There’s a lot more detail in the full paper, and I would love to hear your thoughts and feedback on it!
Check out the preprint here: arxiv.org/pdf/2506.10150
@aakriti1kumar.bsky.social
@aakriti1kumar.bsky.social
There’s a lot more detail in the full paper, and I would love to hear your thoughts and feedback on it!
Check out the preprint here: arxiv.org/pdf/2506.10150
Huge thanks to my amazing collaborators: Fai Poungpeth, @diyiyang.bsky.social, Erina Farrell, @brucelambert.bsky.social, and @mattgroh.bsky.social 🙌
17.06.2025 15:13 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0LLMs, when benchmarked against reliable expert judgments, can be reliable tools for overseeing emotionally sensitive AI applications.
Our results show we can use LLMs-as-judge to monitor LLMs-as-companion!
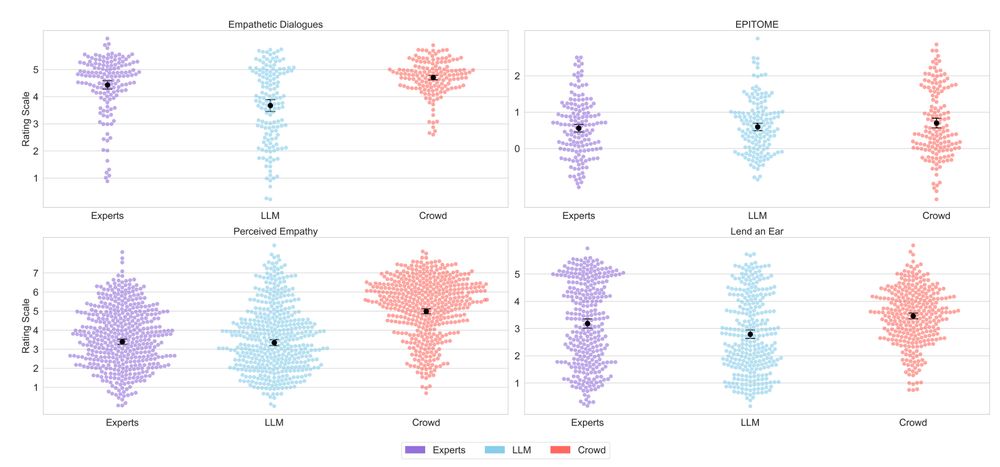
For example, in one of the conversations in our dataset, a response that an expert saw as "dismissing” the speaker’s emotions, a crowdworker interpreted as "validating" their emotions instead!
17.06.2025 15:13 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0These misjudgments from crowdworkers have huge implications for AI training and deployment❌
If we use flawed evaluations to train and monitor "empathic" AI, we risk creating systems that propagate a broken standard of what good communication looks like.
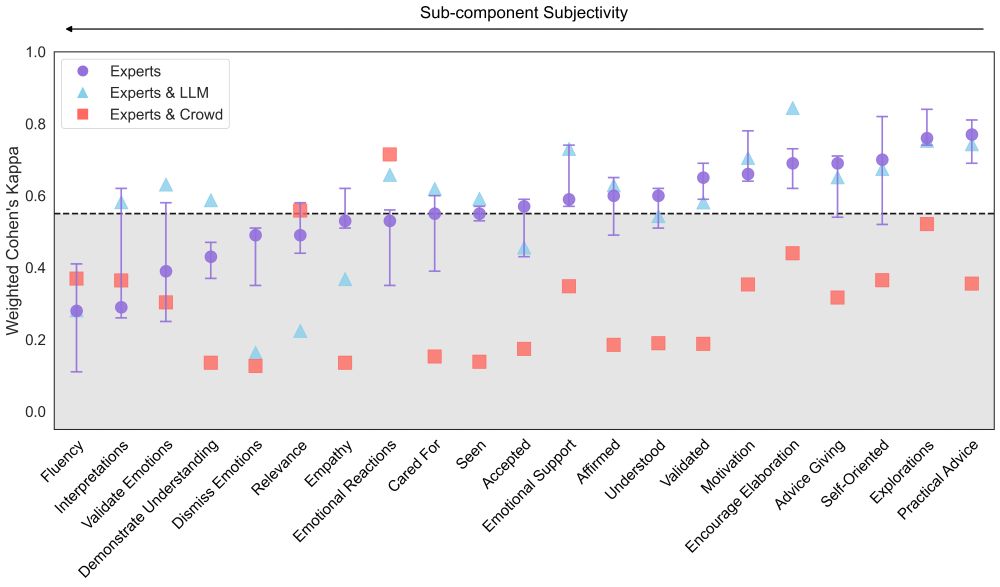
So why the gap between experts/LLMs and crowds?
Crowdworkers often
- have limited attention
- rely on heuristics like “it’s the thought that counts”
- focusing on intentions rather than actual wording
show systematic rating inflation due to social desirability bias
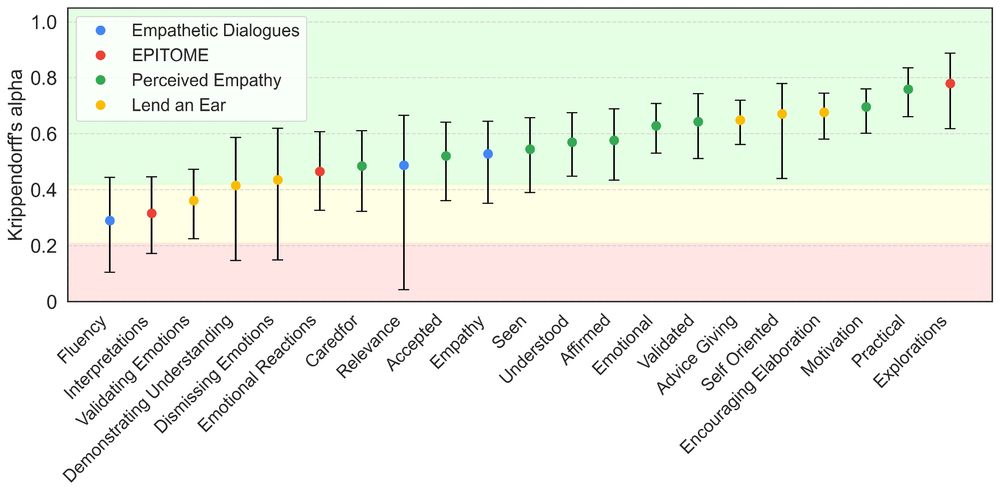
And when experts disagree, LLMs struggle to find a consistent signal too.
Here’s how expert agreement (Krippendorff's alpha) varied across empathy sub-components:
But here’s the catch: LLMs are reliable when experts are reliable.
The reliability of expert judgments depends on the clarity of the construct. For nuanced, subjective components of empathic communication, experts often disagree.
We analyzed thousands of annotations from LLMs, crowdworkers, and experts on 200 real-world conversations
And specifically looked at 21 sub-components of empathic communication from 4 evaluative frameworks
The result? LLMs consistently matched expert judgments better than crowdworkers did! 🔥

How do we reliably judge if AI companions are performing well on subjective, context-dependent, and deeply human tasks? 🤖
Excited to share the first paper from my postdoc (!!) investigating when LLMs are reliable judges - with empathic communication as a case study 🧐
🧵👇
Super cool opportunity to work with brilliant scientists and fantastic mentors @mattgroh.bsky.social and Dashun Wang 🌟🌟
Feel free to reach out!

Our paper: Decision-Point Guided Safe Policy Improvement
We show that a simple approach to learn safe RL policies can outperform most offline RL methods. (+theoretical guarantees!)
How? Just allow the state-actions that have been seen enough times! 🤯
arxiv.org/abs/2410.09361