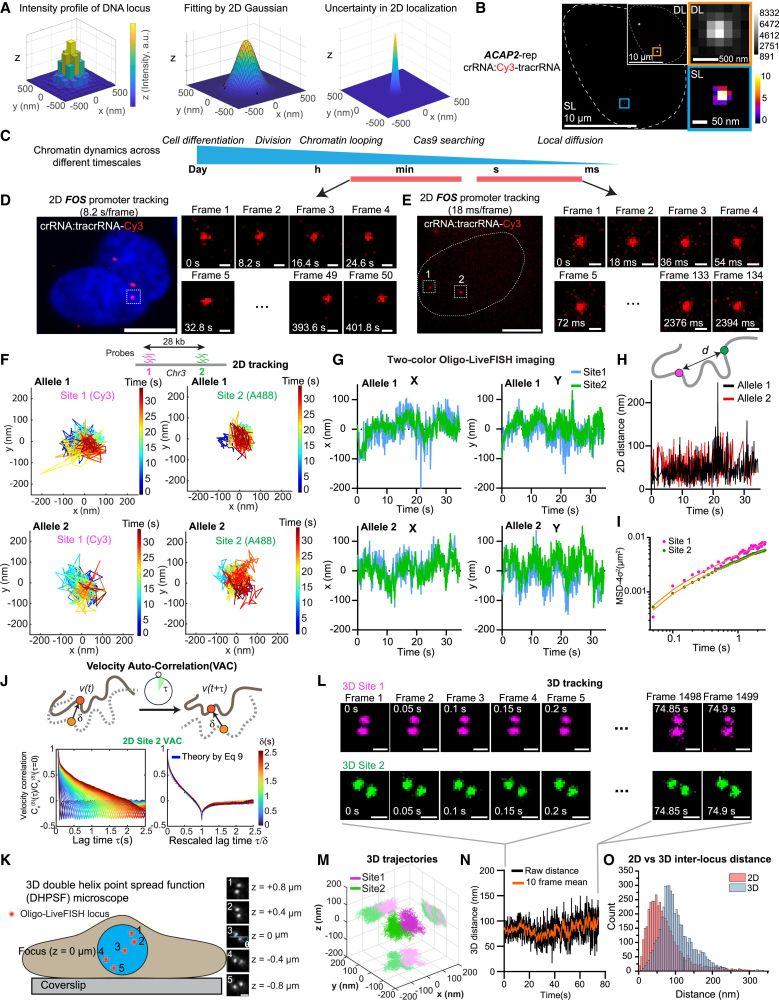
Integrated with 3D super-localization microscopy, Oligo-LiveFISH tracked genomic regions at high spatial (20-nm) and temporal (50-ms) resolution, revealing highly sub-diffusive chromatin motion consistent with fractional Brownian motion.
16.04.2025 23:41 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
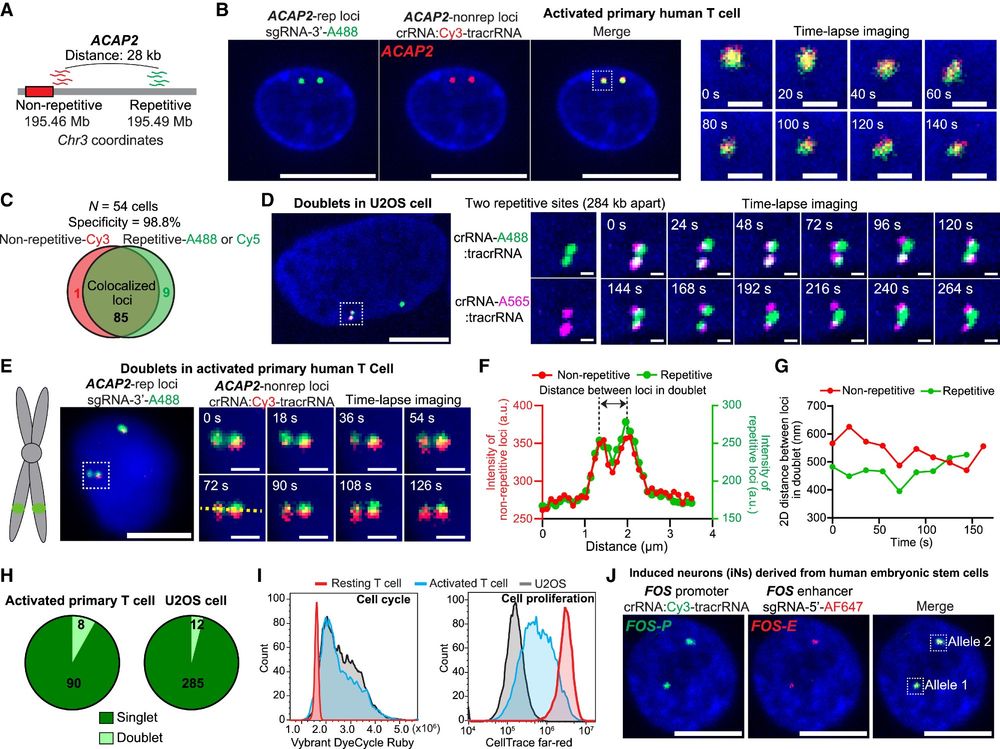
Oligo-LiveFISH enables the tracking of chromatin dynamics in diverse cell types, including hard-to-image cells such as primary T cells and induced neurons (iNs) derived from human embryonic stem cells.
16.04.2025 23:41 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
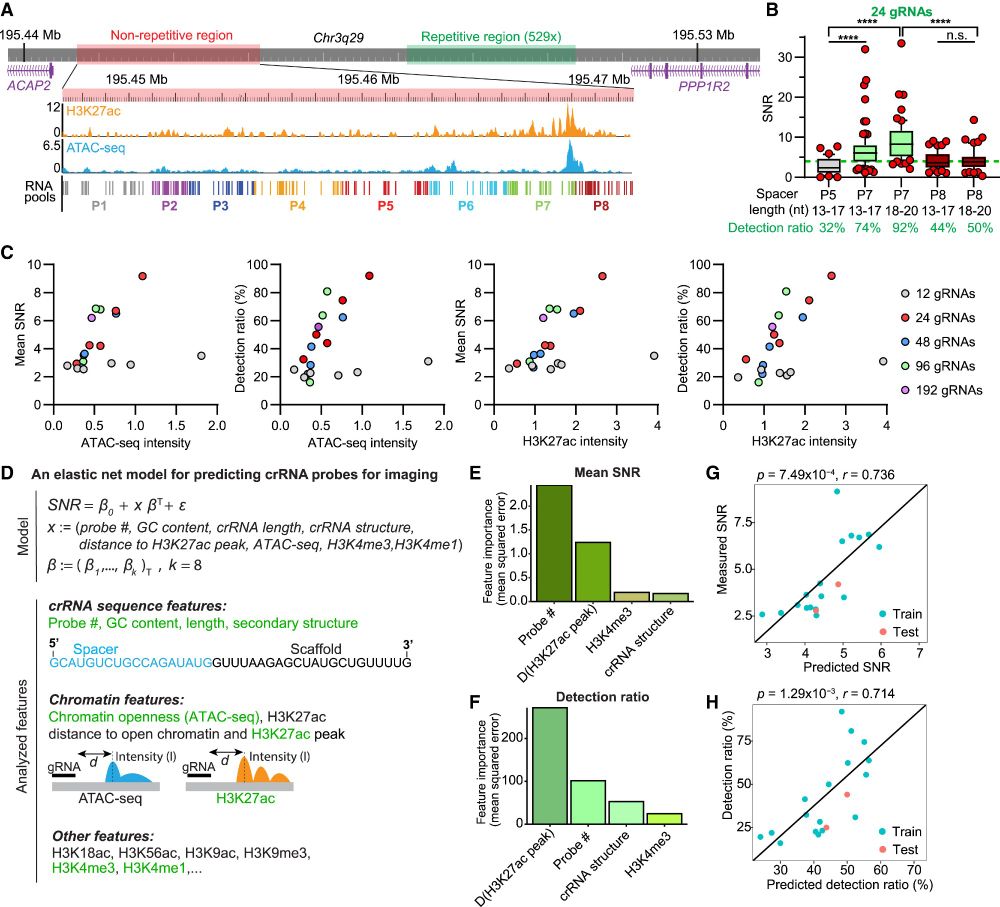
Utilizing machine learning, we characterized key parameters of chromatin and gRNA features on imaging efficiency and established gRNA design principles for live chromatin imaging.
16.04.2025 23:40 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
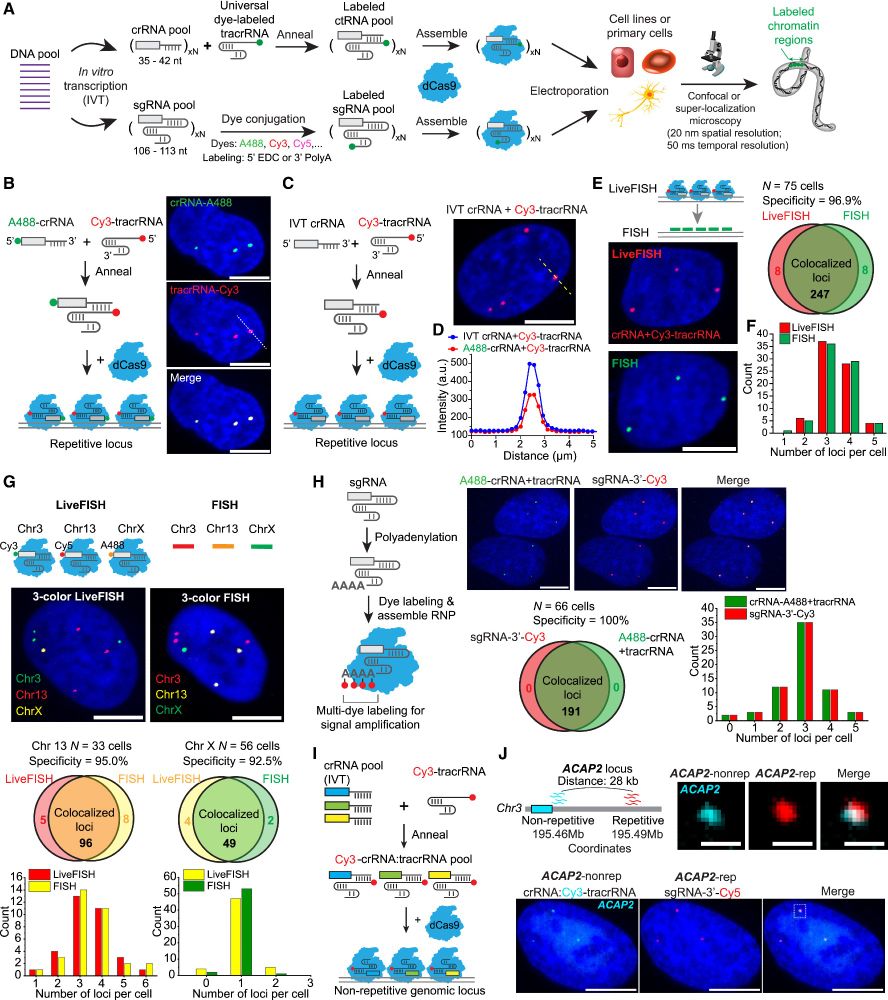
To address this, we exploited approaches to generate effective gRNA pools to image non-repetitive loci by computational design, in vitro transcription, and chemical labeling, delivered as ribonucleoproteins.
16.04.2025 23:40 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
The 3D chromatin dynamics is crucial for gene transcription and cellular function. However, real-time, live-cell DNA visualization remains challenging.
16.04.2025 23:39 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
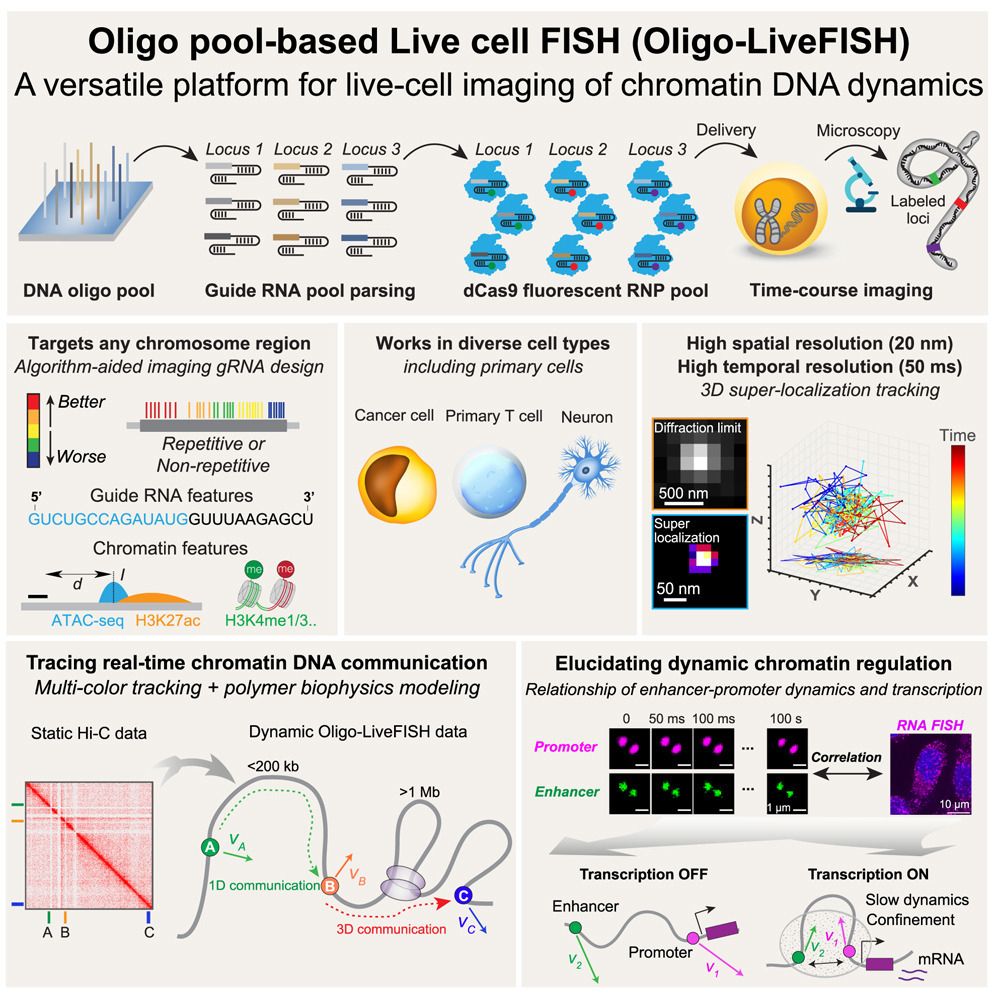
Oligo-LiveFISH is a high-resolution, reagent-based platform for studying 3D genome dynamics and their links to cellular processes in diverse cell types, including primary cells.
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
authors.elsevier.com/c/1kxK7L7PXu...
16.04.2025 23:39 — 👍 14 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 0
Thrilled to share our paper, led by Dr. Yanyu Zhu @yanyuzhu.bsky.social in collaboration with Prof. W.E. Moerner and Prof. Andrew J. Spakowitz, on developing Oligo-LiveFISH technology, in Cell @cellcellpress.bsky.social. A🧵
@stanford-chemh.bsky.social @bioe-stanford.bsky.social
16.04.2025 23:38 — 👍 9 🔁 5 💬 1 📌 2
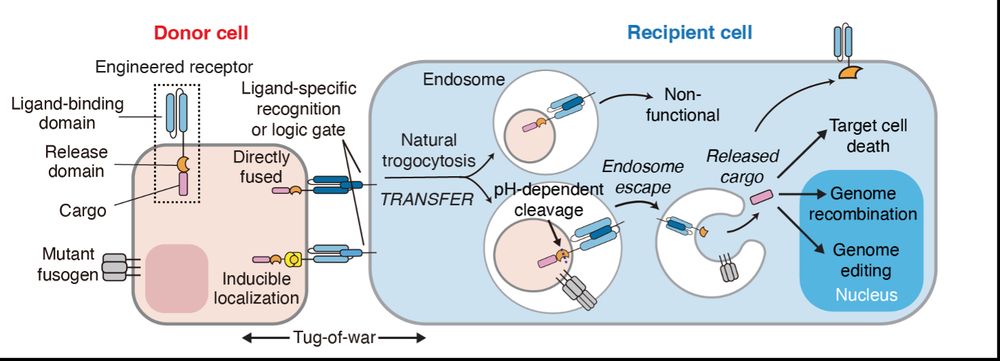
Our study establishes trogocytosis as a novel, programmable framework for cell-based macromolecular delivery. We look forward to seeing further applications enabled by the technology!
20.03.2025 18:03 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
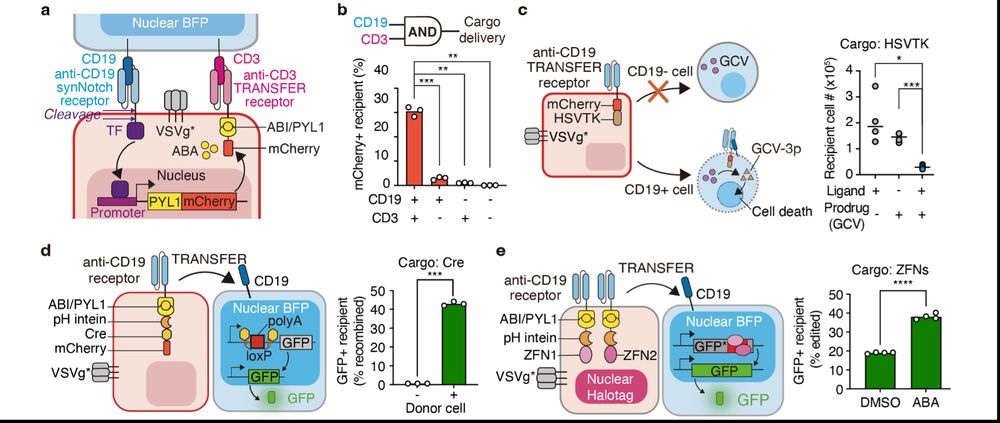
TRANSFER demonstrated superior programmability by (1) recognizing a combination of cell surface markers, and mediating delivery under AND gate logic; (2) being applicable to the delivery of Cre and ZFN for gene editing, and prodrug-converting enzymes for targeted cell ablation.
20.03.2025 18:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
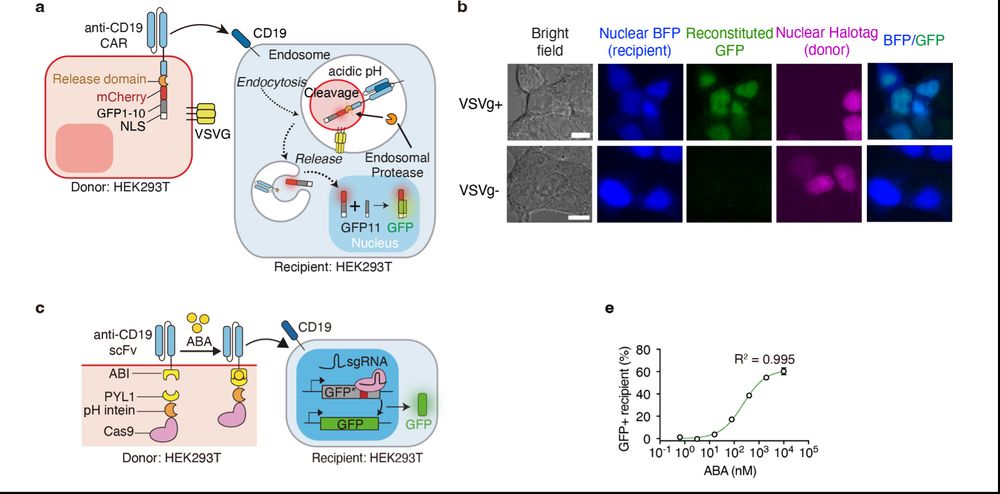
To expand trogocytosis beyond surface molecules, we introduced a pH-sensitive cleavable linker, enabling the translocation of membrane-recruited Cas9 cargos to the nucleus upon transfer. We termed the system trogocytosis-based transfer and functional effector release (TRANSFER).
20.03.2025 18:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0