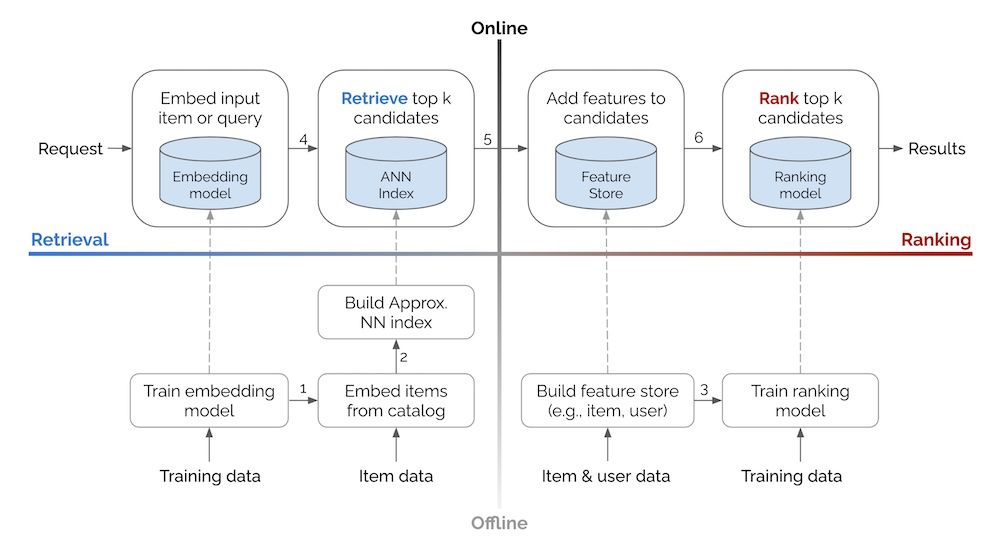
Two-stage recommender system
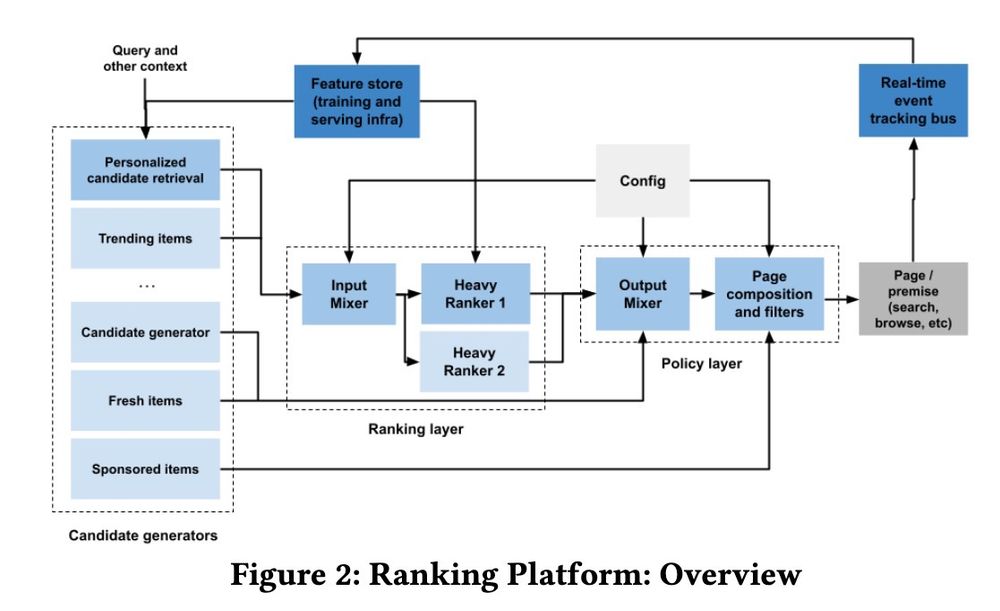
Zalando's recommender system
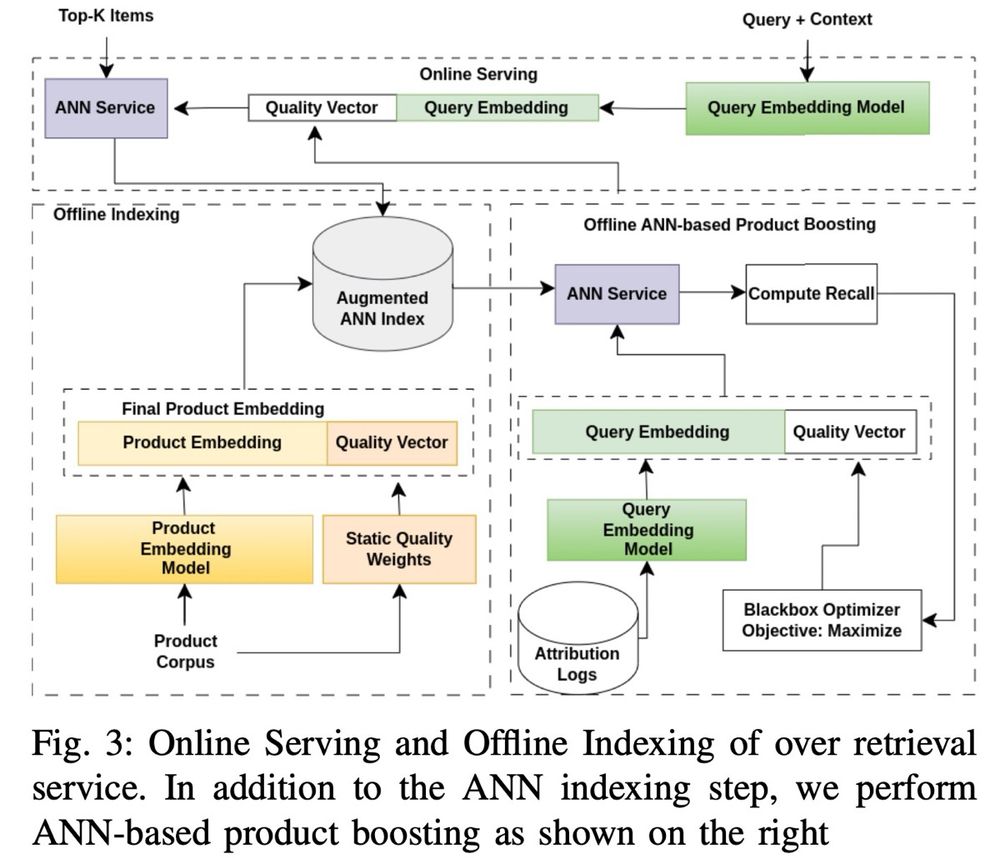
Unified embeddings
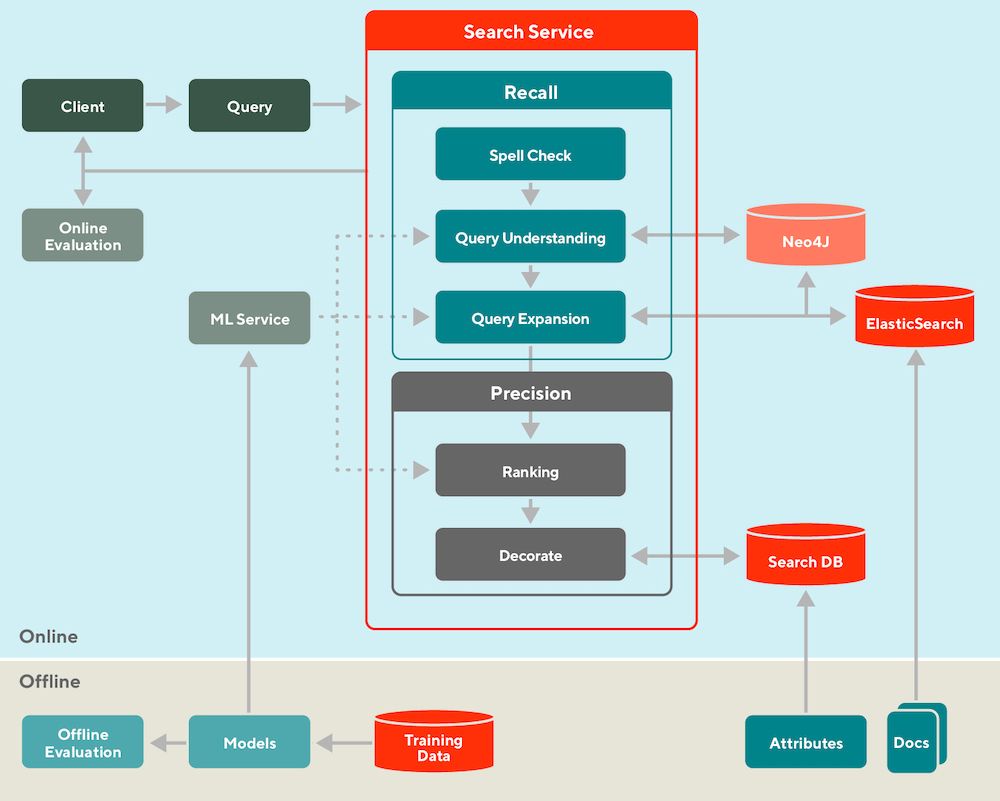
Doordash's search system
Can't wait for when I can vibe code a production recommender system.
Until then, here's some system designs:
• Retrieval vs. Ranking: eugeneyan.com/writing/syst...
• Real-time retrieval: eugeneyan.com/writing/real...
• Personalization: eugeneyan.com/writing/patt...
08.04.2025 05:14 — 👍 47 🔁 4 💬 1 📌 0
Awesome working with the IITB folks. Super happy to see this
25.03.2025 14:52 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Dataset Distillation (2018/2020)
They show that it is possible to compress 60,000 MNIST training images into just 10 synthetic distilled images (one per class) and achieve close to original performance with only a few gradient descent steps, given a fixed network initialization.
05.03.2025 00:23 — 👍 26 🔁 5 💬 2 📌 1

Bayesian posterior approximation has become more accessible to practitioners than ever, thanks to modern black-box software. While these tools provide highly accurate approximations with minimal user effort, certain posterior geometries remain notoriously difficult for standard methods. As a result, research into alternative approximation techniques continues to flourish. In many papers, authors validate their new approaches by testing them on posterior shapes deemed challenging or "wild." However, these shapes are not always directly linked to real-world applications where they naturally occur. In this note, we present examples of practical applications that give rise to some commonly used benchmark posterior shapes.
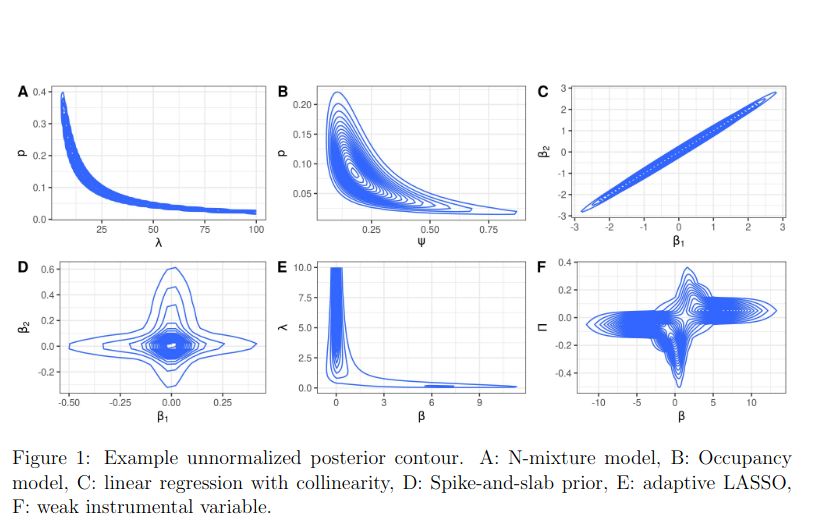
a variety of funky posteriors
"Wild posteriors in the wild"
A cool-looking paper if you're interested in funky posterior geometry
Link: arxiv.org/abs/2503.00239
Code: github.com/YunyiShen/we...
#stats
05.03.2025 03:36 — 👍 45 🔁 6 💬 2 📌 4
Anyone interested in interactive story generation? I genuinely love this stuff, and would love to talk about it with anyone who's interested
This is a little tool I made to experiment with generating like murder mysteries automatically~
28.02.2025 21:29 — 👍 8 🔁 1 💬 2 📌 0
Xiaoyu Deng, Ye Zhang, Tianmin Guo, Yongzhe Zhang, Zhengjian Kang, Hang Yang
ChallengeMe: An Adversarial Learning-enabled Text Summarization Framework
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.05084
10.02.2025 06:36 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Roman Vashurin (Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence), ...
CoCoA: A Generalized Approach to Uncertainty Quantification by Integrating Confidence and Consistency of LLM Outputs
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04964
10.02.2025 06:37 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Haohao Zhu, Junyu Lu, Zeyuan Zeng, Zewen Bai, Xiaokun Zhang, Liang Yang, Hongfei Lin
Commonality and Individuality! Integrating Humor Commonality with Speaker Individuality for Humor Recognition
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04960
10.02.2025 06:38 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0

Also note that, instead of adding KL penalty in the reward, GRPO regularizes by directly adding the KL divergence between the trained policy and the reference policy to the loss, avoiding complicating the calculation of the advantage.
@xtimv.bsky.social and I were just discussing this interesting comment in the DeepSeek paper introducing GRPO: a different way of setting up the KL loss.
It's a little hard to reason about what this does to the objective. 1/
10.02.2025 04:32 — 👍 50 🔁 10 💬 3 📌 0
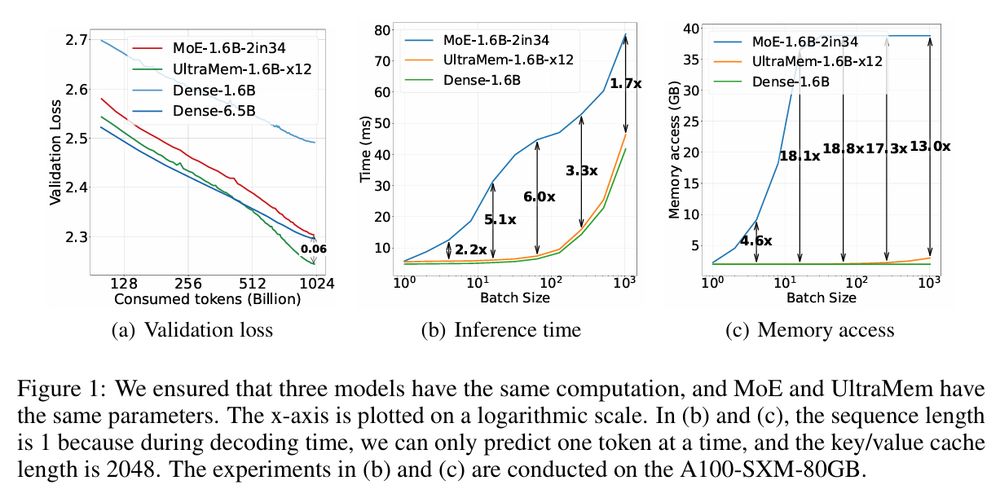
ByteDance's UltraMem
A new ultra sparse model that
- exhibits favorable scaling properties but outperforms MoE
- inference speed is 1.7x to 6.0x faster than MoE
Paper: Ultra-Sparse Memory Network ( arxiv.org/abs/2411.12364 )
10.02.2025 06:42 — 👍 28 🔁 3 💬 1 📌 1
Masato Mita, Ryo Yoshida, Yohei Oseki
Developmentally-plausible Working Memory Shapes a Critical Period for Language Acquisition
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04795
10.02.2025 06:47 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Jing Yang, Max Glockner, Anderson Rocha, Iryna Gurevych
Self-Rationalization in the Wild: A Large Scale Out-of-Distribution Evaluation on NLI-related tasks
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04797
10.02.2025 06:47 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Santiago Gonz\'alez-Silot, Andr\'es Montoro-Montarroso, Eugenio Mart\'inez C\'amara, Juan G\'omez-Romero
Enhancing Disinformation Detection with Explainable AI and Named Entity Replacement
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04863
10.02.2025 06:46 — 👍 1 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Herbert Ullrich, Tom\'a\v{s} Mlyn\'a\v{r}, Jan Drchal
Claim Extraction for Fact-Checking: Data, Models, and Automated Metrics
https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.04955
10.02.2025 06:45 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
"All you need to build a strong reasoning model is the right data mix."
The pipeline that creates the data mix:
26.01.2025 23:30 — 👍 13 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
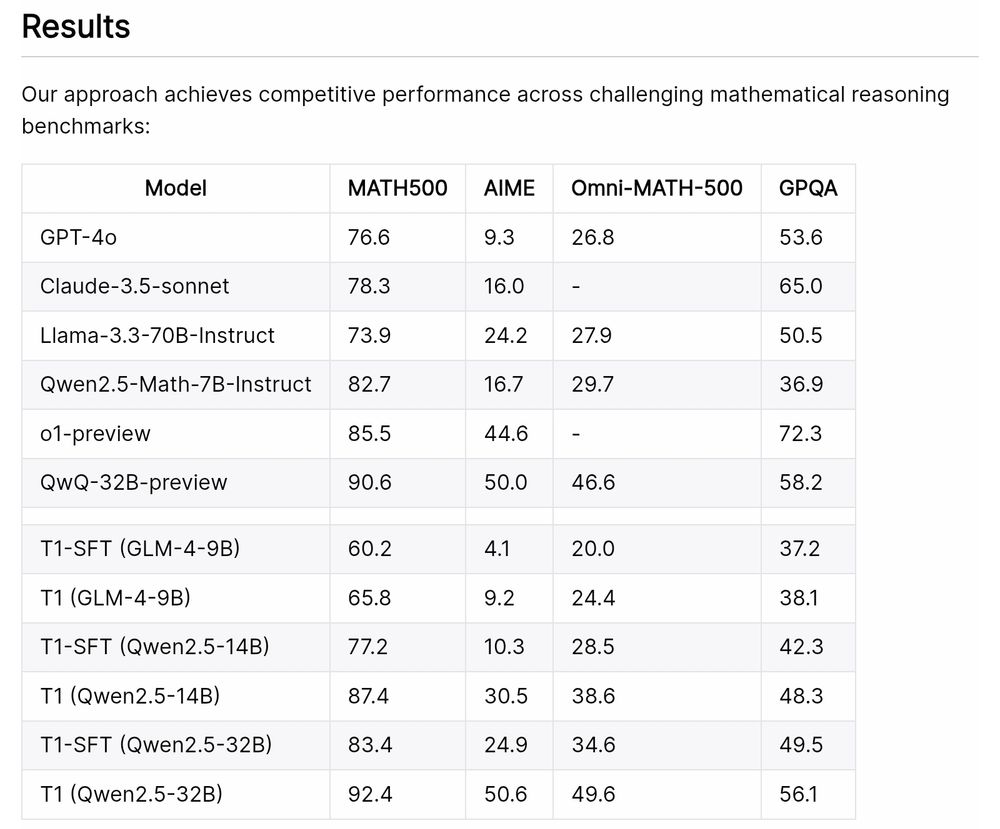
Zhipu AI's T1 (open-source: paper, code, dataset, and model)
Advancing Language Model Reasoning through Reinforcement Learning and Inference Scaling
T1 is trained by scaling RL by encouraging exploration and understand inference scaling.
27.01.2025 01:49 — 👍 10 🔁 1 💬 2 📌 0
Naihao Deng, Sheng Zhang, Henghui Zhu, Shuaichen Chang, Jiani Zhang, Alexander Hanbo Li, Chung-Wei Hang, Hideo Kobayashi, Yiqun Hu, Patrick Ng
Towards Better Understanding Table Instruction Tuning: Decoupling the Effects from Data versus Models
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14717
27.01.2025 05:45 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Ziyao Xu, Houfeng Wang
Investigating the (De)Composition Capabilities of Large Language Models in Natural-to-Formal Language Conversion
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14649
27.01.2025 06:26 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Jia Yu, Fei Yuan, Rui Min, Jing Yu, Pei Chu, Jiayang Li, Wei Li, Ruijie Zhang, Zhenxiang Li, Zhifei Ren, Dong Zheng, Wenjian Zhang, Yan Teng, Lingyu Meng, ...
WanJuanSiLu: A High-Quality Open-Source Webtext Dataset for Low-Resource Languages
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14506
27.01.2025 06:42 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Jie He, Yijun Yang, Wanqiu Long, Deyi Xiong, Victor Gutierrez Basulto, Jeff Z. Pan
Evaluating and Improving Graph to Text Generation with Large Language Models
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14497
27.01.2025 06:43 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Verena Blaschke, Masha Fedzechkina, Maartje ter Hoeve
Analyzing the Effect of Linguistic Similarity on Cross-Lingual Transfer: Tasks and Experimental Setups Matter
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14491
27.01.2025 06:56 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Zeping Yu, Sophia Ananiadou
Understanding and Mitigating Gender Bias in LLMs via Interpretable Neuron Editing
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14457
27.01.2025 07:06 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Xu Chu, Zhijie Tan, Hanlin Xue, Guanyu Wang, Tong Mo, Weiping Li
Domaino1s: Guiding LLM Reasoning for Explainable Answers in High-Stakes Domains
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14431
27.01.2025 07:06 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Xinyu Ma, Yifeng Xu, Yang Lin, Tianlong Wang, Xu Chu, Xin Gao, Junfeng Zhao, Yasha Wang
DRESSing Up LLM: Efficient Stylized Question-Answering via Style Subspace Editing
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14371
27.01.2025 07:12 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Chao-Chung Wu, Zhi Rui Tam, Chieh-Yen Lin, Hung-yi Lee, Yun-Nung Chen
Clear Minds Think Alike: What Makes LLM Fine-tuning Robust? A Study of Token Perplexity
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14315
27.01.2025 07:13 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Lifu Gao, Qi Zhang, Ziwei Liu
A Comprehensive Framework for Semantic Similarity Detection Using Transformer Architectures and Enhanced Ensemble Techniques
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14288
27.01.2025 07:18 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Sadegh Mahdavi, Muchen Li, Kaiwen Liu, Christos Thrampoulidis, Leonid Sigal, Renjie Liao
Leveraging Online Olympiad-Level Math Problems for LLMs Training and Contamination-Resistant Evaluation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14275
27.01.2025 07:24 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Yi Zhao, Youzhi Zhang
Siren: A Learning-Based Multi-Turn Attack Framework for Simulating Real-World Human Jailbreak Behaviors
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14250
27.01.2025 07:24 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Dongming Sheng, Kexin Han, Hao Li, Yan Zhang, Yucheng Huang, Jun Lang, Wenqiang Liu
Test-Time Code-Switching for Cross-lingual Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14144
27.01.2025 07:35 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
The world's leading venue for collaborative research in theoretical computer science. Follow us at http://YouTube.com/SimonsInstitute.
The Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) is a scientific and professional organization for people working on Natural Language Processing/Computational Linguistics.
Hash tags: #NLProc #ACL2025NLP
Math & Art Videos.
* https://youtube.com/Inigo_Quilez
* https://iquilezles.org
Created Shadertoy, Pixar's Wondermoss, Quill, and more.
The Milan Natural Language Processing Group #NLProc #AI
milanlproc.github.io
Professor @milanlp.bsky.social for #NLProc, compsocsci, #ML
Also at http://dirkhovy.com/
We are a centre dedicated to the study of collective behaviour | Integrative and Quantitative | Cluster of Excellence
@uni-konstanz.de, Germany.
Website: https://www.exc.uni-konstanz.de/collective-behaviour/
Behavioral ecologist using drones to study collective behavior of African ungulates. Leader of HerdHover project and co-PI of WildDrone project. Project Leader at the Max Planck Institute for Animal Behavior, currently on TT job market. She/her.
Computer scientist and international rock icon building AI tools for wildlife conservation.
I'm a PhD student at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) in computer science working on AI for Earth. My goal is to use AI for good and make the Earth a better place.
Scientist at CNRS.
https://audio.ls2n.fr
Research fellow at UWI, prev. at UofT
Spatial ecologist | Urban mammals | Modeling animal movement, habitat selection, connectivity, species interactions and HW coexistence. Working with camera traps and GPS tracking data. Twitter was @UrbanZochory
Senior Researcher @ Aarhus University, DK. Acoustic communication, acoustic AI, acoustic monitoring, acoustic individual ID,
focus on cetaceans
🇦🇶 ML Research Scientist @bas.ac.uk, applying computer vision to the Antarctic benthos
assistant professor of environmental policy @ ETH Zurich 🌎🌱
ecology, decision theory, data & algorithmic justice
https://milliechapman.info
stay curious, have fun
Professor of Ecology, QUT, Meanjin Brisbane. Director Conservation AI Network. https://conservationai.net/ Drones, cameras, satellites, acoustics & AI for biodiversity. Focusing on Nature Based Solutions.
Founder of Global Fishing Watch, sci-fi lover, python developer, arduino hobbyist globalfishingwatch.org
Lecturer in Conservation Biology & Ecology. BES Associate Editor. SFHEA. Proud IVF Mama, Birder, & Metalhead. ❤️ Parkrun & steam locos. She/Her. Views are my own 🤘
Software engineer. Previously: Microsoft, U.S. Digital Service. Hacking on Govsky! US Account: @us.govsky.org.
Views expressed here are lukewarm at best and do not represent those of my employer
📝 blog: https://nick.scialli.me
A mathematician/computer-scientist/conservationist doing a PhD at the University of Exeter under K Hockings, D Hodgson and M Mueller using AI and ML algorithms for chimpanzee conservation.
🌊 Ocean conservation research 🪸
Mapping human activity at sea with ML
ᵃˡˢᵒ
🇨🇦 Vancouver snowboarder, surfer, hiker, &
astrophysics PhD. Learning Finnish but god at what cost











