
Came across this paper --- they found that visual memory performance improved when cues were both encoded and decoded in late exhalation.
Pretty cool that breathing phases can affect memory!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
@mott-lab.bsky.social
PhD candidate @SREAL @University of Central Florida | mad scientist | HCI and AR/VR research :: cross-reality interactions and transitions https://mattgottsacker.space/

Came across this paper --- they found that visual memory performance improved when cues were both encoded and decoded in late exhalation.
Pretty cool that breathing phases can affect memory!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

the teenage engineering choir dolls are credited for some of the music in the movie Elio. fun and cool!
teenage.engineering/products/choir
it's a beautiful day ... to spend entirely in a windowless lab working on a #chi2026 paper submission
11.09.2025 13:00 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
screenshot from Spotify of the lyrics from the song Solo (Reprise) rapped by Andre 3000 on Frank Ocean's album Blonde. the lyrics read "I'm so naive I was under the impression that everyone wrote their own verses / it's coming back different and yeah that shit hurts me / I'm humming and whistling to those not deserving / I'm stumbled and lived every word was I working just way too hard?"
me reviewing research papers with a bunch of LLM-generated text
14.08.2025 02:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0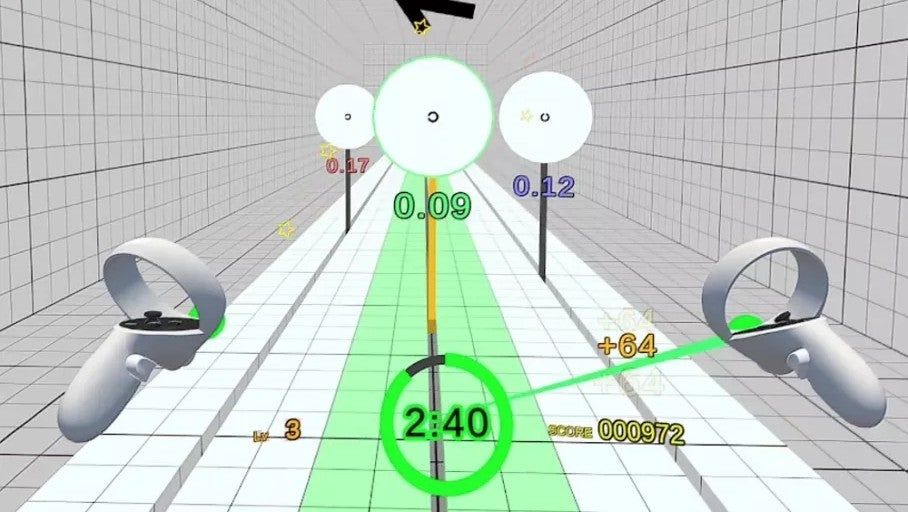
"a visionary new game"
small study (n=10) but interesting idea: using VR to improve eyesight.
I wonder how the display's fixed focal length (i.e. vergeance-accomodation conflict) might affect this.
www.ign.com/articles/thi...

Read more in our paper: ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/doc...
pre-print / no paywall: sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/u...
Or watch me present it at this past IEEE ISMAR: youtu.be/035v6yzO_O0?...
/eof
Some ideas for future work: How do interactive transitions (e.g., guided tasks, subtle movement cues) impact cognitive residue? Can we shrink the time required to clear users' minds by distracting them a certain way (e.g., encouraging more exploration or movement)? 🔭
11/
While this study is a bit future-looking, one scenario where this may already matter is within-subjects VR experiments where participants experience multiple virtual envs back-to-back. And, consider how spatial residue of a user's physical environment might affect them after entering VR. 🤔
10/
Design implications for VR in task-switching contexts:
When reducing cognitive residue is a priority, longer transitions (60s) may be beneficial. A nature scene is a good option for engaging intermediate content that helps shift user focus.
9/
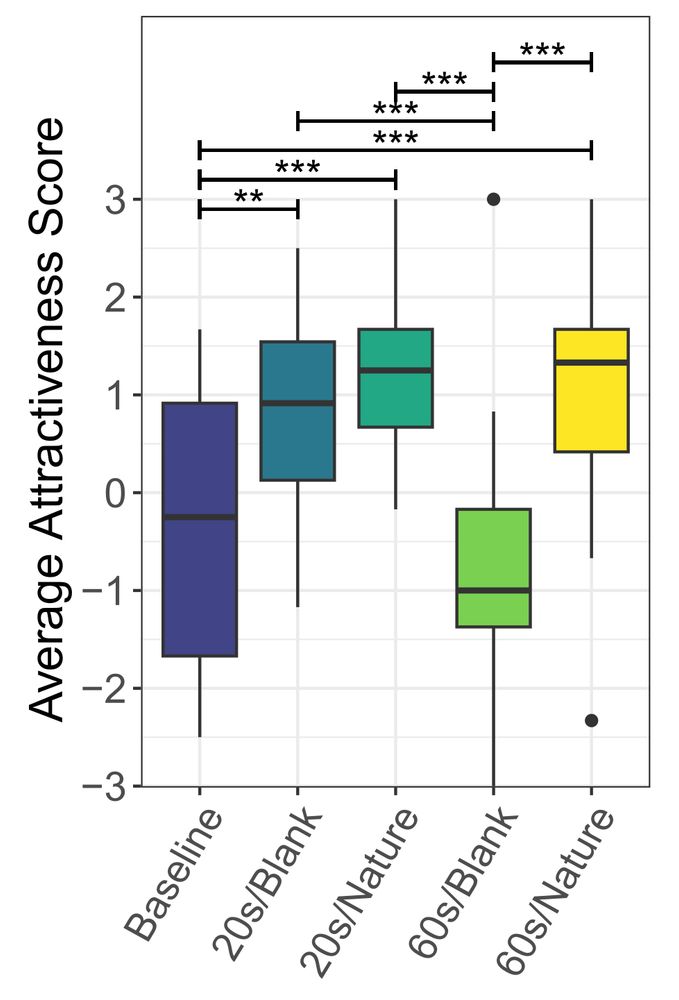
Box plot depicting the subjective questionnaire results for the Attractiveness sub-scale of the User Experience Questionnaire.
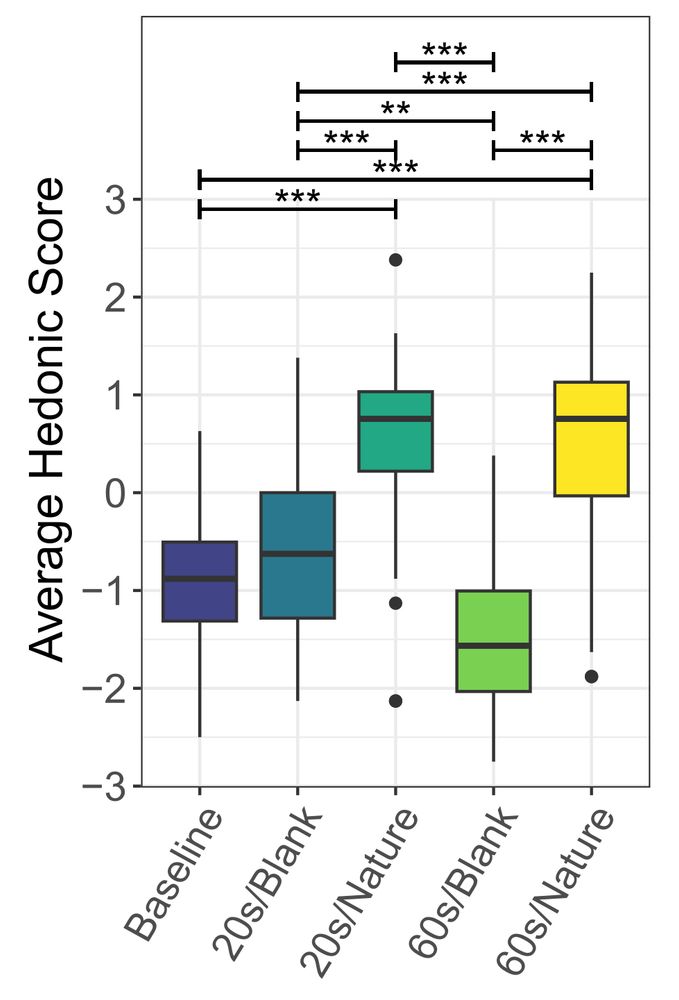
Box plot depicting the subjective questionnaire results for the Hedonic sub-scale of the User Experience Questionnaire.
On subjective questionnaires, participants rated nature scene transitions higher in Attractiveness and Hedonic qualities, meaning they were perceived as more visually appealing and stimulating. This was true even for the 60s version, suggesting users tolerated them despite their longer duration.
8/
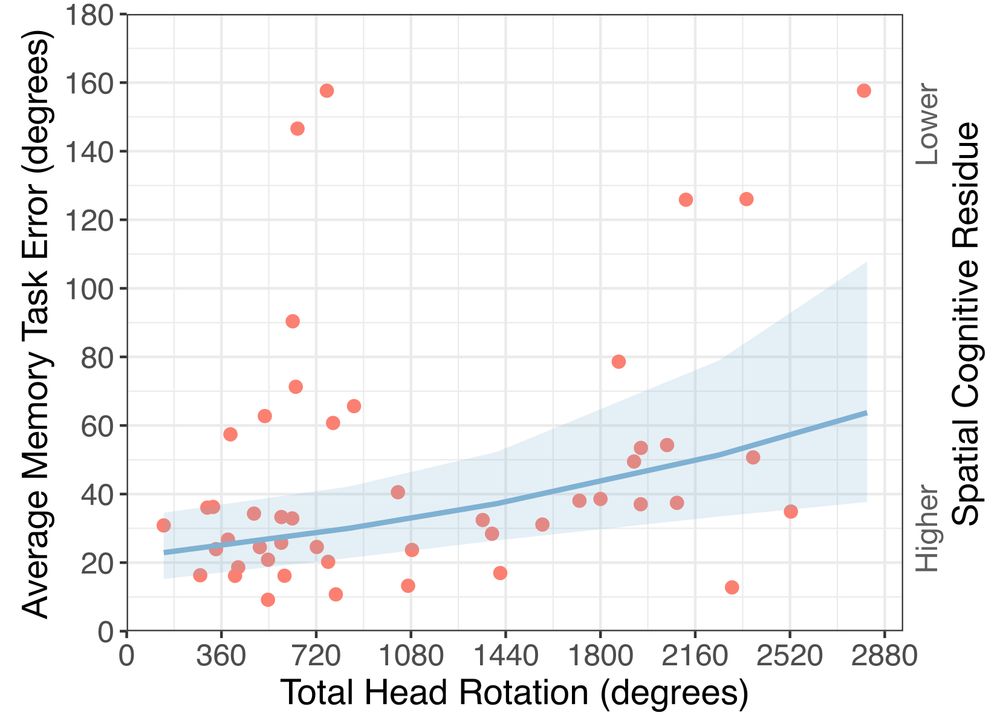
Scatterplot displaying the positive relationship between average angular Memory Task Error and Total Head Rotation for the Nature transitions. The blue line shows the estimated effects of the Head Rotation predictor for the Generalized Linear Mixed Model (GLMM) fitted to our data, with the shaded region representing the 95% confidence interval. The right axis provides a qualitative indication of the inverse relationship between the average angular Memory Task Error and spatial cognitive residue.
Key finding 2: We also analyzed users' motion and found that during the nature scene transitions, greater head rotation correlated with lower spatial residue, suggesting active exploration helps users disengage from their previous environment.
7/
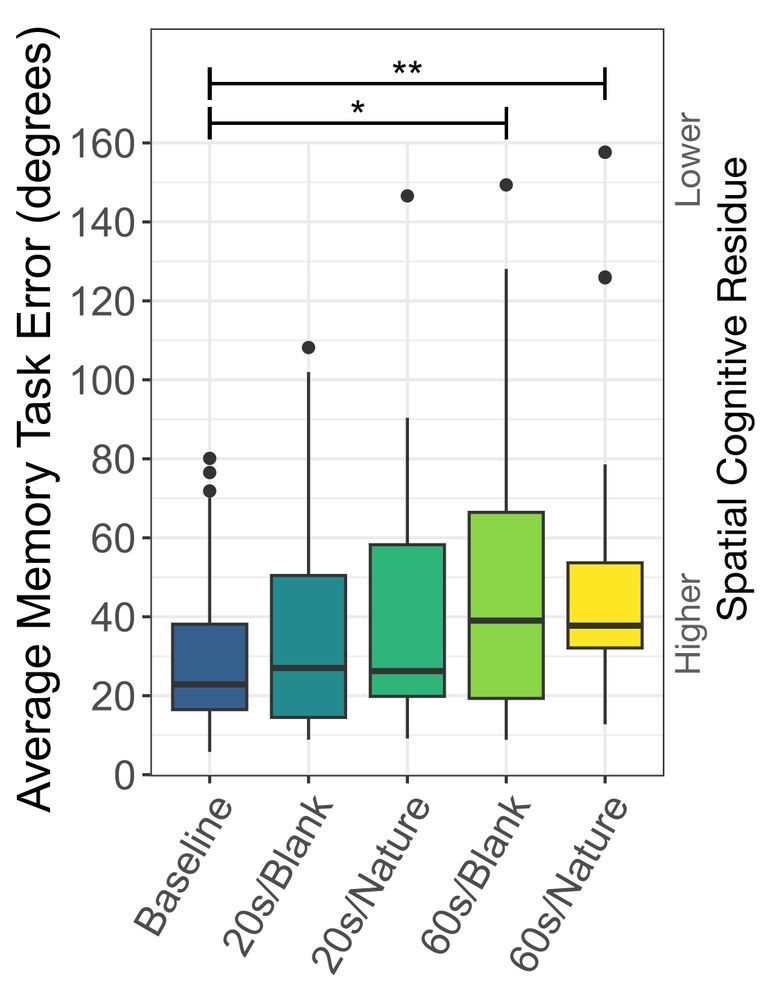
Box plot showing the average Memory Task Error (angular) for each experimental condition. Lower angular error values on the experimental spatial memory pointing task correspond to higher spatial cognitive residue as indicated by the qualitative scale on the right. As indicated by the horizontal whiskers, the 60s/Blank and the 60s/Nature transitions had significantly greater memory task error compared to the Baseline transition (instantaneous cut).
Key finding 1:⏳60s transitions reduced spatial cognitive residue more than an instant cut. Users recalled object locations from their previous environment less accurately, indicating a reduction in residual memory effects.
(here, we are shooting for less residue == more error)
6/
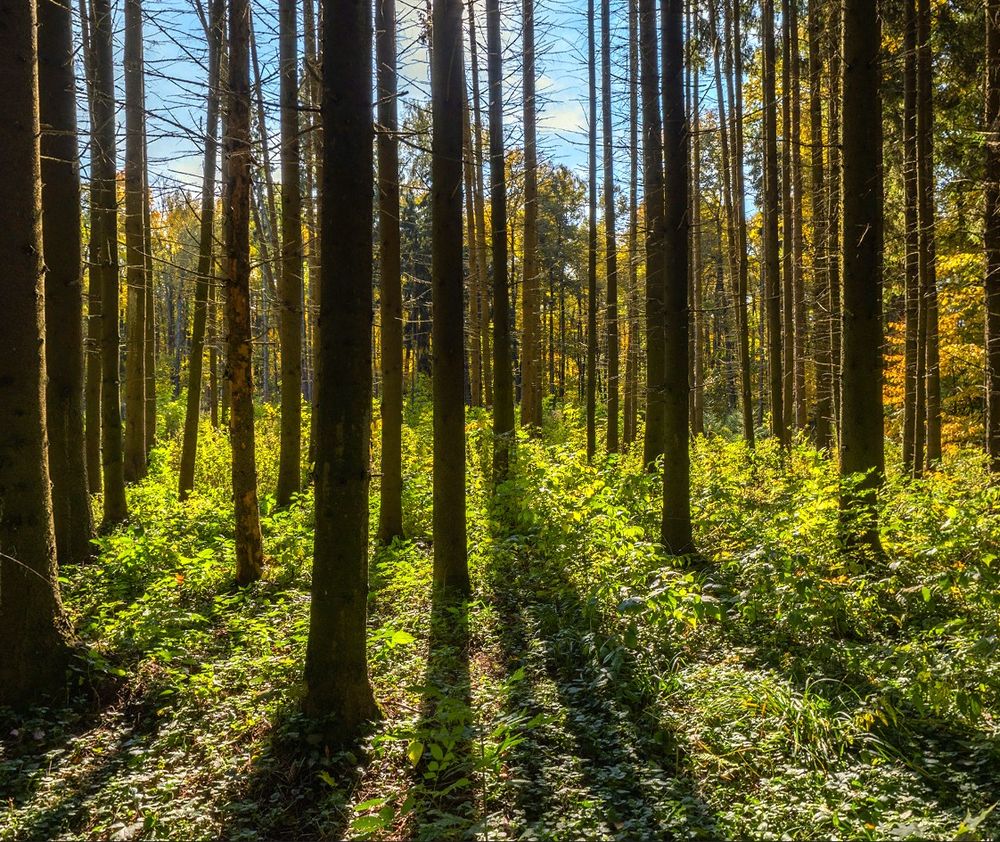

Screenshot from the nature scene transition, which featured a well-lit forest with trees roughly uniformly distributed around the user.
Our study (N=24) tested four transitions with two kinds of visual content and two durations (+ a baseline):
- Instantaneous cut (baseline)
- Fade-to-black (20s & 60s)
- Nature scene (20s & 60s)
5/
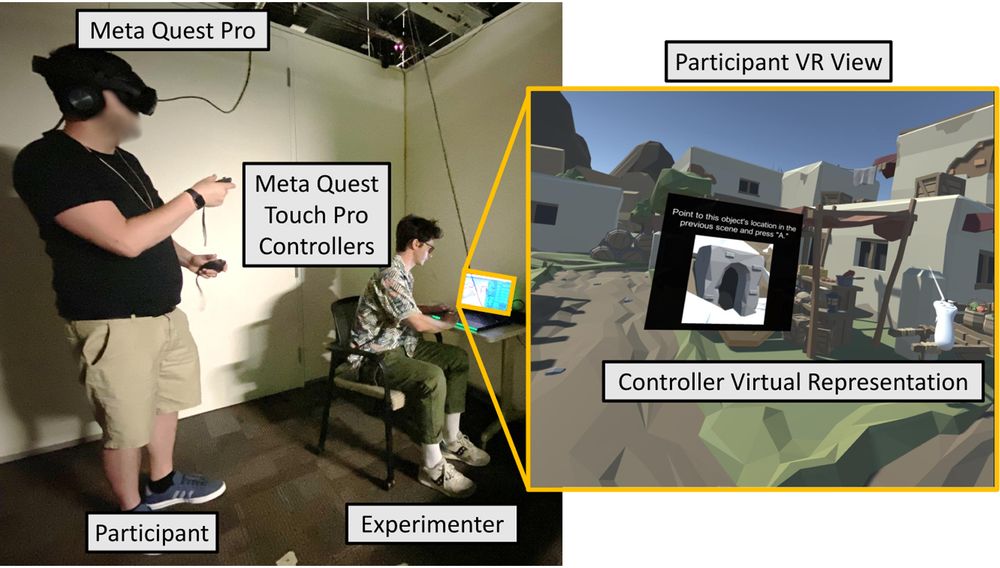
Annotated photo showing a participant in the experiment wearing the VR headset and holding the controller during the task. The experimenter was in the room with the participant and could see what the participant saw in VR. The inset shows the virtual environment from the participant’s view.

Up close view of a UI for a spatial recall task. The UI consists of a black plane with an image of an object that the participant saw in their preview environment and text telling them to point to that object relative to their current position.
We measured spatial memory recall to assess how much information from a previous VR environment stayed with users. After transitioning to a new environment, participants had to point to where they remembered objects from the previous env being (relative to their new orientation).
4/
🔍 In a future in which people are using XR devices for more purposes and for longer durations, they will regularly switch between tasks and environments. So, we wanted to see how cognitive residue might work in a spatial sense.
3/
When switching tasks, people can experience cognitive residue 🧠 where some cognitive resources like attention and memory remain devoted to the previous task even after moving on. This can lead to decreased performance on the following task because your mind is "stuck in the past."
2/
A couple months late here, but I thought I would share some of my recent research I presented at IEEE ISMAR exploring spatial cognitive residue ~the lingering memory of a virtual space~ and how different transitions between VR environments can help clear users' minds. 🚀
1/12
3D User Interfaces by Bowman et al. I think the structure of this book is quite coherent and holds up, i.e., it is easy to fill in more recent work to its taxonomy.
29.01.2025 13:28 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0why spend 30 minutes updating your CV when you can spend an entire afternoon writing code to automate the updating of your CV
30.12.2024 23:51 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Embodied Cognition and the Magical Future of Interaction Design. David Kirsh. dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/...
15.12.2024 03:24 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0- Musical Bodies, Musical Minds: Enactive Cognitive Science and the Meaning of Human Musicality
- The Entangled Brain: How Perception, Cognition, and Emotion Are Woven Together
nice archive! I grabbed a few:
- Plato and the Nerd: The Creative Partnership of Humans and Technology
- From Geometry to Behavior: An Introduction to Spatial Cognition
- Embodying Design: An Applied Science of Radical Embodied Cognition
I research AR/VR UI/UX, mostly studying cross-reality interactions and transitions for the near future where we spatially compute and collaborate in/through/with/across all kinds of devices and realities.
30.11.2024 01:14 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0hello bluesky. I am PhD Candidate at the Synthetic Reality Lab (SREAL) at the University of Central Florida --- though I am currently based in NYC and also working as a research intern with the JPMorganChase Global Technology Applied Research AR/VR group.
30.11.2024 01:14 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0