
KATMAP infers splicing factor activity and regulatory targets from knockdown data - @daspliceisright.bsky.social go.nature.com/47ycrMJ
04.11.2025 15:13 — 👍 15 🔁 9 💬 1 📌 1@robertomunita.bsky.social
Assistant Professor @UChile | RNA lover | Splicing, RNA modifications, ncRNAs, RT-LAMP

KATMAP infers splicing factor activity and regulatory targets from knockdown data - @daspliceisright.bsky.social go.nature.com/47ycrMJ
04.11.2025 15:13 — 👍 15 🔁 9 💬 1 📌 1
a, Next-generation sequencing (NGS)-based methods require pretreatment or pre-labelling of the nucleic acid with antibodies (left), restriction enzymes or endonucleases (middle), or chemicals (right) before sequencing, so that modified and unmodified bases can be distinguished during NGS sequencing. b, Long-read sequencing (LRS)-based methods can directly detect modified bases. In single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing (left), a DNA polymerase (or reverse transcriptase for RNA) is bound within the zero-mode waveguide (ZMW). When a dNTP is incorporated at the polymerase active site, it will emit a fluorescent pulse in the corresponding colour channel. The order of pulses provides the read sequence and inter-pulse duration (IPD) between base incorporation events indicates the presence of a covalent modification in the DNA or RNA template. Nanopore sequencing (right) relies on engineered biological nanopores embedded in a lipid membrane to sequence single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or RNA. The ionic current measured as DNA or RNA gets ratcheted through the nanopore depends on the precise set of nucleotides occupying the constriction point. Modified nucleotides in the ssDNA or RNA introduce distinct current patterns, making it possible to detect the existence of modified bases relative to non-modified nucleotides.
DNA and RNA modification mapping methods based on next-generation sequencing and long-read sequencing technologies
go.nature.com/47yAbPc

ICYMI: New Online! Single-cell research in Latin America and the Caribbean builds genomics datasets for equitable AI-powered precision medicine
12.10.2025 14:33 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
ICYMI: New Online! The new era of single-molecule RNA modification detection through nanopore base-calling models
16.10.2025 12:22 — 👍 4 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0
New Online! Revealing the hidden coding potential of the human genome
03.11.2025 11:09 — 👍 9 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0Hello! Just checking in to see if there are any updates on the progress of the 2'Ome detection model. Is there an estimated release timeline? I'd love to start using it soon!
14.05.2025 00:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0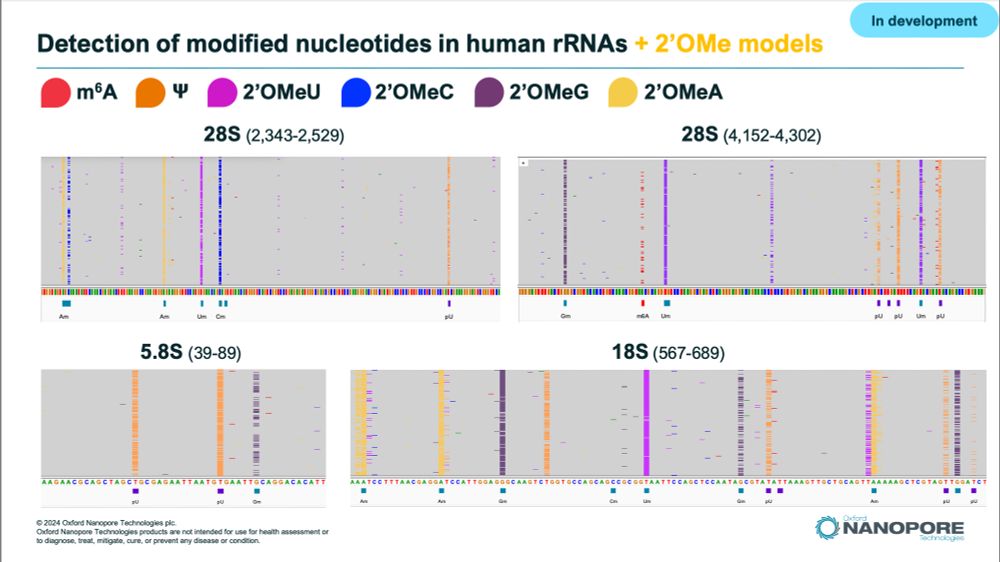
Selected areas of Human rRNAs showing modification calls in IGV. Samples sequenced by ONT direct RNA sequencing with experimental Remora models calling m6A, m5C, PseudoU, and all 4 2'Ome modifications.
We have been busing working on models to detect all 2'Ome-RNA modified nucleotides on top of PseudoU, m6A, m5C and Inosine using @nanoporetech.com direct RNA sequencing.
This is still very preliminary but here are a few examples of what it looks like on Human #rRNA prepared with standard lib prep 🤩