Check out our latest preprint from @jnvmartinson.bsky.social and @leosong.bsky.social! 🌟🦠
We found that conjugative plasmids can actively eliminate recipient bacteria that resist plasmid acquisition. 🧵
12.02.2026 00:41 — 👍 58 🔁 36 💬 2 📌 1
Plasmids weaponize conjugation to eliminate non-permissive recipients https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.64898/2026.02.10.705089v1
11.02.2026 04:16 — 👍 29 🔁 10 💬 0 📌 2
Have you you tried Ansa? Their platform seems to tolerate more sequences than other platforms.
14.10.2025 15:28 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
You can kind of do that with otter.ai
14.08.2025 13:24 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Joff Silberg for 4. Carrie Massiello for 2/3.
20.06.2025 14:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
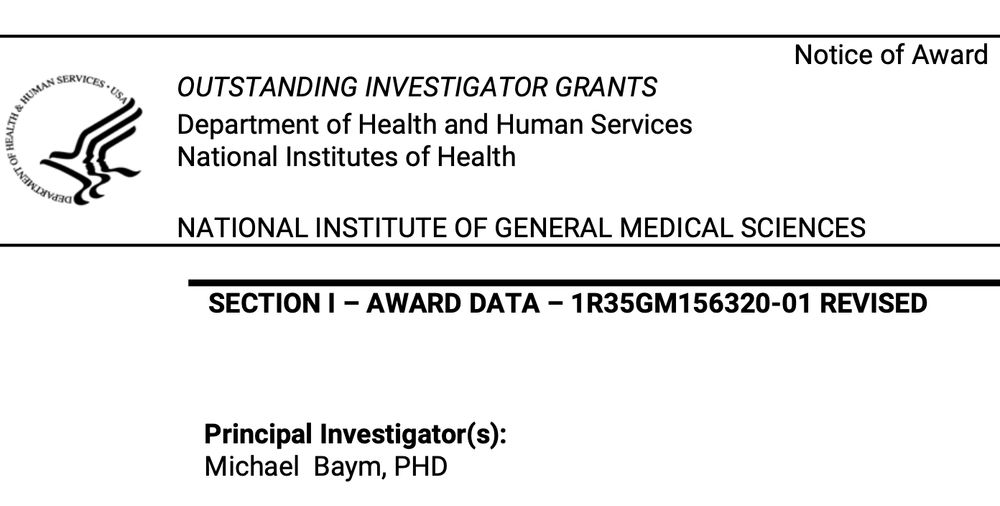
A screenshot of the termination notice showing "Outstanding Investigator Grants"

A screenshot of the termination notice with "This award is terminated effective the date of this award, due to unsafe antisemitic actions that suggest the institution lacks concern for the safety and wellbeing of Jewish students." highlighted
Yesterday, the NIH R35 “Outstanding Investigator” grant to fund scientists in my lab studying antibiotic resistance was terminated for reasons not related to the content of the science, or any actions taken by me or members of my lab
13.05.2025 23:37 — 👍 879 🔁 579 💬 144 📌 73
On the whole, RAM is an exciting tool for phage host-range studies. It could generate massive amounts of data for machine learning pipelines. Control of the barcode also means we can test many experimental conditions in parallel. Additionally, our preliminary data shows it works in lytic phages. 😉
06.05.2025 22:37 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Finally, we dug into one of the elements that determines P1 host range by characterizing hosts associated with P1s two unique tail fibers. RAM detected statistically significant enrichment of hosts infected by phages containing one tail fiber relative to the other tail fiber. 5/6
06.05.2025 22:37 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

The ease with which RAM can be used in real microbial communities is one of its biggest advantages as a host identification tool. When we added our modified P1 to wastewater influent, RAM identified known hosts in the Enterobacterales family and completely novel hosts in the Aeromonadales order. 4/6
06.05.2025 22:37 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

When added to the genome of P1 and P1 phagemids, RAM was able to barcode known P1 hosts in monoculture. We also added the constructs to a synthetic community of ESKAPE pathogens to assay host potential of many organisms at once and identified a novel host of P1 phagemids in Salmonella enterica. 3/6
06.05.2025 22:37 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Information storage across a microbial community using universal RNA barcoding - Nature Biotechnology
Barcoding microbial ribosomal RNA creates a recording of gene transfer events without requiring translation.
RAM is a ribozyme that can be coded into genetic constructs and which splices an RNA barcode onto host 16S rRNA. RT-qPCR can quantify the amount of barcoded 16S rRNA and amplicon sequencing the specific host species. See the recent paper in @natbiotech.nature.com for more info. 2/6
t.ly/AOiGt
06.05.2025 22:37 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Cross-order detection of bacteriophage transduction in communities using ribosomal RNA barcoding
Bacteriophages (phages) facilitate gene transfer and microbial evolution in all ecosystems and have applications as tools for engineering microbiomes and as antimicrobials. Historic efforts to map pha...
Very excited to share a manuscript at the heart of my PhD! We added an RNA-memory device (RAM) to phage P1 to identify transduction hosts in synthetic and wastewater microbial communities in high throughput. Also, I am on the post-doc market, so please reach out if interested! 1/6
t.ly/a8k9O
06.05.2025 22:37 — 👍 30 🔁 10 💬 2 📌 3

Information storage across a microbial community using universal RNA barcoding - Nature Biotechnology
Barcoding microbial ribosomal RNA creates a recording of gene transfer events without requiring translation.
We developed an RNA enzyme that adds barcodes to 16S rRNA to track bacterial DNA exchange in wastewater, identifying plasmid hosts via sequencing. This surpasses fluorescence methods by enabling multi-sample/plasmid analysis. Paper: go.nature.com/440gL5E. More technical details: shorturl.at/Y4KnA
23.03.2025 04:16 — 👍 22 🔁 9 💬 0 📌 0

Information storage across a microbial community using universal RNA barcoding - Nature Biotechnology
Barcoding microbial ribosomal RNA creates a recording of gene transfer events without requiring translation.
Fresh in @NatureBiotech! We developed a synthetic biology tool for tracking gene transfer in microbial communities and applied it to study plasmid hosts in a wastewater microbiome. Awesome collab with James Chappell & @joffsilberg.bsky.social and incredible students. www.nature.com/articles/s41...
18.03.2025 15:56 — 👍 74 🔁 32 💬 3 📌 3









