Interesting study—would love to do something similar again. Surprised they found less sleep duration/efficiency but no change in sleep architecture. Disturbed sleep artchitecture (light sleep and REM rebound) is our main hypotheses to explain the results of our study. So many interesting questions!
23.06.2025 06:19 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
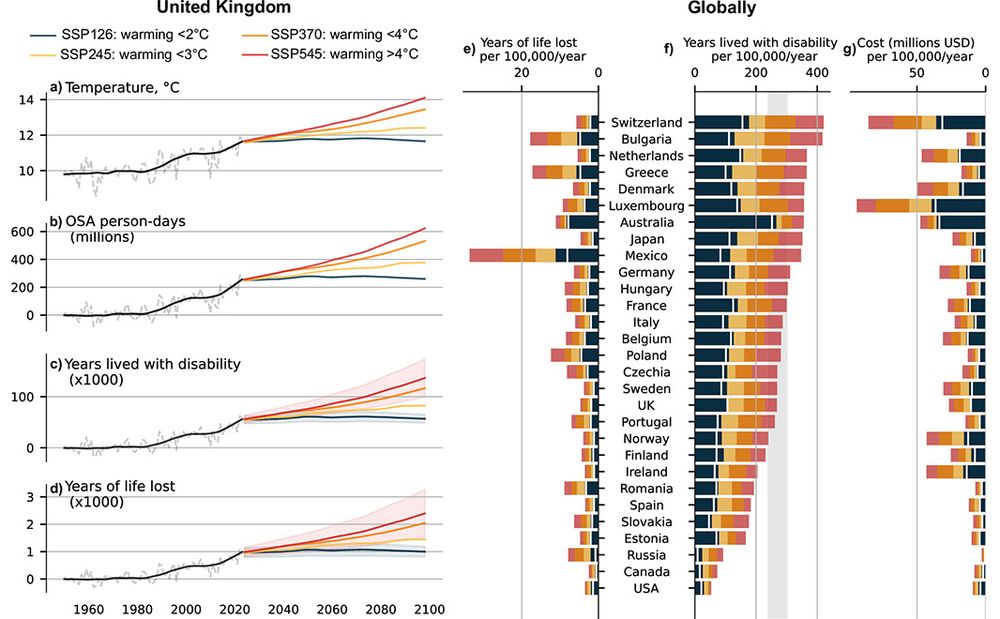
This is figure 3, which shows projected wellbeing burden of warming-related increase in moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) prevalence.
A study in Nature Communications quantifies how rising temperatures linked to climate change would increase the severity of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and reports projected losses of healthy life years and workplace productivity due to OSA. go.nature.com/3HMqsMg #medsky 🧪
22.06.2025 19:16 — 👍 49 🔁 17 💬 1 📌 1
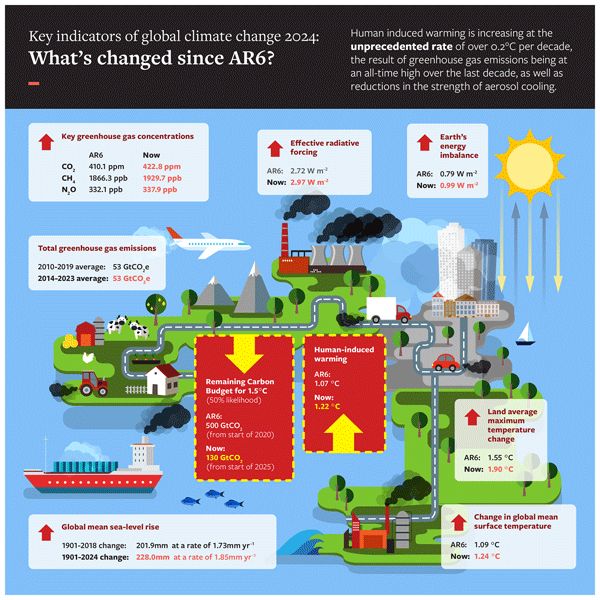
Indicators of Global Climate Change 2024: annual update of key indicators of the state of the climate system and human influence
Abstract. In a rapidly changing climate, evidence-based decision-making benefits from up-to-date and timely information. Here we compile monitoring datasets (published at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15639576; Smith et al., 2025a) to produce updated estimates for key indicators of the state of the climate system: net emissions of greenhouse gases and short-lived climate forcers, greenhouse gas concentrations, radiative forcing, the Earth's energy imbalance, surface temperature changes, warming attributed to human activities, the remaining carbon budget, and estimates of global temperature extremes. This year, we additionally include indicators for sea-level rise and land precipitation change. We follow methods as closely as possible to those used in the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) Working Group One report. The indicators show that human activities are increasing the Earth's energy imbalance and driving faster sea-level rise compared to the AR6 assessment. For the 2015–2024 decade average, observed warming relative to 1850–1900 was 1.24 [1.11 to 1.35] °C, of which 1.22 [1.0 to 1.5] °C was human-induced. The 2024-observed best estimate of global surface temperature (1.52 °C) is well above the best estimate of human-caused warming (1.36 °C). However, the 2024 observed warming can still be regarded as a typical year, considering the human-induced warming level and the state of internal variability associated with the phase of El Niño and Atlantic variability. Human-induced warming has been increasing at a rate that is unprecedented in the instrumental record, reaching 0.27 [0.2–0.4] °C per decade over 2015–2024. This high rate of warming is caused by a combination of greenhouse gas emissions being at an all-time high of 53.6±5.2 Gt CO2e yr−1 over the last decade (2014–2023), as well as reductions in the strength of aerosol cooling. Despite this, there is evidence that the rate of increase in CO2 emissions over the last decade has slowed compared to the 2000s, and depending on societal choices, a continued series of these annual updates over the critical 2020s decade could track decreases or increases in the rate of the climatic changes presented here.
Our new paper updating key metrics in the IPCC is now out, and the news is grim:
⬆️ Human induced warming now at 1.36C
⬆️ Rate of warming now 0.27C / decade
⬆️ Sharp increase in Earth's energy imbalance
⬇️ Remaining 1.5C carbon budget only 130 GtCO2
essd.copernicus.org/...
18.06.2025 23:10 — 👍 654 🔁 483 💬 22 📌 67

Excited to share our latest study, just published in Nature Communications, where we show that rising global temperatures are expected to substantially increase the severity and burden of obstructive sleep apnea worldwide.
Full article here: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
16.06.2025 20:40 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Science for safe & just #Climate future. Scientific Directors: Johan #Rockström, Ottmar #Edenhofer // Website EN: https://www.pik-potsdam.de/en, DE: https://www.pik-potsdam.de/de // All PIK social media channels: https://pik-potsdam.de/socials
The Journal of Physiology publishes original research in all areas of physiology and pathophysiology that illustrates new physiological principles or mechanisms.
Sleep Scientist | Senior Lecturer
Reader at the University of Strathclyde Centre for Sleep Health
Sleep Informatics | University of Kansas Medical Center
The Early Career Network (ECN) under the European Sleep Research Society (ESRS) is dedicated to the collaboration and participation of early career sleep professionals within ESRS.
https://esrs.eu/committee/early-career-network/
Posting content from the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine; follows do not indicate endorsement.
#pulmCC #sleepmed #AJRCCM #RespEd #ATS #medsky
https://www.atsjournals.org/journal/ajrccm
To accelerate global innovation in the advancement of respiratory health through multidisciplinary collaboration, education, and advocacy. https://linktr.ee/atscommunity
The mission of the Insomnia and Sleep Health Council is to improve the sleep of people in Australia and New Zealand, by sharing professional skills and experiences in insomnia research and treatment, and understanding the determinants of sleep health.
Deputy Editor, Our World in Data
Senior Researcher, University of Oxford
Climate, energy, environment, all things data.
We are an international scientific non-profit organisation promoting all aspects of #SleepResearch #SleepMedicine. Making Sleep trendier than caffeine. ☕
Global climate science and policy institute working to accelerate climate action and keep warming below 1.5°C.
Climate science, impacts, policy and 1.5C
Researching human adaptation to global changes in climate, environment, and technology
Physicien climatologue, Directeur de Recherche du CNRS au LMD/ENS/IPSL
Auteur principal du 6e rapport du #GIEC @IPCC_CH, Groupe 1: "Les bases physiques du Climat", 2018-2023.
Co-fondateur des Trains du Climat
Climate Scientist @CNRS, IPCC AR6 lead author
Professor of Creative Pedagogies | Poet | Game Designer | Slow AI
#SciComm #HigherEd #Poetry #GenAI
https://theslowai.substack.com/
https://linktr.ee/sam.illingworth
PhD Physics, enabling continuous cost-downs of renewable technologies.
Simulation, Numerics, Computing.
climate scientist
posts 100% my own
🇨🇦 is my home
distinguished professor & chair, Texas Tech
chief scientist, The Nature Conservancy
board member, Smithsonian NMNH
alum, UToronto and UIUC
author, Saving Us
Extreme weather and climate change expert writing for Yale Climate Connections. Co-founder, Weather Underground; former hurricane hunter.


