Anyone going to ACS Colloids/IACIS in Canada next week?
I'm giving two talks on Tuesday:
1. Spontaneous core-shell coacervate droplets @ 11:20 in NRE 1-001
2. New(!) on getting interaction information from low-Q scattering, i.e. an extension (correction?) to Guinier analysis @ 14:20 in ECERF W2-010
19.06.2025 17:13 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
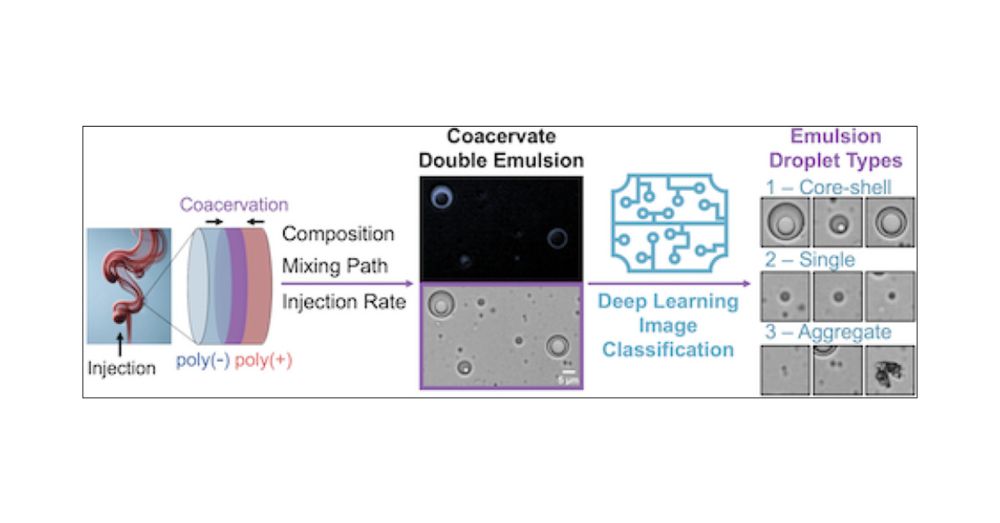
Spontaneous Formation of Core–Shell Microdroplets during Conventional Coacervate Phase Separation
We report the single-step formation and stability of protocell-like, core-shell coacervate droplets comprising a polyelectrolyte-rich shell and a solvent-rich vacuole core from the poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH) and poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) system. These double emulsion (DE) coacervate droplets coexist with single emulsion (SE) droplets, suggesting a kinetic mechanism of formation. We use high-throughput microscopy and machine learning to classify droplet morphologies across various final compositions (polyelectrolyte ratios and salt concentrations) and processing routes (mixing rate and thermodynamic path). We find that DE droplets form preferentially over SE droplets at a wide range of compositions using a slow injection mixing rate. DE droplet formation is enhanced at lower salt (NaCl) levels and near 1:1 charge stoichiometry, showing a preference for polycation excess. DE droplets are stable to the micron scale and retain their core-shell structure even after coalescence. Nevertheless, they are metastable; direct observations of various coarsening phenomena suggest that they are primarily stabilized by the viscoelasticity and high viscosity of the polymer-rich shell. Overall, the scalable, simple mixing process used herein offers a novel mechanism to produce multiphase coacervate droplets that is orthogonal to existing routes, which require either dropwise synthesis or thermodynamic tuning.
New paper from my PhD with @professor-meh.bsky.social! We show a simple route to all-water multiple emulsions, via coacervation with a single(!) dense phase. Amid size/shape variance, we use ML to quantify trends in droplet structure with mixing condition, which diverge from classical W/O/W systems.
25.03.2025 19:21 — 👍 9 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
This was the real session I should have presented in!! :) Really enjoyed that session
22.03.2025 04:04 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Hello world!
21.03.2025 07:21 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Assistant Professor Pharmaceutics @ Utrecht University. Combining polymer / physical chemistry with pharmaceutical sciences
ChBE PhD Candidate in the Stingelin and Silva Groups at Georgia Tech
Kanaka 'ōiwi | polymers & biofilms enthusiast | Assistant Prof
@CUEngineering | HuliLab PI | 😺 parent | she/her
Assistant Professor at UC Irvine CBE
Postdoc @ UIUC | Computational Materials Science, ChemE, MolEng.
Postdoc @ Salk Institute | San Diego vibing | Ph.D. in Bioengineering from 🍚 | 🐐 dog dad
Propel Postdoctoral Fellow at Stanford. Interested in chromatin structure, LLPS, condensate structures.
Assistant Professor; Chemical & Materials Engineering at University of Alberta. I work on the fluid & statistical mechanics of active matter.
Since 1889 🗞️
Sign up for our newsletters and alerts: http://wsj.com/newsletters
Got a tip? http://wsj.com/tips
Follow our staff: https://go.bsky.app/2ppWqxF
❤️ materials, microbes, polymers
Professor, UMass Amherst https://schiffmanlab.org/
Deputy Editor, ACS Applied Engineering Materials
https://pubs.acs.org/journal/aaemdr
working on problems at the intersection of machine learning, structural biology, and physics @ Prescient Design. previously an experimental biophysicist @Stanford.
A postdoc at the Core for Imaging Technology & Education (formerly known as the NIC) at Harvard Medical School that doodles to explain science. Former member of the Dunn lab at Stanford, Dept of Chemical Engineering.
Willard Henry Dow Professor MIT Chemical Engineering, PI in AMR IRG, SMART, Singapore
Clinical diagnostics, mathematical modeling, protein engineering, redox metabolism
Science News from Academic Journals etc.
🌊Frontline intel on the plastic crisis: exposing threats, advancing solutions, and defending our planet’s future!🌎 The mission is clear - join the fight!♻️
Creating breakthrough technologies for national security.
News and information for the Science Explorer (SciX) user community. Explore with us at SciXplorer.org
