Big thanks to @chicagohai.bsky.social team and everyone who submitted ideas on IdeaHub. Special shoutout to the open source community building research agents! We're all learning together.
10.11.2025 22:46 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
All 6 generated repositories with detailed code and reports:
- github.com/ChicagoHAI/l...
- github.com/ChicagoHAI/l...
- github.com/ChicagoHAI/i...
- github.com/ChicagoHAI/i...
- github.com/ChicagoHAI/l...
- github.com/ChicagoHAI/l...
10.11.2025 22:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Hypogenic AI - Shaping the Future of Science
Reimagining science by augmenting scientist-AI collaboration.
Submit your idea, vote on existing ones, or help improve idea-explorer: github.com/ChicagoHAI/i...
Full blog with technical details:
hypogenic.ai/blog/weekly-...
Substack: open.substack.com/pub/cichicag...
10.11.2025 22:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
So why are we doing this openly?
Because agents clearly can accelerate early-stage exploration. But they need human oversight at every step. Transparent benchmarking beats cherry-picked demos. Community feedback improves agents faster. And honestly, we're all figuring this out together.
10.11.2025 22:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Existing agents like AI-Scientist and AI-Researcher are basically overfitted to ML. There are hard-coded prompts that “requires changing hyperparameters and train on HuggingFace datasets” or specific ML agents. Just changing prompt won’t be enough, as ML assumptions are everywhere in the codebase.
10.11.2025 22:44 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
The pattern: we can fix specific bugs with better prompts (bias-variance tradeoff). But we can't prompt our way to knowing when to search, recognizing expertise boundaries, or understanding what rigorous methodology looks like.
That's what I call the "meta intelligence" gap.
10.11.2025 22:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
What didn’t
Some agents run faked human data, used undersized models even though compute was available, or calling simple answer reweighting as "multi-agent interactions". Resource collection and allocation is a bottleneck, but more importantly, the agents do not know when to search or seek help.
10.11.2025 22:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
What worked
Agents can actually design and run small experiments: sometimes to seed bigger studies, sometimes as sanity checks, and sometimes to straight-up refute the original hypothesis. That kind of evidence is way more useful than “LLM-as-a-judge says the idea is good.”
10.11.2025 22:40 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
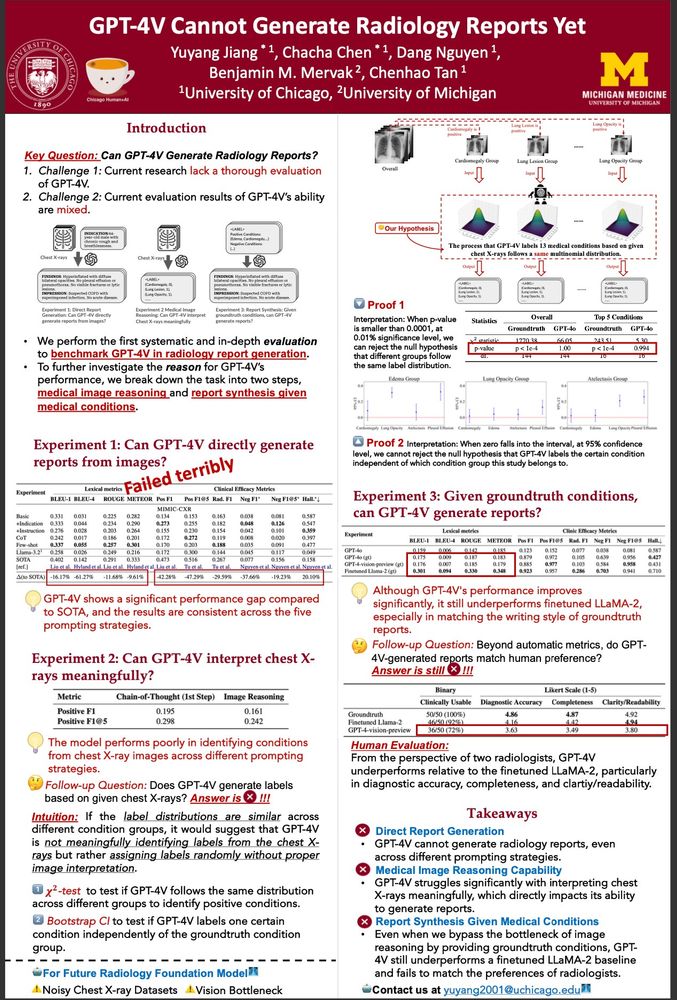
There's a lot of hype on AI agents for science. But what can they actually do? We tested our idea-explorer on ideas from IdeaHub:
Do LLMs have different types of beliefs?
Can formal rules make AI agents honest about their uncertainty?
Can LLMs temporarily ignore their training to follow new rules?
10.11.2025 22:35 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Hypogenic AI - Shaping the Future of Science
Reimagining science by augmenting scientist-AI collaboration.
Here's how it works:
→ Submit your research idea or upvote existing ones (tag: "Weekly Competition")
→ Each Monday we select top 3 from previous week
→ We run experiments using research agents
→ Share repos + findings back on IdeaHub
Vote here: hypogenic.ai/ideahub
10.11.2025 21:33 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

We're launching a weekly competition where the community decides which research ideas get implemented. Every week, we'll take the top 3 ideas from IdeaHub, run experiments with AI agents, and share everything: code, successes, and failures.
It's completely free and we'll try out ideas for you!
10.11.2025 21:32 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 1 📌 0

❓ Does an LLM know thyself? 🪞
Humans pass the mirror test at ~18 months 👶
But what about LLMs? Can they recognize their own writing—or even admit authorship at all?
In our new paper, we put 10 state-of-the-art models to the test. Read on 👇
1/n 🧵
27.10.2025 17:36 — 👍 12 🔁 4 💬 1 📌 1
Replacing scientists with AI isn’t just unlikely, it’s a bad design goal.
The better path is collaborative science. Let AI explore the ideas, draft hypotheses, surface evidence, and propose checks. Let humans decide what matters, set standards, and judge what counts as discovery.
23.10.2025 20:29 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
🚀 We’re thrilled to announce the upcoming AI & Scientific Discovery online seminar! We have an amazing lineup of speakers.
This series will dive into how AI is accelerating research, enabling breakthroughs, and shaping the future of research across disciplines.
ai-scientific-discovery.github.io
25.09.2025 18:28 — 👍 23 🔁 15 💬 1 📌 1
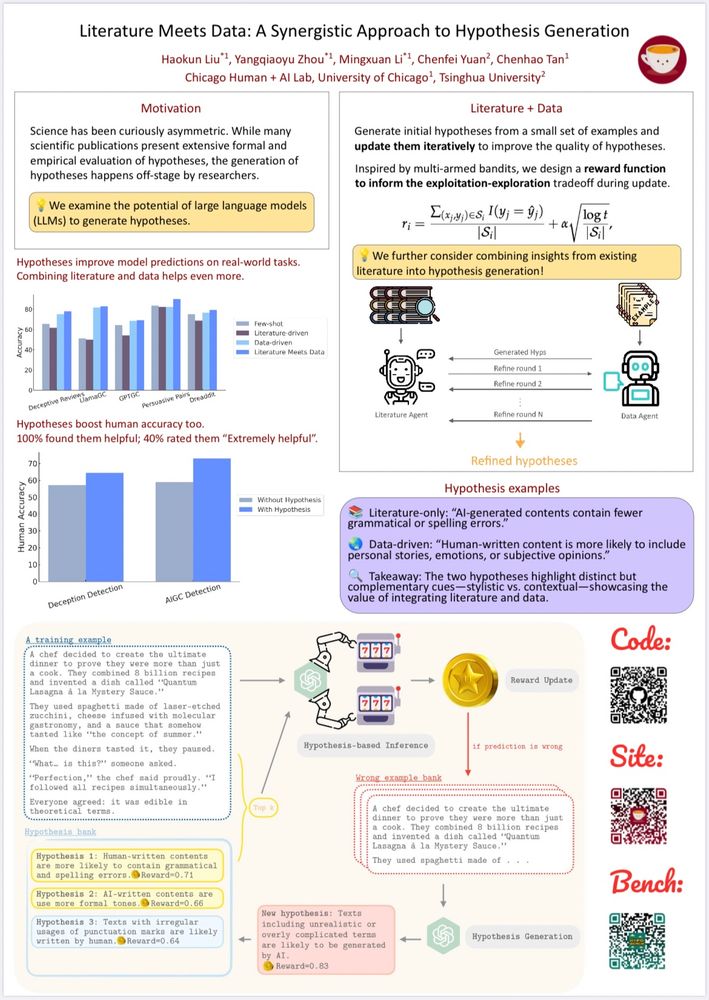
#ACL2025 Poster Session 1 tomorrow 11:00-12:30 Hall 4/5!
27.07.2025 19:27 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 1
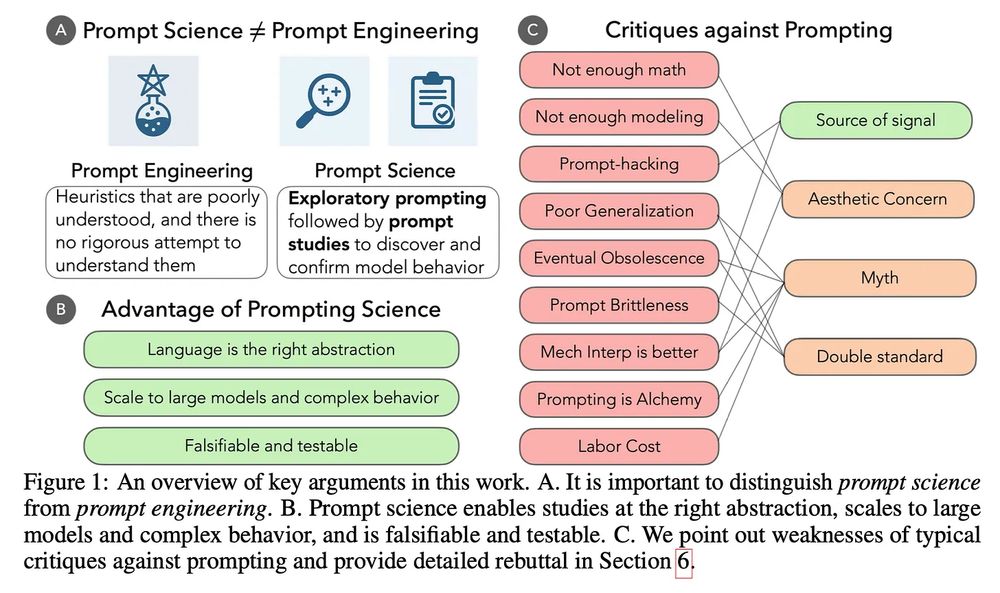
Prompting is our most successful tool for exploring LLMs, but the term evokes eye-rolls and grimaces from scientists. Why? Because prompting as scientific inquiry has become conflated with prompt engineering.
This is holding us back. 🧵and new paper with @ari-holtzman.bsky.social .
09.07.2025 20:07 — 👍 37 🔁 15 💬 2 📌 0
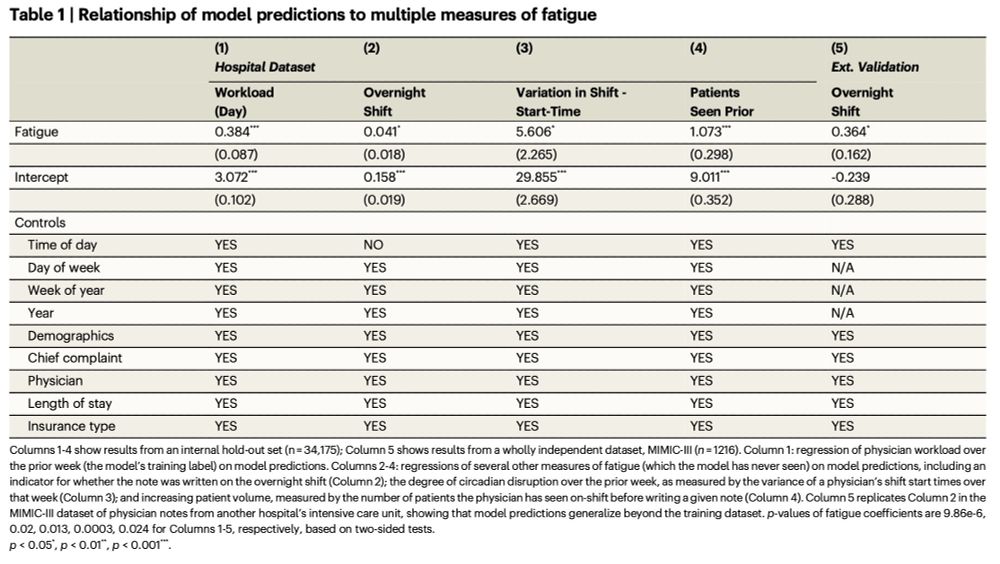
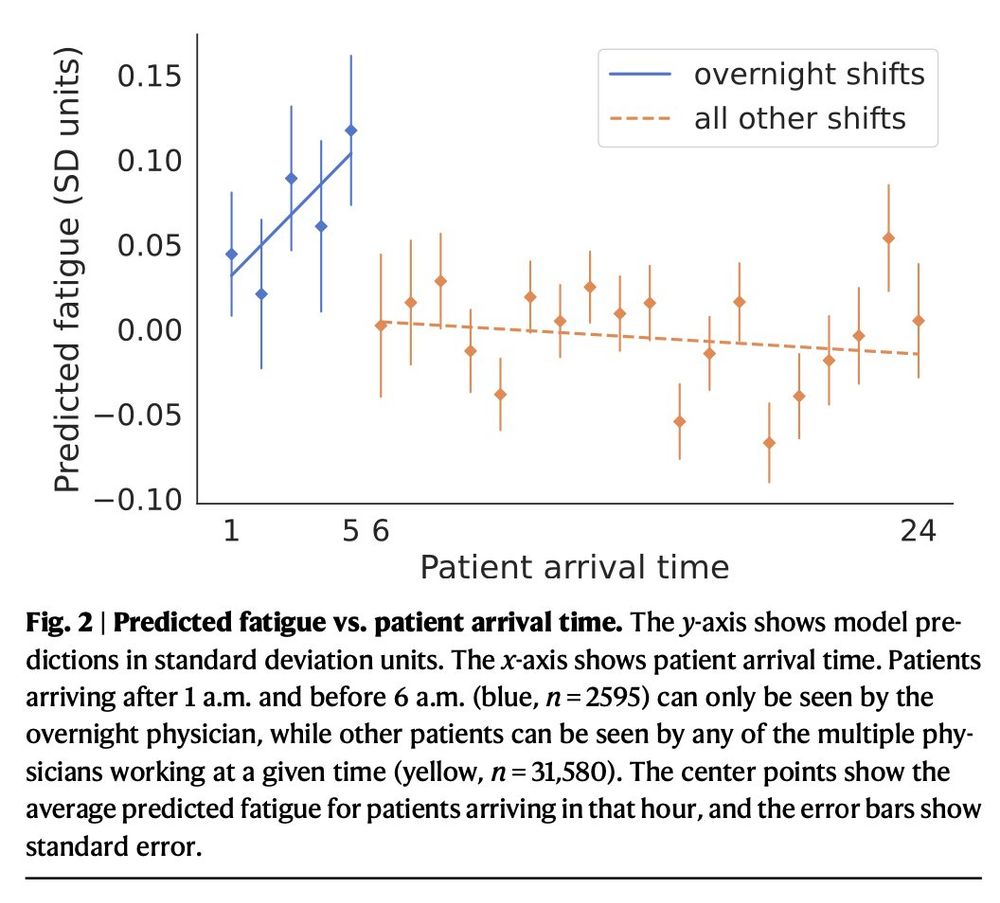
It predicts pretty well—not just shifts in the last week, but also:
1. Who’s working an overnight shift (in our data + external validation in MIMIC)
2. Who’s working on a disruptive circadian schedule
3. How many patients has the doc seen *on the current shift*
02.07.2025 19:24 — 👍 5 🔁 3 💬 1 📌 0

🚨 New paper alert 🚨
Ever asked an LLM-as-Marilyn Monroe who the US president was in 2000? 🤔 Should the LLM answer at all? We call these clashes Concept Incongruence. Read on! ⬇️
1/n 🧵
27.05.2025 13:59 — 👍 28 🔁 17 💬 1 📌 1
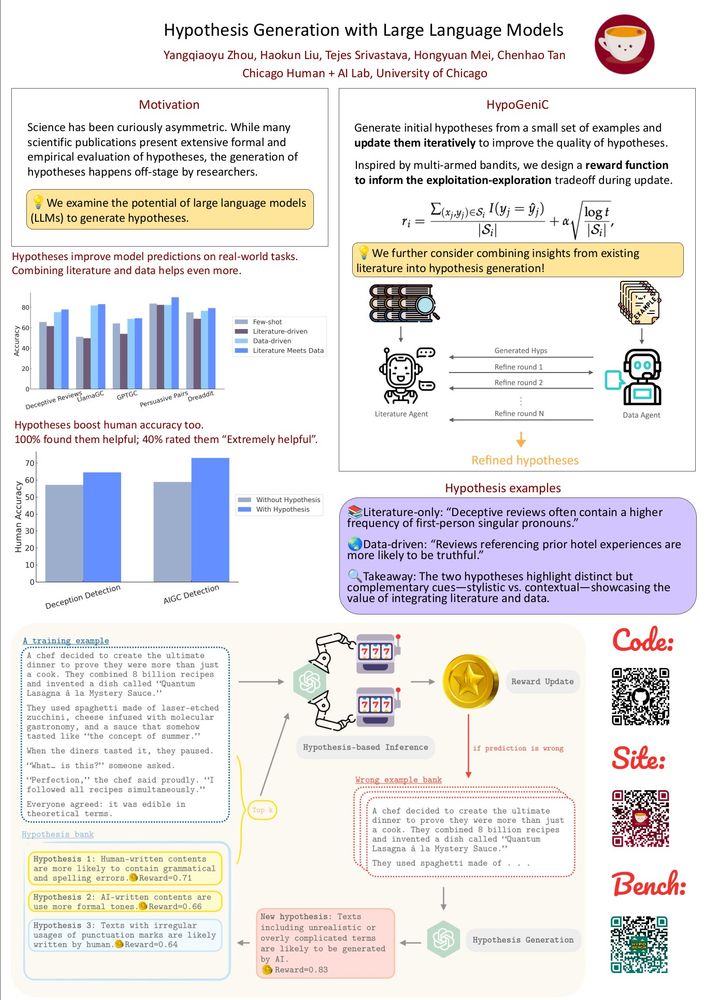
1/n 🚀🚀🚀 Thrilled to share our latest work🔥: HypoEval - Hypothesis-Guided Evaluation for Natural Language Generation! 🧠💬📊
There’s a lot of excitement around using LLMs for automated evaluation, but many methods fall short on alignment or explainability — let’s dive in! 🌊
12.05.2025 19:23 — 👍 22 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 1

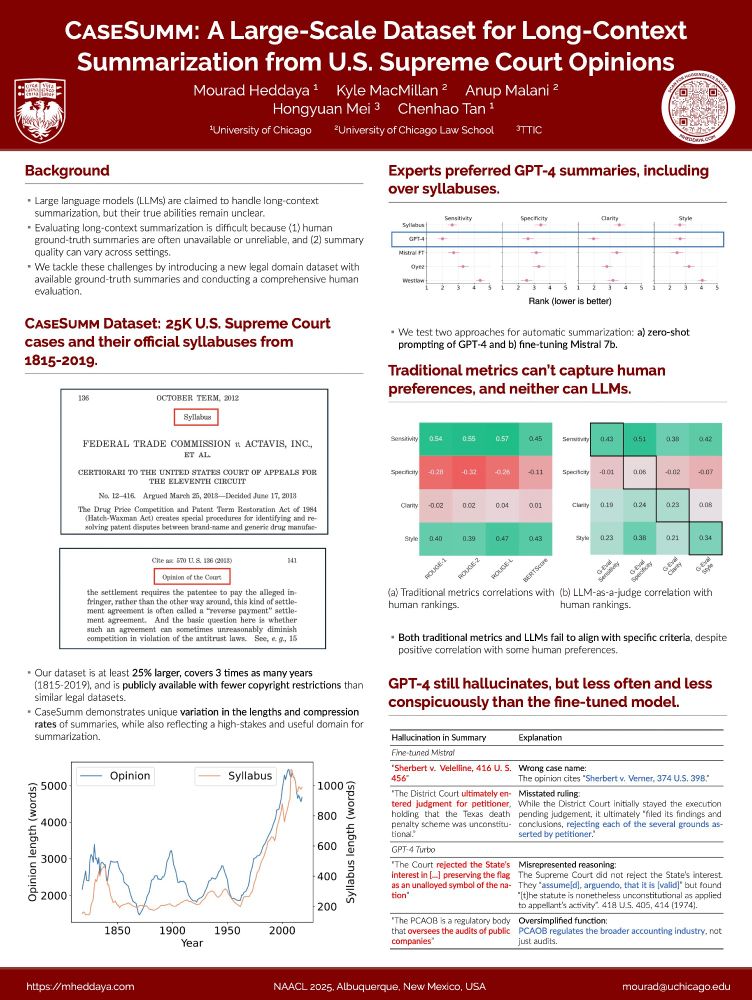
🧑⚖️How well can LLMs summarize complex legal documents? And can we use LLMs to evaluate?
Excited to be in Albuquerque presenting our paper this afternoon at @naaclmeeting 2025!
01.05.2025 19:25 — 👍 23 🔁 13 💬 2 📌 0
13/ Lastly, great thanks to my wonderful collaborators Sicong Huang, Jingyu Hu, @qiaoyu-rosa.bsky.social , and my advisor @chenhaotan.bsky.social !
28.04.2025 19:40 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
11/ Why HypoBench matters: Establishes a structured way to advance AI's role in scientific discovery and everyday reasoning, highlighting both current capabilities and significant challenges.
28.04.2025 19:37 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
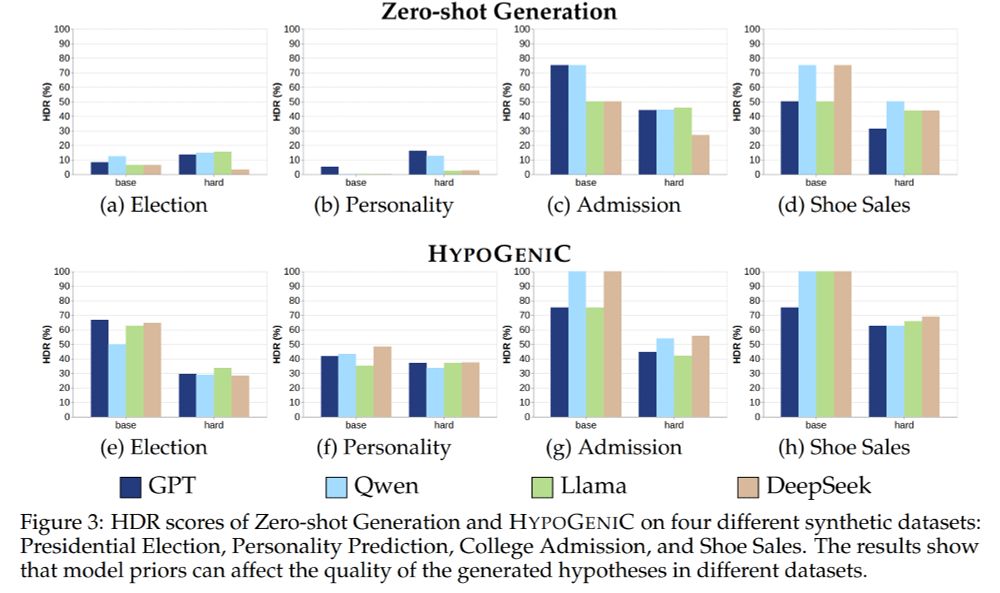
10/ Model priors matter: We see that the models have different priors, which lead to varying behaviors in different tasks—generating good hypotheses is harder when prior knowledge is not helpful.
28.04.2025 19:37 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
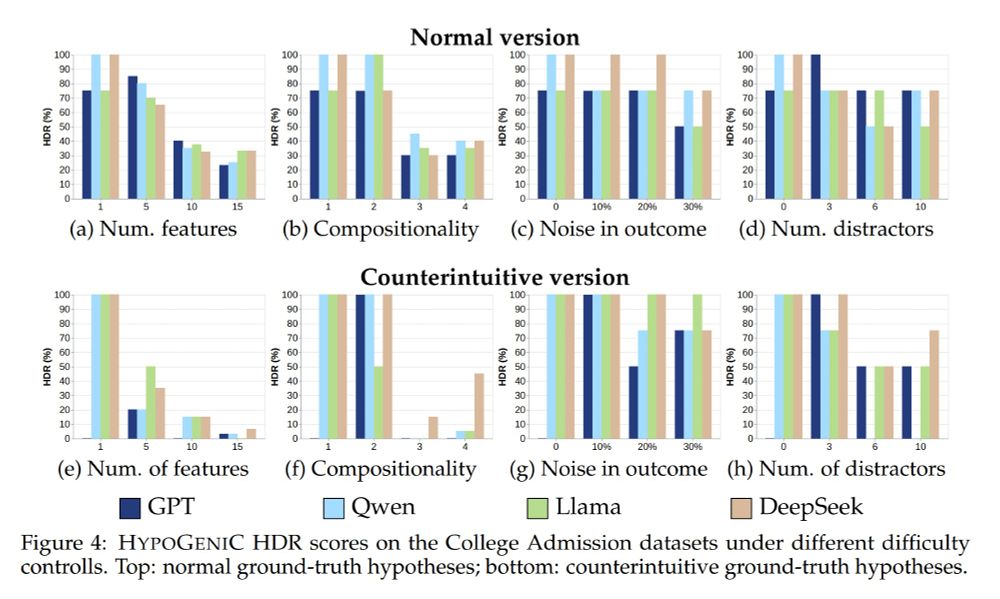
9/ And it gets worse in counterintuitive settings - the models perform significantly worse when the underlying hypotheses are counterintuitive.
28.04.2025 19:37 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
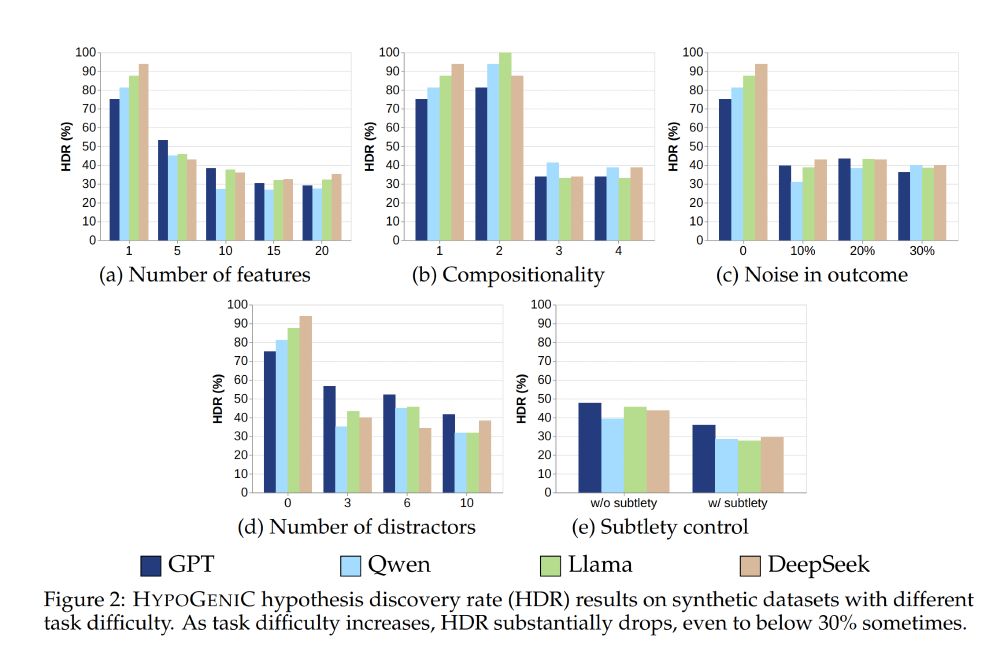
8/ 💡 Synthetic dataset results show: LLMs handle simple interactions well but struggle with increased noise, distractors, or subtleties in text—highlighting significant rooms for improvement.
28.04.2025 19:36 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
he/him. CS PhD @uwmadison studying the role of technology in gender-based violence through decolonial and feminist lenses. AI-hater.
https://naman.github.io
PostDoc at UChicago DSI
#CovidIsAirborne 😷
Biology x AI and trying to find the calm in the storm.
doting father, friend & ally; hyperpolyglot computational philologist & sinologist;
currently teaching AI, deep learning + multilingual NLP/NLU + HPC + humanities data science @UChicago, creating new methods for multilingual intertextuality、古聲韻學、文字學等等
Researching planning, reasoning, and RL in LLMs @ Reflection AI. Previously: Google DeepMind, UC Berkeley, MIT. I post about: AI 🤖, flowers 🌷, parenting 👶, public transit 🚆. She/her.
http://www.jesshamrick.com
Usable decision-making on data-intensive user interfaces: physical activity tracking and interactive dashboards.
HCI, AI, digital health and accessibility.
Reader in Computer Science @ The University of Manchester (UK)
http://www.markelvigo.info
Computer Science PhD student at UChicago | Member of the Chicago Human+AI lab @chicagohai.bsky.social
Manchester Centre for AI FUNdamentals | UoM | Alumn UCL, DeepMind, U Alberta, PUCP | Deep Thinker | Posts/reposts might be non-deep | Carpe espresso ☕
▪️ Founder SuccessCENTER.com
& ThriveInAI.ai
▪ #B2B, #AI, #Startup & Marketing Advisor
▪ #ThriveTOGETHER #F4F
▪ #ThriveInAI - AIAppVault.com
▪ #Author - AI Creation Apps:
777+ Generative AI Tools
w 10,000+ AI Resources
▪ Nature Lover
▪ Be enCOURAGEd!
AI, Ethics, SmartCity
𝗦𝗮𝗽𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘇𝗮 𝗨𝗻𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘀𝗶𝘁𝘆: lecturer Planning and Strategic Management
𝗘𝗡𝗜𝗔: member of National Authority for AI association
𝗧𝗜𝗠: Account Manager
📰 https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-04-2024-0096
🔗 https://www.linkedin.com/in/vriccardi
Incoming Asst Prof @UMD Info College, currently postdoc @UChicago. NLP, computational social science, political communication, linguistics. Past: Info PhD @UMich, CS + Lx @Stanford. Interests: cats, Yiddish, talking to my cats in Yiddish.
The color of my dress means NOTHING. #Midjourney Event Host, Guide, and Community Outreach | Moderator at Hedra | Shares the best I see in AI | Your Fun, Friendly Creator at the Bleeding Edge of #AI . I BLOCKED MAGA words, Cuz I value my peace.
https://linktr.ee/ejackyao.ai
I don't have a course to sell
just sharing my AI journey...
AI Enhanced UK Film and Research Company
ML AI R&D
FX, Graphics, Storyboard, Logistics, Editing Film Production
Co-Founder and Human Capital Specialist at Full Spectrum Leadership Inc. Publisher of WBN News Okanagan and Publisher of WBN News Winnipeg
"Speak your mind to me, even if your voice quakes".
bit.ly/49RbePP
https://chicagohai.github.io/, https://substack.com/@cichicago