
Do you teach #rstats? Do your students complain about how lame and old-fashioned dplyr is? Don't worry: I have the solution for you: github.com/hadley/genzp....
genzplyr is dplyr, but bussin fr fr no cap.
@mariusmaur.bsky.social
Evolution of insect venoms PhD candidate at UiO

Do you teach #rstats? Do your students complain about how lame and old-fashioned dplyr is? Don't worry: I have the solution for you: github.com/hadley/genzp....
genzplyr is dplyr, but bussin fr fr no cap.

Article alert: Maurstad, Hoff; Cerca et al. Reference genome bias in light of species-specific chromosomal reorganization and translocations. Now out in Genome Biol. Congrats to Sissel and the team😀 doi.org/10.1186/s130...
15.10.2025 18:49 — 👍 14 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0Super happy to see our paper out! Reference choice matters, especially if you work with species that has lots of chromosomal rearrangements 🧬🐟
15.10.2025 20:18 — 👍 16 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 0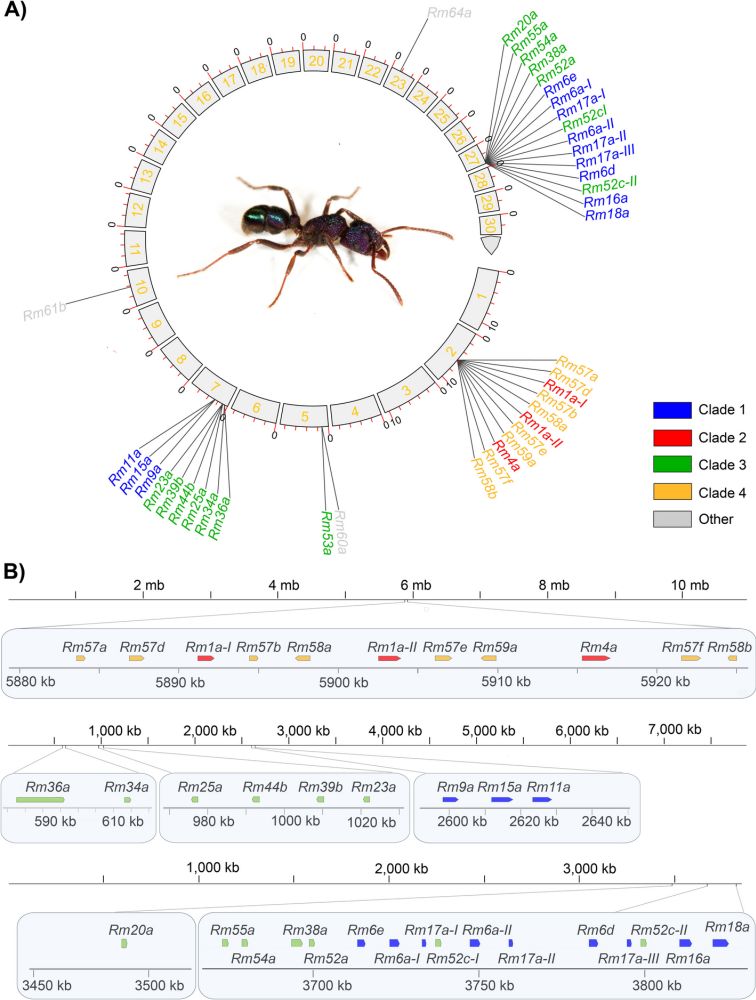
New publication: "Genome of the green-head ant, #Rhytidoponera metallica, reveals mechanisms of toxin evolution in a genetically hyper-diverse eusocial species" with Isaksen, Nachtigall, Araya, Hansen & Undheim from @biovitenskap.bsky.social
Published in Genome Biology by @springernature.com

Crazy discovery in ants 🤯🐜
One mother for two species via obligate cross-species cloning in ants | Nature
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
"Males from the same mother exhibit distinct genomes and morphologies, as they belong to species that diverged over 5 million years ago."

Regjeringen gir 1 milliard kroner til polarforskning og forskningsprosjektet #Polarhavet2050, hvor Universitetet i Oslo er én av fjorten partnere. Dette blir spennende!
@jentoft.bsky.social
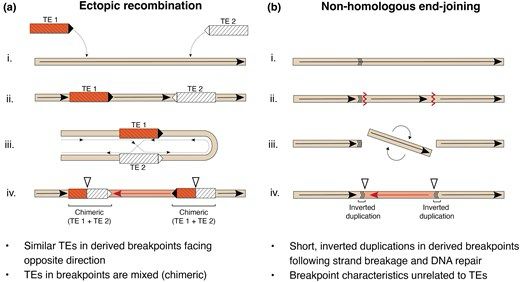
Our paper is now published in GBE!
We find that transposable elements (likely) facilitated several large chromosomal inversions in Atlantic cod.
So proud of the work by our team!
doi.org/10.1093/gbe/...

@robinaraya.bsky.social @naturalselection.bsky.social @kjetillsj.bsky.social et al. investigate TEs in four large inversions in Atlantic cod - TEs accumulate in breakpoints, suggesting they drive inversions through ectopic recombination.
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evaf131
#genome #evolution #TEsky

🆕 ✨ New publication out:
Chromosomal Inversions Mediated by Tandem Insertions of Transposable Elements
We find that transposable elements are the likely mechanism of (some) inversions in cod fishes!
academic.oup.com/gbe/article/...

Presence of DNA transposons in the breakpoints of the inverted genotype in Atlantic cod - perhaps also the case for many other species? Great to see this finally out academic.oup.com/gbe/article/...
21.08.2025 19:40 — 👍 13 🔁 6 💬 0 📌 0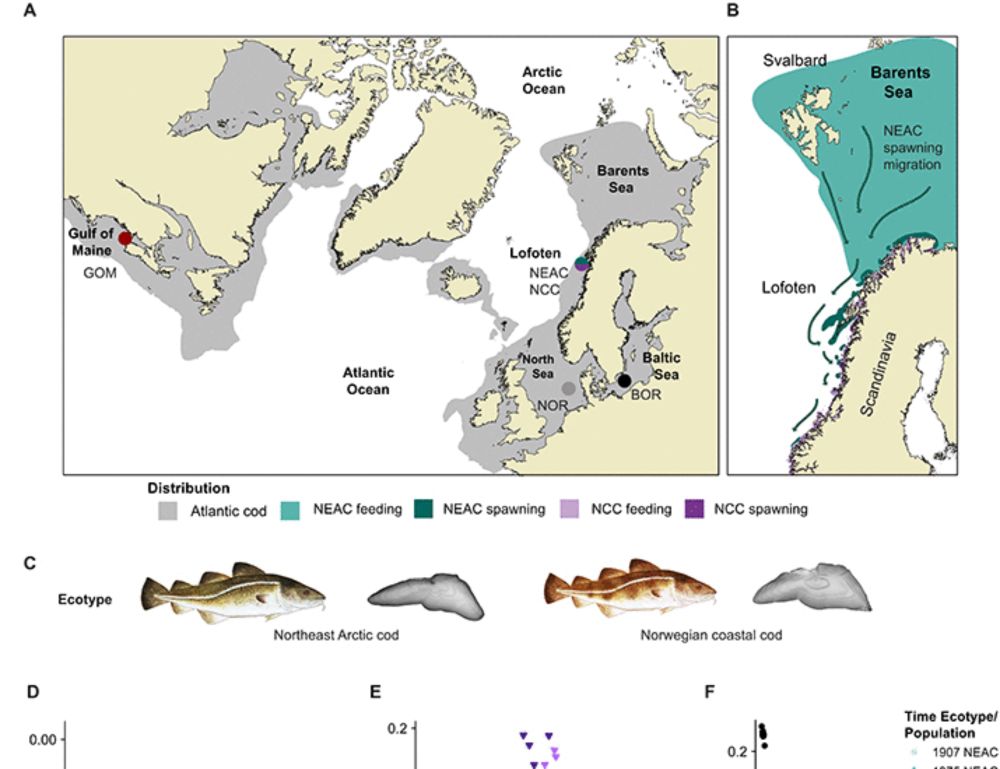
Finally is this story out public!! With an amazing historical dataset from IMR (@havforskningsinstituttet) we demonstrate how human perturbations impact the genomic signal in one of the largest cod stocks in the world: the northeast arctic cod | Science Advances www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
30.07.2025 19:22 — 👍 41 🔁 16 💬 3 📌 0



Phosphaenus hemipterus - one of only 3 firefly species in Czech Republic with both sexes flightless! Was lucky enough to find pupae a while back and now they're already mating in my setup. Fingers crossed for eggs!
17.06.2025 18:53 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
We have a PhD position available at the Department of Biosciences, University of Oslo to work on peptide signaling in plants and insects. Please share.
www.jobbnorge.no/en/available...



New paper out 📝✨
"k-mer approaches for biodiversity genomics"
We discuss k-mer spectra, sex determination, allopolyploid subgenome separation, among other topics - and offer a large tutorial list
Link to paper:
genome.cshlp.org/content/earl...
Link to all tutorials:
github.com/KamilSJaron/...

WASTER’s ability to accurately estimate trees from low-coverage sequencing data without relying on assembly and alignment will lead to substantially reduced sequencing and computational costs in phylogenomic projects. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1... #genomics #evolution #phylogeny
30.01.2025 09:53 — 👍 16 🔁 6 💬 0 📌 0
New publication: "Short tandem repeats delineate gene bodies across #eukaryotes" with William Reinar, Anders Krabberød, Vilde Lalun @vildeol.bsky.social, Melinka Butenko @melinkab.bsky.social, Kjetill Jakobsen.
Published in Nature Communications @nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

[please share widely!]
We have two PhD positions available at the Swedish Museum of Natural History:
[Position 1] Birds, hybridization, genomes, island biology, biogeography, sexual selection 🦚, w/ me, Knud Jønsson, Martin Iredstedt and @stelkens.bsky.social et al
recruit.visma.com/spa/public/a...


🚨 Revolutionising Snakebite Treatments with AI-Designed Proteins 🐍
I'm proud to share our latest study published in hashtag#Nature, driven by Susana Vazquez Torres, and co-led by David Baker (Institute for Protein Design, University of Washington) and myself.

Very happy to share our new paper that just came out: “Chromosomal inversions mediated by tandem insertions of transposable elements”
#TEsky #Transposons
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Ops - forgot the key words: #TEsky #Transposable #TEs #repeats #genome #genomics
14.01.2025 12:50 — 👍 7 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0
We have a new paper out!
"Chromosomal inversions mediated by tandem insertions of transposable elements." 📝 🧬
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Chromosomal inversions mediated by tandem insertions of transposable elements https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.01.09.631634v1
13.01.2025 19:33 — 👍 14 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 2
Chromosome level reference genomes of river and brook lamprey (Lampreta fluvatilis and L. planeri) indicating a species complex: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
16.12.2024 14:24 — 👍 11 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 0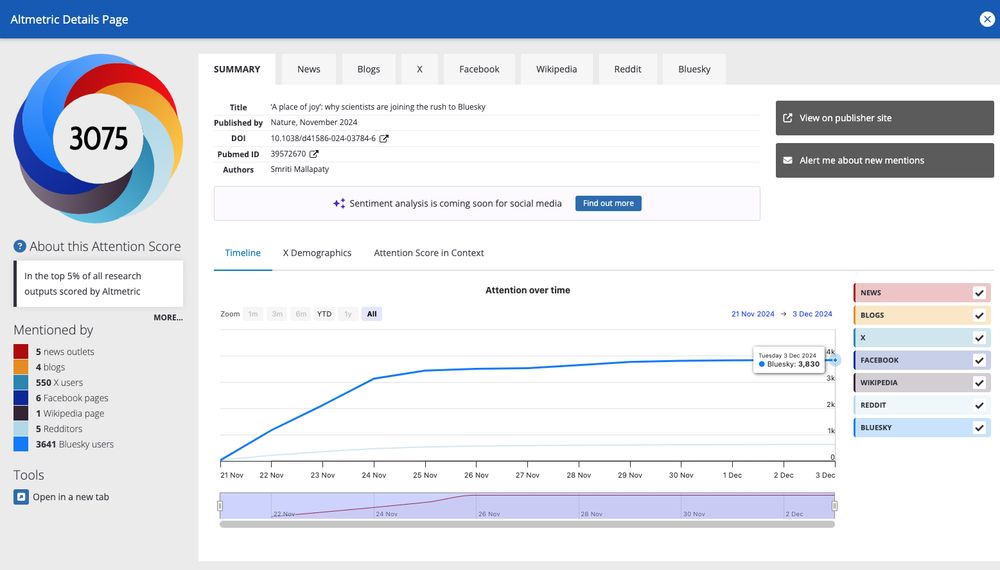
‘A place of joy’: why scientists are joining the rush to Bluesky Researchers say the social-media platform — an alternative to X — offers more control over the content they see and the people they engage with.: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-03784-6
There are already many articles for which there is more attention on Bluesky than on other comparable micro-blogging sites, meaning the academic community and the general public have clearly adopted Bluesky as one of its core places to disseminate and discuss new research.
A Place of Joy.
Dry shipper! I've flown with one within Europe. I recommend getting a backpack for it, as the larger ones can be quite difficult to carry.
21.11.2024 09:01 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0📝 Consistent accumulation of transposable elements in species of the Hawaiian Tetragnatha spiny-leg adaptive radiation across the archipelago chronosequence
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Thread!