Just out📢 Our new paper published in @natmicrobiol.nature.com describes highly potent cross-neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against H5Nx influenza viruses. Close collaboration with Sara Andrews lab and Tongqing Zhou lab at the VRC. Link to the article: rdcu.be/eKV9T 1/2
14.10.2025 15:10 — 👍 17 🔁 8 💬 1 📌 0

How competition can drive allochronic divergence: a case study in the marine midge, Clunio marinus
Synchronizing mating to extrinsic environmental cycles can increase the chance of successful reproduction. However, the resulting temporally-assorted mating may precipitate speciation if coupled with ...
How can larval #competition for space, adult #reproductive #timing and the #tides interact to produce different timing strains, aka #chronotypes, of the marine insect #Clunio?
See our latest preprint with Alec Jacobsen & @gokhalecs.bsky.social
#evolution #ecology #chronobiology #circalunar #clock
17.09.2025 08:11 — 👍 7 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0

WE ARE HIRING!
Please spread widely!
#Postdoc in #Evolutionary #Genomics
-> www.mpg.de/25524526/
#Postdoc in #Molecular #Biology & #Cell #Signalling
-> www.mpg.de/25524509/
@mpi-evolbio.bsky.social @maxplanck.de
#ScienceJobs #EvoBio #MolBio #Ecology #Chronobiology #Marine #EntoSky #Biodiversity
09.10.2025 06:56 — 👍 9 🔁 12 💬 1 📌 1
Adaptive Dynamics of Quantitative Traits in a SteadilyChanging Environment https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.09.28.679017v1
29.09.2025 23:32 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0

Thrilled to share our paper that just came out in PNAS!
We asked a deceptively simple question: What happens when S. aureus adapts to vancomycin, a critical first-line antibiotic?
1/5
27.09.2025 17:32 — 👍 38 🔁 6 💬 3 📌 1
"Editor"
22.09.2025 17:24 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

What future does AI hold? With @paulbrainey.bsky.social, we hypothesize that human-AI coevolution is leading to the emergence of a new evolutionary unit of selection. Science fiction or looming fact? Read our paper and judge for yourself. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
11.09.2025 15:52 — 👍 18 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 2
About 10 years ago, we set up lots of experimental beetle populations, censused monthly. Expecting extinction, I said the workload would drop soon. But they all rescued themselves! 😱 So Vrinda & co kept counting. Many hundreds of thousands of beetles later, we have some neat outcomes. Enjoy!
11.09.2025 02:21 — 👍 26 🔁 5 💬 1 📌 0
All the best!
02.09.2025 09:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Congratulations Gaurav!
25.07.2025 12:55 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
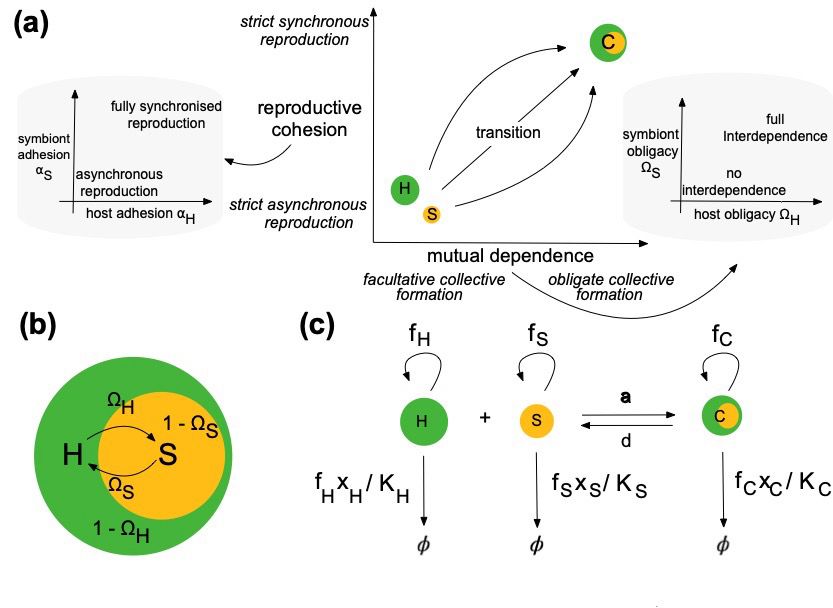
figure 1 from https://doi.org/10.1086/737588 describing (a) our conceptualisation of an evolutionary transition in individuality, (b) an interpretation of the traits that we consider in our mathematical model, and (c) a graphical representation of the population dynamics in the model.
Interested in host-symbiont interdependence, eukaryogenesis, and evolutionary transitions in individuality? my first paper just came out! With @gokhalecs.bsky.social and Pete Czuppon, we study when & how individuality emerges in a host-endosymbiont collective doi.org/10.1086/737588 a short thread🧵:
23.07.2025 14:21 — 👍 67 🔁 27 💬 5 📌 3
So happy to see this paper finally out! Ridiculous amount of work by Mrudula Sane and Shazia Parveen, showing that reversing baseline transition bias is good, as predicted by models from Lindi Wahl and co. Big thanks to @ncbsbangalore.bsky.social and DBT/WT India Alliance for support.
19.07.2025 14:25 — 👍 19 🔁 6 💬 1 📌 0

Figure from Allen (2025): Linear and nonlinear regression models for the benefits of helping behavior.
(A) A standard approach to quantifying the benefit b
and cost c of cooperation is to apply a linear regression model of the form w=w0−cp+bq+ϵ, where w is an individual’s offspring number, w0 is a constant term, p is the genetic propensity of the individual to cooperate, q is the genetic propensity of the individual’s partner to cooperate, and ϵ is a residual term. Benefit and cost are then determined by applying least-squares regression to population data for a single generation. Here, for simplicity, we show hypothetical data for w and q only (blue points), ignoring the effects of p. In this scenario, offspring number peaks at an intermediate level of help. Fitting a linear model w=w0+bq+ϵ (orange line) results in a “benefit” b that sheds little light on the nature of the cooperative trait. (B) Fitting a quadratic model w=w0+b0,1q+b0,2q2+ϵ (orange curve), as van Veelen’s framework allows for, yields a more informative characterization of cooperation in this scenario.
I wrote an Insight piece to accompany new work by Matthijs van Veelen on incorporating nonlinearity into Hamilton's rule.
elifesciences.org/articles/108...
TL;DR: The future of evolutionary theory is nonlinear, and our mathematical tools should reflect that.
15.07.2025 13:57 — 👍 17 🔁 3 💬 4 📌 0
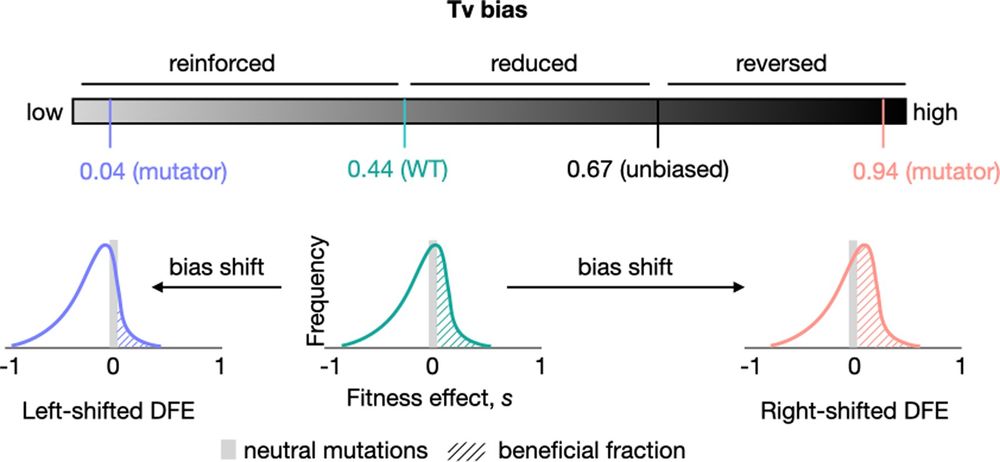
Schematic of the key prediction tested in this work. As the transversion (Tv) mutation bias of WT E. coli is shifted away from the ancestral bias, the resulting distribution of fitness effects (DFE) is predicted to change. Specifically, it should shift left with a bias reinforcement, with a lower fraction of beneficial mutations. In contrast, reversing the ancestral bias is predicted to cause right-shifted DFEs with higher proportions of beneficial mutations.
Mutations generate variation, critical for #evolution, but #MutationBias restricts the choice of mutation type. @deepaagashe.bsky.social &co use #Ecoli strains with different mutation biases to show that changing an old bias should yield more beneficial mutations @plosbiology.org 🧪 plos.io/46LjCRt
15.07.2025 14:11 — 👍 3 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0
Theoretical evolutionary ecologist. Fond of math, coffee, natural history, and metal music. Kokkonut and PhD student at Uni Mainz, Germany.
Past: BS-MS at IISER Pune, India. MS thesis at CES, IISc.
Webpage: https://thepandalorian.github.io
he/him
Group leader and professor at Kiel University, Germany.
Evolutionary biology, fungi, plant-microbe interactions.
Doctoral Researcher modeling protective symbiosis @mpi-evolbio.bsky.social
#evolutionary_theory | #epidemiology | #microbiology
We explore how evolution, ecology and biological clocks interact,
with a focus on lunar rhythms in development and reproduction
of the marine insect Clunio.
+ Genomics | Biodiversity | Behaviour | NeuroBio | MolBio | SciCom
bit.ly/KaiserLab
Studying therapy resistance through the lens of complex systems, ecology, and evolution.
Current Jake Scott postdoc @ Cleveland Clinic
Former Kevin Wood graduate student @ Michigan
Statistician, Computational Biologist, R | Bioconductor. Love stats and ML. https://www.huber.embl.de
Textbook: Modern Statistics for Modern Biology https://www.huber.embl.de/msmb/ (with @sherlockpholmes.bsky.social)
Scientist working on antibiotic resistance, evolution, and mobile genetic elements. Prof at U.Oxford and Fellow of All Souls College
Applied Mathematician, Professor @SwanseaUni. Interests: Mathematical Biology, Mathematical Oncology, All views my own
https://www.swansea.ac.uk/staff/g.g.powathil/
Computational biologist, data scientist, digital artist | he, him | http://clauswilke.com/ | Opinions are my own and do not represent UT Austin.
Mathematical biologist/applied mathematician at the University of Washington. Using math to understand cancer.
Senior Lecturer (≡ associate professor) in applied maths, investigating the evolution and ecology of cancer. Dad of two small kids. On sabbatical @isemevol.bsky.social 🇫🇷 (otherwise @citystgeorges.bsky.social 🇬🇧)
robjohnnoble.github.io
University of Montpellier - Santa Fe Institute. Working these days on intelligence in biological and artificial systems. Website https://mehochberg.wixsite.com/blog/academia
Professor, evolution of drug resistance, modeling, population genetics, coding, SF State University, mom, Dutch
Quantitative Evolutionary Microbiology
Ecology, evolution, systems biology, and biophysics of microbial communities
Assistant Professor, Rutgers University
https://qevomicrolab.org/
Professor of Theoretical Ecology, Kellogg Biological Station, Michigan State University
Lab studying molecular evolution of proteins and viruses. Affiliated with Fred Hutch & HHMI.
https://jbloomlab.org/
Rapid evolutionary dynamics in viruses, cancer and bacteria. Assistant professor at UW Genome Sciences. federlab.github.io
Demographer working on evolutionary ecology, infectious disease dynamics, vaccination
🎓 Theoretical biologist
💻 Group leader @Aix-Marseille Université & CNRS researcher
🦠 Modeling host-associating microbes @LCB & @CENTURI
🎹 Musician when I find the time 🎶














