
Princeton Chemistry demonstrates high-performance Sodium-ion cathode towards new battery technology
"High-Energy, High-Power Sodium-Ion Batteries from a Layered Organic Cathode"
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
@cty-chem.bsky.social
A chemisrt and chemical engineer focusing on material innovations for electrochemical energy storage. Currently a postdoc with Prof. Zhenan Bao at Stanford. PhD with Prof. Mircea Dinca at MIT. Undergrad at CCME of Peking University.

Princeton Chemistry demonstrates high-performance Sodium-ion cathode towards new battery technology
"High-Energy, High-Power Sodium-Ion Batteries from a Layered Organic Cathode"
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...

A five-step guide to communicating your science ethically and accurately
https://go.nature.com/3Et4j3V

I am excited to share our group's latest manuscript, now live on the #ChemRxiv! We show by electron diffraction that Zn3(HOTP)2 isn't a typical 2D MOF, but is instead a 3D connected structure with incommensurate modulations. #crystallography
Read the preprint here: doi.org/10.26434/che...
Best sodium-ion battery cathode out there, bar none! High energy, high power, long lasting, safe and cheap batteries made from C, N, O, H, and Na! #organicbattery #Sodiumbattery pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
05.02.2025 15:07 — 👍 26 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 1In addition to this work, we have previously demonstrated the use of sustainable redox-active organic materials as electrodes for pseudocapacitors (cell.com/joule/fullte... and Li-ion batteries (pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10....)
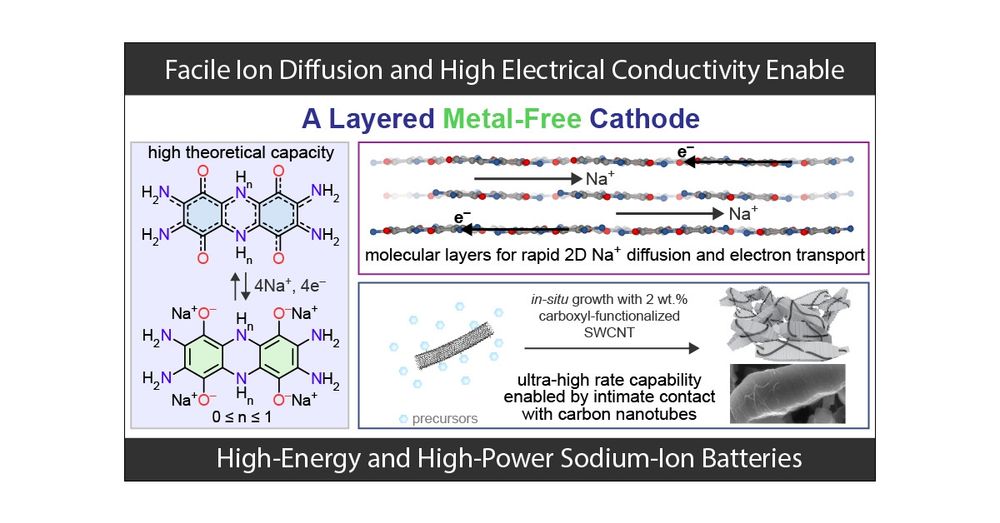
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Altogether, these allow the construction of SIB cells built from an affordable, sustainable organic small molecule, which provide a cathode energy density (at the electrode level) of 472 Wh/kg when charging/discharging in 90 s and a top specific power of 31.6 kW/kg.
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0We then synthesized composites with carboxyl functionalized SWCNTs through an in-situ growth method utilizing H bonding/covalent bonding. The resulting composites contain ~2 wt.% SWCNTs which wrap intimately around active material crystallites, leading to enhanced conductivity.
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Combining electrochemical and operando studies, we found that the (de)intercalation and solid-state diffusion of Na-ion are not the limiting factors of the battery performance. Instead, enhancing the electron transport and transfer are the key to further improve the performance.
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Due to the strong intermolecular interactions, our material is also highly insoluble in common organic solvents and the corresponding electrodes exhibit no dissolution problem even with a high active material content of 90 wt.%. 60~70 wt.% is common for other organic electrodes.
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0This cathode material consists of H-bonded 2D molecular layers that stack through π–π interaction, leading to extended conjugation and low bandgap (<0.5 eV). The layered structure also provides quasi-2D diffusion pathways for Na-ion, a characteristic for high rate performance
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Excited to share our lastest work about high-performance Na-ion batteries from a sustainable organic cathode (pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...). This cathode we (Dinca lab) developed solves the dissolution and insulating problems of organic electrodes for SIBs. Details in 🧵
06.02.2025 21:08 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0