
Online now: Paternal exercise confers endurance capacity to offspring through sperm microRNAs
06.10.2025 18:50 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0@cp-cellmetabolism.bsky.social
A Cell Press journal publishing cutting-edge research in metabolism biology, from molecular/cellular biology to translational and clinical studies.

Online now: Paternal exercise confers endurance capacity to offspring through sperm microRNAs
06.10.2025 18:50 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Catenibacterium mitsuokai promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by binding to hepatocytes and generating quinolinic acid
25.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0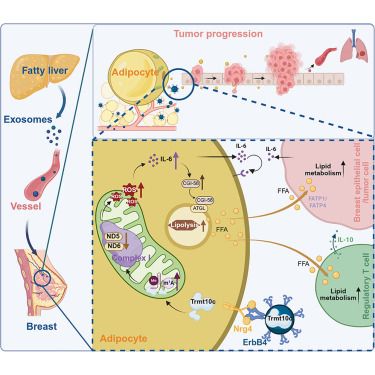
Online now: Liver-breast communication of adipocyte-oriented exosomes drives primary mammary cancer progression
24.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0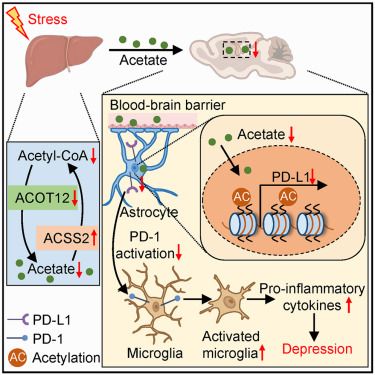
Online now: Hepatic acetyl-CoA metabolism modulates neuroinflammation and depression susceptibility via acetate
23.09.2025 18:50 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: HEBP2-governed glutamine competition between tumor and macrophages dictates immunotherapy efficacy in triple-negative breast cancer
23.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Save the date for Multifaceted mitochondria!
Announcing Cell Symposia: Multifaceted Mitochondria, June 21–23, 2026, Glasgow, Scotland, UK
@CellSymposia #CSMito2026 Save the date!
Keynote speakers: Judy Hirst (University of Cambridge) & Jared Rutter (University of Utah)
Find out more: http://dlvr.it/TN9ZsM

Online now: A closed-loop cholesterol shunt controlling experimental dyslipidemia
18.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Online now: OGFOD1 enables AML chemo- and nutrient stress resistance by regulating protein synthesis
16.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 4 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Portal vein-enriched metabolites as intermediate regulators of the gut microbiome in insulin resistance
05.09.2025 15:43 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Polycystic ovary syndrome: A metabolic disorder with therapeutic opportunities
04.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Mitochondrial dysfunction reveals H2S-mediated synaptic sulfhydration as a potential mechanism for autism-associated social defects
03.09.2025 15:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Cell Symposia
Join us in Seville, Spain, Oct 4–6, 2026 for Cell Symposia: Hallmarks of aging!
Explore the latest in aging biology from molecules to medicine. #CSAging2026 #CellSymposia
Abstract deadline: June 5, 2026
http://dlvr.it/TMlhxk

Online now: Effect of ultra-processed food consumption on male reproductive and metabolic health
28.08.2025 15:42 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0Online now: NANOG Metabolically Reprograms Tumor-Initiating Stem-like Cells through Tumorigenic Changes in Oxidative Phosphorylation and Fatty Acid Metabolism
28.08.2025 12:40 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 1
Online now: Homocysitaconate controls inflammation through reshaping methionine metabolism and N-homocysteinylation
27.08.2025 15:43 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Genetics-nutrition interactions control diurnal enhancer-promoter dynamics and liver lipid metabolism
25.08.2025 15:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor signaling in oligodendrocytes increases the weight-loss action of GLP-1R agonism
13.08.2025 15:43 — 👍 5 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 1
Online now: Tumor-associated Schwann cell remodeling under metabolic stress via lactate sensing orchestrates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development
12.08.2025 15:42 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0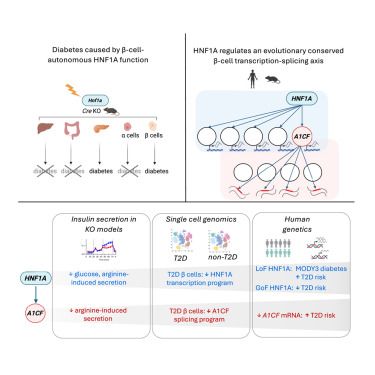
Online now: HNF1A and A1CF coordinate a beta cell transcription-splicing axis that is disrupted in type 2 diabetes
06.08.2025 15:42 — 👍 5 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Glucose-dependent glycosphingolipid biosynthesis fuels CD8+ T cell function and tumor control
05.08.2025 15:42 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Gut substrate trap of D-lactate from microbiota improves blood glucose and fatty liver disease in obese mice
29.07.2025 15:42 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 1
Online now: Xylulose 5-phosphate fosters sustained antitumor activity of progenitor-like exhausted SLC35E2+ CD8+ T effector cells
17.07.2025 15:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Shivering, but not adipose tissue thermogenesis, increases as a function of mean skin temperature in cold-exposed men and women
16.07.2025 15:42 — 👍 5 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Localized GLP1 receptor pre-internalization directs pancreatic alpha cell to beta cell communication
14.07.2025 15:43 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 1
Online now: Microbial riboflavin inhibits ceramide synthase 3 to lower ceramide (d18:1/26:0) and delay colorectal cancer progression
02.07.2025 15:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: RIPK1 senses S-adenosylmethionine scarcity to drive cell death and inflammation
25.06.2025 15:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Sphingomyelins in mosquito saliva reconfigure skin lipidome to promote viral protein levels and enhance transmission of flaviviruses
20.06.2025 15:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0