Welcome to visit our lab’s 1st #AACR poster! STHD: ML/AI method for sub-cellular cell typing for spatial transcriptomics (eg. 2um spots in VisiumHD) by integrating scRNA reference. (Section45 Board27) #AACR2025 Recruiting-ML/AI for Omics at Duke!
28.04.2025 14:18 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Join
Yi Zhang’s computational biology lab at Duke University (2024)
We are recruiting postdocs and students! Interested in computational biology, machine learning, bioinformatics, cancer genomics, single-cell multi-omics, spatial transcriptomics, human genetics, and immunology? - Welcome to join us! yi-zhang-compbio-lab.github.io/join/ 10/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Our first lab preprint is impossible without the collaborative work with our amazing intern student Silas Chuhanwen Sun, and support from our Duke Departments of Neurosurgery and Biostatistics&Bioinformatics, Brain Tumor Center, and Brain Tumor Omics Program. 9/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
STHD is scalable to millions of spots now common in high-resolution spatial omics; the algorithm design also works for other high-resolution, high gene-coverage spatial transcriptomics platforms - under development 8/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
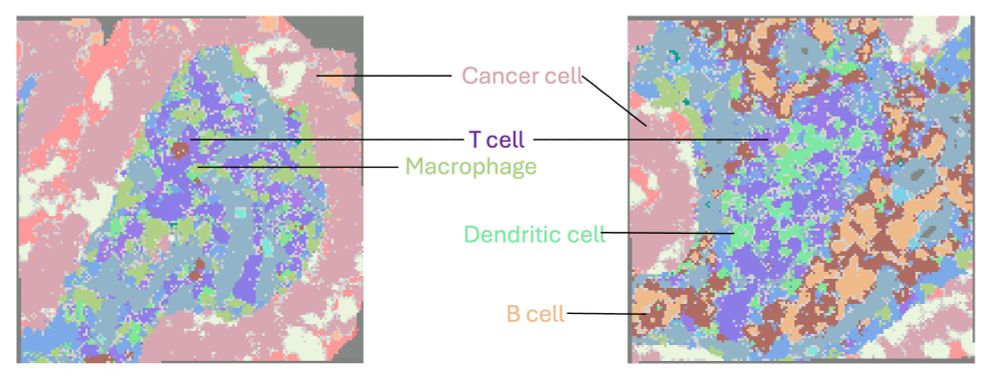
- Locally: identification of multi-cellular neighborhoods and cell-cell interactions, where gene expression mediating cell-cell communications are further revealed. E.g. Various immune hubs enriching different T-myeloid interactions; TLS structure seen in other tumor samples. 7/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
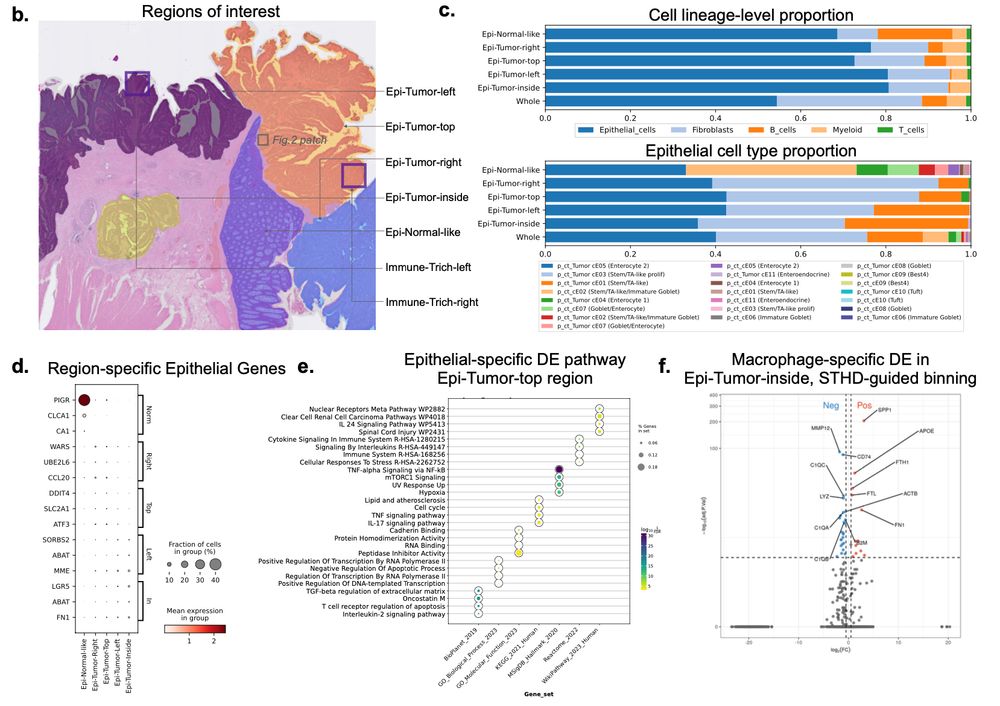
The STHD cell labels enable many analyses- globally: segmentation of tissue structures and detection of cell type-specific differential genes/pathways. e.g. The inside tumor nodule expresses higher epithelial-specific stem genes, and higher macrophage-specific SPP1+ state. 6/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
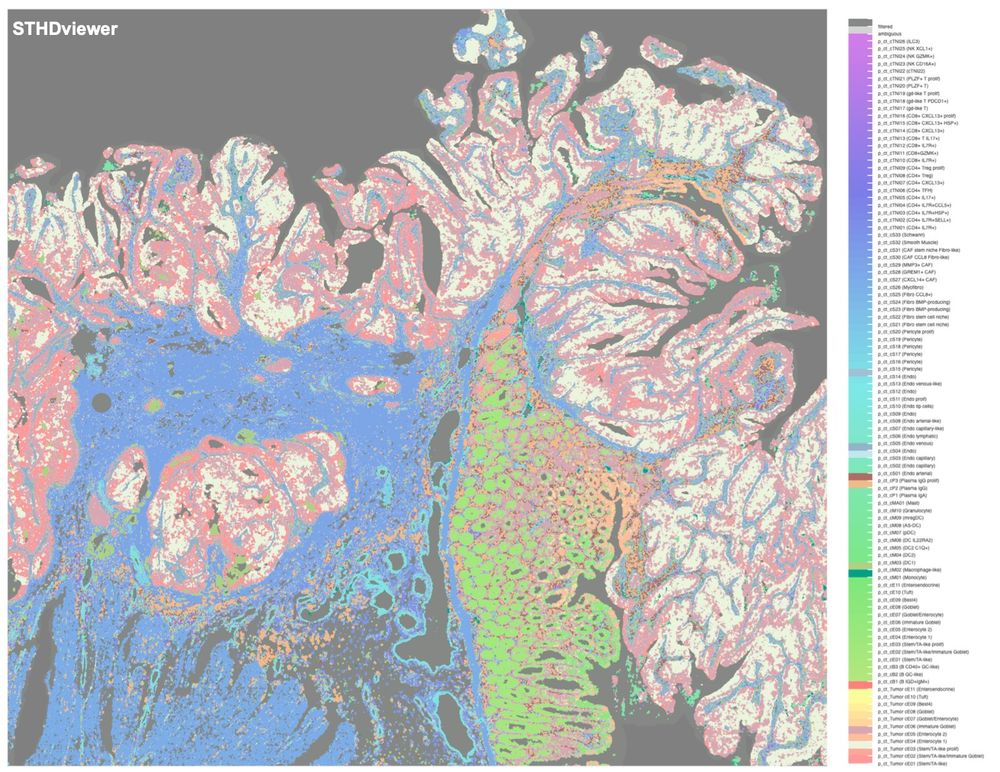
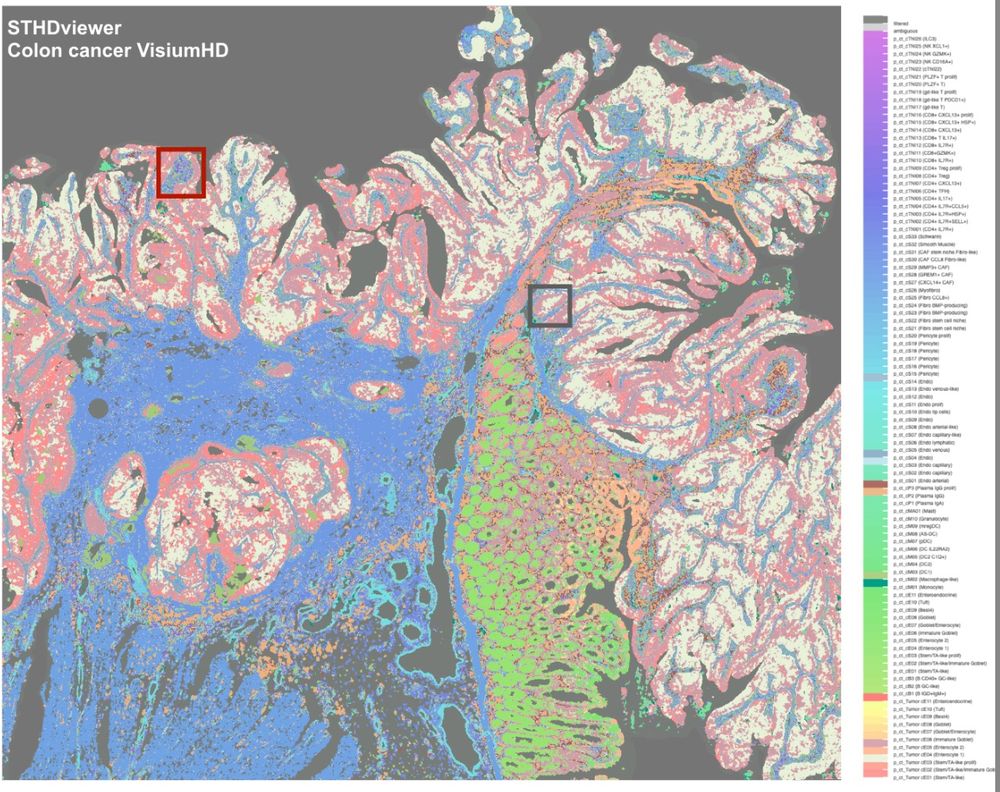
STHD enables scalable spatial inference and interactive exploration of cellular niches and immune hubs, facilitating genome-wide and cell type-specific spatial comparisons. One example full-size colon cancer VisiumHD generated by STHDviewer is at yi-zhang-compbio-lab.github.io/STHDviewer_c.... 5/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
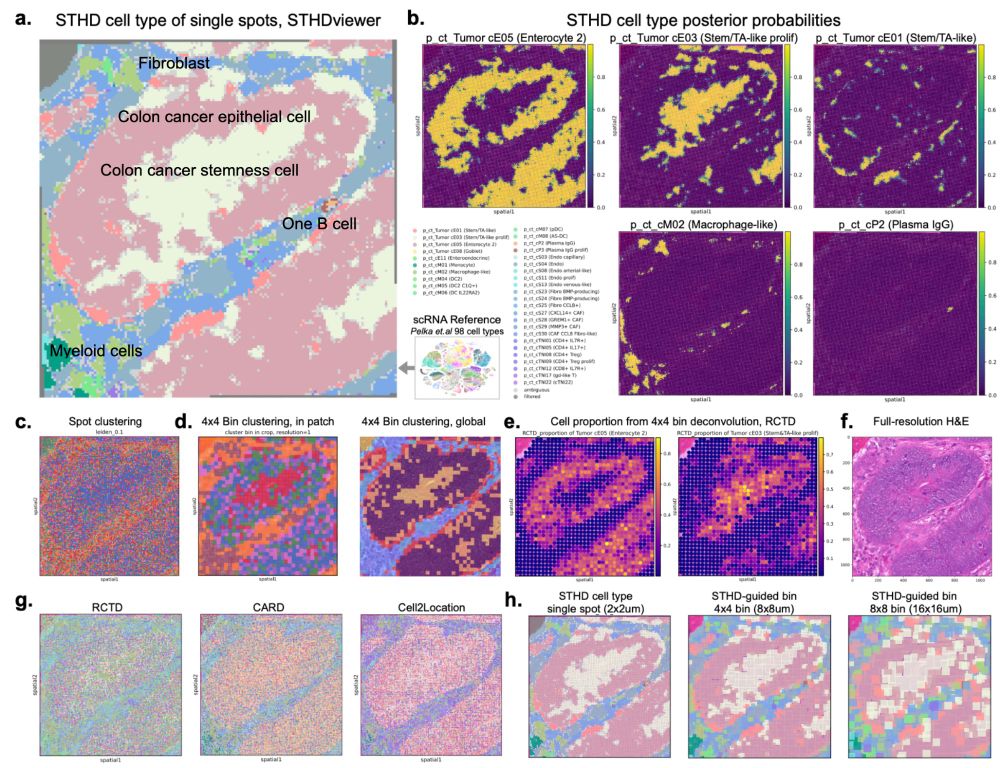
We show that STHD accurately infers cell type identities at subcellular level and guides cell type-specific binning, achieving high performance in benchmarks and preserving cell type-specific expression. Below is a small "tumor bagel" patch (~0.25%) from one colon cancer VisiumHD 4/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
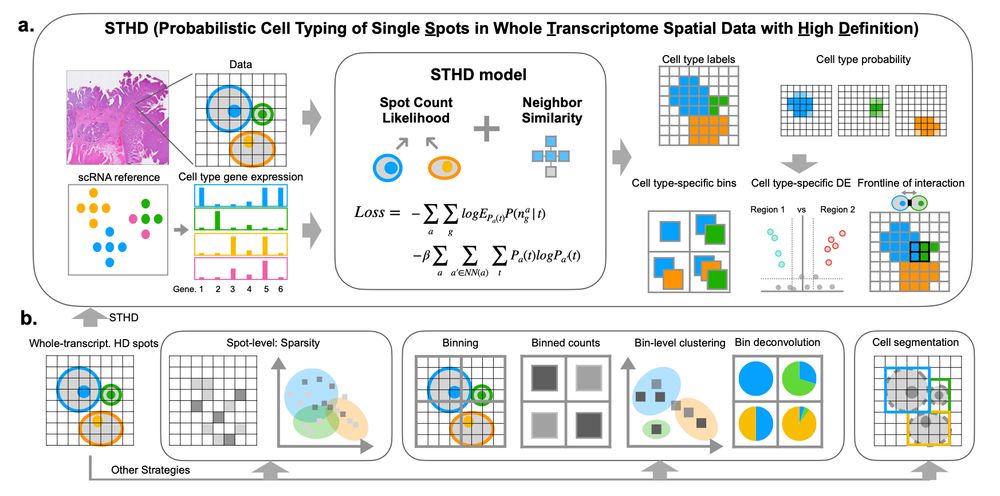
In details, STHD uses machine learning to model high-resolution spots with neighbor regularization, where the loss function addresses sparsity by modeling count statistics, incorporating neighbor similarities, and leveraging reference single-cell RNA-seq data. 3/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

GitHub - yi-zhang/STHD: STHD: probabilistic cell typing of Single spots in whole Transcriptome spatial data with High Definition
STHD: probabilistic cell typing of Single spots in whole Transcriptome spatial data with High Definition - yi-zhang/STHD
Current binning approaches create cell mixtures that complicate deconvolution. Instead, STHD uses ML/AI to achieve high-resolution cell typing and to discover cell type-specific neighborhoods and differential genes/pathways. STHD pipeline is available at github.com/yi-zhang/STHD/ 2/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

STHD: probabilistic cell typing of single Spots in whole Transcriptome spatial data with High Definition
Recent spatial transcriptomics (ST) technologies have enabled single- and sub-cellular resolution profiling of gene expression across the whole transcriptome. However, the transition to high-definition ST significantly increased data sparsity and dimensionality, posing computational challenges in identifying cell types, deciphering neighborhood structure, and detecting differential expression - all are crucial steps to study normal and disease ST samples. Here we present STHD, a novel machine learning method for probabilistic cell typing of single spots in whole-transcriptome, high-resolution ST data. Unlike the current binning-aggregation-deconvolution strategy, STHD directly models gene expression at single-spot level to infer cell type identities without cell segmentation or spot aggregation. STHD addresses sparsity by modeling count statistics, incorporating neighbor similarities, and leveraging reference single-cell RNA-seq data. We show in VisiumHD data that STHD accurately predicts cell type identities at single-spot level, which achieves precise segmentation of both global tissue architecture and local multicellular neighborhoods. The high-resolution labels facilitate various downstream analyses, including cell type-stratified bin aggregation, spatial compositional comparisons, and cell type-specific differential expression analyses. Moreover, STHD labels further reveal frontlines of inter-cell type interactions at immune hubs in cancer samples. STHD is scalable and generalizable across diverse samples, tissues, and diseases, facilitating genome-wide analyses in various spatial organization contexts. Overall, computational modeling of individual spots with STHD facilitates discoveries in cellular interactions and molecular mechanisms in whole-genome spatial technologies with high resolution. STHD is available at <https://github.com/yi-zhang/STHD>. ### Competing Interest Statement The authors have declared no competing interest.
Analyzing high-resolution spatial transcriptomics like VisiumHD? Sharing STHD, a machine learning algorithm for cell type mapping of every high-resolution (2um for VisiumHD) spot by integrating scRNA reference (Updated preprint from Version1 June 2024) : www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1.... 1/
14.02.2025 21:42 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Single cell – ENCODEHomo sapiens clickable body map
Very excited to announce that the single cell/nuc. RNA/ATAC/multi-ome resource from ENCODE4 is now officially public. This includes raw data, processed data, annotations and pseudobulk products. Covers many human & mouse tissues. 1/
www.encodeproject.org/single-cell/...
07.01.2025 21:29 — 👍 288 🔁 86 💬 6 📌 0
Duke Single Cell Initiative (SCI) | Duke Molecular Physiology Institute | Duke Molecular Physiology Institute
Xenium image of healthy lung tissue, courtesy of Jamie Todd
Excited to host Dr. Luca Pinello today at Duke to share insights on computational methods for single-cell genomics and CRISPR genome editing. Duke Single Cell Initiative seminar series: dmpi.duke.edu/duke-single-...
18.12.2024 18:55 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Excited to be visiting Duke University to share insights on computational methods for single-cell genomics and CRISPR genome editing! Thank you for hosting me
@yi-zhang-compbio.bsky.social 🙏
18.12.2024 13:37 — 👍 8 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
Assistant Professor @pennmedicine.bsky.social and @childrensphila.bsky.social. My lab is focused on developing approaches to enhance CAR T cell fitness.
www.theweberlab.org
Assistant Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering at Caltech.
www.trevornolan.science
Associate Dean for data science, and Professor of Medicine and Human Genetics at the University of Chicago.
Professor @jhubiostat.bsky.social, data scientist
Multiomics • Spatial imaging • I-O • AI. Asso Prof #Medicine. PI @ImmunoTiil . Director #Bioinfo @UPMCHillmanCC. Co-Chair #COWG. Lab: http://tiilab.org
Assistant professor @ Duke University BME, guerilla knitter, pipettor of small volumes of liquid. Biologist masquerading as engineer, or the other way around.
Assistant Professor @YaleMed | tissue biology, computation, systems biology |
www.hattiechunglab.bio
Associate Professor @mdanderson.bsky.social | Single-Cell Spatial Omics, Computational Biology, Genomics, Immunology, Data Science | Advancing Precision & Predictive Oncology
Assistant Professor in Biostatistics, MD Anderson Cancer Center
Computational methods for epigenetic, CRISPR genome editing and single-cell genomics. Associate Professor at MGH / Harvard Medical School. http://pinellolab.org
Professor of Biostatistics and Statistics, Harvard U, Genomics, ML, Health
Human genomicist, Assoc Prof @UVA. Deconvolving complex cardiovascular diseases using systems genetics and single-cell omics.
Professor of Biostatistics & Digital Pathology @UPenn | Statistical Genomics | Single-Cell and Spatial Omics | Computational Pathology
Genomics, AI, sequence-to-function models, mechanisms of the cis-regulatory code. Investigator at the Stowers Institute.
RS @Google | Asst Prof @UCLA | PhD @MIT | BS @PKU
#ML, #AI, #health, #medicine
shendure lab |. krishna.gs.washington.edu
Computational Cancer Biology azizilab.com
Irving Associate Professor @Columbia
#compbio #ml #genomics #singlecell #cancerimmunology
Asst prof at Duke University. Co-founder at LayerHealth.
ML and NLP for healthcare.
PhD MIT, BS/MS Stanford. She/her.