An insect on a spiral transforms into an insect on a line thanks to diffusion map.
Our work on practical insights into nonlinear dimensionality reduction with Diffusion Maps is now out! Parametrization, pitfalls & component selection 🚀 Great read for the weekend!
Preprint on arXiv: arxiv.org/abs/2601.20428
30.01.2026 18:48 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
read more:
openreview.net/pdf?id=AkQNt...
18.11.2025 08:41 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Max Kovalenko photography

Max Kovalenko photography
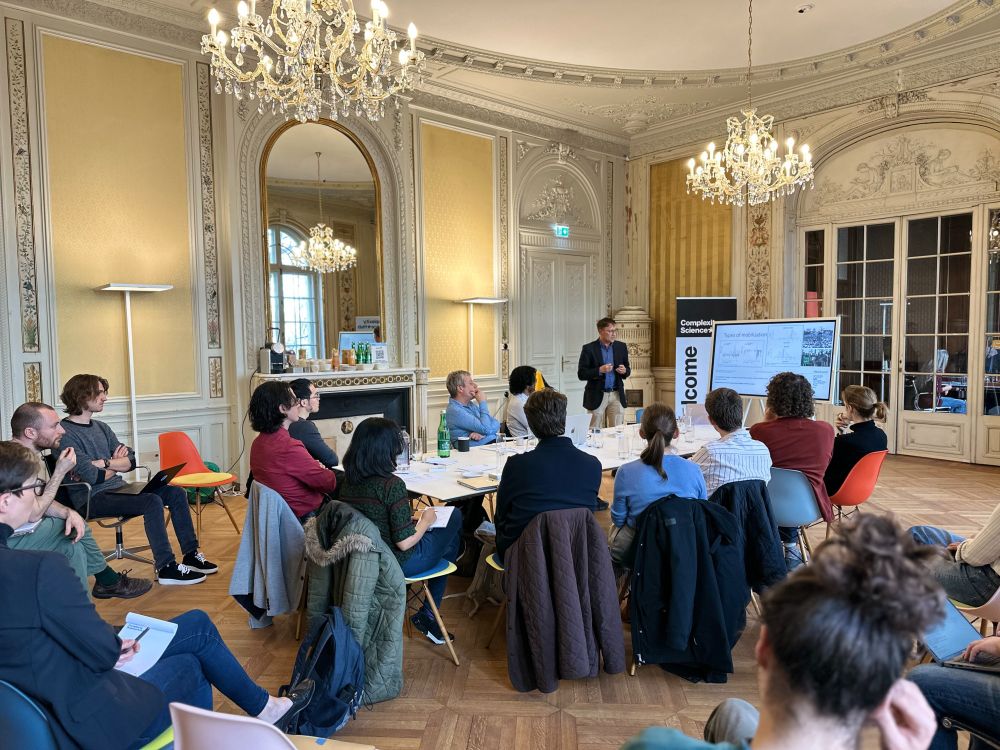
At this Scientific Machine Learning workshop we showed that strong regularization can cause phase transitions in neural networks. By linking these transitions to the geometric curvature of the training landscape, we reveal a new way to understand and optimize how neural networks learn.
18.11.2025 08:41 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0


Had a very enjoyable (and productive!) time at a group retreat of @complexityup.bsky.social, especially since it was in the middle of the famous Elbsandstein climbing region.
29.09.2025 08:28 — 👍 1 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
6/6 🧵In March, we participated in a workshop by @csh.ac.at where political and us physical scientists exchanged and discussed their ideas and research face-to-face.
18.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
5/6 🧵 All that wouldn't be possible without the political groundwork provided by political scientists and the dataset provided by the V-Dem Institute. Our research depends on cooperation.
18.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
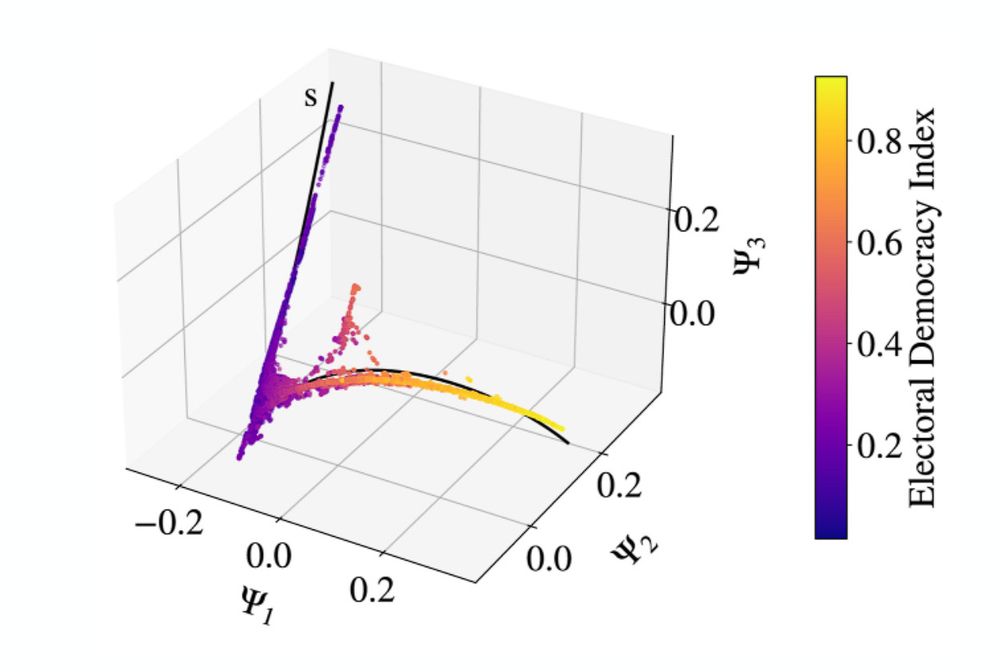
The manifold obtained by applying the Diffusion Map technique on the 25 variables from the V-Dem-Dataset. The three-dimensional curve contains every datapoint for each country in each year from 1900 up until 2021. Each datapoint is assigned an Electoral Democracy Index, represented in the color. The lighter the colour, the more democratic a country is considered in that year.
4/6 🧵 The Diffusion map that we've talked about here on Bluesky is one of them.
It reveals that, apparently, political systems behave like physical systems. Countries, over time, form this well-defined map, and their movement across this map can tell a lot about the stability of the regime.
18.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
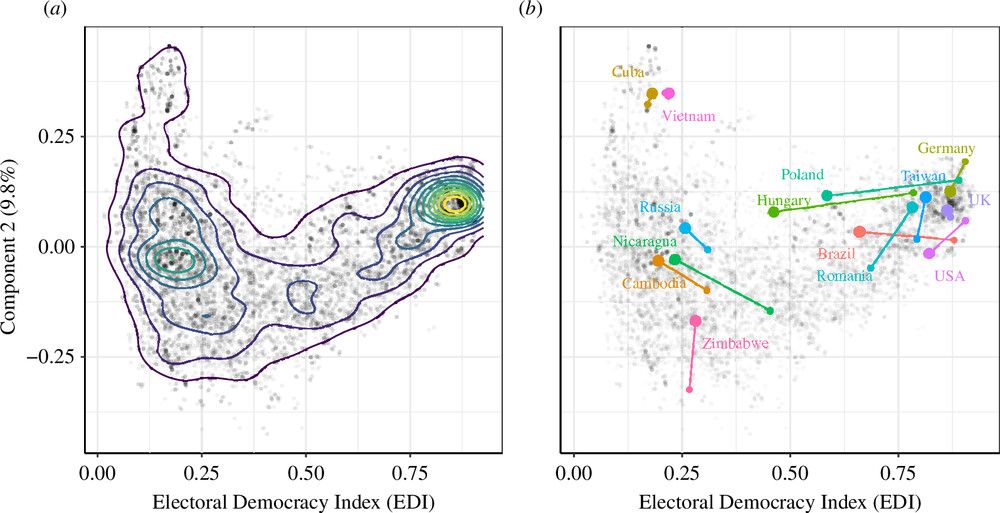
Trade-off between election quality and civil liberties (Principal Component 2) versus EDI for all 12 296 data points, (a) with density lines and (b) with examples for 2011–2021 (small dot–large dot).
3/6 🧵Statistical analysis shows that there are states that differ in election quality, despite having a similar Electoral Democracy Index (EDI, @vdeminstitute.bsky.social).
Differences between autocratic regimes can thus be uncovered.
18.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
2/6 🧵In the course of many years, we have worked on and with different models in this area.
As always, a model is not a depiction of reality, but an approximation. The utility of a model depends on the questions asked. That is why new models are needed to dive into new fields of research.
18.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Illustration (by @dantalionart.bsky.social) of political science in context of complexity science. A diffusion map wraps around an abstract globe, representing international connections that can be modelled physically.
The #Complexity Science Research Group in Potsdam is specialised in two major fields. One of them is the analysis of politcal systems using tools from . 🧪
1/6 🧵Here's a thread on @karowiesner.bsky.social's research and the many papers she has published on this topic!
18.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
With a diverse set of programming projects and theoretical deep dives, the master's students learn to view known phenomena through the lense of CS. It isn't all physics, however. Students also get to discuss concepts like emergence and self-organization on a philosophical level.
30.05.2025 11:07 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Our bachelor's students are given a collection of publications on different matters of complexity: some that built the foundation, some representing the current status in an area. With some programming tasks here and there, the students develop an understanding of the development and history of CS.
30.05.2025 11:07 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
This semester, we've been offering two courses on complexity science 🧪
While the master's students delve deeper into the methods and philosophy of complex systems, the bachelor's students get an introduction to the field with some useful applications.
30.05.2025 11:07 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
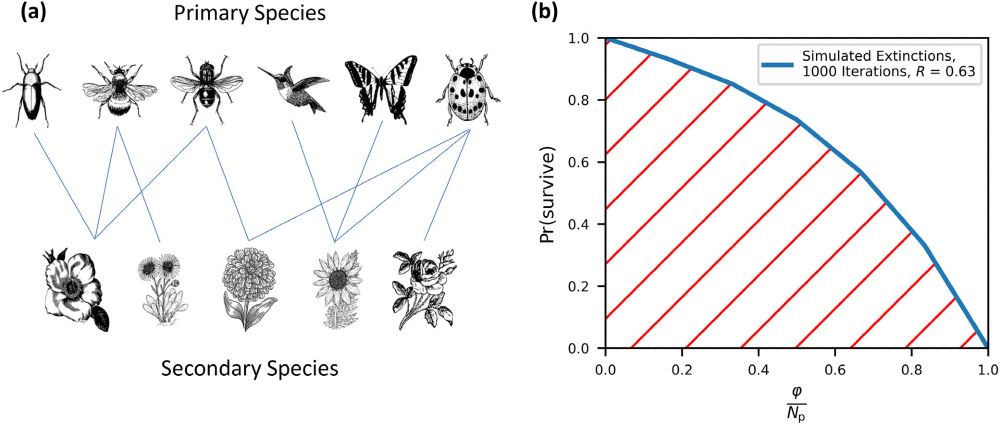
🧪 (a) An example plant–pollinator network and (b) its associated robustness curve. For this network, pollinators are treated as
primary species and plants as secondary species. Random primary extinctions are simulated repeatedly and the proportion of surviving
secondary species is recorded to generate the robustness curve. The greater the red area below the graph, the more robust is the system. Illustrations used in (a) are all available in the public domain under a
CC0 license.
Living beings rely on one another. One species facing the threat of extinction affects other species as well.
Understanding the extent of ecological damages helps take measures against them.
With low computational costs, this model for the robustness of a #complex system can prove useful in future.
26.05.2025 10:27 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Evaluating The Impact Of Species Specialisation On Ecological Network Robustness Using Analytic Methods
Ecological networks describe the interactions between different species, informing us of how they rely on one another for food, pollination and survival. If a species in an ecosystem is under threat of extinction, it can affect other species in the system and possibly result in their secondary extinction as well. Understanding how (primary) extinctions cause secondary extinctions on ecological networks has been considered previously using computational methods. However, these methods do not provide an explanation for the properties which make ecological networks robust, and can be computationally expensive. We develop a new analytic model for predicting secondary extinctions which requires no non-deterministic computational simulation. Our model can predict secondary extinctions when primary extinctions occur at random or due to some targeting based on the number of links per species or risk of extinction, and can be applied to an ecological network of any number of layers. Using our model, we consider how false positives and negatives in network data affect predictions for network robustness. We have also extended the model to predict scenarios in which secondary extinctions occur once species lose a certain percentage of interaction strength, and to model the loss of interactions as opposed to just species extinction. From our model, it is possible to derive new analytic results such as how ecological networks are most robust when secondary species degree variance is minimised. Additionally, we show that both specialisation and generalisation in distribution of interaction strength can be advantageous for network robustness, depending upon the extinction scenario being considered.
With extreme events happening more often due to #climatechange, we need to understand how ecological networks are affected by them 🧪
In this group, Chris Jones examined a model capable of providing such predictions efficiently by analyzing the dependences between species. arxiv.org/abs/2306.15428
26.05.2025 10:27 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
When does #democracy #backslide, what triggers civil #conflict, and how can statistical #physics and #complexity science help us uncover the links between these phenomena? Intense discussions across disciplinary boundaries this last week at @csh.ac.at. Watch this space!
22.03.2025 15:01 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Congratulations to Lea Faber, who dealt with models of global water systems and analyzed their behaviour using computationally efficient #AI!
And also congratulations to @soenbeier.bsky.social, who worked with data on politics and society from the @vdeminstitute.bsky.social among other datasets!
🧪
19.05.2025 15:14 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
This May, two of our Master's students defended their master's theses! 🧪
Both worked on completely different types of systems. However, what connects both of them is clear: #complexity.
19.05.2025 15:14 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Master in Physics of Complex Systems | Fellowships
Master in Physics of Complex Systems.
Official degree offered by the University of the Balearic Islands (UIB)
in collaboration with the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)
📣 IFISC is offering 4 scholarships for students enrolling in the Master in Physics of Complex Systems at UIB for the 25-26 academic year. One of the grants is sponsored by Fundación Sicómoro.
ℹ ifisc.uib-csic.es/master/fello...
Learn about the master's degree:
▶ youtu.be/usn8Ea2kBWk?...
17.03.2025 10:47 — 👍 2 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Check out and engage with the Young Researchers of the Complex Systems Society!
@yrcss.bsky.social is bringing together young scientists with a common scientific interest in complex systems and creates opportunities for them to get together.
11.03.2025 18:18 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Unraveling 20th-century political regime dynamics using the physics of diffusion
10/10🧵
This work is available on ArXiv if you want to read further into it!
arxiv.org/html/2411.11...
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
9/10🧵
Her research is incredibly interesting and relevant for modern #politics.
This approach has the potential to provide a foundation for theories of political change, of emergence of conflict, and of extreme events in autocratic (and transitioning) regimes.
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
8/10🧵
In other words: the regime type of a country is correlated with its position on the manifold curve and its dynamics as it moves around over the years. It can be analyzed with the anomalous diffusion approach known in statistical physics.
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
7/10🧵
Large jumps (super-diffusive behaviour), characterised by the presence of extreme events, have been seen in destabilising autocracies.
Furthermore, small movements (sub-diffusive behaviour) have been identified in democracies and stable autocracies.
We see the history of a state in a graph!
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
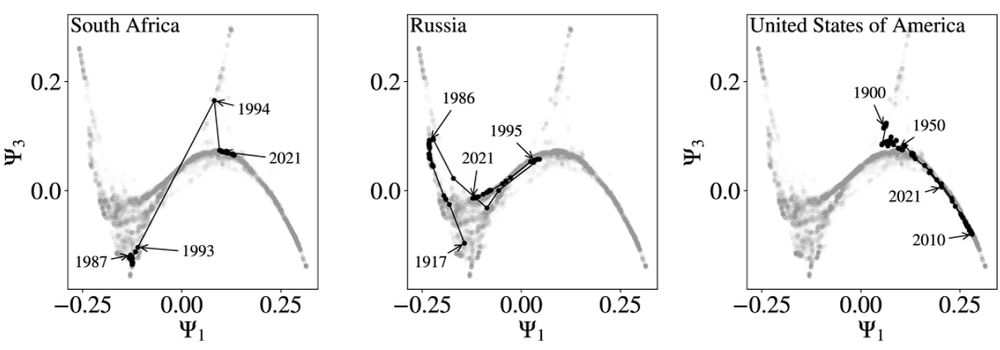
The development of three different countries (South Africa, Russia, USA, respectively from left to right) traced as they move along the manifold curve. South Africa, for instance, shows a large jump from 1993 to 1994, which can be linked to the changes at the end of the Apartheid regime.
6/10🧵
As a country goes through political change, it moves along this curve. Its development can be traced, and jumps and static phases linked to real life events and phases!
Using tools from statistical physics, distinct types of behaviour have been identified in the data.
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
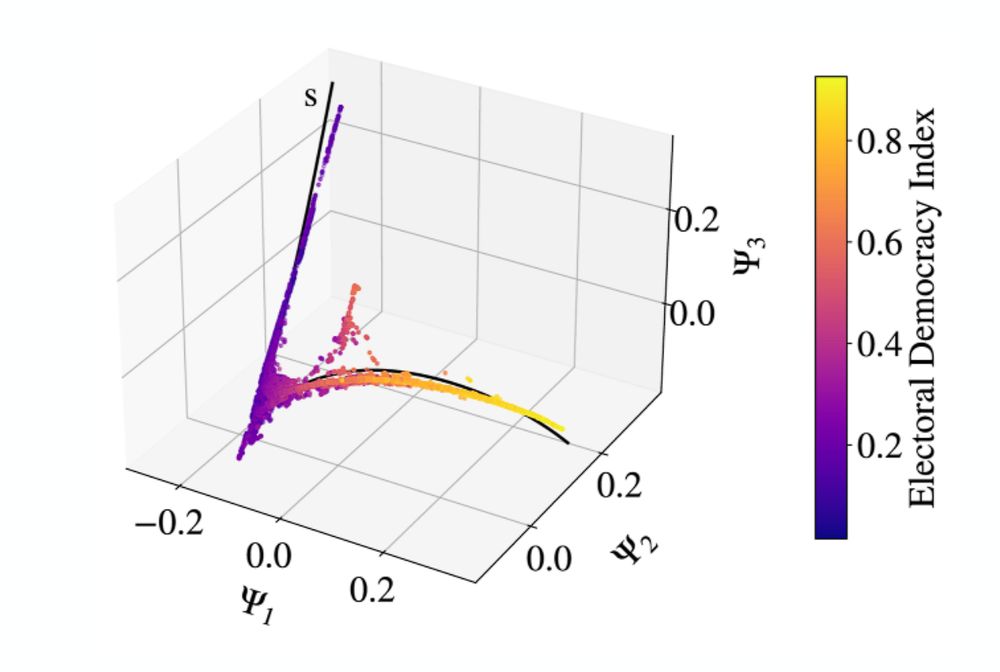
The manifold obtained by applying the Diffusion Map technique on the 25 variables from the V-Dem-Dataset. The three-dimensional curve contains every datapoint for each country in each year from 1900 up until 2021. Each datapoint is assigned an Electoral Democracy Index, represented in the color. The lighter the colour, the more democratic a country is considered in that year.
5/10🧵
Taking 25 variables out of the V-Dem dataset describing the “democraticness” of each country every year and simplifying them using diffusion to fit in a three-dimensional space, the data forms a curve - not a cloud of points - summarising the whole dataset considered.
Surprising, isn't it?
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
4/10🧵
As she analyses the dynamics of political regimes, she is uncovering the patterns that the dataset, covering over 170 countries across more than a century, contains.
Paula investigates the factors that influence regime transformation in either a more democratic or autocratic direction.
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
3/10🧵
Now, Paula is working with political data, analysing political regimes worldwide by examining changes in freedoms of expression, association, and electoral quality throughout the 20th century. For that, she makes use of a huge dataset by the @vdeminstitute.bsky.social - the V-Dem Dataset.
10.03.2025 18:01 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Humboldt Fellow · Uni Potsdam · Institute of Physics PAS
PhD - Uni Warsaw; MA - Uni Cambridge
Modelling timescales and lengthscales in: disordered proteins, marine snow, espresso, river networks, democratic backsliding
radostw.github.io
Philosophy & History of Science, Complex Systems, Knowledge Management. Networks, Harmony, Co-Evolution, Autopoiesis, Neurodiversity ♾️ AuDhD.
Ecology, Digital Revolution ~> Information Paradigm.
Theorist, .. wait!- come back, there's more..
🕺🎶🍞📸🤡
Offizieller Account des Fachschaftsrates Mathe-Physik der Universität Potsdam
🌈
https://www.uni-potsdam.de/de/fsr-maphy
Applying complexity science to product management practices. Follow Complexity Management custom feed at https://bit.ly/3YrhJEM
Located in Austria
Official Bluesky Account of IT:U
https://it-u.at/en/
Der offizielle Bluesky-Account der Universität Potsdam. Hier postet das Presse-Team. Impressum und Datenschutz: https://www.uni-potsdam.de/de/presse/aktuelles/social-media
Complex Systems | Epi-things | Computational Social Science | Physics | Music | Photography.
Postdoc at Denmark Tekniske Universitet (DTU). #epidemics #complexsystems #physics #computationalsocialscience
Facilitating the inclusion of young researchers in the Complexity Science research community since 2011. Check out our initiatives 👇
🔗 https://yrcss.cssociety.org/
🐘 https://datasci.social/@yrCSS
EU Project Consultant, Physicist, Mom, SciComm wannabe
Astrobiology PostDoc at #uniparthenope, Geobiology at #GiovannelliLab. Scientific collaborator at #inaf, #CNR, #unimib, #unina. Visiting at #ukca, #edinburghuniversity and #Cometinterceptor team for #esa.
Future is #Cyberpunk
www.lucatonietti.com
The V-Dem Institute is an independent research institute and the Headquarters of the V-Dem project, based at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. The V-Dem project (Varieties of Democracy) is a unique approach to conceptualizing and measuring democracy.
Dedicated to the promotion of interdisciplinary research in the social sciences. Likes/Reposts/Shared Articles are not necessarily endorsements.
Scientist. Discovering quantum matter. Professor at the University of Geneva. Father of 2.
Homepage: https://vonrohr.unige.ch/
postdoctoral researcher at UNICOG, NeuroSpin neuroimaging and visual neuroscience https://nicogravel.github.io/
Fighting blood cancer🩸with a pipet + Senior Postdoc 🧪🧬 + Berlin + ❤️ cœur perdu à Paris 🇫🇷 + Feminist + mom of 👦🧒 & 🐰🐰+ FirstGen + she/her + not nice + Politics and SciCom mostly in German + Tax the rich
I have kids in this world.
I‘m allowed to be mad.
policy analyst @pik-potsdam.bsky.social directors team
climate policy, the EU & economics.
Potsdamer Neueste Nachrichten. Was Potsdam, Potsdam-Mittelmark und Brandenburg bewegt.
Official Bluesky account of the Institute of #Geosciences at the University of #Potsdam. #Teaching #Research #Studium #Forschung
At our institute we study fundamental processes of plant physiology and development and the interaction of plants with their environment.
Science for safe & just #Climate future. Scientific Directors: Johan #Rockström, Ottmar #Edenhofer // Website EN: https://www.pik-potsdam.de/en, DE: https://www.pik-potsdam.de/de // All PIK social media channels: https://pik-potsdam.de/socials


















