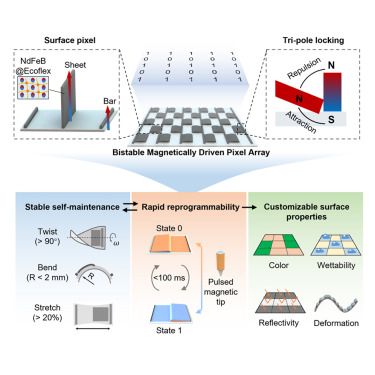
Reprogrammable and bistable magnetically driven pixel array with customizable surface properties
08.08.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0@cp-device.bsky.social

Reprogrammable and bistable magnetically driven pixel array with customizable surface properties
08.08.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0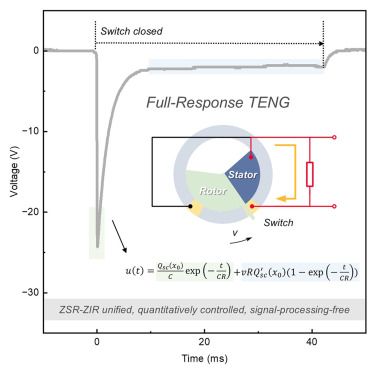
Full-response triboelectric nanogenerator modeling and sensing framework: Zero state and zero input in synergy
31.07.2025 18:48 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0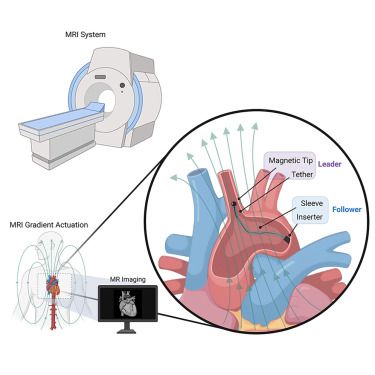
Gradient pulling of a tethered robot via a magnetic resonance imaging system
31.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0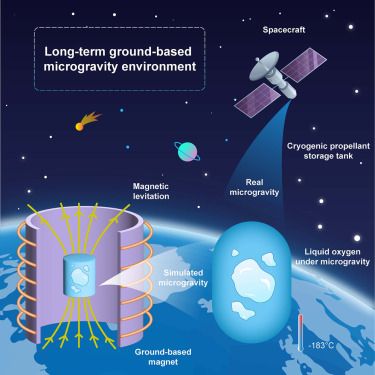
Stable long-term ground-based microgravity environment for cryogenic fluids
28.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Gastrointestinal neuromuscular interfaces: Bioelectronic device design for gastrointestinal motility
25.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0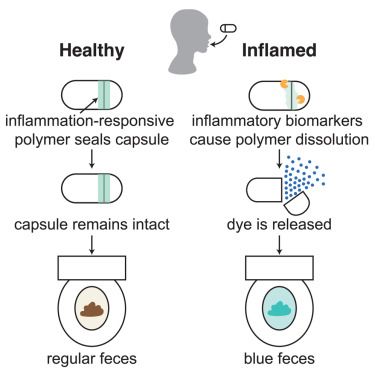
A radically simple, ingestible colorimetric biosensor pill for cost-effective, non-invasive monitoring of intestinal inflammation
24.07.2025 15:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0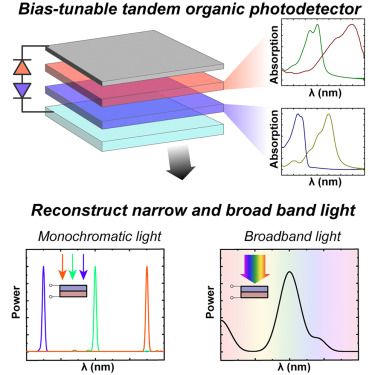
Single-pixel spectrometer based on a bias-tunable tandem organic photodetector
22.07.2025 18:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0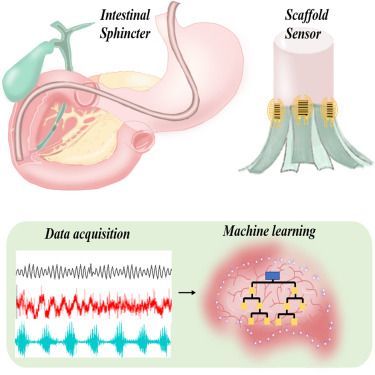
Janus adhesive hydrogel scaffold for monitoring pressure and shape changes in human intestinal sphincter
22.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0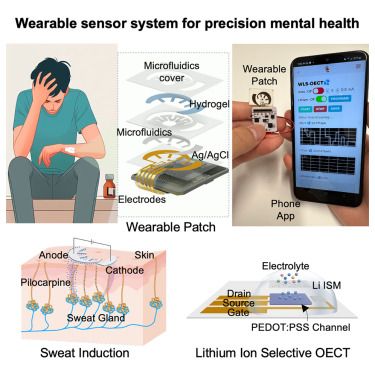
Wearable organic-electrochemical-transistor-based lithium sensor for precision mental health
18.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0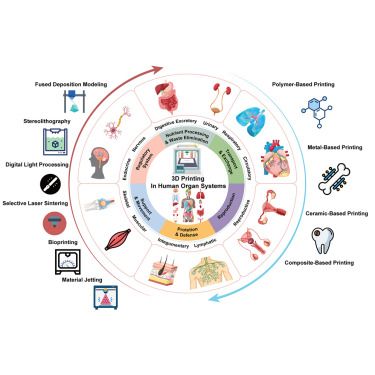
A roadmap for the implementation of 3D-printed organs in healthcare
16.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0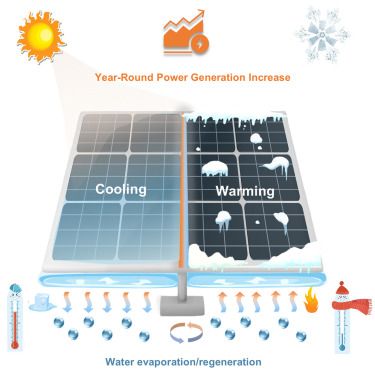
Enhancing year-round photovoltaic performance using the dual cooling and warming functions of hydrogels
10.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0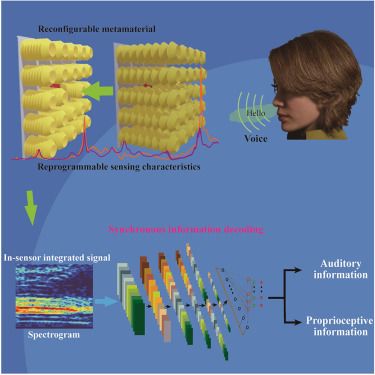
In-sensor integrated mechanoacoustic perception through reconfigurable metamaterial
04.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0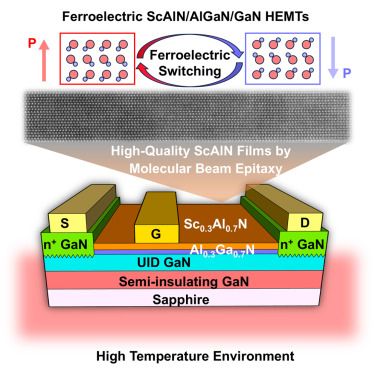
High-temperature memory devices based on ferroelectric ScAlN/AlGaN/GaN high-electron-mobility transistors
03.07.2025 15:21 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Tile displaying key metrics surrounding Device's first impact factor: 8.0 impact factor, over 940K downloads, over 1500 citations, 3 days to out to review decision, authors spanning 24 countries.
The Cell Press journal @cp-device.bsky.social has just received its first partial #ImpactFactor, coming in at 8.0!
Learn more about #Device and the research we've published here: http://dlvr.it/TLgSsD