🤍
12.12.2025 07:37 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0🤍
12.12.2025 07:37 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Thank you Amanda! It has been great to meet you.
Thank your for your engagement and all the best for the next steps!!
And a very special thank you to my co-organizing mate, Raquel Peixoto!
27.10.2025 14:10 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Thank you to our inspiring, diverse, and brilliant keynote speakers @symbionticism.bsky.social @momedinamunoz.bsky.social @jcamthrash.bsky.social Laura Steindler, Morten Limborg, Lone Gram, @cibiocm.bsky.social, @nicoledubilier.bsky.social, Jens Walter, @reefgenomics.bsky.social, Torsten Thomas.
27.10.2025 14:10 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0A huge thank you to our generous sponsors @isme-microbes.bsky.social @moorefound.bsky.social @amiposts.bsky.social @biologists.bsky.social @minderoo.bsky.social
27.10.2025 14:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

The #TMHMS25 has just wrapped up!
It’s been four amazing days of stimulating discussions and sharing our science in a wonderfully relaxed and supportive atmosphere.
There was a truly genuine sense of community among all participants, which I really cherish.
Cheers, to the next one! 🌊




Live from the Italian Dolce Vita at the Trends in Marine Host-Microbe Symbiosis Conference hosted by the illustrious @memartino.bsky.social and @raquelpeixoto.bsky.social with the best scholars/friends @momedinamunoz.bsky.social @sabinallarosa.bsky.social @jcamthrash.bsky.social et al.
24.10.2025 22:37 — 👍 23 🔁 3 💬 2 📌 0
We're very much looking forward to connecting with young scientists and making the marine holobiont community grow and evolve!
Looking forward to seeing many of you there!
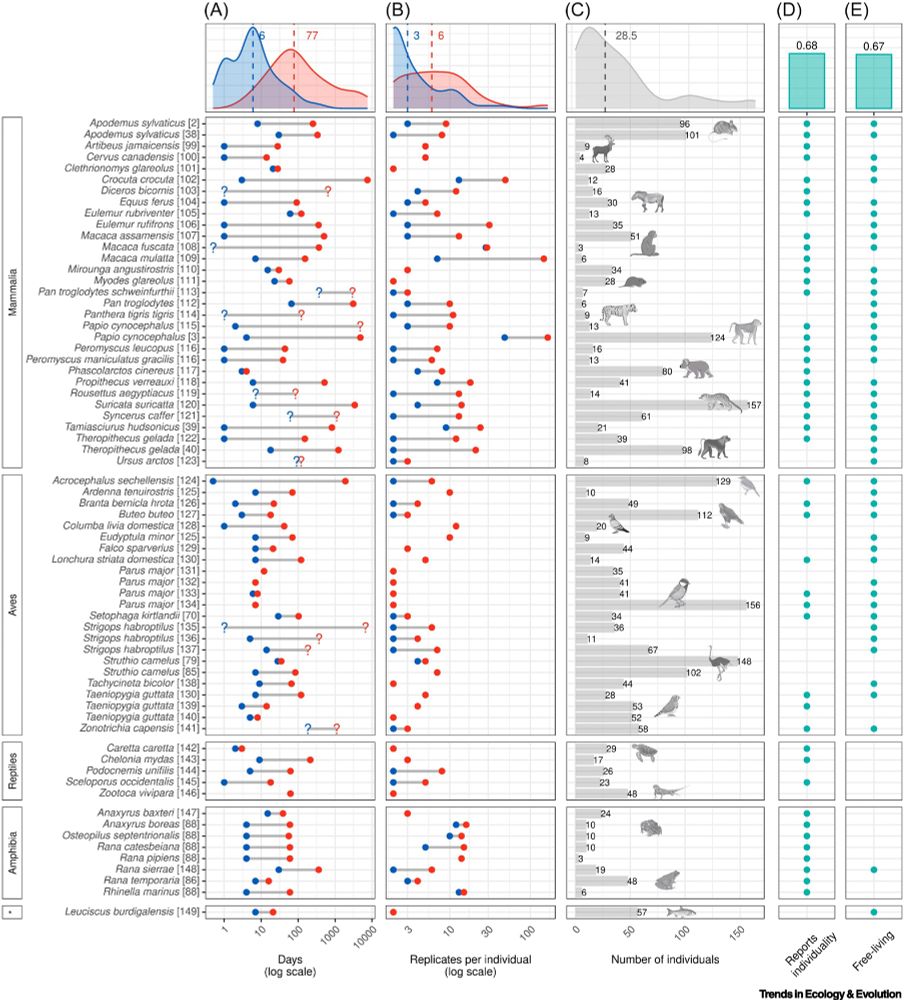
Figure from linked paper. “Figure 1. Longitudinal host microbiome studies in vertebrate species organized by taxonomic class. The class marked by an asterisk (*) is the Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish). We excluded studies on humans, livestock species, and laboratory model organisms, as well as those for which metadata, sample size, and/or sampling details were missing. If multiple studies used the same dataset we used either the reference that reports within-individual variation or the one with the largest sample size. Data sources are cited next to the scientific name of each species. The literature search was completed on 31 August 2024. (A) The minimum (blue) and maximum (red) time intervals (number of days, log scale) between sampling events within individuals. To include as many studies as possible, we estimated some values based on the available information (indicated with question marks). (B) The minimum (blue) and maximum (red) numbers of repeated samples per individual. (C) The total number of individuals with repeated sampling (≥2 samples). (D) Dot plot indicating whether information about within-individual variation in the host microbiome was reported ('individuality', yes/no). We considered a broad range of methodologies to evaluate individuality, including repeatability analysis and other variance partitioning methods such as testing for the fixed effect of individual IDs in beta diversity analyses. Some studies mention analyses that control for repeated sampling but the results (e.g., variation explained by ID) are not reported in the main text. Such studies are indicated as not reporting individuality. (E) Dot plot indicating whether a study was conducted in the field ('free-living', yes/no). In (A–C), a density plot is shown at the top and indicates the median (dashed line and number). In (D) and (E) bar plots at the top show the proportion of studies with 'yes'.”
Can’t wait to read! 👀
Gillingham et al. 2025. @cp-trendsecolevo.bsky.social
“The costs and benefits of a dynamic host microbiome”
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

Extending microbiome research across diverse organisms is key to understand the complexity of host–microbe symbioses
In our latest study, we developed a protocol to generate #gnotobioticclams
We hope it will be useful for a wide range of bivalves to test microbial traits in nature and aquaculture
@jcamthrash.bsky.social @nicoledubilier.bsky.social @symbionticism.bsky.social @utehentschel.bsky.social @reefgenomics.bsky.social @momedinamunoz.bsky.social @cibiocm.bsky.social
19.08.2025 13:45 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Join us! This is more than a scientific meeting, it's a platform to catalyze collaboration, share knowledge openly and develop solutions for safeguarding marine ecosystems in a changing world. Great line-up of speakers and early bird rate still available!
Please RT!
🚨 Just 4 days left to submit your abstract for #TMHMS25!
Don’t miss your chance to be part of cutting-edge discussions on marine holobionts with leading and inspiring researchers.
🌊🏆 The top 10 abstracts will receive free registration and travel support!
@schwarzergnoto.bsky.social @francoisleulier.bsky.social 🥂
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0They could also play a valuable role in #animalnutrition, including the use of #probiotics in insect rearing and as alternative nutrient sources.
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0These results have a wide range of potential applications. Selected strains could be tested to boost growth in key agricultural species, offering a promising alternative to antibiotics and helping reduce reliance on expensive, protein-rich feeds in animal farming.
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Despite this specificity in adaptation, both strains (the ancestral WJL and the evolved IGFL1) show transferable potential in terms of animal growth promotion, as they are highly beneficial in flies and mice both under conditions of nutritional deprivation and under normal nutritional conditions
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Our results demonstrate the high adaptive potential of L. plantarum, and indicate that bacterial improvements of the benefits to its animal hosts are strictly context dependent.
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Whole genome sequencing revealed the presence of four mutations in IGFL1 genome that may be related to more effective utilization of nutrients, leading to the observed further improvement in benefits for the fruit fly.
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Administration of IGFL1 to conventional C57Bl/6j male mice under both nutrient deprivation (A-D) and normal dietary conditions (E-H) significantly increased body length and weight growth rates compared to placebo-fed animals. In mice, these effects were comparable to those of the ancestral strain.
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
After ten Drosophila generations, we identified an evolved strain (L. plantarum IGFL1) that significantly improved Drosophila juvenile growth compared to the ancestral strain and other growth promoting strains of L. plantarum
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0In this study, we experimentally evolved a Drosophila growth-promoting strain of #L.plantarum (WJL) under conditions of nutrient deprivation with the aim of maximizing its growth-promoting benefits, while concurrently evaluating the translation of this phenotype in Drosophila and mice
23.05.2025 08:44 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
A few years back, we experimentally evolved a poorly growth-promoting strain of #Lplantarum and isolated strains with enhanced benefit in insects
We then asked: how far can these benefits be optimized? Do they persist in well-fed mammals? 🦠🐭
Find out in our new paper now online!
Thread 👇
They could also play a valuable role in #animalnutrition, including the use of #probiotics in insect rearing and as alternative nutrient sources.
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0These results have a wide range of potential applications. Selected strains could be tested to boost growth in key agricultural species, offering a promising alternative to antibiotics and helping reduce reliance on expensive, protein-rich feeds in animal farming.
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Despite this specificity in adaptation, both strains (the ancestral WJL and the evolved IGFL1) show transferable potential in terms of animal growth promotion, as they are highly beneficial in flies and mice both under conditions of nutritional deprivation and under normal nutritional conditions
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Our results demonstrate the high adaptive potential of L. plantarum, and indicate that bacterial improvements of the benefits to its animal hosts are strictly context dependent.
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Whole genome sequencing revealed the presence of four mutations in IGFL1 genome that may be related to more effective utilization of nutrients, leading to the observed further improvement in benefits for the fruit fly.
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Administration of IGFL1 to conventional C57Bl/6j male mice under both nutrient deprivation (A-D) and normal dietary conditions (E-H) significantly increased body length and weight growth rates compared to placebo-fed animals. In mice, these effects were comparable to those of the ancestral strain.
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
After ten Drosophila generations, we identified an evolved strain (L. plantarum IGFL1) that significantly improved Drosophila juvenile growth compared to the ancestral strain and other growth promoting strains of L. plantarum
23.05.2025 07:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0