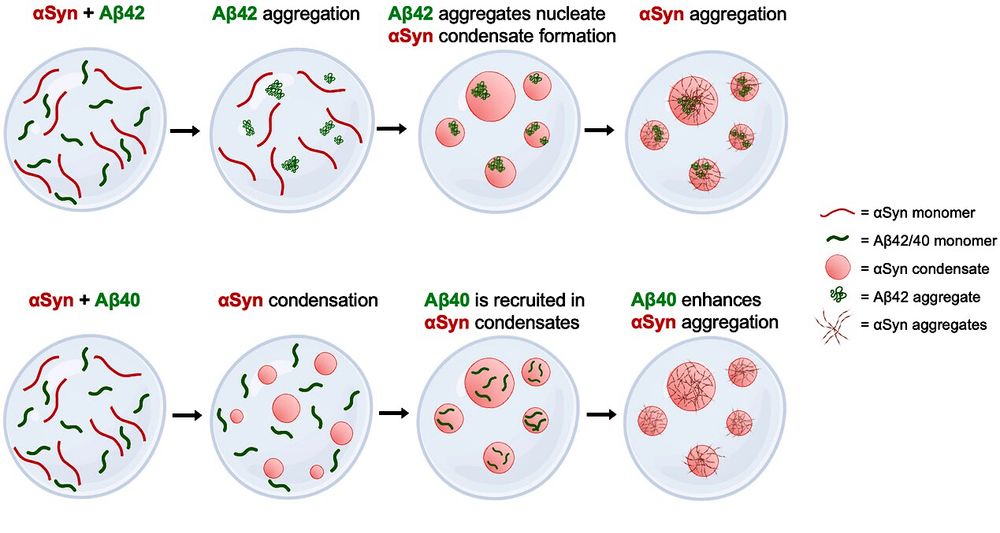
Amyloid-β modulates the phase separation and aggregation of α-synuclein www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
03.08.2025 12:07 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0@elamberti.bsky.social
neurology @unipd.bsky.social

Amyloid-β modulates the phase separation and aggregation of α-synuclein www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
03.08.2025 12:07 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0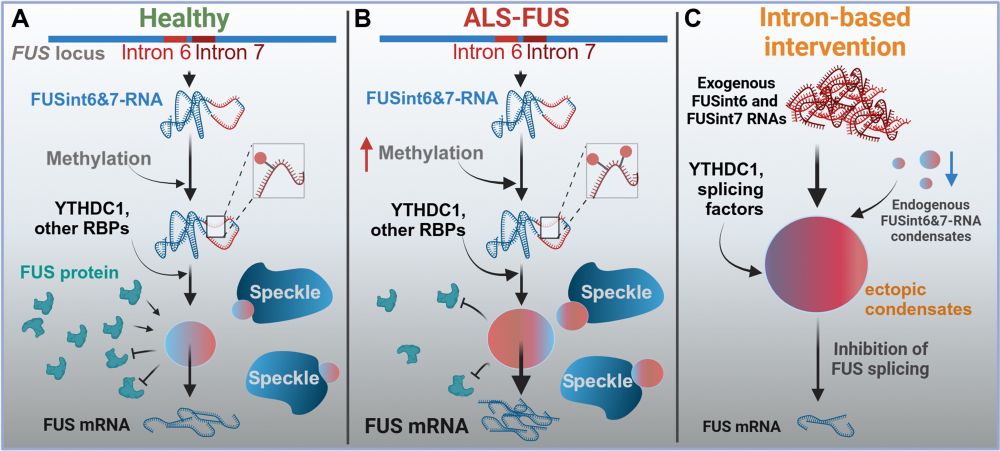
M6A-dependent RNA condensation underlies FUS autoregulation and can be harnessed for ALS therapy development www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
26.07.2025 10:18 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0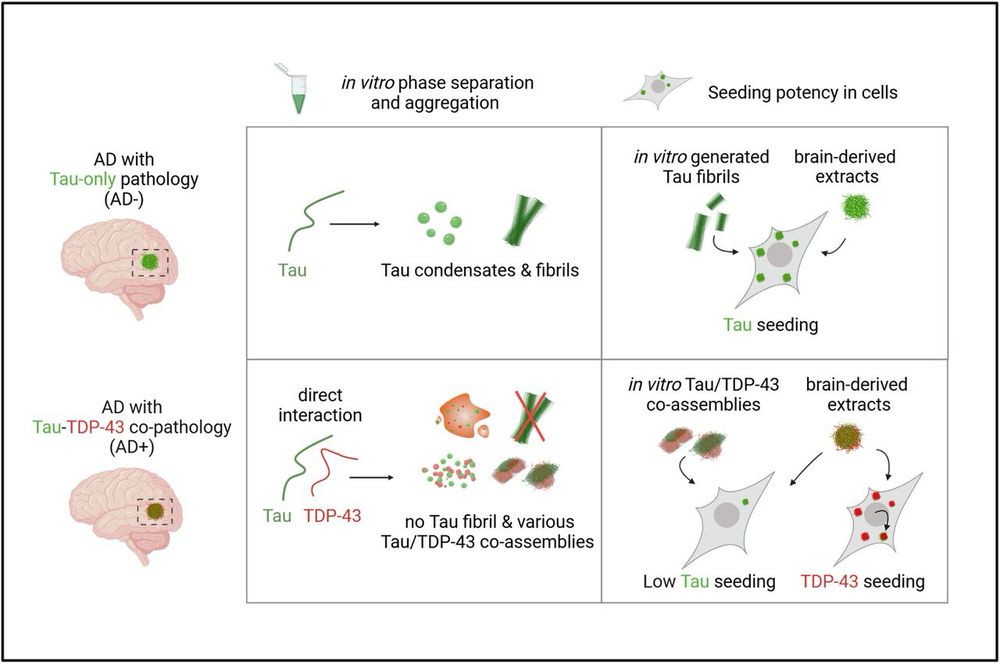
Direct binding of TDP-43 and Tau drives their co-condensation, but suppresses Tau fibril formation and seeding www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
20.07.2025 21:01 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0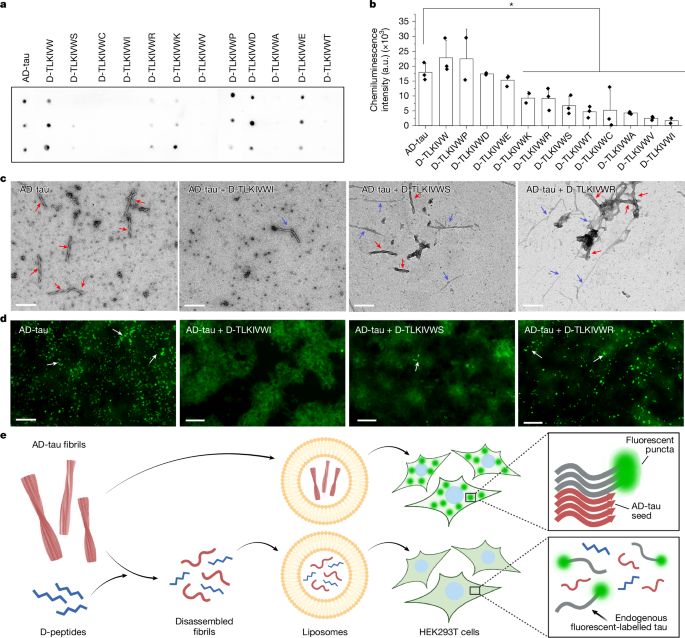
Nature research paper: How short peptides disassemble tau fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease
go.nature.com/44Bsian
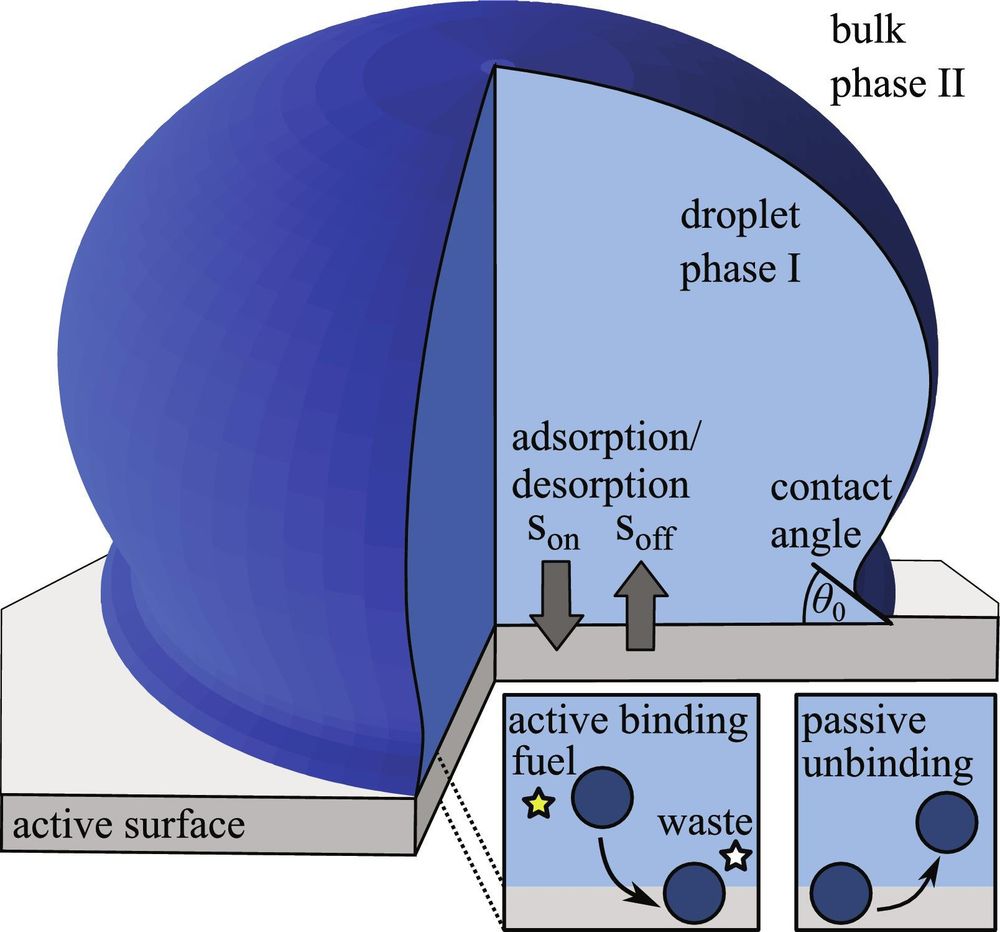
Chemically active wetting www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1...
07.07.2025 22:39 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0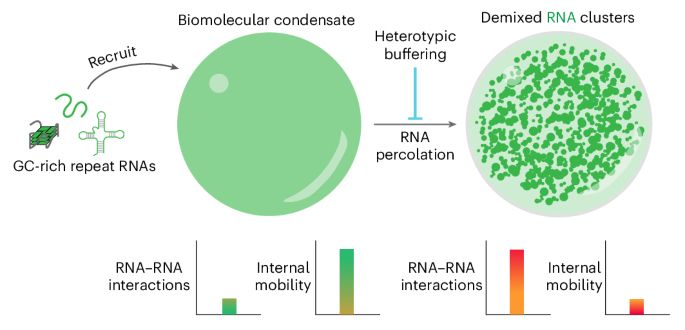
Homotypic RNA clustering accompanies a liquid-to-solid transition inside the core of multi-component biomolecular condensates www.nature.com/articles/s41...
06.07.2025 11:13 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0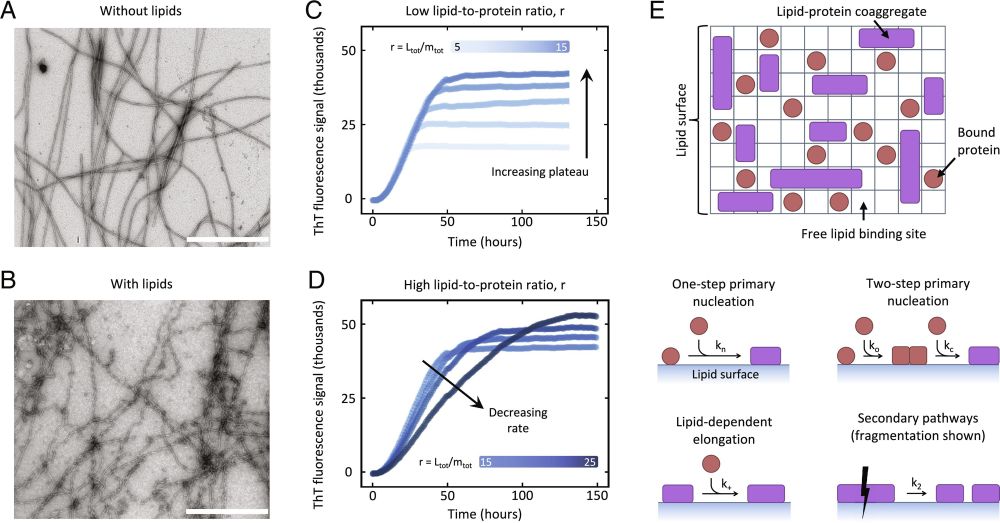
Global kinetic model of lipid-induced α-synuclein aggregation and its inhibition by small molecules
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
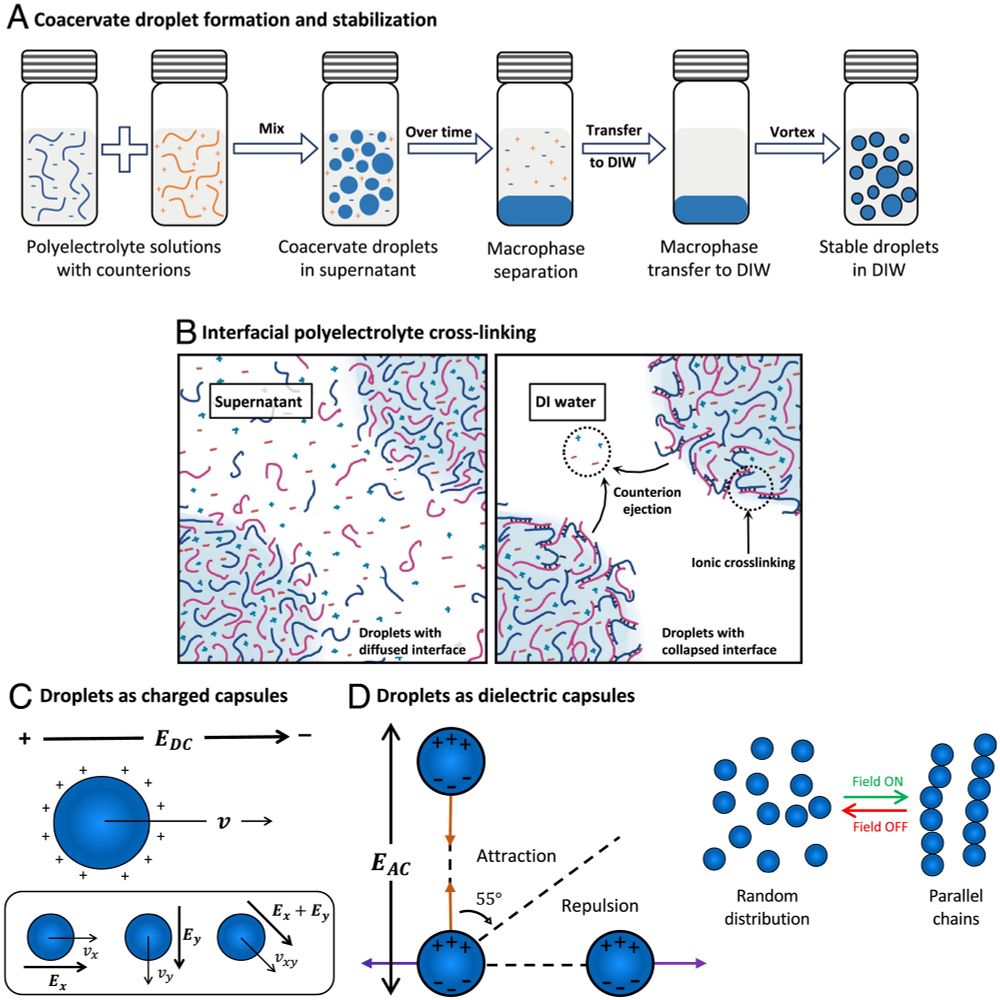
Manipulation of coacervate droplets with an electric field doi.org/10.1073/pnas...
07.06.2025 16:10 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0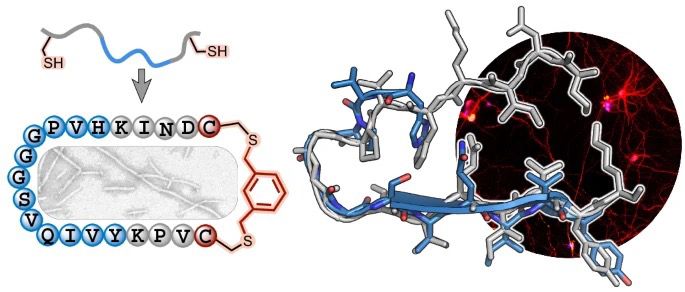
Macrocyclic β-arch peptides that mimic the structure and function of disease-associated tau folds rdcu.be/enCNK
25.05.2025 20:53 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Small-molecule dissolution of stress granules by redox modulation benefits ALS models rdcu.be/emsBr
17.05.2025 13:23 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0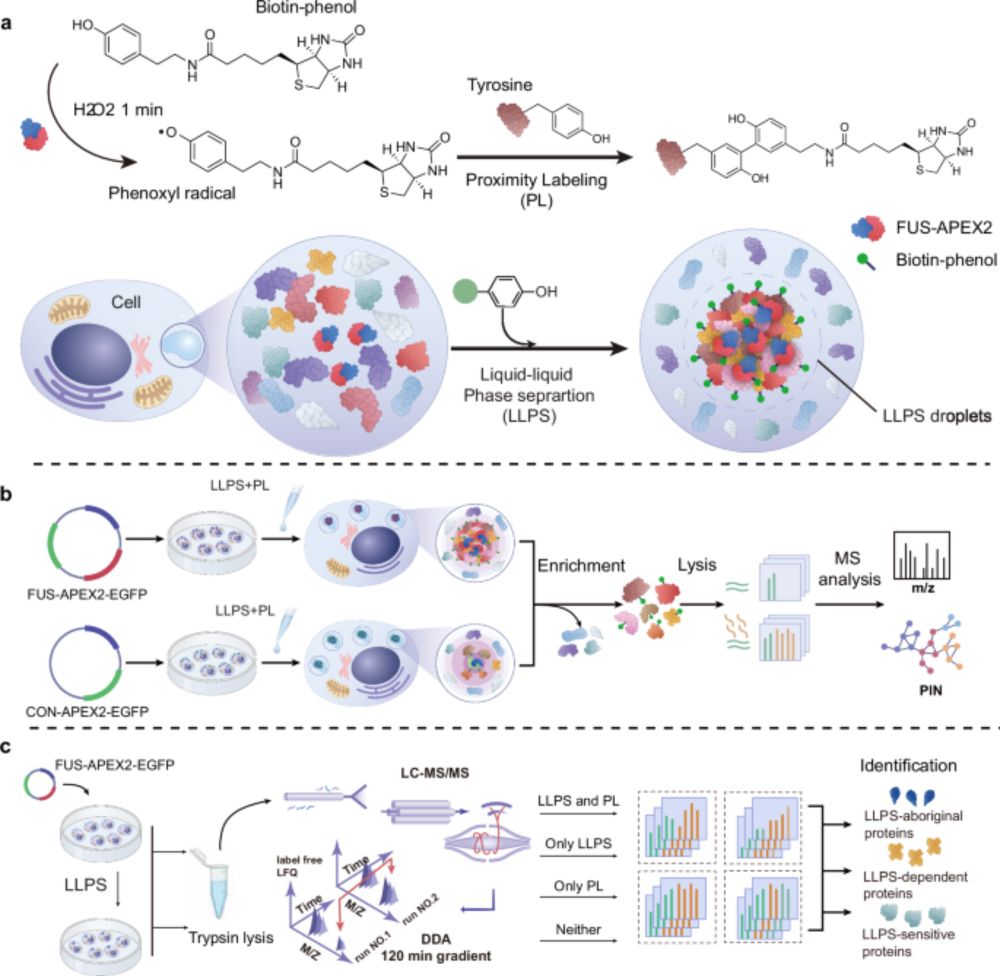
Spatiotemporal deciphering of dynamic the FUS interactome during liquid-liquid phase separation in living cells #NatCommun #MassSpec www.nature.com/articles/s41...
10.05.2025 18:27 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0MOAG-4 promotes the aggregation of α-synuclein by competing with self-protective electrostatic interactions - Journal of Biological Chemistry www.jbc.org/article/S002...
26.01.2025 23:07 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Simple Model of the Effect of Solution Conditions on the Nucleation of Amyloid Fibrils | The Journal of Physical Chemistry B pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
19.01.2025 15:04 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0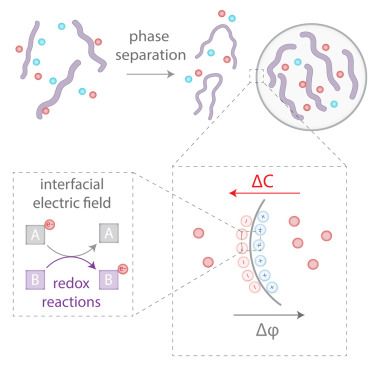
Interface of biomolecular condensates modulates redox reactions www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
11.01.2025 20:55 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0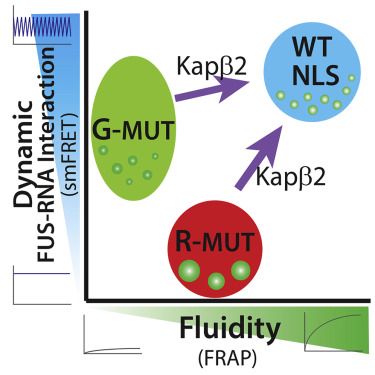
Loss of Dynamic RNA Interaction and Aberrant Phase Separation Induced by Two Distinct Types of ALS/FTD-Linked FUS Mutations: Molecular Cell www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
09.01.2025 22:33 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0