🎉 So excited to host the next CompleNet conference 🎉
Don’t miss it 👇 See you next May in Zaragoza!!!
GOTHAM lab
@gotham-lab.bsky.social
Group of Theoretical and Applied Modeling at @www.unizar.es Website: https://gotham.bifi.es/
@gotham-lab.bsky.social
Group of Theoretical and Applied Modeling at @www.unizar.es Website: https://gotham.bifi.es/
🎉 So excited to host the next CompleNet conference 🎉
Don’t miss it 👇 See you next May in Zaragoza!!!

This week we are hosting Olga Vasilieva from Univalle (Colombia), to discuss new approaches to mitigate vector-borne diseases in both plants and human populations.
Yesterday we had the pleasure of attending her talk on control mechanisms to eliminate Diaphorina citri, super interesting!!!

4/4 Finally, we establish a general correspondence between our model and broader classes of competing social contagion dynamics with symmetry breaking, recovering previous results as limiting cases.
09.09.2025 08:59 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
3/4 Groups induce discontinuous (explosive) transitions between fully honest and fully corrupt regimes, separated by a bistable phase!
Importantly, this abrupt behavior disappears in the pairwise limit, highlighting the destabilizing effect of group interactions.

2/4 We introduce a higher-order model to study the emergence of systemic corruption in populations where individuals interact through group structures. By including groups, we capture the influence of peer pressure in group settings.
09.09.2025 08:59 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
🚨 New article about corruption, HOs interactions & explosive transitions
pubs.aip.org/aip/cha/arti...
1/4 Great work done by Elisa, Clara, Verónica, Gabriela together w. @santiagolaot.bsky.social Hugo Perez-Martínez & @gomezgardenes.bsky.social
MS also available here arxiv.org/abs/2509.04764


Asado grupal para cerrar el curso académico. A pesar del calor a la brasa sabe mejor!!!
28.06.2025 17:19 — 👍 8 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0

Hoy pleno de GoThAM en la sesión de posters de #Fises25 !! @difensc-rsef.bsky.social
19.06.2025 14:42 — 👍 10 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
🚨 New preprint out!
Our latest work explores the interface between complex networks, epidemic spreading, and eco-evolutionary dynamics arxiv.org/abs/2506.03279
By a great team: @santiagolaot.bsky.social + Octavio Rotita + Alex Arenas + @sorianopanos.bsky.social + @gomezgardenes.bsky.social
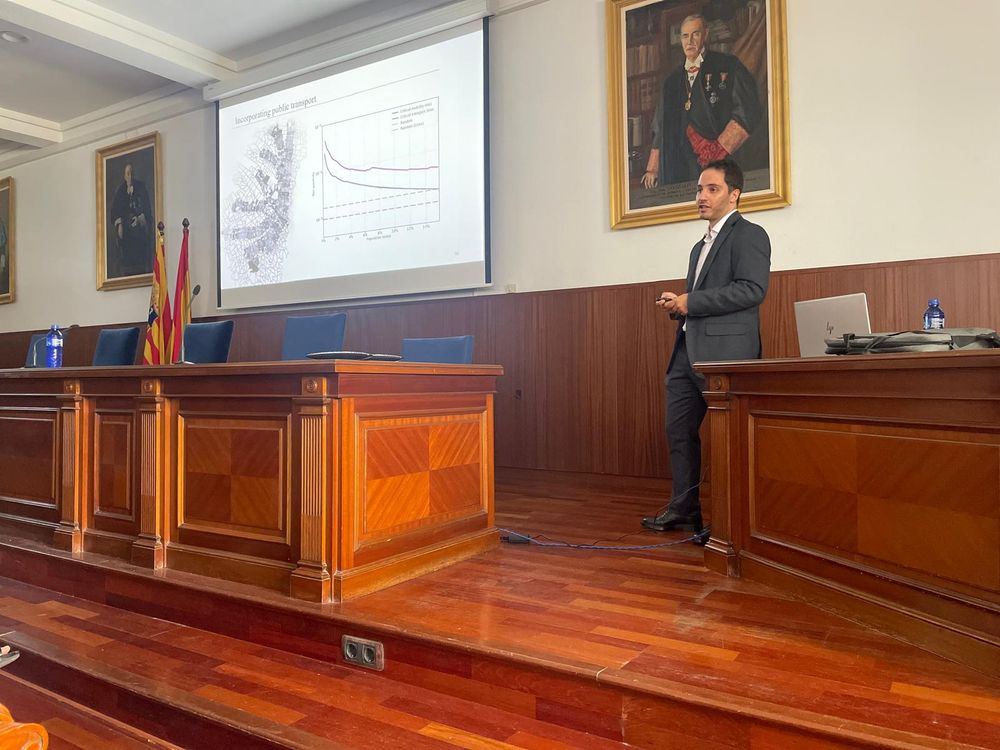
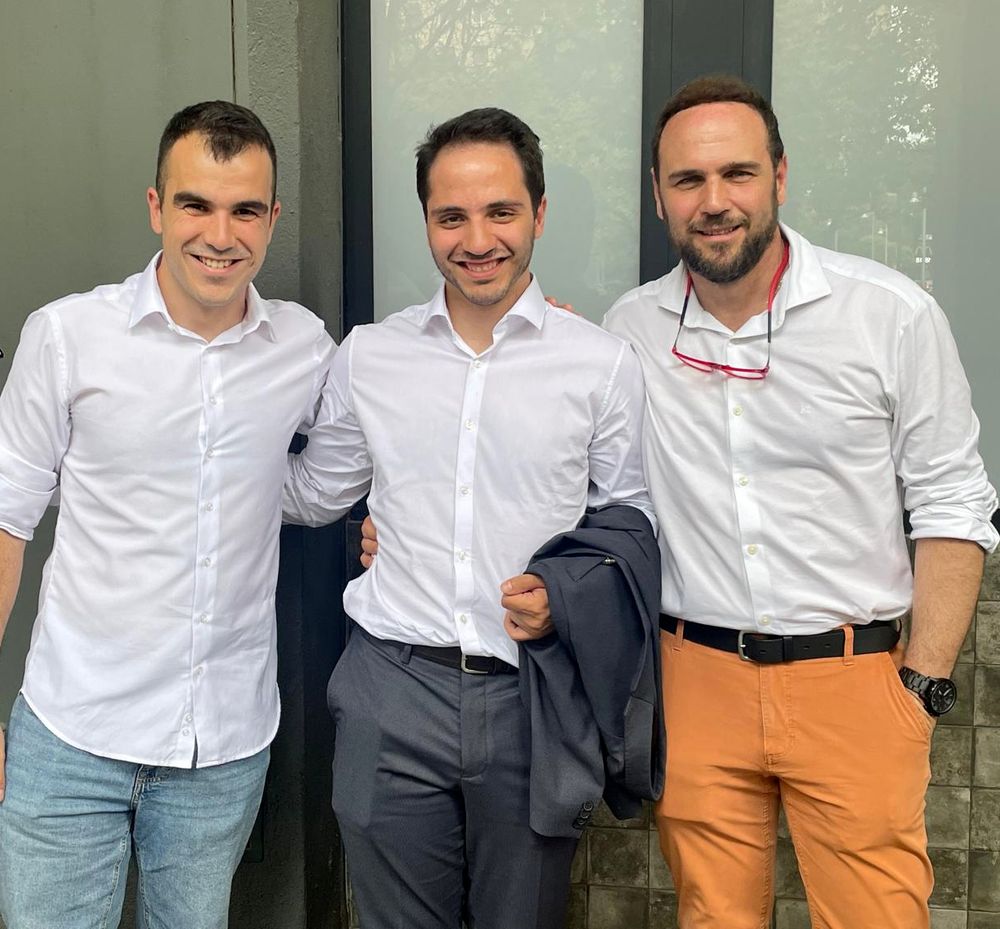
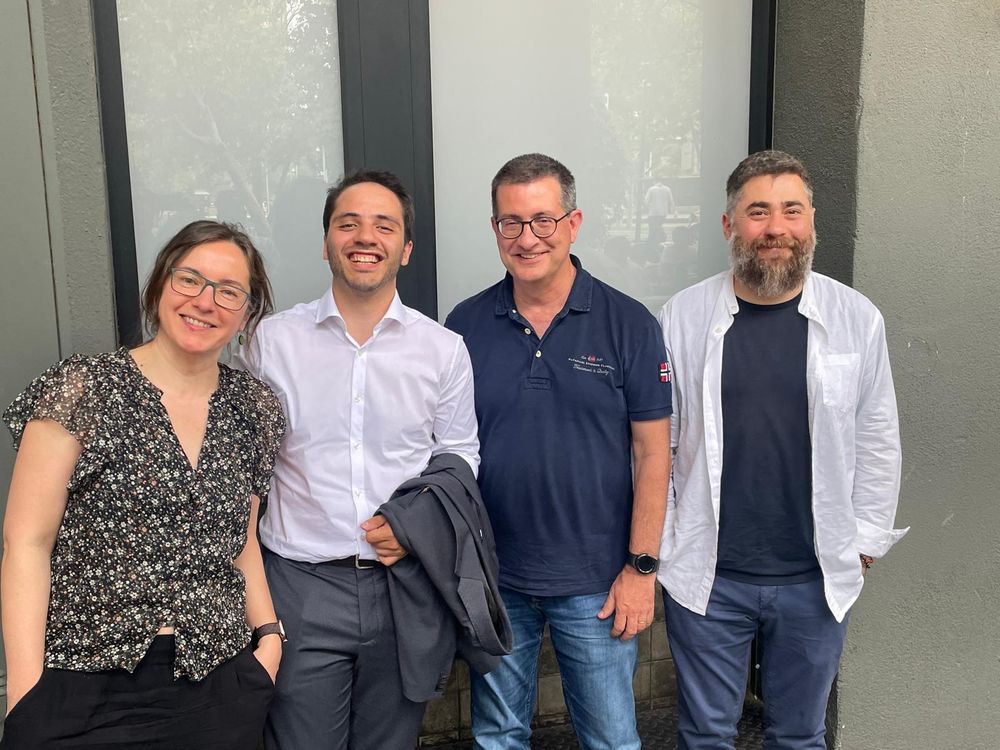



Habemus new doc in the lab! 🎓
Big congrats to @pvalganon.bsky.social for a superb PhD thesis!
It has been great to have you with us these years and wish you a vibrant and exciting scientific journey ahead. 🚀
Congrats also to the supervisors @sorianopanos.bsky.social & @gomezgardenes.bsky.social
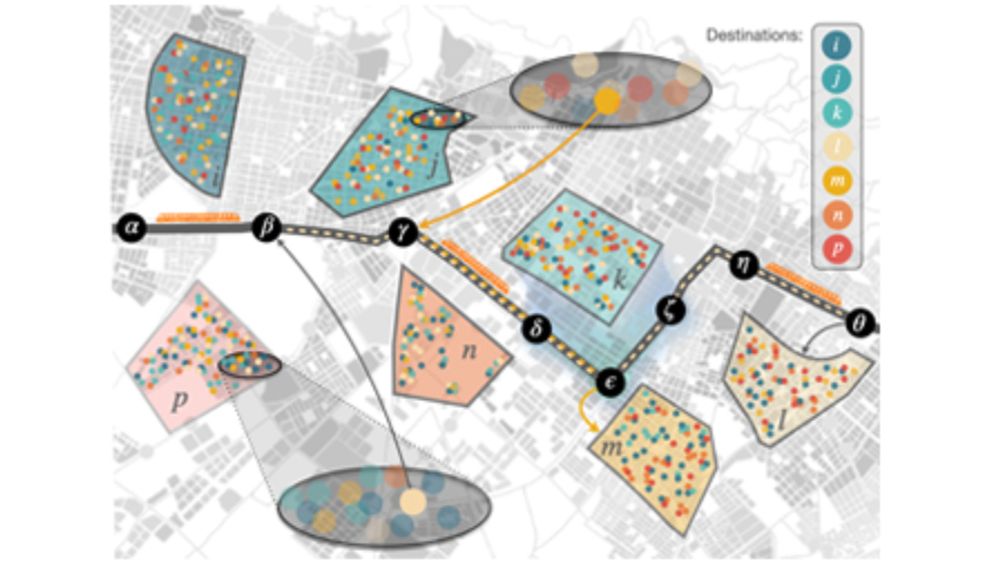
6/6 To round off:
🚍 In itinere contagions are critical for understanding real-world epidemics in cities.
They reshapes both the magnitude and spatial profile of outbreaks—vital insights for designing effective containment strategies.
📄 Read the full paper here: doi.org/10.1063/5.02...
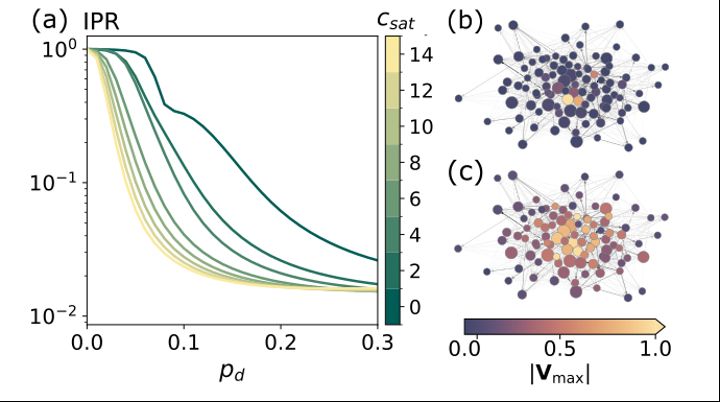
5/6 📍It doesn't end there….in itinere contagions are also a key force behind epidemic delocalization.
We find that they precipitate a transition from localized outbreaks (confined to vulnerable patches) to a widespread propagation.
🧭 This drastically shifts the spatial epidemic landscape.
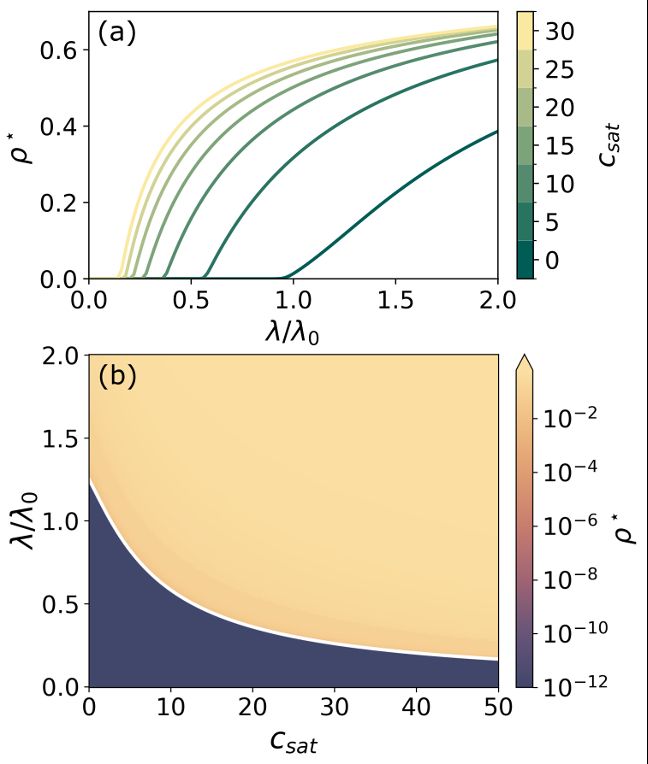
4/6 🧨 In itinere contagion counteracts 🥊 epidemic detriment – the idea that mobility (up to a critical value) suppresses epidemic spread.
We show that transit-based infections reshape this boundary, modifying the critical conditions under which mobility boosts or suppresses epidemic outbreaks.
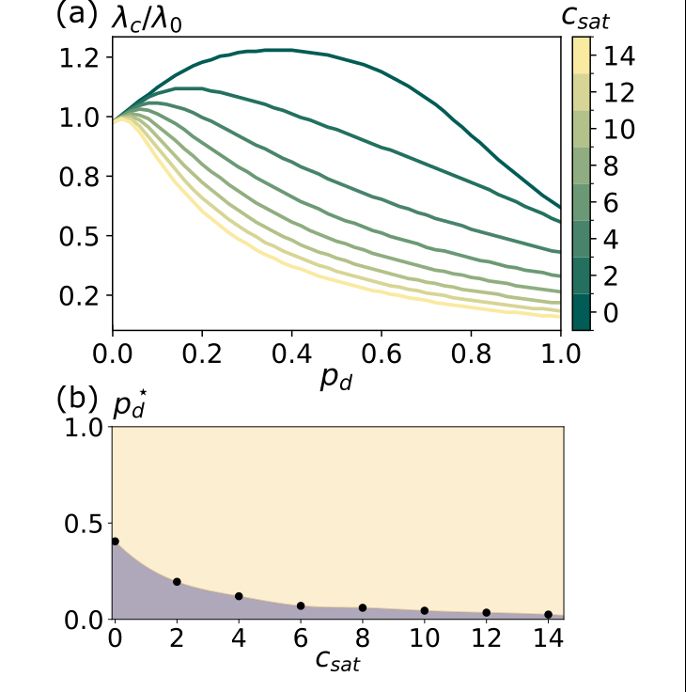
3/6 ⚠️ Including in itinere infections significantly lowers 🔻 the epidemic threshold and increases disease prevalence!
We show that neglecting in-transit infections leads to a serious underestimation of epidemic severity and population vulnerability. A hidden risk that standard models miss 🧩
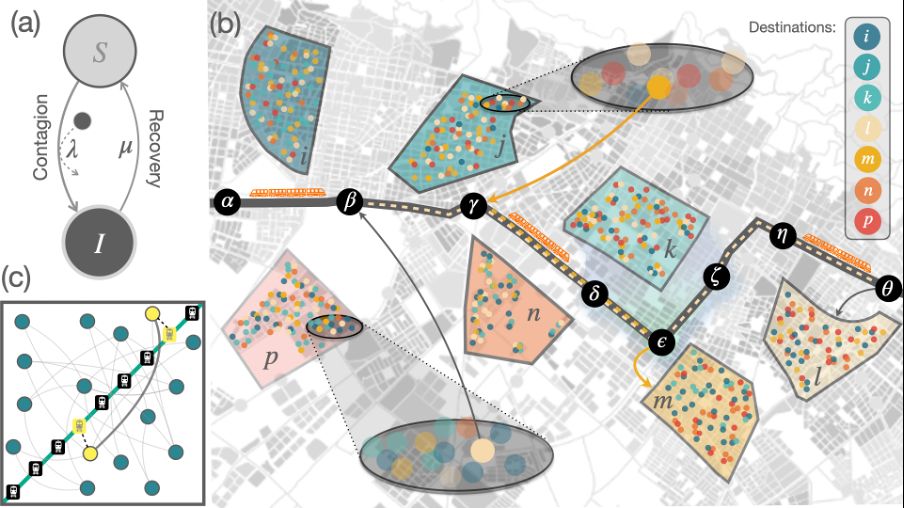
2/6 Most metapopulation-based epidemic models assume people only spread disease within specific locations.
🚌 But what about infections acquired on the move?
We extended our MIR framework introducing infections that happen while commuting, in particular on public transport, key in urban settings.

🚨New paper out:
1/6 We are happy to share our work "In itinere infections covertly undermine localized epidemic control in metapopulations" published in CHAOS by @frandilisante.bsky.social @pvalganon.bsky.social @sorianopanos.bsky.social & @gomezgardenes.bsky.social
🔗 doi.org/10.1063/5.02...
 26.04.2025 12:56 — 👍 10 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 1
26.04.2025 12:56 — 👍 10 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 1
We are happy & honored of being the next host of @complenet.bsky.social
Can’t wait to welcome you to Zaragoza next May 2026!!!


@gallartaspablo.bsky.social talking about the emergence of innovations and the role of reputation at @complenet.bsky.social !
23.04.2025 17:16 — 👍 10 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 0

@santiagolaot.bsky.social now at @complenet.bsky.social in Fortaleza talking about higher-order interactions and the emergence of collective states #complenet2025
22.04.2025 19:07 — 👍 9 🔁 6 💬 0 📌 1
🚨 New preprint arxiv.org/abs/2504.07849 showing that "in itinere" 🚋🚋🚋 contagions 🦠 undermine local epidemic control, lowering thresholds & driving early outbreak delocalization across urban 🏢 areas.
Francesca Dilisante @pvalganon.bsky.social @sorianopanos.bsky.social & @gomezgardenes.bsky.social
5/5 Overall, our study pinpoints that balancing commuting and roaming can help contain outbreaks without drastic traffic cuts, offering insights for targeted interventions that reduce the risk of global epidemic spread.
More info at: journals.aps.org/pre/abstract...
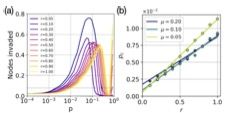
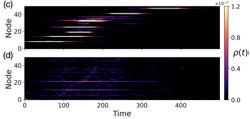
4/5 We then explore the “invasion” threshold (i.e. how local outbreaks can become global 🌏) for low mobility scenarios.
Agents with low exploratory behavior spend less time in new places, reducing the spread window and raising the required mobility to generate a global epidemic.
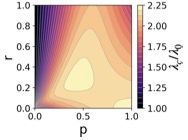

3/5 By creating the new generation matrix, we obtain the epidemic threshold ⚠️.
Interestingly, it depends on how frequently agents return versus how much they roam:
Random-walk–dominated dynamics (low return, high mobility) typically yield a higher threshold for 🦠 to spread!
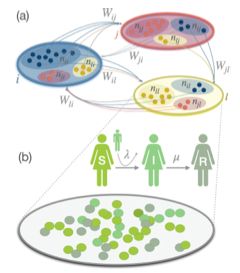
2/5 We developed a metapopulation formalism in which the key parameter is the “return” probability, blending commuting and exploratory behaviors in a balanced way:
High return → more commuting 🚌 (agents quickly go back), low return → more exploration 🧭 (random walks).
📌 New paper alert!!!
1/5 How is the spread of epidemics shaped by both random walks and commuting? We answer this question in this paper appeard in Physical Review E by @pvalganon.bsky.social, A Brotons, @sorianopanos.bsky.social & @gomezgardenes.bsky.social 👇
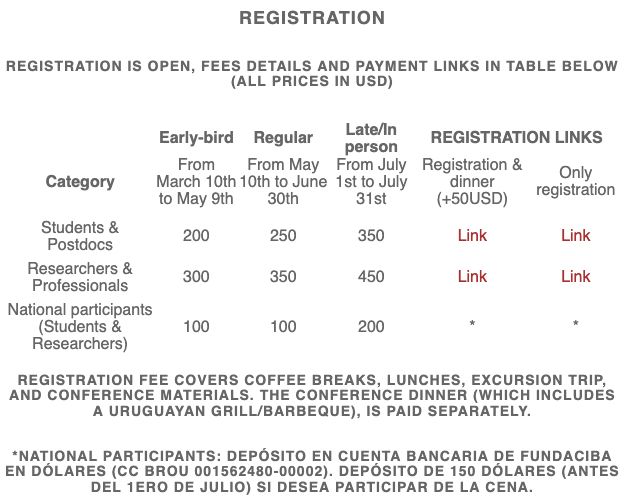
@lanetconference.bsky.social será uno de los mejores eventos de sistemas complejos de este año. ¡INSCRIPCIONES ABIERTAS! (lanet2025.uy) Contamos con inscripciones anticipadas, regulares y presenciales, para estudiantes, postdoctorados, investigadores y nacionales. Será una gran experiencia.
04.03.2025 13:57 — 👍 3 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 06/6 Our results emphasize the crucial role of structural details and correlations in higher-order systems, paving the way for applications in diverse fields where collective behaviors and higher-order interactions are pivotal such as brain dynamics.
More details in: go.aps.org/3FfNGJ6
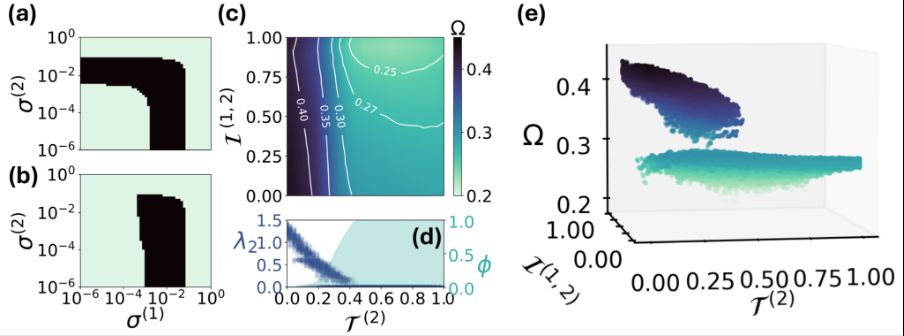
5/6 These spectral changes have profound effects on synchronizability:
☑️ Large hyperedge overlap hinders synchronizability. In particular, large intra-order overlap can fragment structures, making global synchronization impossible!
☑️ On the other hand, large overlap promotes local synchronization
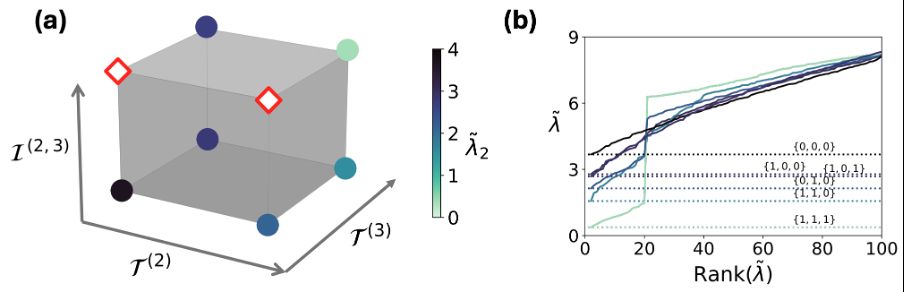
4/6 Intra-order overlap polarizes the Laplacian eigenvalue spectrum by promoting mesoscale clusters.
Inter-order overlap can promote the mesoscale localization (large overlap) or distort it (low overlap).
There is a hierarchy 🥇🥈🥉, the larger the interaction order, the stronger these effects!!!