The 2020 US election shows how state election policies can fuel conspiracy theories about voting | USAPP
States that allowed pre-Election Day processing saw a reduction of over a third in expected misinformation compared to states with restrictive rules.
Recently published work from colleagues Morgan Wack (postdoc at University of Zurich) & Joey Schafer (UW PhD candidate) showing how state election policies that delayed vote counting fueled rumoring and conspiracy theorizing around the 2020 election: blogs.lse.ac.uk/usappblog/20...
07.10.2025 20:25 — 👍 46 🔁 13 💬 2 📌 0
How often do you see papers that suggest easy policies that could reduce electoral misinformation? Here's one I worked on with a great team out of UW and led by @morganwack.bsky.social and @schafer.bsky.social
14.07.2025 17:32 — 👍 33 🔁 15 💬 3 📌 0
Thrilled to finally see this paper out in print several years after @schafer.bsky.social and I started this project alongside @ikennedy.bsky.social, @beeeeeers.bsky.social, @emmaspiro.bsky.social & @katestarbird.bsky.social! Unfortunately the detrimental policies we discuss remain relevant.
11.07.2025 16:19 — 👍 22 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Proud to have co-led this paper with @morganwack.bsky.social (and other coauthors @ikennedy.bsky.social @beeeeeers.bsky.social @emmaspiro.bsky.social @katestarbird.bsky.social) looking at the impacts of state-level election laws on uncertainty and election integrity rumors!
11.07.2025 15:10 — 👍 16 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 1
Screenshot from DCWeekly in October 2023, accessed through the Internet Archive.
A study of a propaganda site with ties to Russia shows that using AI allows propagandists to dial up the volume of their content without sacrificing persuasiveness. The authors call for action to combat the threat. In PNAS Nexus: academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/ar...
07.04.2025 19:36 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0

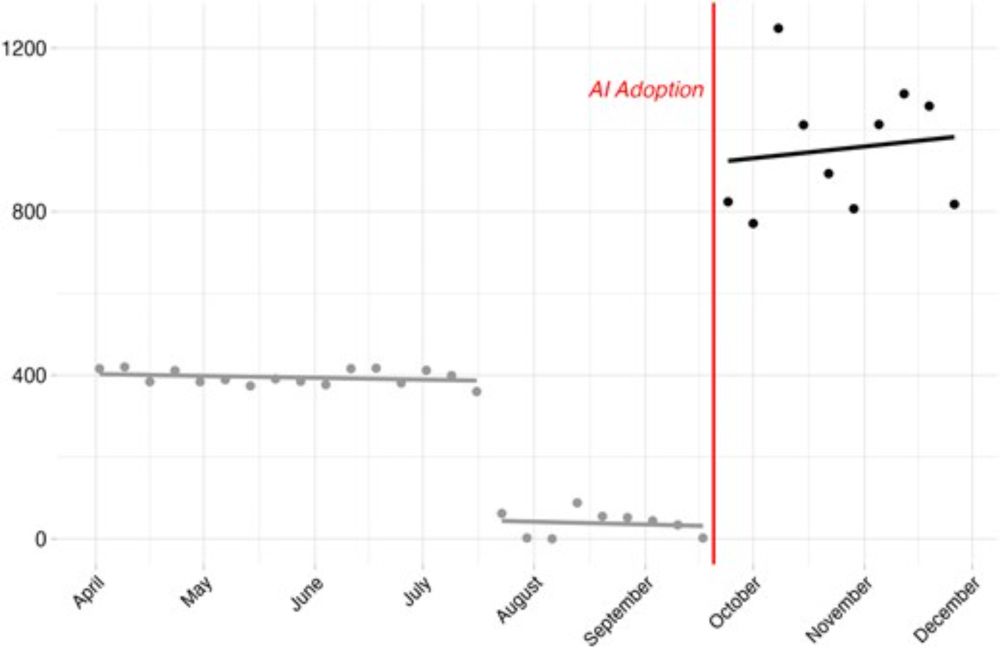
Violin plot of NLI-derived topic scores for June (prior to AI adoption) and October (after AI adoption) of 2023
A study of a Russian-backed propaganda outlet finds that AI is already being used to enhance messaging and expand disinformation campaigns, raising concerns about its growing impact on global influence operations.
In @sciencex.bsky.social: phys.org/news/2025-04...
07.04.2025 19:39 — 👍 4 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Finding Three 📝: Even with the shift to AI, the persuasive potential and credibility of the articles persisted. This finding suggests that even in rapid scaling article production the website did not need to sacrifice its perceived authenticity or potential impact. 6/
01.04.2025 20:06 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Finding Two 📊: AI-use corresponded with greater topic breadth. By rewriting stories, the website covered more diverse subjects (from gun crime to the Ukraine invasion). Prompt leaks also suggest use of AI to rate potential materials by their alignment with campaign goals. 5/
01.04.2025 20:06 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Finding One 📈: AI use significantly increased the quantity of disinformation. This aligns with the idea that generative models reduce the cost/time of writing, editing, and curating. Once the site adopted LLM tools, weekly post counts soared. 4/
01.04.2025 20:06 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We focus on a site identified by the Clemson Forensics Hub that presented itself as a genuine U.S. news outlet but which was actually part of a Russian-affiliated influence operation. By pinpointing a transition away from human-editing to LLM-edited content, we show: 3/
01.04.2025 20:06 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
There have been growing concerns about the use of large language models (LLMs) in the production of disinformation, but real-world evidence has been difficult to track. Our paper provides a direct look at a Russian-linked campaign which used AI tools to target Americans. 2/
01.04.2025 20:06 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

🚨 Excited to see our new paper out at @pnasnexus.org w/@pwarren.bsky.social, Darren Linvill, & Carl Ehrett!
Using data from a Russia-backed influence operation running puppet website DCWeekly, we show how LLMs are being used to scale global disinfo campaigns: 1/ 🧵
academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/ar...
01.04.2025 20:06 — 👍 7 🔁 2 💬 2 📌 0

📢 #RwandaClassified : la désinformation des autorités rwandaises persiste.
Alors que le conflit en RDC s’intensifie, les réseaux de Kagame restent actifs : la guerre au Nord-Kivu et le trafic de minerais restent des sujets tabous pour le régime rwandais. 🔍
forbiddenstories.org/fr/actualite...
18.02.2025 17:48 — 👍 1 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0

Thrilled to share my new publication w/ @morganwack.bsky.social & Kevin Aslett in Social Science Quarterly: “Silence in the Stands: Assessing the Impact of Russian State-Linked Sportswashing on Online Fan Behavior Following the Full-Scale Invasion of Ukraine.” onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
21.01.2025 19:02 — 👍 8 🔁 2 💬 3 📌 0
How right wing media is like improv theater. My coauthor @danielletomson.bsky.social and I are really proud of this piece which builds upon ~10 years of research at UW studying the participatory nature of rumors/disinformation and Danielle’s dissertation studying right-wing influencers for 5+ years.
05.12.2024 14:53 — 👍 175 🔁 70 💬 15 📌 8

⏰Another opening for a PhD position in our (w @morganwack.bsky.social and @esserfrank.bsky.social ) SNF project on political social media influencers! 🥳 If you are into computational methods, social media, and political communcation, we are looking for you 🔎 All details here: tinyurl.com/44arrawh
29.11.2024 14:08 — 👍 22 🔁 18 💬 3 📌 2

I’ve been studying misinformation for a decade — here are the rumours to watch out for on US election day
We can anticipate many false claims, including alleged mass voting by non-citizens or ‘suspicious vans’ outside polling booths. We should quickly counter them.
Just published a Nature comment highlighting a few of the rumors our UW team expects to see going into the Nov 5 election — from rumors that falsely frame election errors as impactful and intentional to rumors about "non citizen voters" and "suspicious behaviors". www.nature.com/articles/d41...
22.10.2024 16:14 — 👍 400 🔁 216 💬 12 📌 9
Multi-disciplinary blog covering all aspects of USA governance, economics, politics, culture and society. Also covers Canada and Mexico. Part of the LSE Phelan United States Centre.
Read all our articles at https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/usappblog/
PhD candidate at MPI MiS, Lattice and SciencesPo médialab | Computational Social Science, Narratives, NLP, Complex Networks | https://pournaki.com
PostDoc FU Berlin & Research Affiliate WZB | PhD from EUI | Populism, Parliamentary Behaviour, Party Communication, Protest Behaviour, Text-as-Data | https://rebecca-kittel.eu/
Postdoctoral Researcher
Researching the use of data, analysis and technology in campaigning & its effects on voters (#advertising #targeting #canvassing)
📍 Political Communication Lab, Department of Comm, U of Mainz
📱 https://linktr.ee/simonkruschinski
Research fellow at the Council on Foreign Relations studying terrorism and extremism. Opinions are my own and RT ≠ endorsement.
https://bookshop.org/p/books/god-guns-and-sedition-far-right-terrorism-in-america/20097522?ean=9780231211222&next=t
political scientist at uni lausanne, wrote a book on Shared Rule in Federal Theory and Practice: https://academic.oup.com/book/57551
Host of The Ringer Fantasy Football Show.
Staff Writer at The Ringer & Spotify
On the job market | Ph.D. Candidate @CommUcsb researching online privacy & digital inequality
https://scholar.google.nl/citations?user=Eumt3-kAAAAJ&hl=en
Interdisciplinary journal, published by Cambridge University Press. Launched in 2017
Official Account for the Office of California Governor Gavin Newsom.
Building a #CaliforniaForAll.
🔗 linktr.ee/CAgovernor
Professor of Psychology at NYU (jayvanbavel.com) | Author of The Power of Us Book (powerofus.online) | Director of NYU Center for Conflict & Cooperation | trying to write a new book about collective decisions
Scrivner Professor of Public Policy, Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs, and Director of the Scrivner Institute of Public Policy at the Josef Korbel School of Global and Public Affairs, University of Denver | Principal, Bridging the Gap | 🏳️🌈
she/her 🏳️🌈 | PhD candidate @polcomvienna.bsky.social
@yecrea.bsky.social PolComm section representative
Algorithmic Content Moderation | Inclusive Technologies | User-Agency & Effects 💭
https://polcom.univie.ac.at/team/anna-maria-planitzer/
Assistant professor @polsciuibk.bsky.social | Austrian politics, political communication & civic education | Royals, tennis, television | Ich laufe lang und fahre Rad.
European Communication Research and Education Association (ECREA) is a learned society of communication scholars devoted to development of communication research and higher education in Europe.
Official website: https://ecrea.eu/
ECREA section promoting thought-provoking research on the dynamic relationship between #media, #communication and #democracy 👇https://t.co/7NN8ijQSh8