
Excited to share our latest paper - now out in @science.org - we showed how oxytocin modulates maternally-directed behavior in young mice (P15).
12.09.2025 15:21 — 👍 104 🔁 34 💬 4 📌 1@zhenggang.bsky.social
Sanford Fellow @UCSDCompassion Alumni @HHMI, Identifying 🧬 for self/social motivation with 3D spatial omics

Excited to share our latest paper - now out in @science.org - we showed how oxytocin modulates maternally-directed behavior in young mice (P15).
12.09.2025 15:21 — 👍 104 🔁 34 💬 4 📌 1
Proposal recommended for funding! Which means we have a fresh, 3-year-funded position available for a computational postdoc interested in studying dynamics of social interactions in rats, with simultaneous Neuropixels data to follow 🐀🐀🐀
Proper job ad pending, but email me if interested!
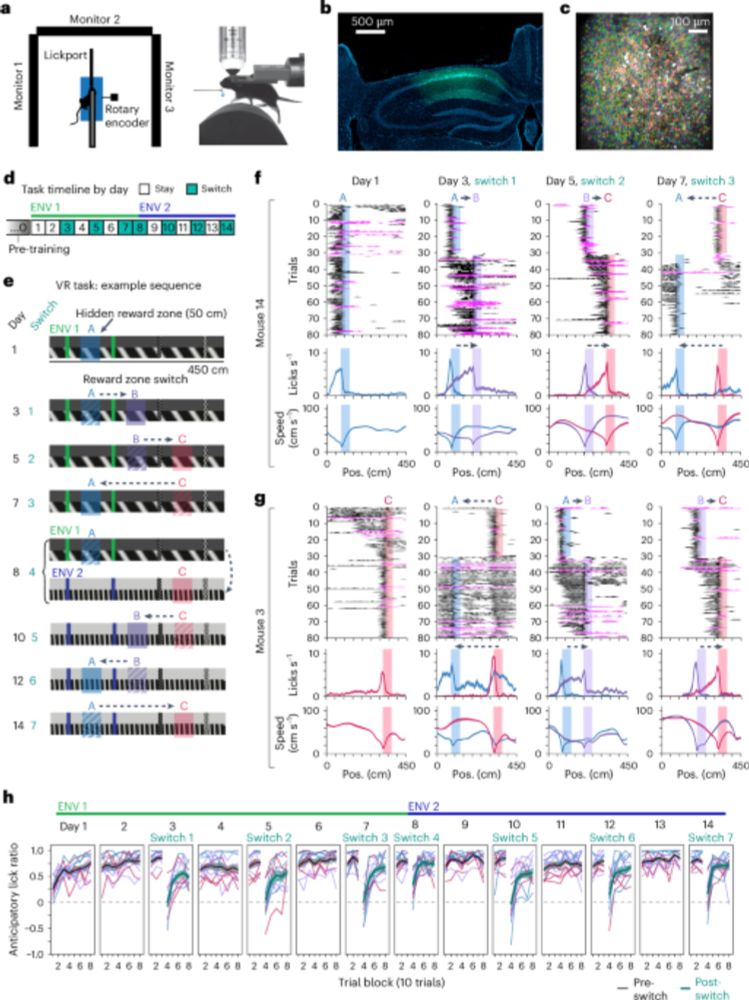
It's officially published!! In my main postdoc work with @markplitt.bsky.social and @lgiocomo.bsky.social, we found that the hippocampus simultaneously encodes an animal's spatial position and its experience relative to reward in parallel population codes. 🧵
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

The firing of neural populations is high-dim even if their subthreshold activity is low-dim! This work by @bio-emergent.bsky.social and @haydari.bsky.social shows how, with a solvable model, a data analysis technique, and data from mouse visual cortex: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
09.06.2025 11:49 — 👍 90 🔁 29 💬 0 📌 1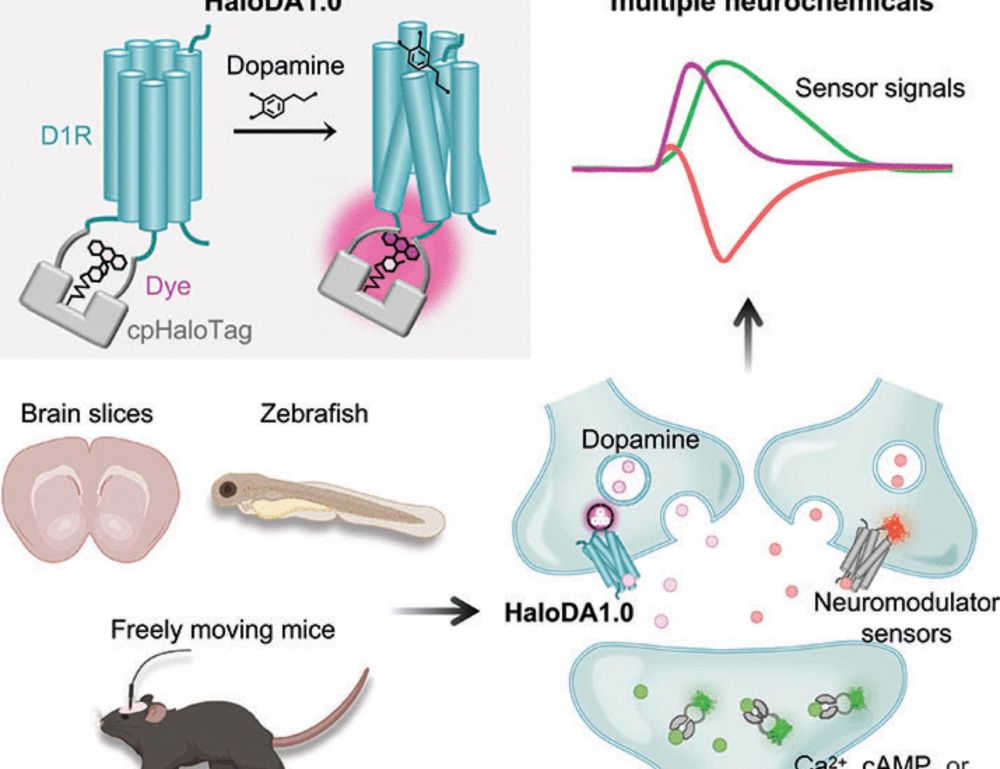
Excited to share our Science paper on HaloDA1.0-the first genetically encoded far-red dopamine sensor! 🥳It enables powerful multiplex imaging in neurons, brain slices, and live animals.🧠🔬 #GRABsensors #Dopamine www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
06.06.2025 05:20 — 👍 124 🔁 38 💬 1 📌 0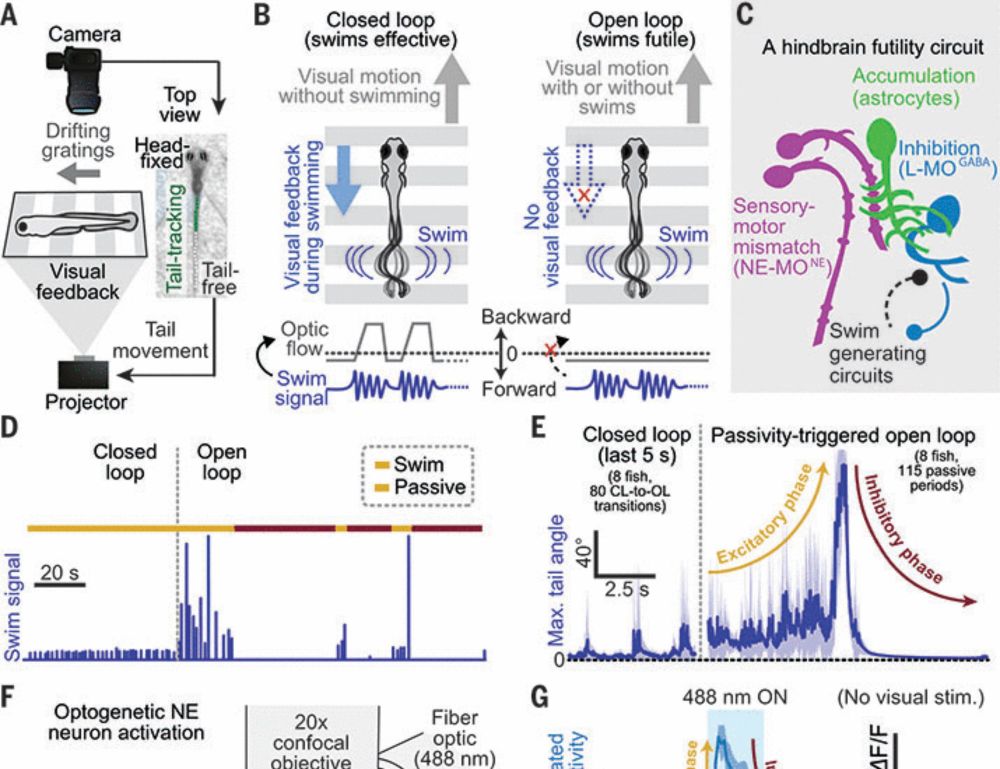
Excited to share that the astrocyte-centered half of my thesis work is now out @science.org ! With @mishaahrens.bsky.social and @marcduque.bsky.social
science.org/doi/10.1126/... 1/8
Congrats, Josh and Xiaowei!
14.05.2025 23:52 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Congratulations! Well deserved!
07.05.2025 17:08 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0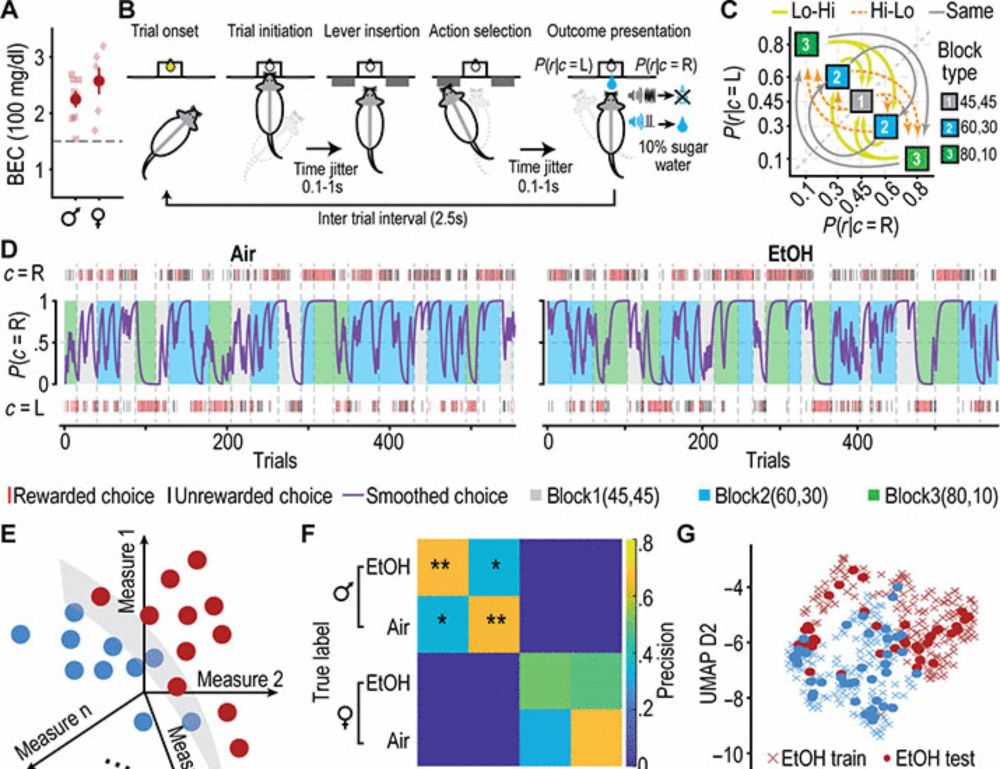
Thrilled to share our work in ScienceAdvances: “Chronic ethanol exposure produces sex-dependent impairments in value computations in the striatum.” Huge thanks to Tricia @janaklab.bsky.social, Daeyeol @ungteoriz.bsky.social, Angela, and my friend Robin!
www.science.org/doi/full/10....
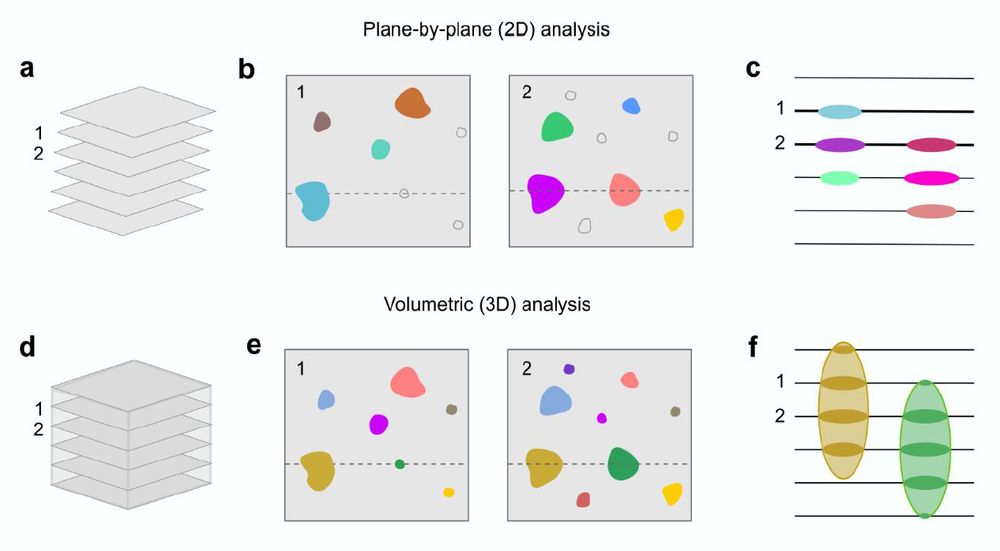
Many of us use 2p scopes to image 3D volumes of brain. But then we analyze the data plane by plane, resulting in duplicated neurons, missed neurons, and low s/n. Let's go 3D!
Suite3D: Volumetric cell detection for two-photon microscopy
by @haydari.bsky.social & team.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats! Very important work!
02.04.2025 19:33 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0(n/n) This work wouldn’t have been possible without the incredible efforts of the entire Sternson Lab (@BrainCaRMA, @ronggong, @vicente-rodriguez.bsky.social) and many others—whose contributions have been invaluable. Special thanks to @hhmi.org and @ucsdmedschool.bsky.social. Thank you for reading!
30.03.2025 03:36 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
(10/n) Thanks to Dr. Dana Small for the insightful Science Perspective article on our work www.science.org/doi/10.1126/... www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
30.03.2025 03:32 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(9/n) In short, our study shows that VTADA neurons encode food palatability at intermediate timescales, sustaining hedonic eating. Precise dopamine release timing is key for controlling the consumption phase, while GLP-1R activation during palatable food intake dampens this dopamine-driven effect
30.03.2025 03:29 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(8/n) We tested semaglutide (Ozempic), with a ramped daily dose to engage satiety pathways. Initially, it shortened feeding bouts and suppressed VTADA responses to palatable food. Yet as the dose increased, VTADA neurons rebounded—driving overconsumption, an effect reversed by targeted inhibition
30.03.2025 03:26 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(7/n) Do VTADA neurons truly sustain hedonic eating? We boosted their activity during feeding and observed a hedonic contrast effect: laser-OFF blocks elicited a negative response, while stimulation significantly prolonged feeding bouts. Conversely, suppressing VTADA neurons reduced bout duration
30.03.2025 03:22 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0(6/n) Switching from high- to low-palatability food abruptly reduces feeding and VTADA signals—revealing a “hedonic contrast” effect—while lower-palatability food elicits shorter bout durations and negative DA responses. VTADA neurons may encode food palatability to sustain hedonic eating over time
30.03.2025 03:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(5/n) Prior work shows VTADA neurons respond to food cues, reward utility, and post-ingestion, yet how they encode palatability at intermediate timescales remains unclear. We found VTADA neurons remain active throughout palatable food consumption, with their activity scaling to palatability
30.03.2025 03:13 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(4/n) The VTA is diverse—its inhibitory VTAVGAT neurons can suppress VTADA cells. So how do the periLCVGLUT2 neurons fit in? We uncovered a pathway where periLCVGLUT2 neurons activate VTAVGAT neurons, which then dampen VTADA signaling to the nucleus accumbens by reducing dopamine release
30.03.2025 03:09 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(3/n) Our group discovered that the peri‐locus coeruleus (periLC), downstream of hunger centers, plays a key role in promoting hedonic eating via double-negative inhibition. But how exactly does it work? Intriguingly, we identified a direct periLC→VTA pathway that selectively prolongs feeding bouts
30.03.2025 03:05 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(2/n) Hedonic eating means indulging in food for pleasure rather than necessity—think of the “salted-nut phenomenon.” In our study, we offered a highly palatable Ensure alongside a less tasty version and found that the tastier option led to longer feeding bouts, though not more bouts overall
30.03.2025 02:58 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
(1/n) Why is it so hard to stop eating when something tastes amazing? Our new @ science.org paper reveals that dopamine helps sustain our drive for tasty treats—and may explain how anti-obesity Ozempic tames those urges. doi.org/10.1126/science.adt0773
30.03.2025 02:51 — 👍 57 🔁 10 💬 2 📌 0Congratulations!!! Truly grateful for your outstanding contribution!
29.03.2025 15:13 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0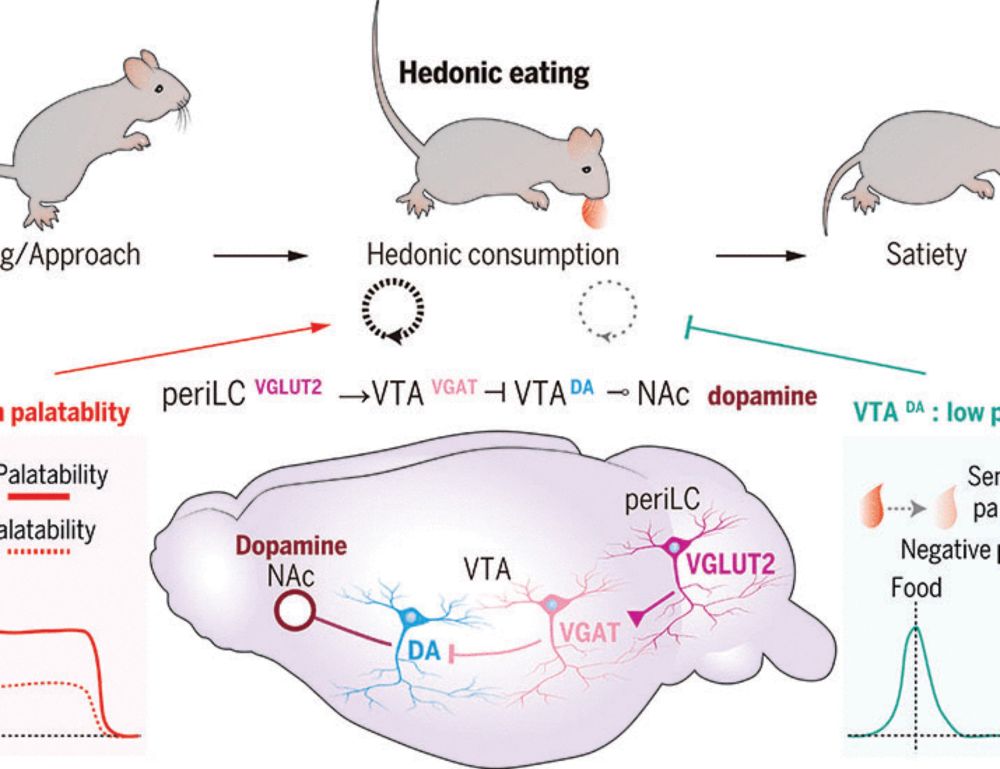
New @science.org
Hedonic eating (eating for pleasure, not need) is mediated by dopamine neurons (in the brain ventral segmental area, VTA) and they are antagonized by GLP-1 drugs, such as semaglutide, leading to weight loss
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
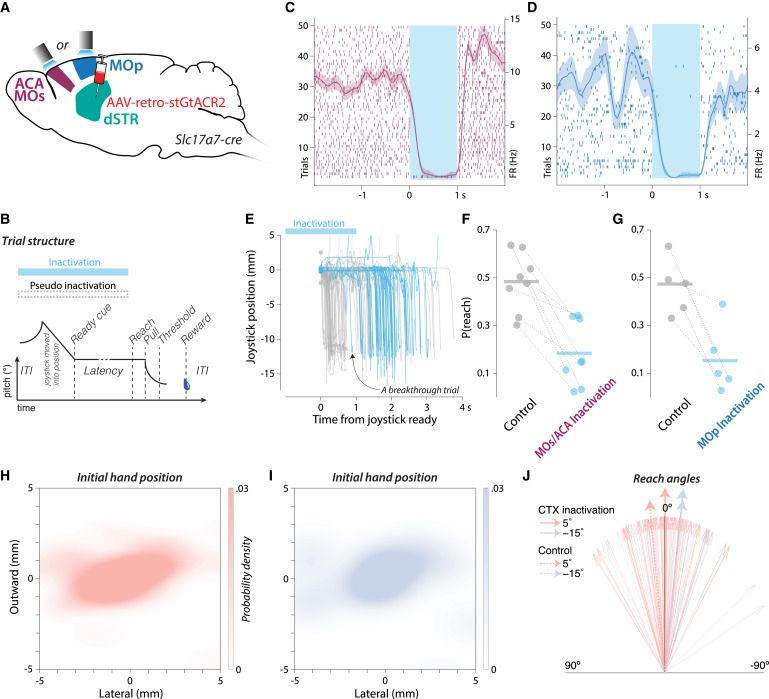
Our paper from Junchol Park and collaborators that has been brewing for a while. Trying to capture our thinking about what action specification in striatum means and what would constitute evidence for such a model. Longer thread soon, but it’s online now. www.cell.com/neuron/fullt...
24.01.2025 01:34 — 👍 52 🔁 18 💬 1 📌 0HCN1 channels in GABAergic amygdalar neurons underpin male-biased aggressive behaviors https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.12.07.627305v1
08.12.2024 13:15 — 👍 14 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 1