
A timetree of Fungi dated with fossils and horizontal gene transfers
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
@loreament.bsky.social
Evolutionary biologist interested in genomics, speciation, reproductive strategies, fungi, and biodiversity. And cats! She/her

A timetree of Fungi dated with fossils and horizontal gene transfers
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Wooo!
01.10.2025 05:47 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
How do species diverge? Could the relative immobility of plants increase their likelihood of speciating in the same place?🧵
22.09.2025 14:10 — 👍 3 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
Hybridization and introgression are major evolutionary processes. Since the 1940s, the prevailing view has been that they shape plants far more than animals. In our new study (www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
), we find the opposite: animals exchange genes more, and for longer, than plants

"Rapid establishment of species barriers in plants compared with that in animals" by Monnet et al
#Speciation
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

mRNA A-to-I editing in vegetative cells of Fusarium
#fungionsky #fungi #epigenetics
link.springer.com/article/10.1...
I think their point is “they occur more in the populations where they are adaptive”, which makes me uncomfortable haha. Having said, I haven’t read the paper carefully and I didn’t understand their method on a quick scan.
06.09.2025 11:24 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Uhm 🤔, another "mutation is not random" paper:
#mutation #genomics
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

Population diversity declines between inoculated and exposed guinea pigs. Viral titers in nasal lavage samples are indicated by the overall height of the bar. Red lines show LOD (50 PFU/mL). Colors within the bars represent unique barcodes, and the height of each color indicates barcode frequency within the sample. Plots for individual animals are paired with those of their cage mate. Representative pairs for direct contact (top half) and aerosol (bottom half) exposure are shown from three experimental replicates. Guinea pig ID numbers are shown in the upper right corner of each plot.
What causes viral transmission bottlenecks? This study uses barcoded virions to show that in the case of #influenza A #virus, early within-host replication dynamics (rather than a reduced inoculum population) drive loss of diversity during transmission @plosbiology.org 🧪 plos.io/4ngicDK
03.09.2025 07:51 — 👍 19 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 0
🌎👩🔬 For 15+ years biology has accumulated petabytes (million gigabytes) of🧬DNA sequencing data🧬 from the far reaches of our planet.🦠🍄🌵
Logan now democratizes efficient access to the world’s most comprehensive genetics dataset. Free and open.
doi.org/10.1101/2024...
Check out our new paper on adopting a trait-based framework for protist diversity! We make the case for a unified protist trait database, how to build it, and how it could transform research on protist ecology and evolution.
#protistsonsky

Sclerotina and its weird-ass arrangement of different chromosomes in two separate nuclei still follow normal meiosis, it turns out.
#fungi #meiosis
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
I'm super bummed to be missing #ESEB2025 @eseb2025.bsky.social due to a cancelled flight! Here's a quick overview of my talk "Gene- and genome-focused perspectives on microbial pangenomes" slated to be part of The Evolution of Microbial Pangenomes -- which I recommend you attend tomorrow (Fri) !
1/n

Our paper describing our new improved GFmix models for phylogenetic inference that capture site-and-branch heterogeneity in amino acid composition.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
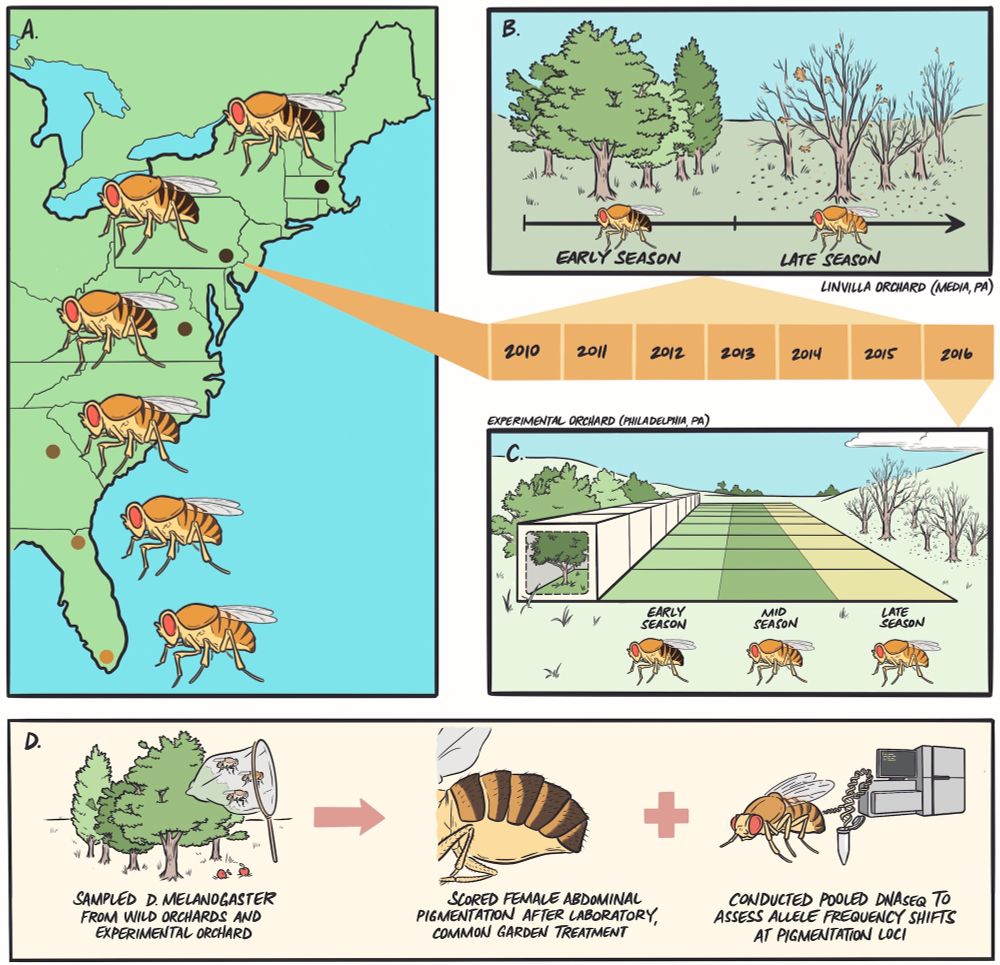
Figure showing the experimental overview as a graphic. Remaining alt text taken from the figure caption in the paper: (A) we sampled flies from six wild orchard populations ranging from Homestead, FL, to Lancaster, MA, and established isofemale lines in the laboratory. (B) We returned to a focal orchard in Media, PA, at early- and late-season timepoints and collected flies to capture evolutionary patterns following winter and summer conditions. (C) We then seeded outdoor mesocosms (N = 9) with an outbred population originating from early-season collections in Media, PA, and sampled flies at the end of summer (mid-season) and fall (late-season) to determine if seasonal patterns are recapitulated in experimental populations controlled for migration, drift, and cryptic population structure. (D) Across each wild or experimental context, we sampled flies, established lines in the lab, completed common garden treatment to remove environmental effects, and scored females for abdominal pigmentation. We also conducted pooled DNA sequencing on additional flies sampled from each population to map genomic patterns for candidate pigmentation SNPs.
How predictably does complex trait adaptation proceed over space and time in wild populations?
doi.org/10.1093/evle...
Now in @evolletters.bsky.social by @skylerberardi.bsky.social, @paulrschmidt.bsky.social et al.
📷: Dr. Rush Dhillon
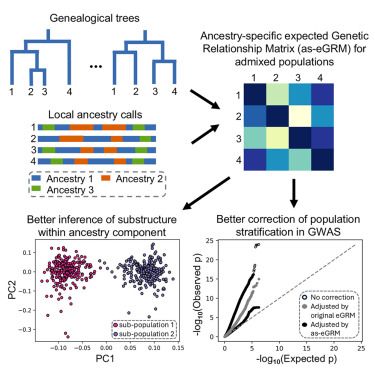
@charleston.bsky.social and colleagues introduce the ancestry-specific expected genetic relationship matrix (as-eGRM), an analysis framework that estimates the relatedness within ancestry components between admixed individuals, in the @ajhgnews.bsky.social latest article: bit.ly/3U5p0aI #ASHG
31.07.2025 20:08 — 👍 18 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 0A pangenomics-enabled platform for the high-throughput discovery of antifungal resistance factors in crop pathogens https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.07.18.665620v1
20.07.2025 04:17 — 👍 15 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 1
The auditorium is slowly filling up for the opening session and our inaugural keynote speech...
#SMBE2025
Our description of the transcriptomic changes during sexual development in #Podospora anserina is out in @genomics.peercommunityin.org ! peercommunityjournal.org/articles/10....
@i2bcparissaclay.bsky.social @univparissaclay.bsky.social
New preprint: we advertise DAFNEE, a database of academia-friendly eco-evo-archaeo journals. 1/6
#AcademicPublishing #ecoevo #archaeology #EthicalPublishing #SocietyJournals #DiamondOpenAccess
doi.org/10.32942/X24...
This work was done in both Stockholm and Bordeaux Universities as part of my Vetenskapsrådet postdoc mobility grant. I am grateful to my co-authors and to everybody who supported me along the way! Yay!!
02.07.2025 18:10 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
So in conclusion, het-d and het-e independently evolved the capacity of recognizing het-c, even in the presence of interparalog repeat exchange! This little story is relevant for NLRs in general, as ~13% of all fungal NLRs and a lot of bacterial NLRs have HIC repeats! end/n
#Bacteria #immunity
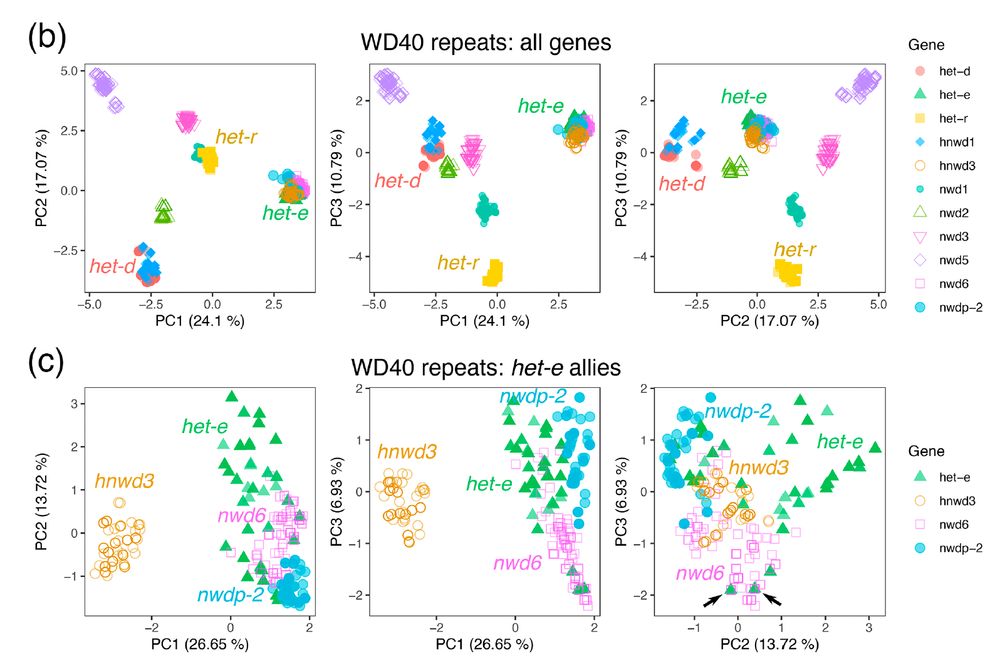
For the repeat domain, we extracted >1100 individual repeats and performed a PCA of their nucleotide sequences. Indeed, het-d and het-e are not that similar, but we discovered that het-e seems to be exchanging repeats with another gene! 8/n
02.07.2025 18:10 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0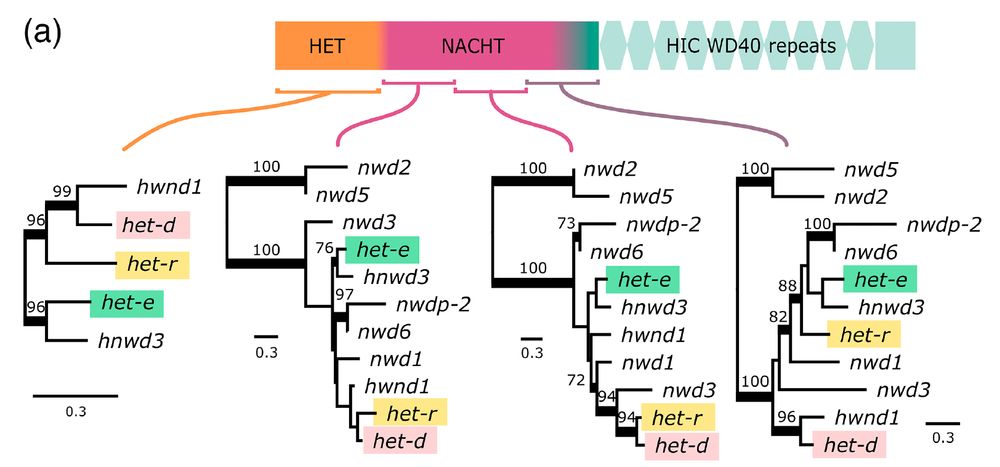
Are het-d and het-e capable of recognizing het-c because of shared ancestry? No! It turns out they are not that closely related, judging by phylogenies along the gene for a bunch of NLRs in Podospora. 7/n
02.07.2025 18:10 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0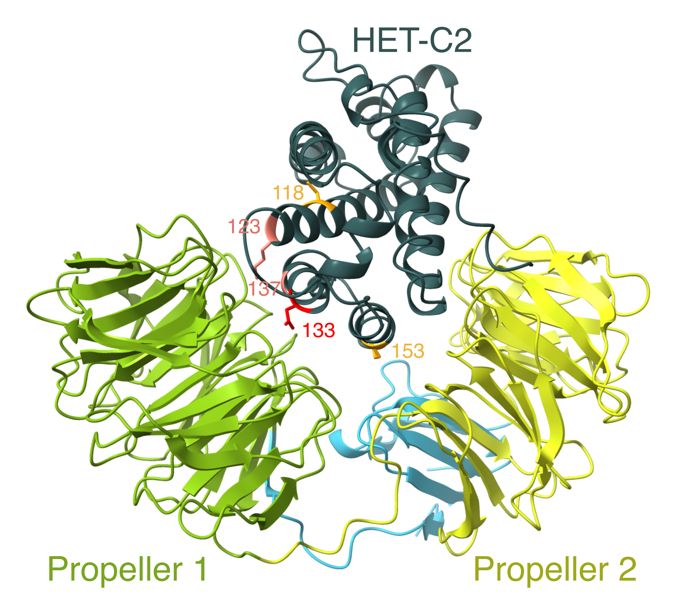
We sequenced a panel of strains with known alleles, which can now be used to assign a phenotype to wild-type strains. With this information in hand, we determined that reactive alleles fold into two beta-propellers that likely embrace their cognate ligand HET-C like a clam. 6/n
#AlphaFold
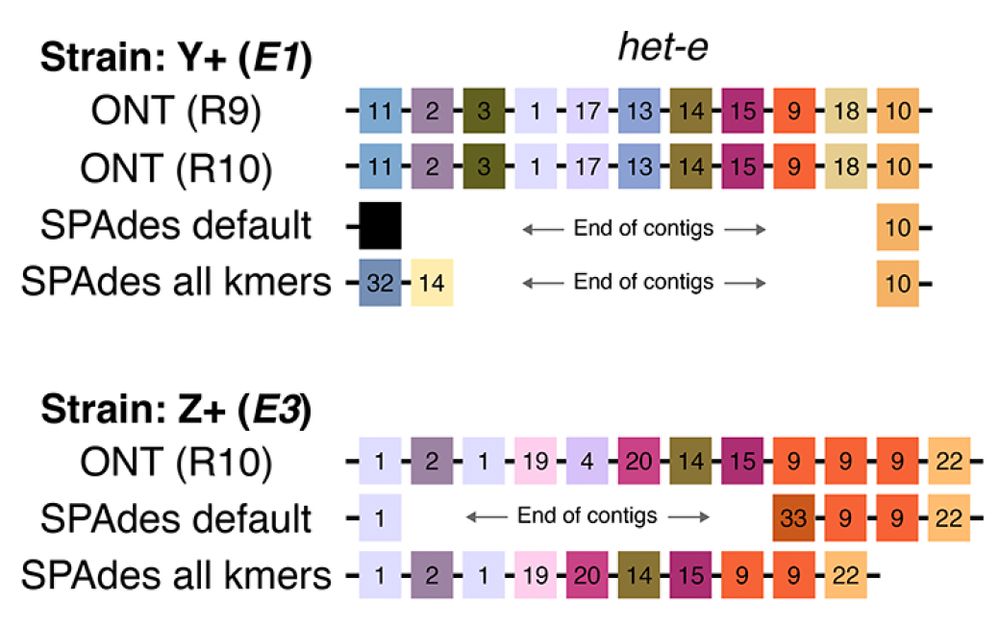
Of course, these HIC repeats are hard to sequence. We showed that assemblies of Illumina reads often recover broken or incorrect (!) allele reconstructions. But #PacBio and #Nanopore data get them just fine. 5/n
#genomics
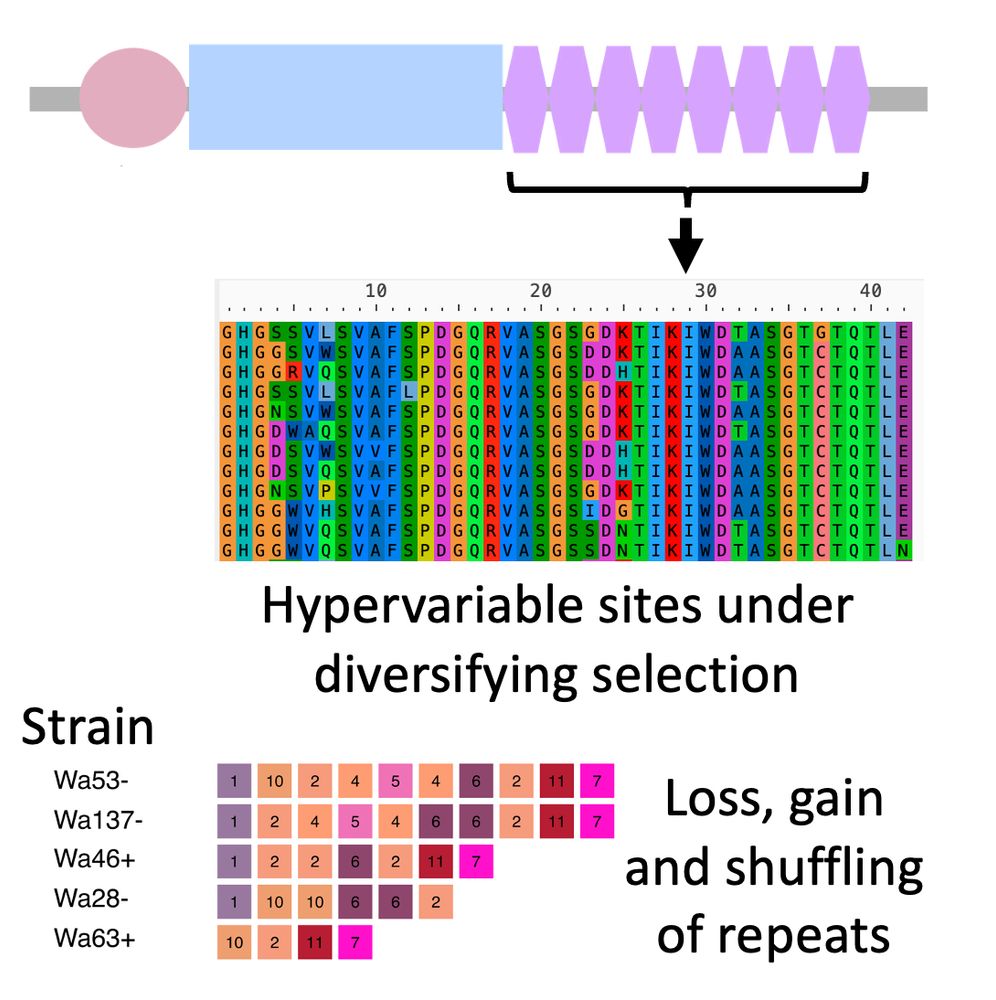
het-d/e have "high internal conservation" (HIC): their C-term domain is made out of nearly identical WD40 repeats. Only a few sites are different and evolve under diversifying selection. Concerted evolution (or something) homogenizes the repeats and leads to loss, gain, and shuffling of repeats. 4/n
02.07.2025 18:10 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0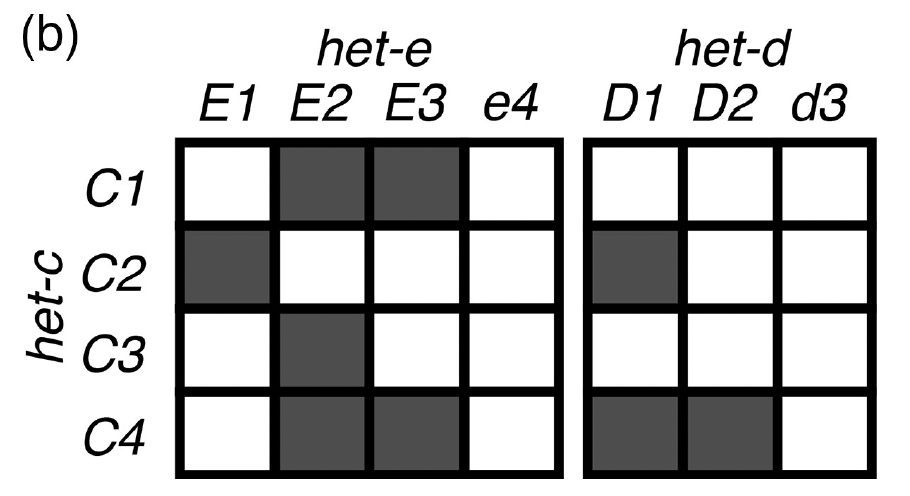
In the model fungus #Podospora anserina, the het-d
and het-e NLRs are highly polymorphic genes, whose products recognize different alleles of another gene, het-c. If two confronting strains have incompatible het-e/d and het-c alleles, a rejection reaction occurs. 3/n
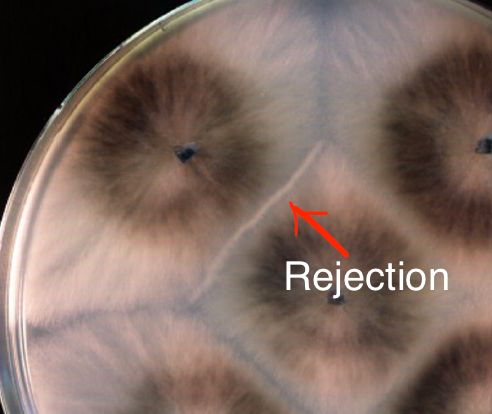
NOD-like receptors (NLRs) are intracellular proteins that play key roles in the innate immune system of plants and animals. But in fungi we know the function of only a few cases: they all work in heterokaryon incompatibility (rejection between different strains during vegetative fusion). 2/n
02.07.2025 18:10 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Happy to see this out! "Reconstructing NOD-like receptor alleles with high internal conservation in #Podospora anserina using long-read sequencing", now in @microbiologysociety.org! 🧬
Keep reading for a simple explanation 🧵 1/n
#Fungi #Allorecognition
www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...