
Online now: Governance strategies for biological AI: beyond the dual-use dilemma
07.10.2025 15:15 — 👍 0 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0@cp-trendsbiotech.bsky.social
Trends in Biotechnology publishes reviews and original research in biobased technology. https://www.cell.com/trends/biotechnology/home

Online now: Governance strategies for biological AI: beyond the dual-use dilemma
07.10.2025 15:15 — 👍 0 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Bioinspired thermoreversible bioink orchestrates focal adhesion-dependent osteogenesis
03.10.2025 15:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: How a kidney microenvironment atlas can advance kidney tissue engineering
02.10.2025 15:15 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Emerging applications of carbon dots in plant (epi)genomics
01.10.2025 15:14 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Nanobodies: a new frontier in plant disease management
30.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Microalgae-made biopharmaceuticals and their potential role in the One Health approach
29.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Rational bioengineering of polysaccharide in designing of microbiome modulation
28.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Brown adipose tissue engineering: advances, challenges, and future directions
27.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Plant genome editing goes viral: balancing innovation and biosafety
26.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Virus-like particles as modular interfaces for biomaterial functionalization
25.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Staying productive under pressure: systems evaluations of β-carotene production in Yarrowia lipolytica under continuous fermentation
24.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0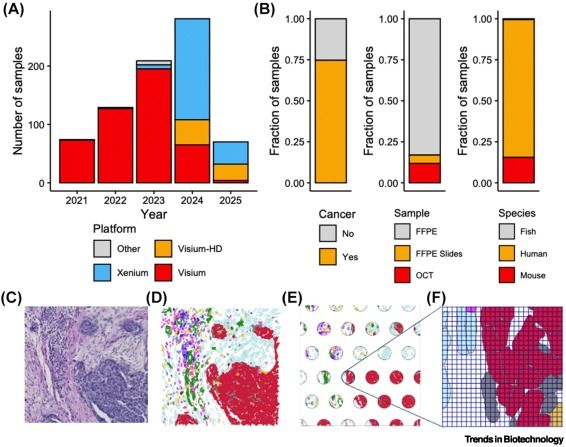
Online now: A practical guide to spatial transcriptomics: lessons from over 1000 samples
23.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0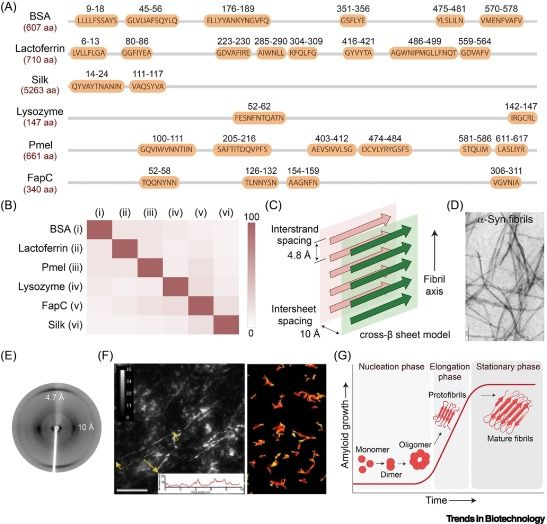
Online now: Are amyloid-based materials conducive to tissue engineering?
22.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Viral genome editing: striking a balance between promises and precautions
21.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Microbial tools and regulatory innovations for climate-resilient winemaking
20.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0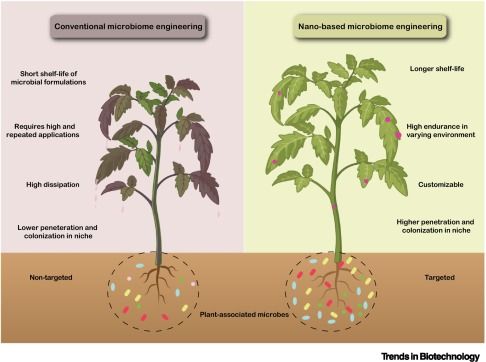
Online now: Nanobotic microbiomes against emerging vascular pathogens in agriculture
19.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Online now: Towards scalable anammox: mechanistic insights and emerging strategies
18.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0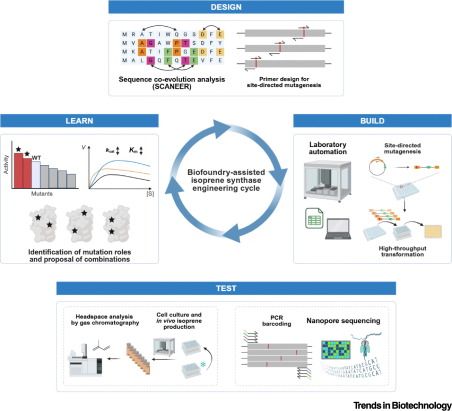
Online now: Semi-automated biofoundry workflows for sequence coevolution-guided isoprene synthase engineering
14.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Ethical and legal considerations of digital animal models: pioneering reduction and replacement
13.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Sustainable protection of multiple hosts against polyphagous pests using Plant Probiotic-Based Gene Silencing
12.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Food production from air: gas precision fermentation with hydrogen-oxidising bacteria
11.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Metabolic and immunomodulatory control of type 2 diabetes via generating cellular itaconate reservoirs by inflammatory-targeting gene-therapy nanovesicles
09.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Flying seed-inspired sensors for remote environmental monitoring on Earth and beyond
07.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 1
Online now: Engineering chimeric signaling proteins for microbial whole-cell biosensors: from design to deployment
06.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Highly efficient prime editors for mammalian genome editing based on porcine retrovirus reverse transcriptase
05.09.2025 15:14 — 👍 0 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Online now: Engineering infrared light detection in blind human retina using ultrasensitive human TRPV1 channels
04.09.2025 15:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Cell Symposia
Feeding the world while tackling climate change is one of science’s biggest challenges.
Join us #CellSymposia #CSSustainAgri2025, Oct 19–21, 2025 | Sanya, China
Explore genomics, bioengineering & smart tech with global experts.
http://dlvr.it/TMspnT