Influenza hemagglutinin subtypes have different sequence constraints despite sharing extremely similar structures
Hemagglutinins (HA) from different influenza A virus subtypes share as little as ∼40% amino acid identity, yet their protein structure and cell entry function are highly conserved. Here we examine the extent that sequence constraints on HA differ across three subtypes. To do this, we first use pseudovirus deep mutational scanning to measure how all amino-acid mutations to an H7 HA affect its cell entry function. We then compare these new measurements to previously described measurements of how all mutations to H3 and H5 HAs affect cell entry function. We find that ∼50% of HA sites display substantially diverged preferences for different amino acids across the HA subtypes. The sites with the most divergent amino-acid preferences tend to be buried and have biochemically distinct wildtype amino acids in the different HA subtypes. We provide an example of how rewiring the interactions among contacting residues has dramatically shifted which amino acids are tolerated at specific sites. Overall, our results show how proteins with the same structure and function can become subject to very different site-specific evolutionary constraints as their sequences diverge. ### Competing Interest Statement JDB consults for Apriori Bio, Invivyd, Pfizer, GSK, and the Vaccine Company. JDB and BD are inventors on Fred Hutch licensed patents related to the deep mutational scanning of viral proteins. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, R01AI165821, 75N93021C00015 U.S. National Science Foundation, DGE-2140004 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, https://ror.org/006w34k90
In new work by @jahn0.bsky.social and I in @jbloomlab.bsky.social, we investigate how sequence constraints differ across influenza HA subtypes.
We find ~50% of sites in HA display substantially different amino-acid preferences across H3, H5, and H7.
doi.org/10.64898/202...
21.01.2026 19:22 — 👍 23 🔁 10 💬 1 📌 0
Just out📢 Our new paper published in @natmicrobiol.nature.com describes highly potent cross-neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against H5Nx influenza viruses. Close collaboration with Sara Andrews lab and Tongqing Zhou lab at the VRC. Link to the article: rdcu.be/eKV9T 1/2
14.10.2025 15:10 — 👍 19 🔁 9 💬 1 📌 0
Finally, we plan to repeat this effort in ~6 months prior to next vaccine strain selection. If you have sera cohorts that you think would be well suited for this type of study and are potentially interesting in collaborating, please feel free to reach out.
08.09.2025 21:55 — 👍 10 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Thanks to @ckikawa.bsky.social & @huddlej.bsky.social for leading study, also: Andrea Loes, Sam Turner, Jover Lee, Ian Barr, Ben Cowling, Jan Englund, Alex Greninger, Ruth Harvey, H Hasegawa, Faith Ho, K Lacombe, Nancy Leung, Nicola Lewis, Heidi Peck, Shinji Watanabe, Derek Smith, Trevor Bedford
08.09.2025 21:55 — 👍 8 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

GitHub - jbloomlab/flu-seqneut-2025
Contribute to jbloomlab/flu-seqneut-2025 development by creating an account on GitHub.
Many more analyses are possible w these data. But we have made all data & code available now at github.com/jbloomlab/fl...
Reason is to provide near real-time titer data that can be leveraged by scientific community for real-time decisions like vaccine strain selection.
08.09.2025 21:53 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

Above visualizations just scratch surface of data: there is tremendous heterogeneity across sera from different individuals not easily summarized by median/mean.
Indeed, we previously found this heterogeneity may be important for influenza evolution: elifesciences.org/reviewed-pre...
08.09.2025 21:53 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
auspice
Working w @huddlej.bsky.social & Trevor Bedford, we mapped neutralization titers on interactive Nextstrain trees to visualize neutralization across subclades and natural mutations.
See:
nextstrain.org/groups/blab/...
nextstrain.org/groups/blab/...
08.09.2025 21:52 — 👍 7 🔁 4 💬 1 📌 0
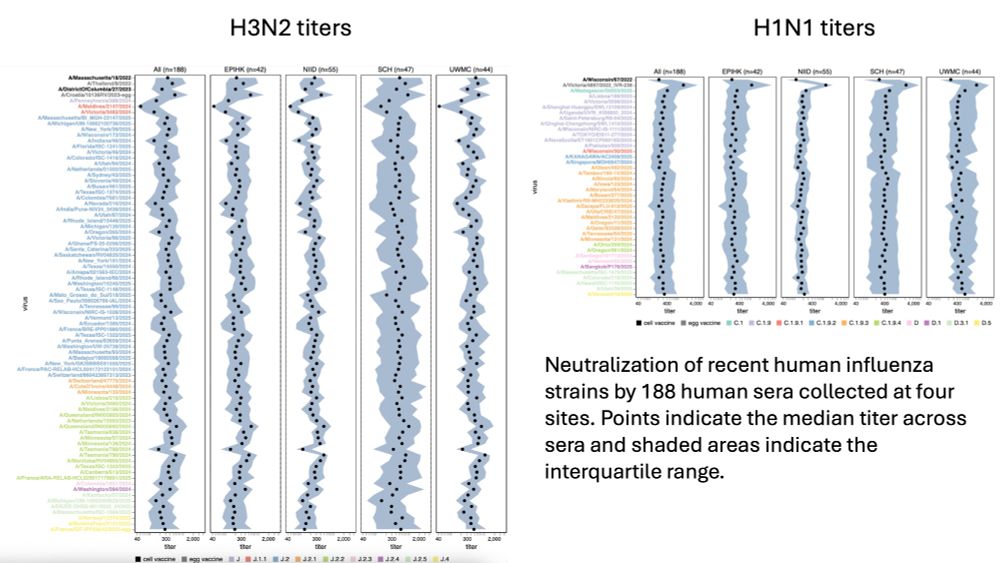
We then measured how 188 human sera recently collected at four different sites neutralized all 140 influenza strains in library.
Titers are summarized below; can be examined interactively at jbloomlab.github.io/flu-seqneut-... & jbloomlab.github.io/flu-seqneut-...
08.09.2025 21:51 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

In spring of 2025, we designed library of naturally occurring human seasonal influenza strains that represented diversity of available sequences at that time; this library continues to cover most sequenced diversity of H3N2 and H1N1 hemagglutinin today.
08.09.2025 21:51 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

To do this, we used sequencing-based neutralization assays that measure many neutralization curves simultaneously (journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/... & elifesciences.org/reviewed-pre...)
Approach enabled one grad student (@ckikawa.bsky.social) to measure ~26,000 neutralization curves in ~5 months.
08.09.2025 21:51 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

But because it takes time to perform experiments, measurement of how current strains are neutralized by human serum antibodies can lag timeline for vaccine strain selection.
Our goal was to use new approach to characterize human antibody landscape at scale in near real-time.
08.09.2025 21:49 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
As background, seasonal influenza evolves to erode antibody immunity.
Viruses w more antibody escape spread in human population & people more likely to be infected by strains their antibodies neutralize less well.
Vaccine updated bi-annually to keep pace w viral evolution.
08.09.2025 21:49 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

Data in interactive form at dms-vep.org/CHIKV-181-25...
Thanks to Xiaohui Ju for leading study
Special thanks to @msdiamondlab.bsky.social for help
Also Will Hannon, Caelan Radford, Brendan Larsen, Daved Fremont, Ofer Zimmerman, Tomasz Kaszuba, Chris Nelson, Israel Baltazar-Perez, Samantha Nelson
04.09.2025 23:20 — 👍 7 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Overall, these results shed light on how Chikungunya virus naturally infects cells from highly diverse species.
Sequence-function information can aid in immunogen engineering, and loss-of-tropism mutants could be useful in vaccines as well.
04.09.2025 23:17 — 👍 12 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

After using pseudoviruses & reporter particles to show mutations *loss* of function, we engineered into Chikungunya virus: mutants lost ability to infect human or mosquito cells.
So we reduced natural tropism for both human & mosquito cells to just one type of cell.
04.09.2025 23:16 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We next used non-replicative single-cycle alphavirus reporter particles (which provide another safe way to study mutations) to validate that mutations identified in deep mutational scanning indeed specifically impaired entry in human or mosquito cells only.
04.09.2025 23:16 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Sites where mutations specifically impair entry in 293T-MXRA8 cells mostly at MXRA8 binding interface.
We also find sites where mutations specifically impair entry in C6/36 cells. Although mosquito receptor unknown, we hypothesize these sites at its binding interface.
04.09.2025 23:15 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Most mutations similarly affect entry in all three cells, but some have cell-specific effects.
For instance, mutations at E2 site 119 are generally tolerated in C6/36 and 293T-TIM1 cells, but deleterious in 293T-MXRA8 cells.
(See dms-vep.org/CHIKV-181-25... for interactive plot.)
04.09.2025 23:15 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We then measured how mutations affect entry in two other cells: the mosquito cell-line C6/36, and 293T cells expressing TIM1 which enables envelope protein independent cell binding by virion associated phosphatidylserine.
04.09.2025 23:14 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We first measured how mutations affect entry in 293T cells expressing human receptor MXRA8.
Below is constraint mapped on structure; see dms-vep.org/CHIKV-181-25... for interactive heatmap of these data.
04.09.2025 23:14 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We used pseudovirus deep mutational scanning to measure effects of all mutations to envelope proteins in context of single-cycle pseudotyped particles that provide a safe way to study viral protein mutations outside context of fully infectious virus.
04.09.2025 23:13 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Chikungunya virus enters cell using its envelope proteins, which are also target of neutralizing antibodies and vaccine design.
A receptor for these viral proteins in mammalian cells is the protein MXRA8, but receptor in mosquito cells is unknown.
04.09.2025 23:13 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

As background, Chikungunya virus has transmission cycle that involves infecting both mosquitoes & humans or other primates.
Infection can cause fever and severe joint pain in humans.
Outbreaks are growing due to expanding mosquito range: www.nytimes.com/2025/08/19/h...
04.09.2025 23:12 — 👍 4 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
Pseudovirus deep mutational scanning of SARS-CoV-2 spike from KP.3.1.1 strain
Data, figures, and analysis for KP.3.1.1 spike .
All data available in interactive form at dms-vep.org/SARS-CoV-2_K... and we encourage exploration of that site.
Study led by the incomparable @bdadonaite.bsky.social, w help from Sheri Harari, Brendan Larsen, Lucas Kampman, Alex Harteloo, Anna Elias-Warren, & Helen Chu.
20.08.2025 05:28 — 👍 15 🔁 3 💬 1 📌 0

Finally, we measured how mutations affect neutralization by three relevant monoclonal antibodies. As shown below, all antibodies adversely affected by mutating site 505 which fortunately remains highly constrained for ACE2 binding. We discuss this interesting site more in preprint.
20.08.2025 05:26 — 👍 12 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0

We used this fact to estimate how much mutations at each site affect RBD up-down motion, as shown below.
Many of these sites have mutated during SARS-CoV-2 evolution in humans, demonstrating importance of RBD motion and its effects on ACE2 binding & antibody neutralization.
20.08.2025 05:26 — 👍 15 🔁 4 💬 1 📌 0

This tradeoff between serum antibody escape and ACE2 binding is because mutations that put the RBD more up enable ACE2 binding but also promote antibody binding. Mutations that put the RBD more down do the opposite.
20.08.2025 05:25 — 👍 15 🔁 5 💬 1 📌 1
PhD student in Jesse Bloom’s lab at Fred Hutch. I’m interested in influenza and viral evolution! 🧬🧫
Duke University alumn. Virologist in progress, most recently as research specialist in the Sheahan Lab at CVRG (y'know, at that other blue school). Looking for a new home base thanks to grant terminations🫠 Pop punk millennial. she/they. ✡️•🏳️🌈•🖖
virtual seminars on arbovirus biology, by the community for the community (organised by Tem Morrison, @tulilab.bsky.social and
@clive-mckimmie.bsky.social
Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution
Assistant Professor, Koita Centre for Digital Health, IIT Bombay
Genome of India: https://genomeofindia.substack.com
https://saketlab.in/
An open-source reactive Python notebook: reproducible, git-friendly, execute as scripts, share as apps!
GitHub: https://github.com/marimo-team/marimo
Discord: https://marimo.io/discord?ref=bsky
Phylogeneticist and evolutionary biologist. Research fellow at UCL Biosciences | Communications Officer for @systassn.bsky.social
Postdoctoral Fellow in the McLellan Lab at the University of Texas at Austin
Assistant Prof. at Stanford & Innovation Investigator at @arcinstitute.org | Studying metabolites and their impact on physiology and disease 🦠🧪
www.arcinstitute.org/labs/levylab
Influenza virologist in ViralVaxLab at TheDohertyInst
https://www.viralvaxlab.com/
Influenza immunity, evolution & vaccines.
scalable data analysis, modeling, AI, software design at HHMI Janelia
https://mastodon.social/@herrsaalfeld
Evolutionary Biology @ Emory
https://biology.emory.edu/people/bios/faculty/bazykin-georgii.html
Structural virologist who also loves sports
@veeslerlab.bsky.social
Frustrated football player, I moved to a less relevant work: microbiologist interested on mobile genetic elements
RNA Virologist working on zoonosis



















