


partycoloR is now on CRAN! Started as a simple idea 6 years ago, now it's a full-featured package. Extract party colors and logos from Wikipedia with one line of code. It's already powering ParlGov Dashboard.
install.packages("partycoloR")
@lwarode.bsky.social
Political Science PhD Student, University of Mannheim. lwarode.github.io



partycoloR is now on CRAN! Started as a simple idea 6 years ago, now it's a full-featured package. Extract party colors and logos from Wikipedia with one line of code. It's already powering ParlGov Dashboard.
install.packages("partycoloR")
The app shows how German politicians associate words with "left" or "right" based on ideological in- and out-group narratives and contested concepts. For example, both ideological sides claim the term "freedom."
21.01.2026 08:19 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0This question became the topic of my 2nd dissertation paper. I also considered creating an app to communicate the results efficiently and allow you to explore the patterns yourself. I’ve used Shiny for years, but "AI-assisted agentic engineering" (aka vibe coding 😂) really helped here a lot.
21.01.2026 08:19 — 👍 5 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Words like "patriotism" and "racism" are often associated with the right, while "solidarity" and "socialism" are associated with the left.
But who uses these associations, and how do political positions matter?
📊 App: lukas-warode.shinyapps.io/lr-words-map/
📄 Paper: www.nature.com/articles/s41...

"When Conservatives See Red but Liberals Feel Blue: Labeler Characteristics and Variation in Content Annotation" by
Nora Webb Williams, Andreu Casas, Kevin Aslett, and John Wilkerson.
www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/10.1086/...
Congrats!!
19.01.2026 10:48 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Serienempfehlungen: Fargo, The Sopranos, vielleicht noch Narcos :)
13.01.2026 10:20 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
The Call for Papers and Panels for #COMPTEXT2026 in Birmingham (23-25 April) is out; feel free to circulate: shorturl.at/gRg0p!
Deadline: January 16!
 23.11.2025 12:11 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
23.11.2025 12:11 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Leben und Tod der DiD
19.11.2025 20:37 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Dissertation track? 😉
19.11.2025 15:37 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Slavoj Žižek meme image
“You see, the endless renovation of the Stuttgart train station is a symbol of our late-capitalist condition: the project is always ‘in progress,’ yet nothing ever progresses. The construction site itself becomes the true destination.”
19.11.2025 13:17 — 👍 55 🔁 7 💬 2 📌 1
www.instagram.com/p/DQPf_pJiG8...
Is it a fit?
Job Alert! We are hiring two post-docs (full time, 4+ years) in our project SCEPTIC - Social, Computational and Ethical Premises of Trust and Informational Cohesion with @annanosthoff.bsky.social @guzoch.bsky.social and Prof. Andreas Peters (uol.de/informatik/s...)
17.10.2025 09:15 — 👍 28 🔁 32 💬 3 📌 2
📣 New Preprint!
Have you ever wondered what the political content in LLM's training data is? What are the political opinions expressed? What is the proportion of left- vs right-leaning documents in the pre- and post-training data? Do they correlate with the political biases reflected in models?

Can large language models stand in for human participants?
Many social scientists seem to think so, and are already using "silicon samples" in research.
One problem: depending on the analytic decisions made, you can basically get these samples to show any effect you want.
THREAD 🧵

We present our new preprint titled "Large Language Model Hacking: Quantifying the Hidden Risks of Using LLMs for Text Annotation". We quantify LLM hacking risk through systematic replication of 37 diverse computational social science annotation tasks. For these tasks, we use a combined set of 2,361 realistic hypotheses that researchers might test using these annotations. Then, we collect 13 million LLM annotations across plausible LLM configurations. These annotations feed into 1.4 million regressions testing the hypotheses. For a hypothesis with no true effect (ground truth $p > 0.05$), different LLM configurations yield conflicting conclusions. Checkmarks indicate correct statistical conclusions matching ground truth; crosses indicate LLM hacking -- incorrect conclusions due to annotation errors. Across all experiments, LLM hacking occurs in 31-50\% of cases even with highly capable models. Since minor configuration changes can flip scientific conclusions, from correct to incorrect, LLM hacking can be exploited to present anything as statistically significant.
🚨 New paper alert 🚨 Using LLMs as data annotators, you can produce any scientific result you want. We call this **LLM Hacking**.
Paper: arxiv.org/pdf/2509.08825
Implications for political behaviour, communication, and representation are manifold, as 'left' and 'right' are central categories in polarised public discourse – which is particularly evident in pejorative usage, such as labelling political opponents as 'racist' or 'socialist'.
26.08.2025 09:38 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Both in- and out-ideological associations are externally validated by serving as seed words to scale parliamentary speeches. The resulting ideal points reflect party ideology across different specifications in the German Bundestag.
26.08.2025 09:38 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
The mapping is based on associations from open-ended survey responses in German candidate surveys. Words are mapped into a semantic space using word embeddings and weighted by frequency. Construct validity is ensured by using alternative embeddings and frequency weightings.
26.08.2025 09:38 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Words associated with both left and the right are mapped to the semantic centre, where connotations can vary: 'freedom' has a positive connotation (it is primarily used by the respective in-group to describe left and the right), while 'politics' has a rather neutral connotation.
26.08.2025 09:38 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
This framework yields associations that are driven by positive (in-ideology) and negative (out-ideology) associations. Examples: 'justice' (left) and 'patriotism' (right) are in-ideological associations; 'socialism' (left) and 'racism' (right) are out-ideological associations.
26.08.2025 09:38 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Left and right are essential poles in political discourse. We know little about how they are associated across the spectrum. I propose a 2-dimensional model that accounts for both semantics – is a term left or right – and position – are associations coming from the left or right.
26.08.2025 09:38 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
My 2nd dissertation paper is out in @nature.com Humanities and Social Sciences Communications: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
I study and explore how associations with 'left' and 'right' vary systematically by semantic and political position.
Ja, die goldene Twitterzeit ist leider over
25.08.2025 13:02 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

📢 New Publication Alert!
Our (@msaeltzer.bsky.social)
latest article, "Issue congruence between candidates' Twitter communication and constituencies in an MMES: Migration as an exemplary case", has just been published in Parliamentary Affairs.
academic.oup.com/pa/advance-a...
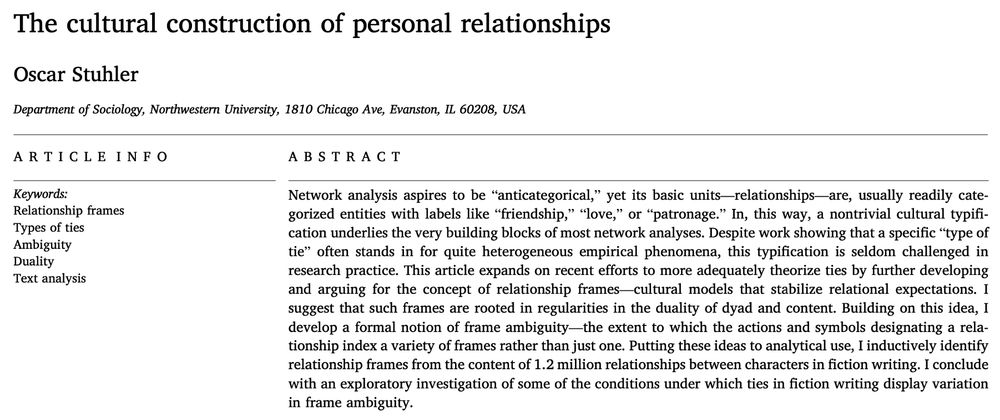
Title and abstract of the paper.
Now out in Social Networks
Network analysis aspires to be “anticategorical,” yet its basic units—relationships—are usually readily categorized ('friendship,' 'love'). Thus, a nontrivial cultural typification is asserted in the very building blocks of most network analyses.
doi.org/10.1016/j.so...

Calling all parliaments experts!
Say there's a debate in parliament, and a related vote. How frequently would these be on different days? different weeks? I don't mean different readings of bills, because these will also have different debates.
@sgparliaments.bsky.social #polisky #parlisky

Can banning political ideologies protect democracy? 🛡️🆚🗣️
Our (w. @valentimvicente.bsky.social) paper finds: punishing individuals might backfire. We study a West German policy banning "extreme left" individuals from working for the state.
#Democracy #PoliticalScience
🧵
url: osf.io/usqdb_v2