Rivers et al. (2026) found that both overt (typed) and covert (mentally generated) prequestions improved test performance, with no reliable differences between the two formats. This finding suggest that covert prequestioning is a time-efficient strategy to support comprehension.
28.01.2026 07:57 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Redirecting
Using a multiverse analysis, Weissgerber et al. aimed to replicate the study by Lehmann et al. (2016): they found no disfluency benefit, even not for learners with higher working memory capacity (i.e., no Disfluency x WM interaction effect). Article: doi.org/10.1016/j.li...
26.01.2026 07:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Redirecting
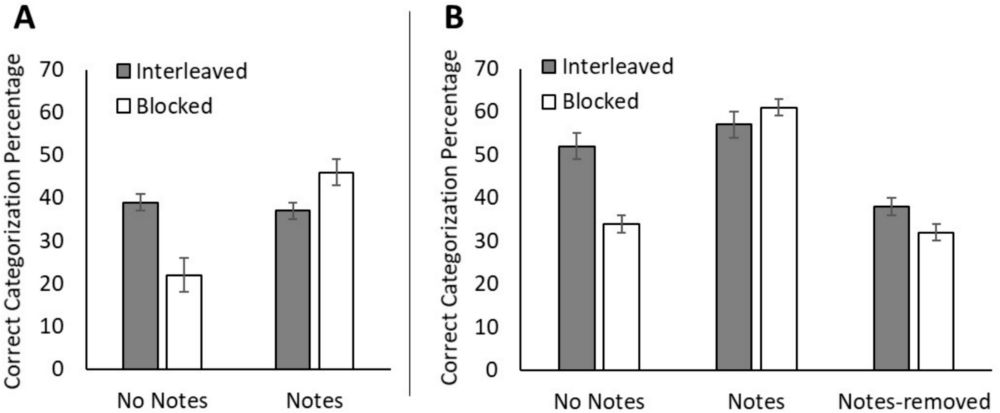
Interleaved practice helps conceptual understanding, but a study by Danzglock et al. (as part of our lasting learning DFG FOR 5254) shows it alone is ineffective with complex material. Combining interleaved practice with collaboration leads to learning gains.
🔐 Article: doi.org/10.1016/j.le...
25.01.2026 15:00 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
APA PsycNet
Schweppe et al. from DFG FOR 5254 show that students learn better from an expository text when they (unsuccessfully) attempt to answer questions beforehand, compared with reading learning objectives or just reading the text without a pre-instructional activity.
🧠 Article: doi.org/10.1037/xap0...
24.01.2026 17:32 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
07.01.2026 09:35 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Applying retrieval and distributed practices to enhance student learning and achievement in a university course | Advances in Physiology Education | American Physiological Society
Among the “desirable difficulty” (DD) strategies developed by cognitive scientists, retrieval practice and distributed practice are two of the most robust and advantageous. This study evaluated a three-component intervention to enhance student learning that consisted of instruction about the advantages of retrieval and distributed practices, encouragement of independent application of these methods, and the use of pop quizzes to facilitate retrieval and foster distributed studying. Student exam scores were compared in two sections of a university sports nutrition course that differed in only one experimentally relevant way: one received the three-component intervention (DD Strategy Group), whereas the other did not (Control Group). During the DD Strategy Group’s first class meeting, the instructor gave the students a 30-minute tutorial in which he introduced retrieval and distributed practices and then summarized the evidence demonstrating the learning advantages of each. The DD Strategy Group also completed 10 pop retrieval quizzes during the semester, each of which consisted of three to five short-answer questions and took roughly 10 min to complete. A multivariate ANOVA with follow up t tests revealed that the DD Strategy Group outscored the Control Group on course exam 1 (t45 = 2.50, P = 0.02, d = 0.8), exam 2 (t45 = 3.35, P < 0.001, d = 1.0), exam 3 (t45 = 4.38, P < 0.001, d = 1.3), and exam 4 (t45 = 4.33, P < 0.001, d = 1.3). In summary, the DD Strategy improved exam performance by nearly 16%, making it a practical and effective way to enhance student learning. NEW & NOTEWORTHY A three-component strategy that included educating students about the counterintuitive benefits of retrieval and distributed practices, encouraging independent application of these methods, and utilizing pop quizzes to facilitate retrieval and foster distributed studying habits resulted in significant increases in student exam performance in a university course.
Dobson (2025) showed that teaching students to use retrieval and distributed practice – plus adding pop quizzes – led to big gains in a university course. 🧠 The intervention improved exam scores by about 16%, proving “desirable difficulties” work. #EduSky
➡️ doi.org/10.1152/adva...
12.12.2025 12:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
New article:
Gonçalves et al. (2025) found that retrieval practice gives a small but reliable learning advantage over elaborative strategies overall (g = 0.14), but this benefit depends on conditions.
Check it out using the following open access link:
link.springer.com/content/pdf/...
05.12.2025 08:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
APA PsycNet
New study from our @learningfor5254.bsky.social members.
Pan et al. (2025) found that answering ChatGPT-generated prequestions before reading boosts later memory and comprehension of the text.
Check it out using the following open access link:
psycnet.apa.org/record/2026-...
03.12.2025 08:20 — 👍 0 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
APA PsycNet
New study:
Ingendahl & Undorf (2025) found that making immediate judgments of learning (JOLs) changes how people study, boosting memory for related word pairs but harming memory for unrelated ones.
Check it out using the following open access link:
psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?d...
23.11.2025 14:39 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
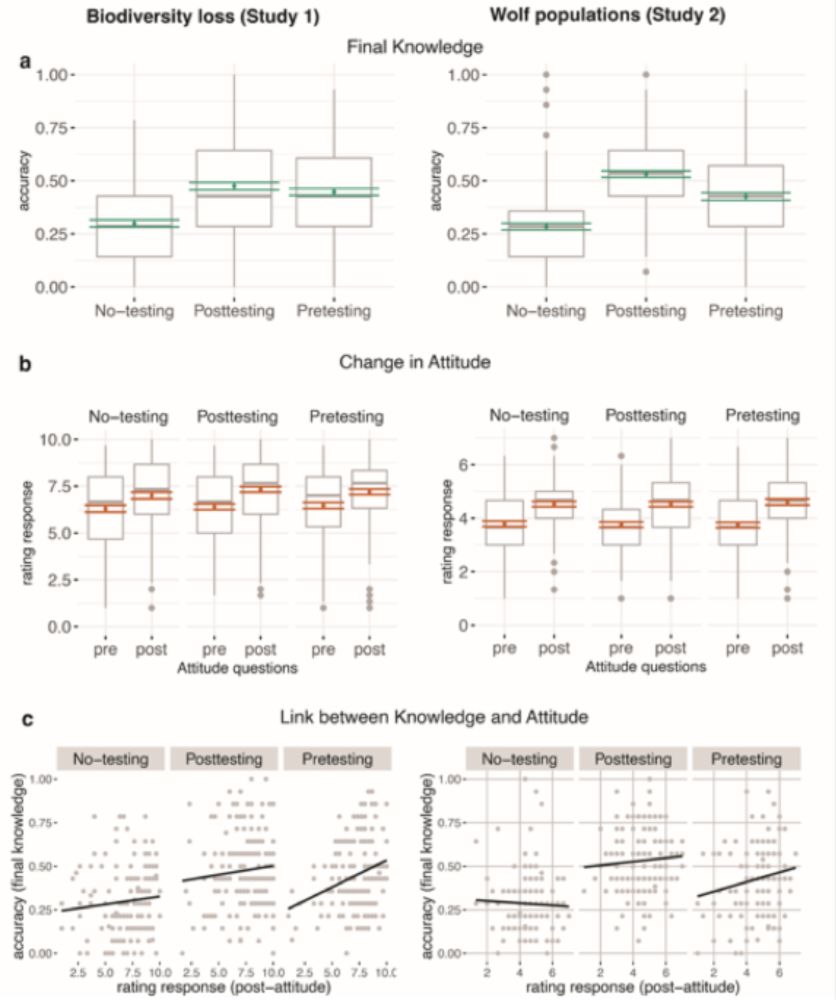
Practice testing enhances learning but not attitude change from persuasive texts - Scientific Reports
Scientific Reports - Practice testing enhances learning but not attitude change from persuasive texts
New study
Galeano Weber et al. (2025) found that practice testing—both pretesting (guessing before reading) and posttesting (retrieving after reading)—enhanced factual learning from persuasive texts 🧠 but did not increase attitude change.
Check it out:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
07.11.2025 18:50 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
LinkedIn
This link will take you to a page that’s not on LinkedIn
von Aufschnaiter et al. (2025) showed that inconsistent arrow representations in mechanics diagrams can confuse learners and hinder understanding of motion and force concepts.
www.researchgate.net/publication/...
05.11.2025 19:16 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Redirecting
Nemeth et al. (2025) from our @learningfor5254.bsky.social research group found that tailoring study sequences to individual confusion patterns did not outperform random interleaving, suggesting that adaptivity may not provide additional benefits. #EduSky #FOR5254
▶️ doi.org/10.1016/j.li...
30.10.2025 12:44 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Frequent Testing vs. Second-chance Testing: An Exploration | Proceedings of the 2025 ACM Conference on International Computing Education Research V.1
Herman et al. (2025) compared frequent testing with second-chance testing on learning. They found no difference in final exam performance but frequent testing led to better first attempts and students felt more stressed in the less frequent testing group. 📚
doi.org/10.1145/3702...
28.10.2025 06:56 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
LinkedIn
This link will take you to a page that’s not on LinkedIn
Fiorella, Capobianco, and Jaeger (2025) found that explaining or drawing boosts comprehension only when learners translate across formats but these benefits didn’t extend to transfer, suggesting that generative activities alone may not foster deep application without added support.
lnkd.in/e5mP_Dx2
25.10.2025 16:52 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

How does interest in a course interact with course learning?
The present study modeled how students' interest in a course of study changes and how those changes fit into their broader course experiences.The pres…
Fryer et al. (2025) found that postgraduate students’ initial and growing course interest strongly predicted post-course self-efficacy and domain interest, while higher prior knowledge was linked to lower initial course interest and less growth.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
24.10.2025 19:48 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
APA PsycNet
Laursen and Fiacconi (2025) demonstrated that perceptual learning can influence JOLs for new material, even when prior learning occurred 24 hours earlier. Fluency derived from previous experience can bias metacognitive evaluations, leading to overconfidence in memory. doi.org/10.1037/cep0...
16.10.2025 07:09 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Client Challenge
New study by @marinaklimovich.bsky.social & Tobias Richter from our @learningfor5254.bsky.social research group: Interleaved practice enhanced the acquisition of spelling rules in third graders and the combination with instructional guidance produced lasting transfer gains. #EduSky🔗 rdcu.be/eKh4Y
14.10.2025 10:36 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0

Üben im Mathematikunterricht – Konsolidierende Übungsformate und ihre lerntheoretische und empirische Fundierung - Unterrichtswissenschaft
For decades, in German-speaking areas, well-founded recommendations for practice formats in the mathematics classroom have been available, and instructional models of practice are also examined in empirical research on learning and instruction. While empirical studies often focus on consolidating factual knowledge and skills, suggestions typically adopt a broader view of goals for practice: Consolidation then refers to both skills and conceptual understanding, often in connection with each other. This article discusses the research available as well as the possible implications for practice in mathematics classrooms and for desirable further research on practicing.For the design of practice phases, it is first necessary to specify the goals (especially mathematical concepts and mathematical procedures and strategies) and then identify the associated psychological types of knowledge (factual knowledge, skills, and understanding) and the function of the practicing (securing, flexibilizing, or deepening). These determinations then allow for the selection and design of suitable practice formats, of which the following five types—each with their theoretical foundation, empirical evidence, and considerations for practical implementation—are presented: (1) Retrieval practice, (2) distributed practice (primarily for declarative factual knowledge or simple skills), (3) interleaved practice with the implicit possibility for comparisons (especially for easily confusable facts or skills) or with explicit comparison prompts (also for more complex types of knowledge, such as procedural flexibility or understanding), (4) elaborative practice (with a focus on understanding), and (5) combinatory practice as an “intelligent” integration of multiple practice goals. While the first three practice formats have been systematically researched, the last two are more commonly found under the umbrella term “productive practice” in theoretically justifiable but less extensively studied practical recommendations.
Leuders & Loibl (2025) argue that effective math practice depends on aligning instructional formats with learning goals—retrieval, distributed, interleaved, elaborative, and combinatory practice each serving to secure, flexiblize, or deepen knowledge.
Check it out:
link.springer.com/article/10.1...
11.10.2025 16:57 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Our member @heikeruss.bsky.social from our #DFG #LastingLearning research group @learningfor5254.bsky.social presented one of our recent studies “When Does Learning by Non-Interactive Teaching Work?" at the 𝗔𝗤𝗨𝗔_𝗱 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝗳𝗲𝗿𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲 at PH Karlsruhe
--> doi.org/10.1007/s106...
#EduSky
Übersetzung anzeigen
11.10.2025 16:56 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Die Unterstützung des Konsolidierens – eine zentrale, aber vernachlässigte Dimension von Unterrichtsqualität - Unterrichtswissenschaft
Supporting consolidation, understood as the strengthening of declarative knowledge and the automation of procedural knowledge, represents a central dimension of teaching quality. Despite its importance, research on teaching quality has largely overlooked this aspect. This article brings together perspectives from educational psychology and subject-specific pedagogy to examine the key mechanisms of consolidation and to clarify its role in disciplinary learning processes. The analysis focuses on two main functions of consolidation: the stabilization of declarative knowledge and the optimization of procedural knowledge. From a subject-specific pedagogical perspective, the article presents instructional designs and task formats that effectively support these functions in classroom practice.The article concludes with a comparative analysis of the contributions in this thematic section. From the perspective of educational psychology, the mechanisms of consolidation are well understood, but their implementation in school settings remains insufficiently studied. From the perspectives of mathematics, language arts, and physical education pedagogy, consolidation appears as a highly relevant aspect of teaching and learning, but it remains theoretically and empirically underdeveloped. Future work should attend more closely to aligning consolidation practices with specific learning content, addressing students’ prior knowledge, and managing the frequency and intensity of consolidation opportunities in instruction.
Keller et al. (2025) argue that supporting consolidation—strengthening declarative and automating procedural knowledge—is a key yet neglected dimension of teaching quality 🧩.
Check it out using the following open access link:
doi.org/10.1007/s420...
08.10.2025 08:38 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Look like me or act like me? Charlotte Vössing presented a study about key features of model observer similarity to support students' situational interest in emotional design at the #PAEPS2025 conference at @uni-jena.de in collaboration with our @learningfor5254.bsky.social @dfg.de research group. ✨
06.10.2025 14:08 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

At the #PAEPS2025 conference at @uni-jena.de @marinaklimovich.bsky.social from our research group on @learningfor5254.bsky.social presented 2 experiments on enhancing the acquisition of Japanese Hiragana through interleaved practice - showing lasting effects after 1 week. #EduSky @dgps.bsky.social
02.10.2025 13:09 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Research on Communication: Voice, Face, Dyslexia, Prosopagnosia, Thalamus, Multisensory | Chair of Cognitive and Clinical Neuroscience @TU Dresden | Vice-Dean Faculty of Psychology | More info on: https://tu-dresden.de/mn/psychologie/ifap/kknw?set_langua
Instructional specialist, former Spanish teacher, news junkie, Cuse fan, dabbler in CogSci, mom of two grown-ups; Teacher training isn't good enough — let's fix that
Educational Psychologist and Teacher.
K-12 instructional coach in search of ways to leave the world more playful than I found it. Would make an excellent podcast guest. #UDL
https://sites.google.com/cccsd.org/levelup
Finance/Accounting/Tech. Interested in cognitive and social psychology, neuroscience, and policy.
Jamaican 🇯🇲 | White Room Student | True Neutral
Not a bot | Not a follow farmer | I suck at posting so I lurk and like
Educational psychology | Learning sciences | Master's student at Yonsei 🇰🇷 | Interests: learning strategies, metacognition, and motivation | Bi 🏳️🌈 🏳️⚧️
Dad | Professor of applied sciences @AcademicaUoAS | Dubliner | PhD @KingsCollegeLon | Keats devotee | persecuted by an integer
https://www.carlhendrick.com/
PhD 👨🎓 | Research Associate @tuchemnitz | Integrating best practices of cognitive load measurement into multimedia learning research 💻 | Passion for soccer, politics, and Lego 🧱
Professor of Educational Psychology / Technology-Enhanced Instruction
The Society for Text and Discourse is an international society of researchers who investigate all aspects of discourse processing and text analysis.
Metascience, statistics, psychology, philosophy of science. Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands. Omnia probate. 🇪🇺
Facilitator, Educator, Author: Passionate about experiential, brain-based approaches to teaching, community building, reflection, counseling, social and emotional learning.
I make teaching and learning memorable. She/her, Ph.D., cognitive scientist, associate professor, author of Powerful Teaching and Smart Teaching Stronger Learning
Newsletter: retrievalpractice.org/subscribe
Follow me: linktr.ee/retrievelearn
Psychology: education and politics - focusing on motivation, emotions and civic education // PhD @univienna // Postdoc @TU Dortmund // http://elisabeth.graf-at.eu/
// (c) Foto: Ines Blatterer
Asst Prof of Psychology @ NUS | Cognitive scientist | Learning Sciences Laboratory | UCSD, UCLA alum | Likes/RT ≠ endorsements | he/him
Social & personality psychology, psychological assessment | the role of Need for Cognition and Authoritarianism in climate change and perception of politicians | love reading escpecially historical (crime) novels, cooking and eating | views my own
Das Leibniz-Institut für Psychology (ZPID) ist die zentrale, überregionale Infrastruktureinrichtung für die Psychologie in den deutschsprachigen Ländern. | The ZPID is the supra-regional research support facility for psycholgy in German-speaking countries.