Enteropathogenic bacteria evade ROCK-driven epithelial cell extrusion - Nature
The bacterial ubiquitin ligase NleL evades host defence mechanisms both by inhibiting pyroptosis and by preventing infected intestinal epithelial cells from being extruded into the lumen and expelled ...
#EveryCellIsAnImmuneCell! Luchetti @rauchlab.bksy.social Dixit &co show @nature.com that enteropathogenic bacteria evolved a virulence factor that degrades non-canonical #inflammasome & targets ROCKs necessary for luminal extrusion of infected intestinal #epithelial cells, favoring bacterial growth!
22.10.2025 21:40 — 👍 10 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 0
No budget increase for the Australian Research Council 😡
25.03.2025 08:50 — 👍 38 🔁 16 💬 1 📌 4
Congrats Michelle, @kaiwenchen-lab.bsky.social and team
25.03.2025 02:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
I’m happy to share that my first first-author publication is now out! 🎉
24.03.2025 12:59 — 👍 9 🔁 1 💬 3 📌 0
This is amazing!!!
07.03.2025 20:14 — 👍 9 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
Group Leader
Group Leader
We are recruiting a group leader in laboratory research at Peter Mac Cancer Centre in
Melbourne, Australia 🔬🦘💥
Work in a cutting edge research environment in a vibrant world city!
We value research excellence, creativity and diversity.
Join us!
careers.petermac.org/job/MELBOURN...
05.03.2025 08:04 — 👍 30 🔁 34 💬 0 📌 5

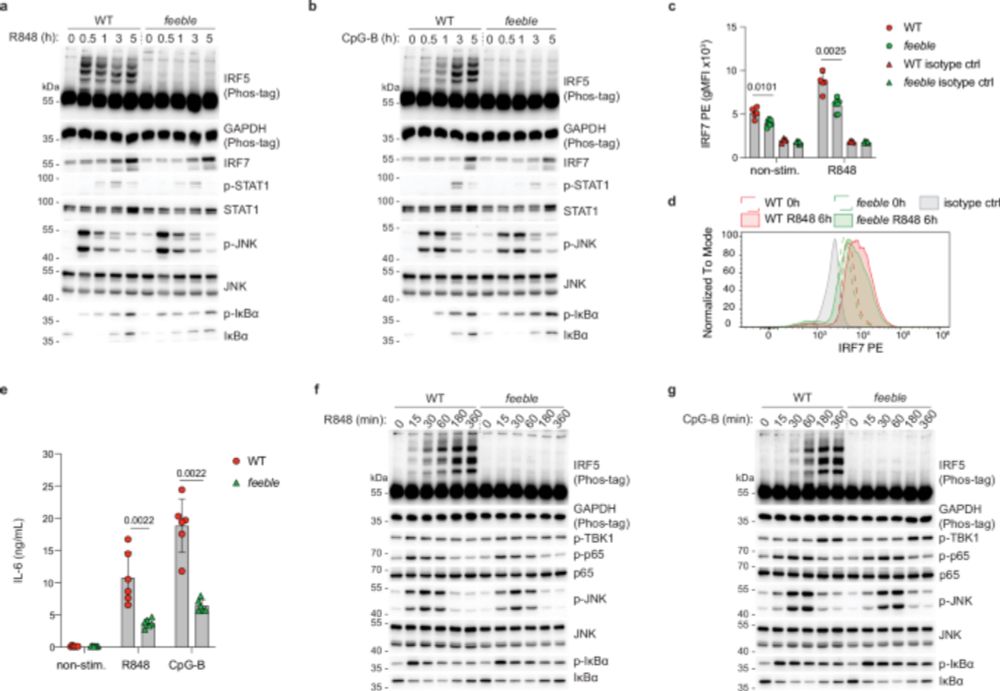
NHMRC Investigator grant success 2025
Research into autoinflammatory diseases, hypertension, cancer and perinatal brain injury has been funded by NHMRC Investigator grants.
I am incredibly fortunate and delighted to have been awarded a NHMRC Emerging Leadership Level 1 Investigator Grant this year! 🥳 This funding will provide crucial support for my research on interferon epsilon in cancer over the next 5 years. @hudsonresearch.bsky.social #nhmrc #investigatorgrant
26.02.2025 03:22 — 👍 18 🔁 2 💬 3 📌 0
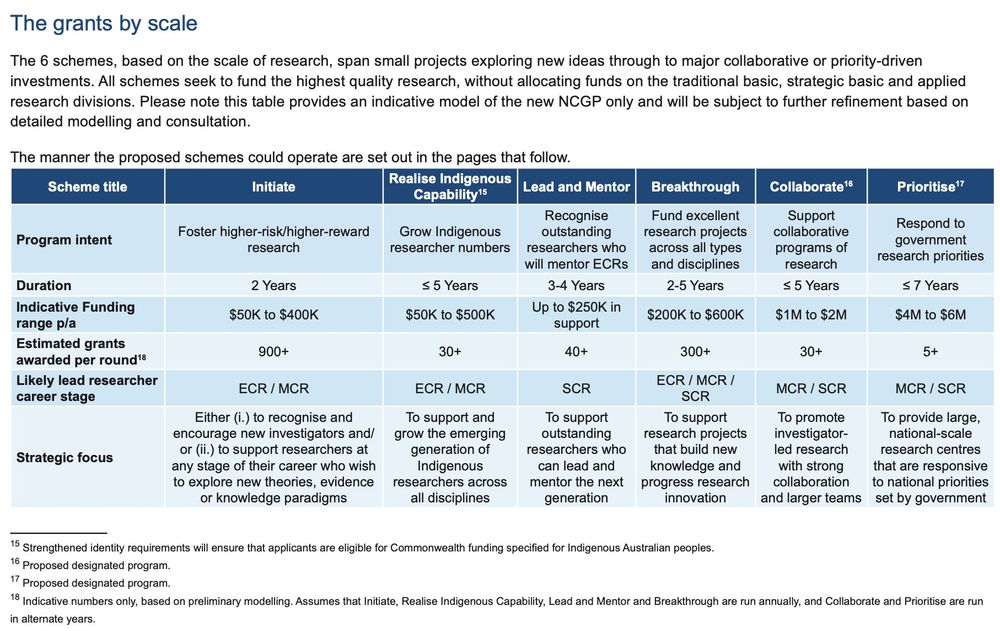
Table from page 25 of the proposed restructure of ARC grants. Back text on white background, with the table delineated by a dark blue header row and alternating light and very light blue rows.
The ARC Board has proposed a major shake-up of the National Competitive Grants Program ▶️ www.arc.gov.au/engage-us/co...
I've only skimmed so far, but they propose reducing 13 grant schemes to 6, with intent & scope in the table👇
Submissions are being accepted in response until 13 April. Get to it!
25.02.2025 03:45 — 👍 69 🔁 53 💬 15 📌 15
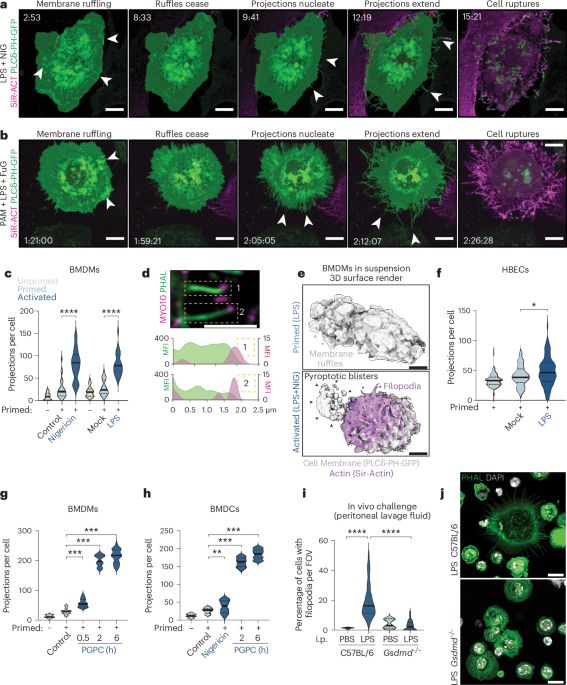
Excited to share our latest preprint! We find that DCs undergo heterogeneous cell death- either pyroptosis or apoptosis upon bacterial blockade of host translation- to restrict Legionella infection. Congrats to my PhD student @vvazquez.bsky.social & co-authors! Check out his bluetorial 🧵 below! 👇
21.02.2025 18:43 — 👍 31 🔁 10 💬 0 📌 0
Would love to talk to ECRs who might be interested in applying for a post-doctoral fellowship to study human inflammasomes! The Royal Society Newton International Fellowships are open to anyone outside the UK. More details in the post below
30.01.2025 13:33 — 👍 2 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0

Confirmed speakers:
A. Ablasser
L. Andreeva
@audeber.bsky.social
@jelenalab.bsky.social
V. Dixit
@v-hornung.bsky.social
B. Lemaitre
O. Majer
@manellab.bsky.social
E. Miao
@oliveiramann.bsky.social
M. Pasparakis
@inflammasomelab.bsky.social
@sparrerlab.bsky.social
R. Vance
@lozanzi.bsky.social
28.01.2025 14:33 — 👍 10 🔁 5 💬 1 📌 0

Antigen-presenting cell activation requires intrinsic and extrinsic STING signaling after the phagocytosis of DNA-damaged cells
Both cytosolic DNA species and innate immune STING signaling are required for stressed cells to activate phagocytes.
#WeekendRead! #EveryCellisAnImmuneCell! Park, Ahn & Barber show @sciimmunology.bsky.social that DNA-damaged cells activate cGAS-STING secreting factors & induce endosomal vesicles that activate in antigen-presenting cells cGAS-STING inducing immune activation! www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
22.12.2024 16:27 — 👍 33 🔁 10 💬 0 📌 0
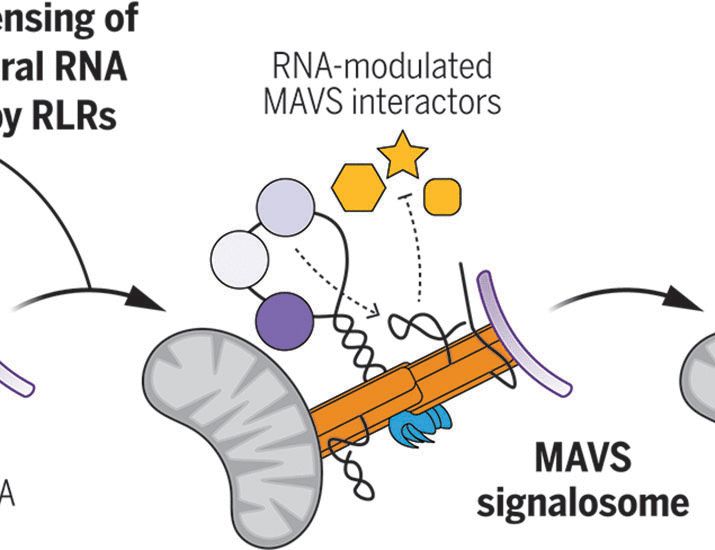
Cellular RNA interacts with MAVS to promote antiviral signaling
Antiviral signaling downstream of RIG-I–like receptors (RLRs) proceeds through a multi-protein complex organized around the adaptor protein mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS). Protein co...
#InterferonPower! Fantastic @science.org by @nandangokhale.bsky.social @ramlabuw.bsky.social &co! MAVS is intrinsically capable to sense via an unstructured region the 3’ UTRs of self mRNA (ISGs too!) to potentiate the response to viral RNA via phosphorylation of IRF3 & NFkB!
19.12.2024 21:39 — 👍 51 🔁 19 💬 0 📌 0
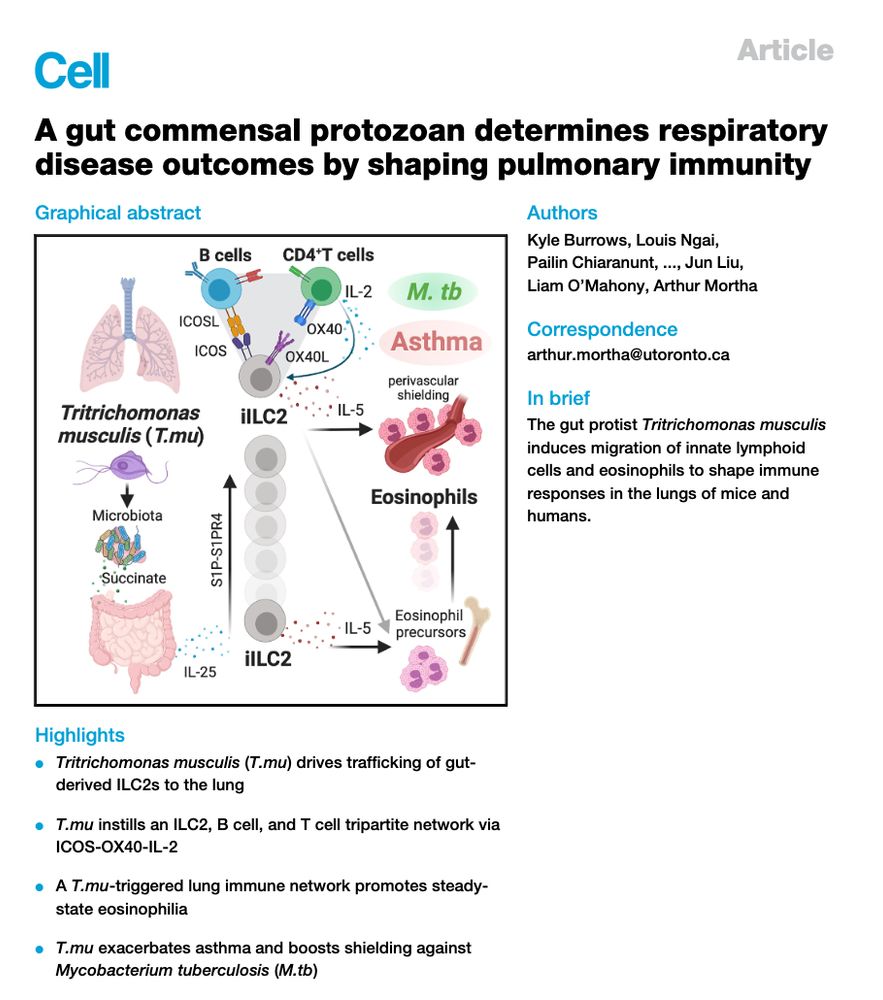
Ever wondered how gut microbes control immune responses at extra-intestinal locations?
Here #theonlylabever reports how a gut protozoan commensal shapes pulmonary immunity to exacerbate asthma and limit the dissemination of mycobacteria.
@cellpress.bsky.social ⬇️(1/x)
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
19.12.2024 21:30 — 👍 103 🔁 39 💬 10 📌 3
Chief Scientific Research Officer – Olivia Newton John Cancer Research Institute
Are you a strong leader who wants to make a difference in cancer research? Become part of a dynamic, forward-thinking leadership team @onjcri.org.au and contribute to groundbreaking work that improves the lives of cancer patients. www.onjcri.org.au/join-our-tea...
12.12.2024 23:47 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Chief Scientific Research Officer – Olivia Newton John Cancer Research Institute
@onjcri.org.au is seeking a visionary Chief Scientific Research Officer (CSRO) to lead cutting-edge cancer research. If you have the qualifications and passion to make a real impact, don’t miss this chance! Submit your EOI here: www.onjcri.org.au/recruitment/...
#CancerResearch #Anticancer
10.12.2024 23:04 — 👍 4 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Happy to share our latest preprint from 1st author & PhD student @vvazquez.bsky.social examining how GM-CSF potentiates cytokine responses in human monocytes during bacterial infection! Congrats to Victor, his undergrad mentees Allyson Lu & Madison Dresler, & postdoc @mikelhaggadone.bsky.social! 🧪
11.12.2024 02:05 — 👍 51 🔁 13 💬 0 📌 2

The inflammatory microenvironment of the lung at the time of infection governs innate control of SARS-CoV-2 replication
Recent or ongoing respiratory inflammation in the lung regulates antiviral immune responses to SARS-CoV-2.
Excited to share this paper from my post-doc at @niaidnews.bsky.social out now in Science Immunology! We show that recent or ongoing 🫁 infections or other pulmonary environmental exposures at the time of infection with SARSCoV2 can vastly influence early replication of the virus in mice.
07.12.2024 23:47 — 👍 37 🔁 9 💬 2 📌 0
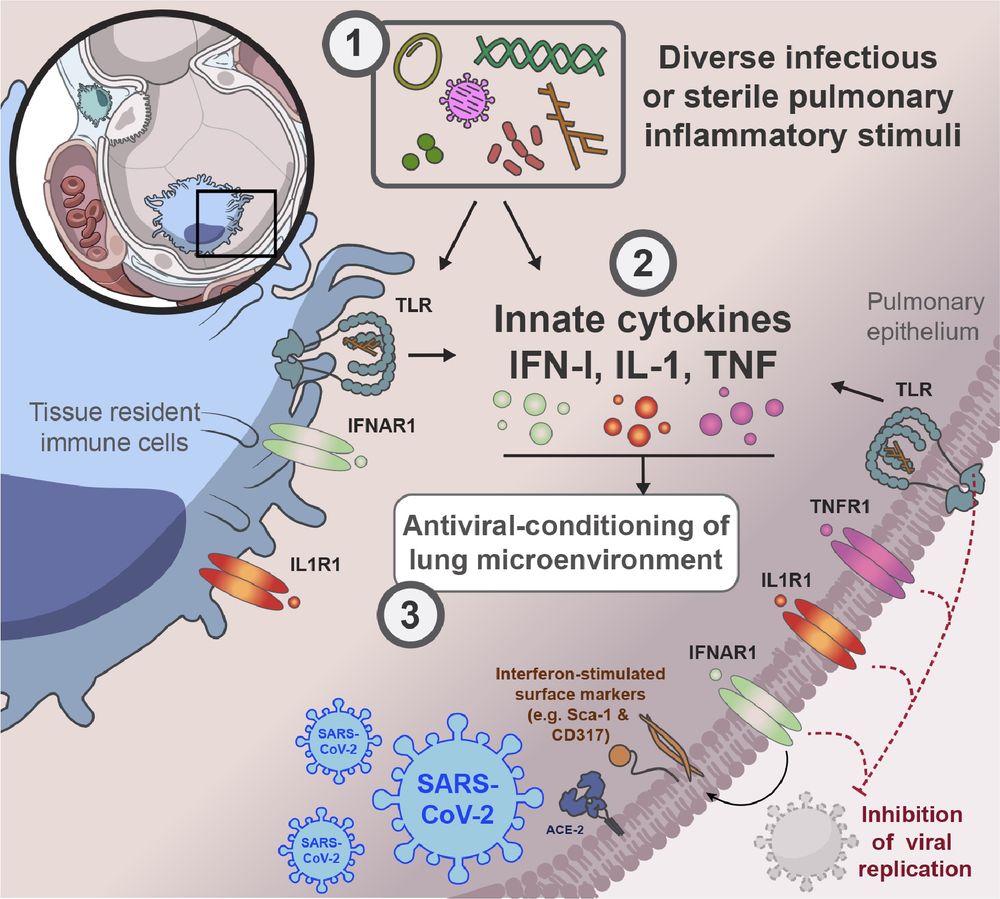
Graphical summary of our paper. In mice, prior lower airway exposure to diverse inflammatory stimuli, including chronic bacterial infections such as M. tuberculosis, acute bacterial infections such as pulmonary S. aureus, viral infections such as Influenza A, type-II allergic responses such as the OVA-Alum model, activation of pulmonary TLR9 by CpG or pulmonary TLR1/2 by Pam3CSK4
leads to reduced viral burden upon subsequent infection with SARS-CoV-2 (SCV2). (2) This SCV2 restriction occurs prior to induction of SCV2-specific adaptive immune responses
and is mediated through innate immune responses, including the induction of IFN-I, TNFα and IL-1 and sustained changes to the TRM (Tissue resident macrophage) cellular
compartment and the pulmonary epithelium. (3) Innate cytokine and TLR signaling to both recruited immune cells and the pulmonary epithelium creates a microenvironment in the
lung that limits early replication of SCV2. IFN-I signaling to pulmonary ECs (epithelial cells) increases expression of interferon-stimulated genes, that likely cell-intrinsically limit viral
replication. TNF- or IL-1 suppress SCV2 independently of IFN-I signaling. TNF acts exclusively through radio-resistant cell types such as the lung epithelium, whereas IL-1 affords
control both direct and indirectly, through either stromal and hematopoietic cell types, to restrict overall early SCV2 burden.
Best #Nikolaus 🎅! Our paper on how the 🫁 microenvironment can shape #innate immunity against #viruses is out @sciimmunology.bsky.social This was a herculean effort brilliantly led by @pauljbaker.bsky.social who singlehandedly established the model in the lab during the pandemic. 🧪 #Immunosky 1/9
06.12.2024 22:37 — 👍 295 🔁 84 💬 28 📌 9
Structural biologist studying proteins that move things from A to B. University of Queensland, Institute for Molecular Bioscience. Centre for Cell Biology of Chronic Disease.
He/Him.
https://imb.uq.edu.au/research-groups/collins
🔬 Assistant Prof, Pathology @Duke | Director, Clin Micro Lab
🧫 Former Clin Micro Fellow @Memorial Sloan Kettering
👩🏻🔬 Former Postdoc @broadinstitute.org
🎓 PhD @The Rockefeller University
Focus: Diagnostics, AMR, Structural Biology
The Centre for Innate Immunity and Infectious Diseases (CiiiD) is a world-leading centre advancing research into the immune system’s role in infection, inflammation, and cancer. We decode innate immunity to develop diagnostics and therapies.
PhD in molecular biology.
Human immunogenetics of multifactorial diseases. | Studying the molecular cascades involved in adaptive immune response.
Open to postdoctoral positions🧬
🇦🇺 cell biologist in 🇨🇿 currently studying primary cilia biology through the lens of the kinase TTBK2 and a 🔬 | past scientific history: inflammatory cell death, pseudokinases | used to dispatch ambulances | she/her
Part human, part bot, 100% UNOFFICIAL. I track Australian Research Council grant outcomes. Bot checks outcomes announcements each min. DMs open. FAQ: https://tinyurl.com/ARC-Tracker-FAQ
A/Prof Michelle Tate's Laboratory at Hudson Institute of Medical Research, Australia
influenza, silicosis, pulmonary inflammation, host-directed therapies
Head of the Translational Kidney Therapies Group at Monash University, Melbourne Australia. Researching autoimmune kidney diseases, vasculitis, neutrophil NETs, cell death pathways and manipulation of the gut microbiome to reduce kidney inflammation.
Cell Biology meets Immunology and Virology, spiced up with nanobodies
Postdoc @kaiwenchen-lab.bsky.social studying cell death, inflammation and host-pathogen interaction at National University of Singapore
Riding a curiosity-driven research EV.
Postdoctoral fellow in Lalaoui lab @petermaccc.bsky.social. Studying how inborn genetic mutations cause diseases. All things cell death, inflammation and RIPK1.
Biomedical researcher at WEHI. BCL2, mitochondria, apoptosis and targeted therapies for leukemias/lymphomas.
Keen on discoveries in bacterial cell biology and bacteriophages, working to impact AMR. Fan of the ocean. Opinions my own.
🔬 Bringing together the Australasian cell death research community. Supporting researchers with seminars, networking sessions, mentoring programmes, and professional development.
Curious & passionate group leader at @cniostopcancer.bsky.social
Myeloid cells, Cancer & Immunotherapy.
https://casanovaacebeslab.com/
Deputy Editor at Journal of Experimental Medicine, interested in host-pathogen interaction, innate immunity and beyond. Opinions are my own.
Cell & Developmental Biology. Vascular Biology. Lymphatics. Zebrafish.
Associate Director of Laboratory Research at Peter Mac Cancer Centre. Professor at The University of Melbourne.
Postdoctoral Scientist @Rutgers NJ Medical School. PhD from @HansbroResearch,Centre for Inflammation,Centenary Institute & GSH, UTS, Sydney,Australia
Respiratory Immunology| Host-Pathogen Interactions| Immunometabolism| Chronic Lung Disease
Department of Immunology
Institute of Nutritional Medicine
#unihohenheim
#immunosky
https://immu.uni-hohenheim.de/en
Innate immunologist, virologist, #cGAS, #STING, #Vaccines. Harpo Marxist.