Cost-effectiveness of rapid, ICU-based, syndromic PCR in hospital-acquired pneumonia: analysis of the INHALE WP3 multi-centre RCT | Critical Care
INHALE WP3 RCT health economic analysis now published in Critical Care.
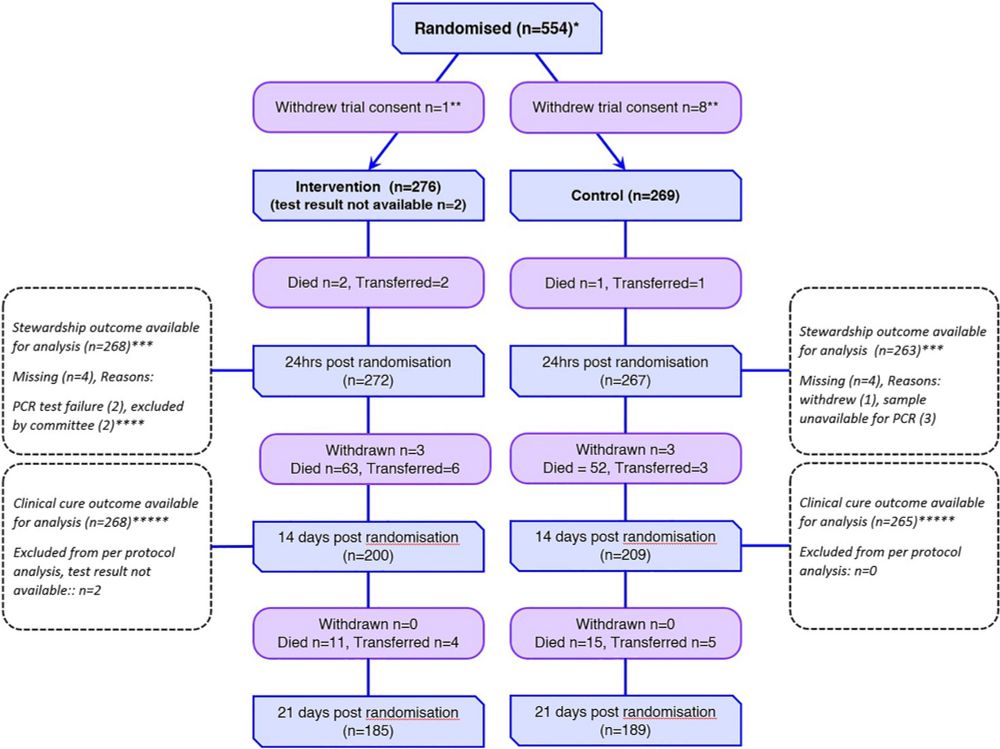
The Pneumonia Panel PCR had lower average ICU costs and was cost effective for antimicrobial stewardship, but not clinical cure.
Read in full at: rdcu.be/eAmSD
12.08.2025 08:52 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
YouTube video by INHALE Trial
INHALE Poem II - A Slight Diversion
‘INHALE Poem II – A slight diversion’ shares the journey of the INHALE study, describing its hopes, challenges and the implications of the research.
This poem was written and performed by Amander Wellings, of the INHALE Patient, Carer and Public Involvement (PPI) group.
youtu.be/-UUBzbSmEo0?...
10.06.2025 07:36 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

What is the impact of seeking pathogens by rapid molecular diagnostic methods on antibiotic stewardship and the clinical outcomes in hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia (HAP and VAP)?
Visual abstract below and full paper available online at rdcu.be/ehlAu
25.04.2025 16:06 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

INHALE compared rapid testing with standard care used to diagnose pneumonia in intensive care. Rapid testing gave faster results than standard care and improvements in antibiotic use. But, the machine did not improve cure of pneumonia, so more research is needed to understand why.
26.02.2025 14:16 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
3/4 Implementation strategies for technological solutions to antimicrobial resistance must be ‘behaviourally intelligent’, recognising the challenges facing clinicians when making ‘life or death’ prescribing decisions.
20.02.2025 11:19 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
2/4 limiting the application of these tests in practice.
Findings underscore the challenge of changing prescribing decisions based on technical results or guidelines, highlighting factors such as clinicians’ previous experience, and ‘knowledge in practice, to be more proximal drivers of decisions.
20.02.2025 11:19 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
1/4 Rapid molecular diagnostic tests for pathogens and resistance genes may improve antibiotic prescribing decisions and stewardship. However, clinicians’ desire to protect their patient with an antibiotic often overrides more distal concerns about possible resistance selection,
20.02.2025 11:19 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
Also sub-group analysis didn't suggest difference in outcomes between sample types but admittedly we didn't have many BALs.
19.02.2025 12:05 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
No, we didn't formally assess here as had done & published before in same population. Informal analysis suggested results similar, and PCR found more organisms than culture. The method is semi-quant so you can have some clues to colonisation vs. infection - but no current method is 100% on this.
19.02.2025 12:02 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
2/2 More research on clinical impact is urgently needed. A holistic approach, including behavioural intervention to optimise antibiotic prescribing, is likely needed to fully realise the potential benefits of rapid diagnostics and their role in mitigating AMR.
18.02.2025 15:11 — 👍 2 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
A UKCRC-registered clinical trials unit based in the Medical School at the University of East Anglia.
https://norwichctu.uea.ac.uk/
Stay up-to-date in Infectious Diseases, Clinical Pharmacist, Antibiotics, #IDTwitter t✨p influencer #interstellar #dune
🌹❤️Misk #idsky #medsky #AMSsky #idxposts
Bassam Ghanem,PharmD MS BCPS BCIDP
Critical care evidence dissemination - science for all.
https://criticalcarereviews.com
Centre for Behavioural Medicine, UCL School of Pharmacy.
A research group with a global portfolio of research exploring patient perspectives of illness and treatment.
All opinions are our own.
🌍Direct DNA/RNA analysis for anyone, anywhere
🧬Short to ultra-long reads in real-time for rapid insights
🔬Products for research use only
We are global leader in in vitro diagnostics committed to improving public health worldwide. Since 1963, our innovative diagnostics solutions help healthcare professionals make confident decisions to enhance patient outcomes.
Associate Prof /ICU Dr @Cambridge, UK
nosocomial infections, pneumonia, neutrophil biology & sepsis immune dysfunction
Medical director for Sepsis Research FEAT.
orcid.org/0000-0002-3211-3216
https://www.path.cam.ac.uk/directory/dr-andrew-conway-morris
Healthcare professional, educator and researcher, Manchester, UK
https://research.manchester.ac.uk/en/persons/paul.m.dark 🇬🇧 🇨🇭
official Bluesky account (check username👆)
Bugs, feature requests, feedback: support@bsky.app