Prakhar, in a recent thought-provoking paper and thread, boldly claimed that the learning-rate biases may be mere “statistical ghosts” of decaying learning rates
We took up the challenge and put this claim to the test. Here are our findings (w/ @romanececchi.bsky.social). 1/n
osf.io/preprints/ps...
07.12.2025 11:55 —
👍 28
🔁 8
💬 1
📌 1

Reference Point-Dependent Reinforcement Learning in Humans and Rats
Previous studies indicate that rewards and punishments in reinforcement learning are encoded in a relative manner. Reference point-dependence, a valuation bias shared by eminent adaptation level and p...
🚨 New study alert! 🚨
Ever wondered if rats and humans learn in the same way? 🐭🧑🔬
We tested this — and the answer is yes, at least when it comes to how we value rewards in context.
(with @shaunaparkes.bsky.social Lachlan Ferguson, Magdalena Soukupova)
🧵Thread 👇
1/
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
14.04.2025 08:48 —
👍 35
🔁 18
💬 1
📌 1
Honest people don’t lie. Or do they? Liars aren’t honest. Or are they?
One puzzling conundrum in contemporary politics is that politicians who seem to be estranged from facts and evidence are nonetheless considered honest by their followers.
1/n
10.04.2025 10:47 —
👍 250
🔁 91
💬 14
📌 35
OSF
Again, a big thank you to @ranimo.bsky.social and Ray Dolan for guiding this work!
In the full paper, we go in depth into these results, and propose several mechanisms of how some of these biases can emerge, escalate and progressively bias our beliefs.
osf.io/preprints/psya…
13/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 2
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0
However, you may still under-correct these news, perceive neutral sources as biased in favor of vaccines, and, when receiving factual information, revise your opinion of the source rather than your vaccine beliefs. This will make you more vaccine-skeptical over time!
12/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 2
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
So what does this mean in the real world? Imagine you frequently read anti-vax news. You know it’s biased. You think you’re reading critically.
11/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0

We found that biases systematically distorts beliefs, even when:
✔️Biases are non-ideological, simple and additive
✔️Participants are highly motivated to learn
✔️They have clear chances to detect/correct biases
Bias silently takes hold—even when we're trying to resist it!
10/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 1
🔁 1
💬 1
📌 0
3️⃣Third finding: People care for learning about the sources over getting money
Participants directed too many cognitive resources to learn how sources are biased, but this hurt their ability to make good bandit choices. Sometimes attempts to correct for biases may backfire!
9/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 2
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
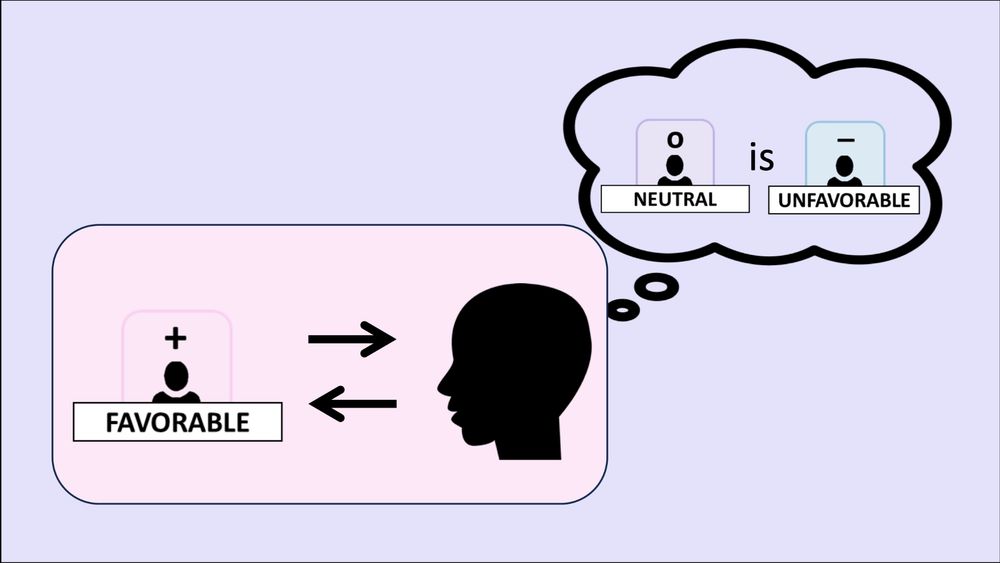
2️⃣Second finding: people misperceive neutral sources as being biased.
After interacting with a biased source (e.g., favorable), a neutral source was perceived as biased in the opposite direction (e.g., unfavorable). And this only emerged after the ground truth was withheld.
8/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
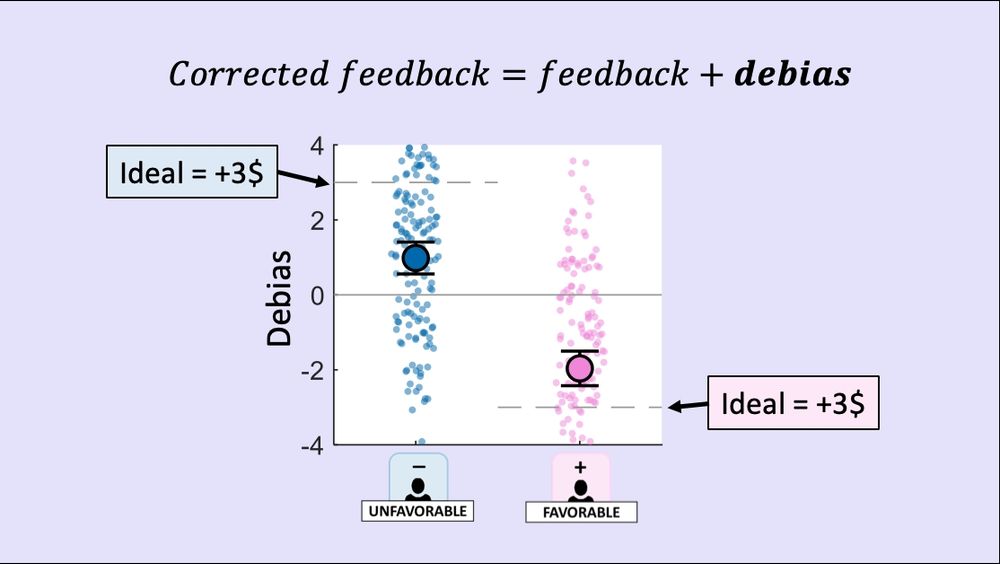
So, what did we find?
1️⃣First big finding: People don't fully correct for bias.
Even when they’ve had ample opportunity to learn that a source is biased, they still under-debiased. Participants became biased in the same directions as the sources that informed them!
7/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
In phase 2, these feedback sources can be treated like our "biased weight scale".
By adding/subtracting 3£ to estimates of unfavorable/favorable sources respectively one can fully correct for their reports and learn the true value of paintings!
6/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
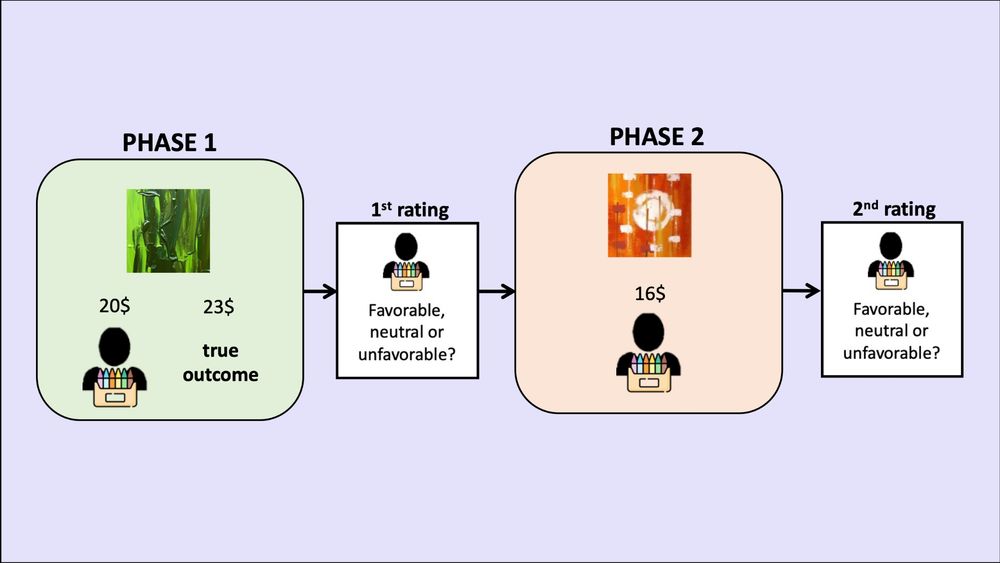
The task had two phases:
🟢Phase 1: true outcomes and source feedback were shown, so that could learn about source biases.
🟠Phase 2: only source feedback was shown (no true outcomes), so they had to infer the values of paintings.
We also asked them to classify the bias of each source.
5/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
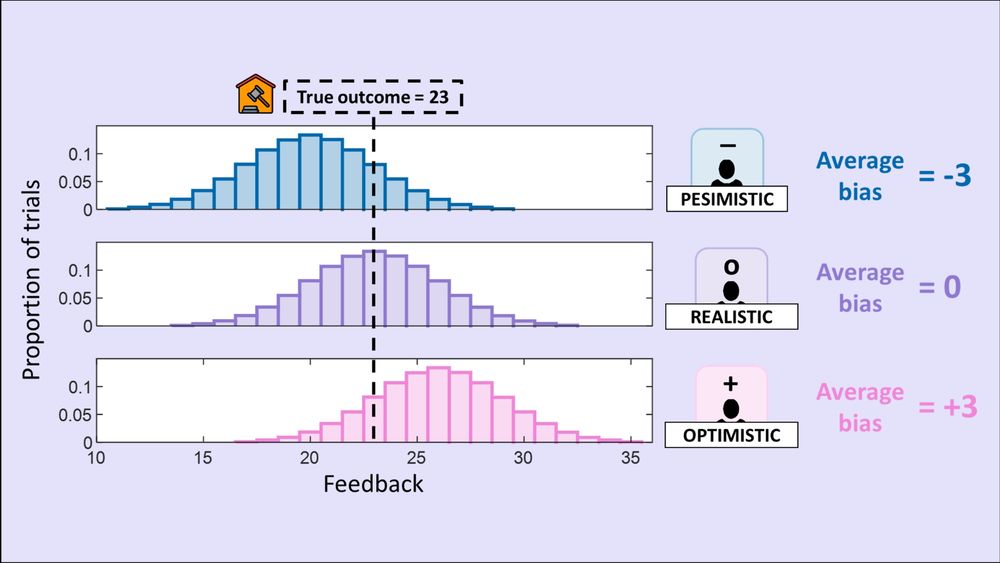
Instead, they relied on external sources that estimated the selling price of selected paintings. But these sources could give biased estimates:
➕Favorable sources overestimated true selling prices by ~3$.
⚫Neutral sources (unbiased) ➖Unfavorable sources underestimated by ~3$
5/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
We tested this using a multi-armed bandit reinforcement learning game where participants played art dealers selling painting copies (=bandits).🖼️ Paintings varied in price.
The goal: to choose more expensive paintings.
The challenge: they didn’t get to see the TRUE prices
4/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 1
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
Even more interesting, bias is theoretically correctable!
Imagine a scale that always adds 5kg. If the scale reads 75kg, you can infer your true weight is 70 kg. So, in principle, if we know an info-source is biased, we should be able to adjust for it. Right?
Not quite…
3/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 1
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
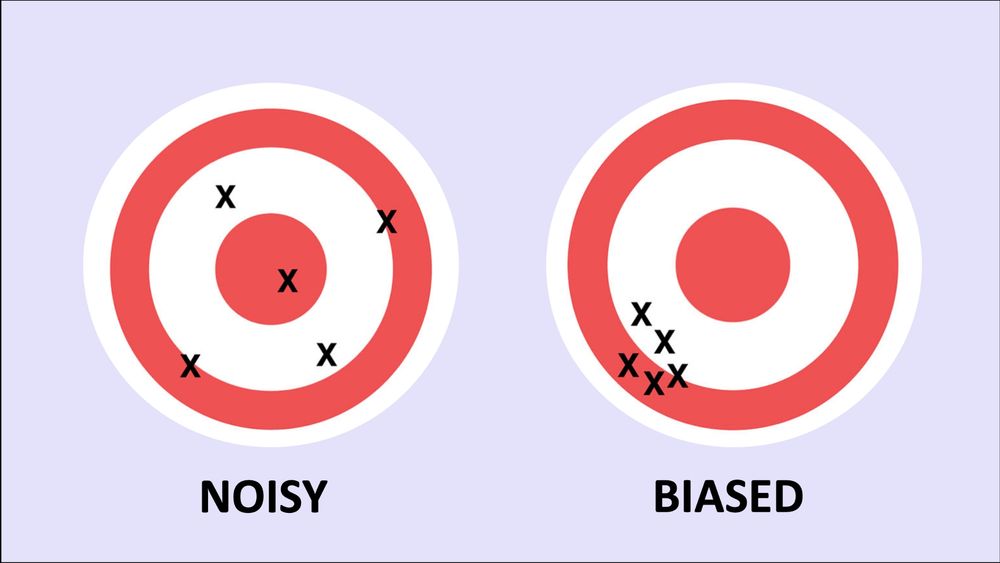
First, bias is not noise.
•Noise is like a coin flip—random and directionless.
•Bias is systematic—it consistently skews things in a certain direction.
And here's the kicker: while noise cancels out over time, bias can accumulate. 2/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 0
🔁 0
💬 1
📌 0
OSF
🚨 New preprint alert! 🚨
w/ @ranimo.bsky.social 📝 osf.io/preprints/psya…
From partisan news to algorithmically curated content, we constantly receive biased misinformation. With biased input, can our beliefs be accurate?
Turns out, biased misinformation distorts our beliefs! 👇🧵 1/13
07.04.2025 16:54 —
👍 5
🔁 5
💬 1
📌 1
When populist regimes target scientific institutions - as is happening in the US today - it is not because their core constituency is anti-science but exactly because even they respect the authority of science.
Science is a dangerous counter-power for the populist leaders.
(2/4)
16.03.2025 11:36 —
👍 25
🔁 6
💬 1
📌 0
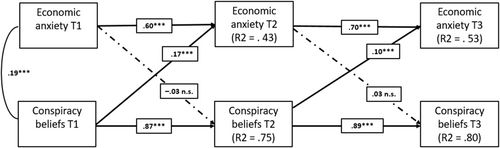
We know that economic anxiety & conspiracy beliefs are related. Often this is used to argue that it is key to fix economic conditions to avoid widespread conspiracy beliefs.
But a new study shows that causality runs the other way. The conspiracy beliefs drive the anxiety: doi.org/10.1111/pops...
13.03.2025 10:21 —
👍 326
🔁 107
💬 13
📌 17

Last year, we published a paper showing that AI models can "debunk" conspiracy theories via personalized conversations. That paper raised a major question: WHY are the human<>AI convos so effective? In a new working paper, we have some answers.
TLDR: facts
osf.io/preprints/ps...
18.02.2025 16:30 —
👍 317
🔁 105
💬 19
📌 30










