
Advancing regulatory variant effect prediction with AlphaGenome - Nature
AlphaGenome, a deep learning model that inputs 1-Mb DNA sequence to predict functional genomic tracks at single-base resolution across diverse modalities, outperforms existing models in variant effect...
AlphaGenome is out! Input 1 Mb DNA -> predict gene expression, transcription initiation, chromatin accessibility, histone modifications, transcription factor binding, chromatin contact maps, ..., up to single-base-pair resolution! Trained on human and mouse data 🧪🧬🖥️🦠✨
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
11.02.2026 05:40 —
👍 18
🔁 6
💬 0
📌 1
Bacteria may be engineered to learn, but natural evolution rarely favors this.
Protein-based memory inside a cell is metabolically expensive and dilutes quickly.
Instead, cells may rely on simpler probabilistic strategies like bet hedging, so no memory is required.
#MEvoSky #evobio ⚙️🧫🧠🧬
11.02.2026 20:16 —
👍 11
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0
Loving those Goodsell-style protein illustrations! And cool circuits in the figures too
10.02.2026 22:08 —
👍 1
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0

What kinds of cognitions are possible? Are there discrete classes of cognition? Here's our new paper with @brigan.bsky.social @jordiplam.bsky.social @mitibennett.bsky.social @mkhochb.bsky.social and @drmichaellevin.bsky.social arxiv.org/abs/2601.12837 We explore basal, neural and human-AI spaces.
21.01.2026 10:06 —
👍 66
🔁 25
💬 1
📌 0

If you are looking to integrate your latest genetic creation into the genome of your favourite bug, you might find our latest review now out in OUP Synthetic Biology useful. 🧬⚒️ Work led by Riesa Rohmat with input from Thea Irvine and Shivang Joshi. #genome #synbio doi.org/10.1093/synb...
06.01.2026 10:58 —
👍 28
🔁 15
💬 0
📌 0

Circadian rhythms as a modulator of gut microbiota-tumor microenvironment crosstalk
review in Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
link.springer.com/article/10.1...
#ChronoSky #ChronoMicrobiology
04.12.2025 08:32 —
👍 5
🔁 2
💬 0
📌 0
If you ever post/publish about that, I'll be eager to read it!
13.11.2025 17:34 —
👍 3
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0
Very interesting!
Do you think this framework could be tweaked to work for ants–pheromones too? As they've also been shown to "solve" the shortest path problem in a "ring", at least in laboratory conditions.
12.11.2025 17:52 —
👍 3
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
Love that the preprint for that is already online!!
12.11.2025 04:25 —
👍 1
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0

How “intelligent” is a slime mold? When it solves mazes, it might not be thinking:it’s obeying physics. Our new paper with
@jordiplam.bsky.social shows how it follows a least action principle,letting physics do the job arxiv.org/pdf/2511.08531
@drmichaellevin.bsky.social @docteur-drey.bsky.social
12.11.2025 04:17 —
👍 100
🔁 29
💬 11
📌 5

Sunday morining at @sfiscience.bsky.social
09.11.2025 20:20 —
👍 20
🔁 1
💬 1
📌 0
fans of T4P pili (and 'pili pili') take note 👇
#MicroSky
13.10.2025 21:47 —
👍 9
🔁 2
💬 0
📌 0
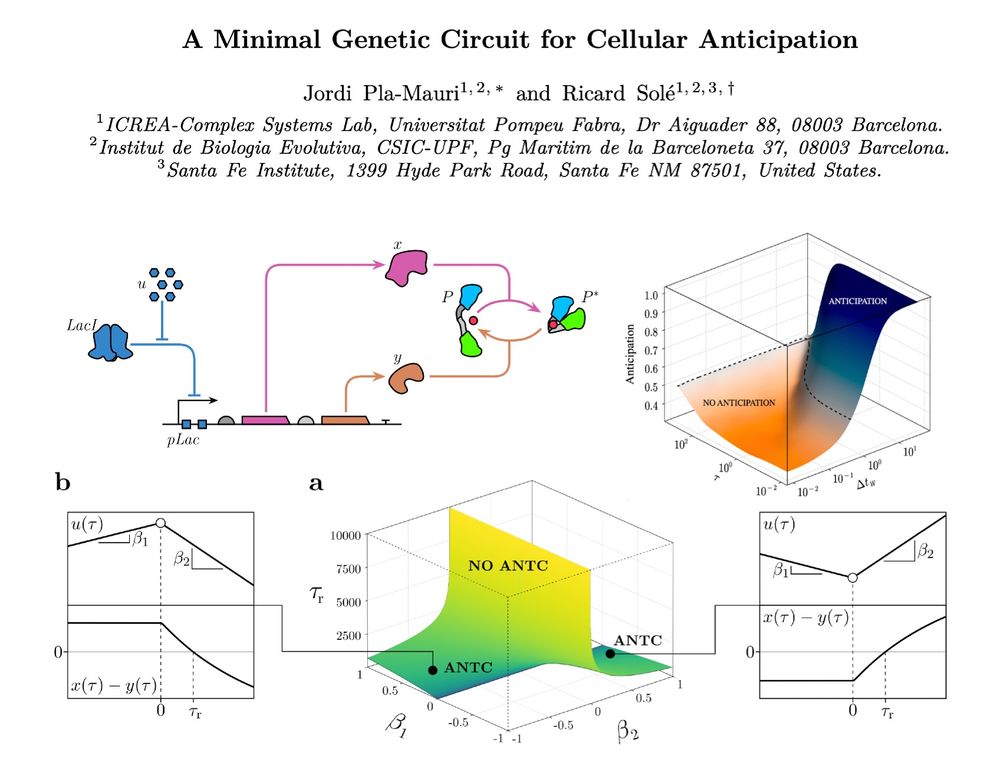
How can biological systems anticipate future events? In our new paper with @jordiplam.bsky.social, we show how a simple genetic circuit can predict future trends through a simple (and perhaps widespread) mechanism @drmichaellevin.bsky.social @koseskalab.bsky.social www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
28.04.2025 22:42 —
👍 97
🔁 29
💬 5
📌 3
Bacterial two-hybrid systems evolved: innovations for protein-protein interaction research
#MicroSky 🦠
16.09.2025 12:14 —
👍 8
🔁 4
💬 0
📌 0

The landscape of microbial associations in human cancer
Differences between cancer types, infectious disease, and potential prognostic markers are uncovered by studying microbes within cancer DNA.
The landscape of microbial associations in human cancer www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
TLDR -- most cancers do not have microbiomes...but a few do have consistent microbe associations (i.e., colorectal and oral cancers). Make sense!
12.09.2025 19:40 —
👍 64
🔁 27
💬 1
📌 3
Looks interesting: fluorescent proteins being strung together in a fiber as a recording of transcriptional history in cells.
13.09.2025 12:02 —
👍 11
🔁 2
💬 0
📌 0

Abstract: Under the banner of progress, products have been uncritically adopted or
even imposed on users — in past centuries with tobacco and combustion engines, and in
the 21st with social media. For these collective blunders, we now regret our involvement or
apathy as scientists, and society struggles to put the genie back in the bottle. Currently, we
are similarly entangled with artificial intelligence (AI) technology. For example, software updates are rolled out seamlessly and non-consensually, Microsoft Office is bundled with chatbots, and we, our students, and our employers have had no say, as it is not
considered a valid position to reject AI technologies in our teaching and research. This
is why in June 2025, we co-authored an Open Letter calling on our employers to reverse
and rethink their stance on uncritically adopting AI technologies. In this position piece,
we expound on why universities must take their role seriously toa) counter the technology
industry’s marketing, hype, and harm; and to b) safeguard higher education, critical
thinking, expertise, academic freedom, and scientific integrity. We include pointers to
relevant work to further inform our colleagues.

Figure 1. A cartoon set theoretic view on various terms (see Table 1) used when discussing the superset AI
(black outline, hatched background): LLMs are in orange; ANNs are in magenta; generative models are
in blue; and finally, chatbots are in green. Where these intersect, the colours reflect that, e.g. generative adversarial network (GAN) and Boltzmann machine (BM) models are in the purple subset because they are
both generative and ANNs. In the case of proprietary closed source models, e.g. OpenAI’s ChatGPT and
Apple’s Siri, we cannot verify their implementation and so academics can only make educated guesses (cf.
Dingemanse 2025). Undefined terms used above: BERT (Devlin et al. 2019); AlexNet (Krizhevsky et al.
2017); A.L.I.C.E. (Wallace 2009); ELIZA (Weizenbaum 1966); Jabberwacky (Twist 2003); linear discriminant analysis (LDA); quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA).

Table 1. Below some of the typical terminological disarray is untangled. Importantly, none of these terms
are orthogonal nor do they exclusively pick out the types of products we may wish to critique or proscribe.

Protecting the Ecosystem of Human Knowledge: Five Principles
Finally! 🤩 Our position piece: Against the Uncritical Adoption of 'AI' Technologies in Academia:
doi.org/10.5281/zeno...
We unpick the tech industry’s marketing, hype, & harm; and we argue for safeguarding higher education, critical
thinking, expertise, academic freedom, & scientific integrity.
1/n
06.09.2025 08:13 —
👍 3786
🔁 1897
💬 110
📌 390
Synthetic promoters has relied on naturally occurring TFs or Cas9. With de novo designed DNA binding proteins, there are so much potential for synbio, whether it's targeting natural promoters or designing synthetic ones.
12.09.2025 12:01 —
👍 19
🔁 4
💬 0
📌 0
Can engineered genetic circuits reveal principles and constraints of biological cognition?
🧬🦠🖥️ #synbio #systemsbiology #cognition
12.09.2025 11:07 —
👍 4
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0
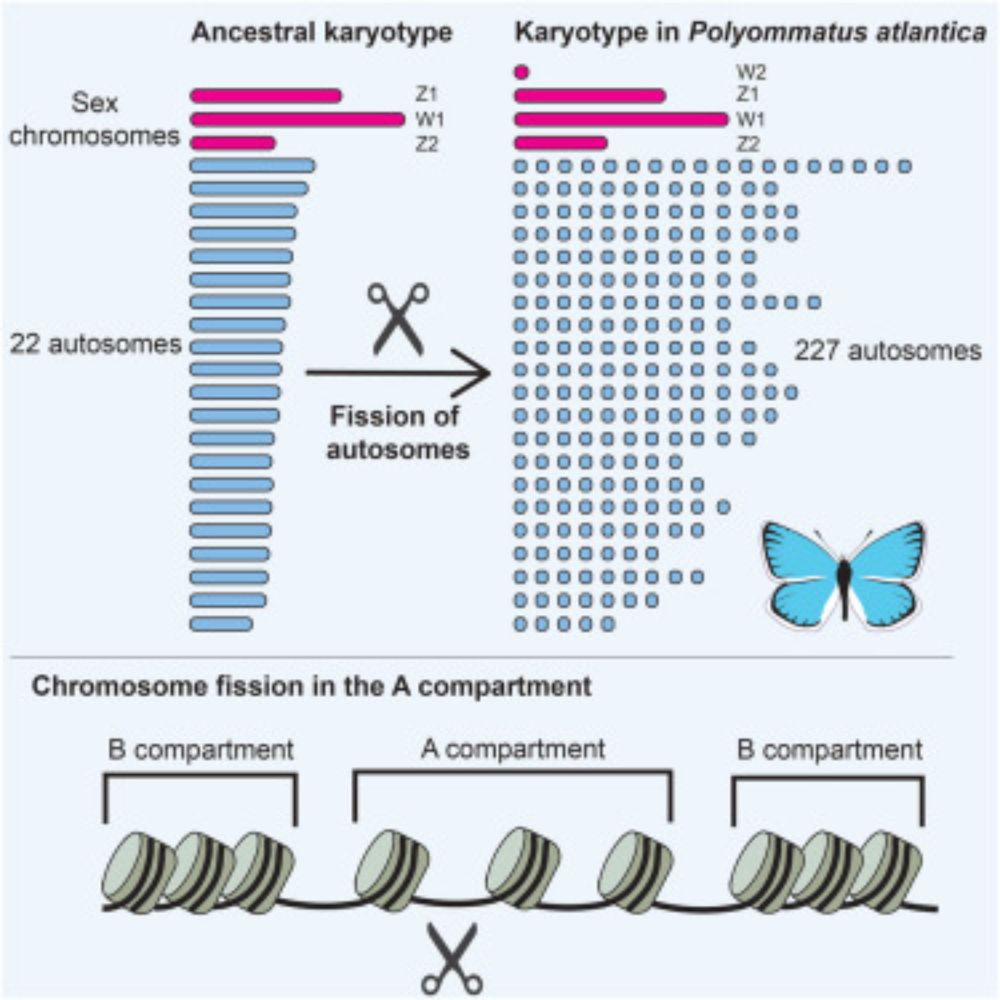
Constraints on chromosome evolution revealed by the 229 chromosome pairs of the Atlas blue butterfly
The genome of the Atlas blue butterfly contains ten times more chromosomes than most
butterflies, and more than any other known diploid animal. Wright et al. show that
this extraordinary karyotype is ...
How many chromosomes can an animal have?
In our paper out now in @currentbiology.bsky.social we show that the Atlas blue butterfly has 229 chromosome pairs- the highest in diploid Metazoa! These arose by rapid autosome fragmentation while sex chromosomes stayed intact.
www.cell.com/current-biol...
11.09.2025 15:21 —
👍 214
🔁 99
💬 4
📌 6
YouTube video by TeselaGen Biotechnology, Inc.
Revolutionizing Cell Therapy with AI
This podcast explores TeselaGen software and its role in revolutionizing cell therapy research and development. Discover how this cutting-edge AI-powered platform helps scientists design, build, and optimize biological products:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=O9HE... #biotech #synbio #AI
09.09.2025 18:25 —
👍 1
🔁 1
💬 0
📌 0





















