Today in the @bmj.com, @thomwetzer.bsky.social and I argue that legal developments in recent years effect unprecedented limits on corporate and state climate conduct. The chasm between legal duties and many actors' conduct leaves legal risk widespread for many firms. Read more at the link below 👇
07.01.2026 17:17 — 👍 6 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0

Quantifying the regional to global climate impacts of individual fossil fuel projects to inform decision-making - npj Climate Action
npj Climate Action - Quantifying the regional to global climate impacts of individual fossil fuel projects to inform decision-making
For so long, fossil fuel projects have said their contribution to climate change is "negligible".
Turns out that's wrong.
Our research in NPJ Climate Action proves it.
Every tonne of CO2 matters.
@21stcenturyweather.bsky.social
@minderoo.bsky.social
#climatechange
www.nature.com/articles/s44...
13.10.2025 10:07 — 👍 171 🔁 86 💬 3 📌 6

"Health losses attributed to anthropogenic climate change," a brief communication in the journal Nature Climate Change. There's a map showing regions of the world, and pie charts of relevant studies as they apply to different health impacts like "heat-related deaths" and "maternal and child health"
🚨 NEW: Climate change is already causing 30,000 deaths per year - a global annual economic loss of $100-350B USD - but the true damage is probably 10x higher. Out TODAY in Nature Climate Change: the first systematic look at the science of "health impact attribution" 🔓 www.nature.com/articles/s41...
17.09.2025 11:57 — 👍 877 🔁 504 💬 22 📌 34
The paper was co-authored with @anavicedo9.bsky.social Sihan Li @frediotto.bsky.social Kristine Belesova, Andy Haines @harrinluke.bsky.social Jeremy Hess, Rashmi Venkatraman @thomwetzer.bsky.social Alistair Woodward @krisebi.bsky.social - @smithschool.ox.ac.uk
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Finally, we quantified individual companies' emissions' contributions to heat-related deaths using a simple 'market-share' approach that quantifies attributable deaths in proportion to emissions. The six highest-emitting companies globally caused at least one additional death each summer since 2004.
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
A benefit of this approach was that we could use daily observed mortality data to quantify heat-related deaths, rather than mean mortality for the day of the year, allowing us to more precisely quantify how many attributable deaths occured on any given day.
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
To quantify heat-mortality during and outside of heatwaves, we modified the approach used elsewhere and calculated counterfactual temperatures by subtracting attributable temperature anomalies from observations, producing a 50-yr time series that matches observed temperature flucturations.
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We then quantified heat-mortality during and outside heatwaves. The hottest temperatures often get the most attention - and heat deaths are indeed highest then - but three-quarters of heat mortality attributable to human influence on the climate in 2018 occurred outside of the 12-day heatwave.
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

in KlimaSeniorinnen v Switzerland to justify its finding that Switzerland needed to reduce emissions: "Although the applicants could agree that adaptation was also crucial, it was not an answer to what Switzerland should have done to mitigate climate change." hudoc.echr.coe.int/eng#_ftnref178
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
Our finding shows that changes in vulnerability can reduce heat-mortality, but at least in Zurich, it's still not been enough. Only ceasing GHG emissions will stop the burden of climate change-caused deaths from rising further. As a preprint, the European Court of Human Rights cited this result...
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We conducted experiments where we applied the heat-mortality relationship from the 1980s/90s to 2004-2018 as a 'constant vulnerability' baseline and found that >700 deaths had been avoided by declining vulnerability. But attributable heat-related deaths had continued to rise in any case.
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We knew that vulnerability to heat changes with time: e.g. behavioural/infrastructual adaptation to heat would be reducing vulnerability while population ageing has the opposite effect. But what is the overall effect of changing vulnerability? Could it be enough to counteract the effects of warming?
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Out now: our new study shows that climate change caused nearly 1,700 heat-related deaths in Zürich over 50 years.
We assessed the effects of changing vulnerability to heat, heat-mortality within and outside of heatwaves, and the contribution of individual companies' emissions to heat deaths.
10.09.2025 08:45 — 👍 38 🔁 24 💬 1 📌 1
The guidance is designed to be inclusive and method-agnostic, identifying key steps for robust, high quality analyses. We hope that it will prove useful to study authors, reviewers, journal editors and research funders.
Available here: link.springer.com/article/10.1...
23.07.2025 23:09 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
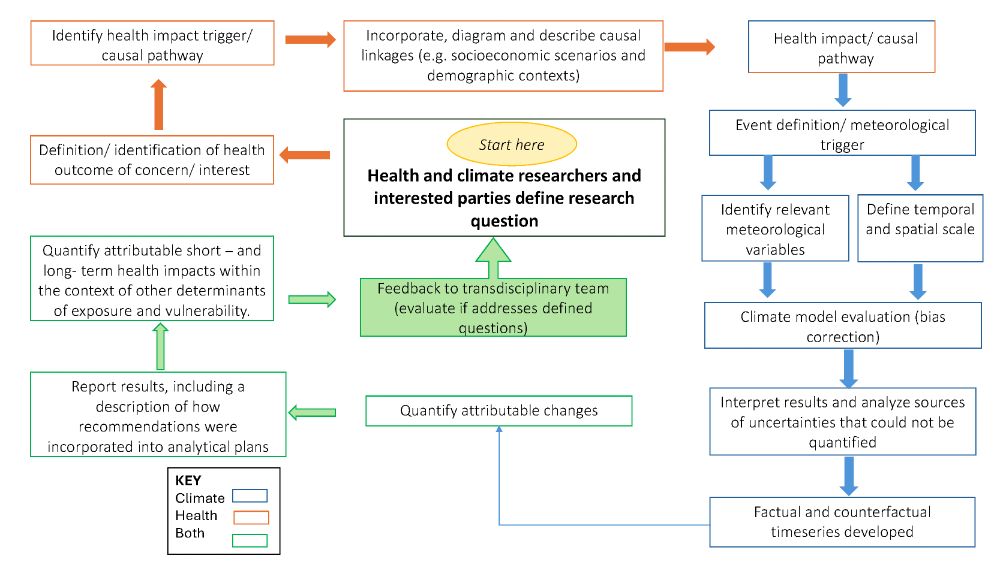
Out now: new guidance for research that attributes health outcomes to climate change led by @krisebi.bsky.social, Andy Haines @lshtm.bsky.social, myself, supported by a fantastic team of co-authors and @wellcometrust.bsky.social.
23.07.2025 22:42 — 👍 6 🔁 5 💬 1 📌 0
We need CDR. 🧩
But the ambiguity & lack of transparency regarding #CDR in states‘ climate plans jeopardize the PA. ❌
We unpack this issue by reviewing strategies of 70+ states concerning their CDR plans. 📑
👇 More in the thread by lead author Rupert Stuart-Smith & our study doi.org/10.1080/1469...
14.07.2025 17:28 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
New research on limits to CO2 removal (CDR). CDR is key to our ambition to stop adding climate pollution to the atmosphere. Because it's uncertain how much will be delivered and it clearly comes with risks of social & environmental side-effects, legal issues arise. This paper provides an overview. 👇
14.07.2025 09:54 — 👍 24 🔁 9 💬 2 📌 0
Legal analysis, in conjunction with the risks associated with CDR-dependent targets assessed here, could clarify states’ mitigation obligations under international law and facilitate progression past a risk-blind and indiscriminate use of scientific pathways in assessing states’ targets. More soon!
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
That previous work was published in @science.org and can be found here: www.science.org/doi/full/10....
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
To minimise risks associated with reliance on CO2 removal, states should prioritise pathways that minimise overshoot and dependence on removals to reach net-zero. Risks associated with high CDR dependence might render state action inconsistent with norms and principles of international law.
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 7 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
-- Reliance on international cooperation to deliver CO2 removal (e.g. via carbon trading mechanisms) is also common in states' plans and amplifies these risks.
-- Non-delivery of planned CO2 removal would raise global temperatures further, worsening the impacts of climate change.
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 7 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
-- There is pervasive lack of transparency and ambiguities in states' international reporting, with respect to how states intend to meet their climate targets.
-- However, dependence on high levels of CO2 removal is widespread and substantial risks to delivery of planned CO2 removal exist.
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 7 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
-- Inadequate near-term emission reductions are common, jeopardise the Paris climate targets and create substantial long-term dependence on CO2 removal to eliminate a temperature overshoot, with its associated risks.
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 6 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
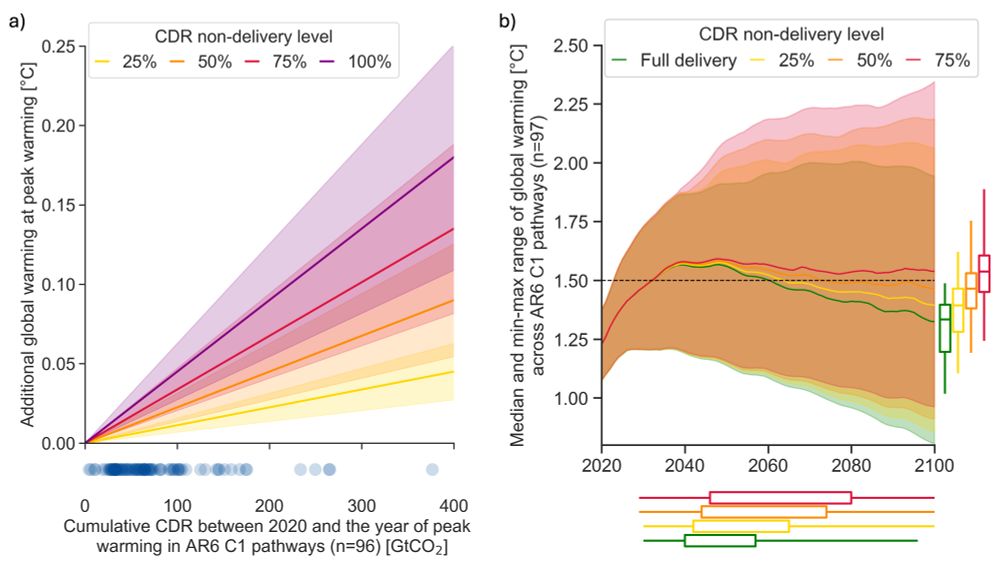
🚨 Out now in @climate-policy.bsky.social: New research with @thomwetzer.bsky.social @rubenpruetz.bsky.social @joerirogelj.bsky.social Lavanya Rajamani, Marianne Wood and Ewan White: States are depending heavily on CO2 removal to meet climate targets, risking the Paris Agreement goal.
14.07.2025 07:34 — 👍 20 🔁 10 💬 2 📌 2
Last days to apply for this exciting new role within my team at @oxfordgeography.bsky.social @ox.ac.uk. If you are a climate scientist with experience in climate change attribution or projections and an interest in climate change impact modelling, we would love to hear from you!
09.07.2025 08:40 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Germinated in 1991 at the University of Oxford
One of the world’s first interdisciplinary research institutions, continuing to tackle the challenges of environmental change, its causes, impacts, and adaptive solutions.
Climate scientist at IIASA. IPCC AR7 CLA. Responsive climate projections. The guy behind the fair model and radiative forcing barchart. Occasional runner and guitarist.
github.com/chrisroadmap | cjsmith.eu
Professor and Director, Master of Public Policy, @BlavatnikSchool
@StAntsCollege @UniofOxford
How can we solve global problems effectively & fairly?
https://www.bsg.ox.ac.uk/people/thomas-hale
The Smith School of Enterprise and the Environment is a leading interdisciplinary academic hub at the University of Oxford focused upon teaching, research, and engagement with enterprise on climate change and long-term environmental sustainability.
Postdoc in Climate Damage Attribution at the Grantham Institute of Imperial College London | IPCC AR7 Lead Author
🔹 Loss and damage
🔹 Climate change adaptation
🔹 Extreme weather event impact attribution
PhD student Vrije Universiteit Brussel Climate Science | climate extremes, attribution, impacts, youth-led climate litigation
Climate Scientist at University of Melbourne. Interested in climate change and weather extremes. 🏳️🌈
Climate researcher at Leipzig University - Climate Causality & Attribution group (https://lim-climate-causality.github.io)
interested in atmospheric circulation and weather extremes | cloud lover
NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies Impacts Group co-Director making Earth information useful to people and systems at risk; IPCC AR6 WGI CLA + SYR Core Writing Team Member; Columbia University; AgMIP Science Coordinator & Climate Team Lead
🌱🌏 Researcher at @iiasa.ac.at 🌞🌱
Climate scientist at LMD-IPSL
Je suis Directeur de recherche CNRS en sciences du climat au laboratoire LSCE de l’Université Paris-Saclay, et auteur principal du 7eme rapport du GIEC. Mon expertise principale est l’attribution des événements météorologiques extrêmes
We are a world-leading department tackling global challenges through research and teaching. Follow us for updates from our SoGE community +
@ecioxford.bsky.social
@tsuoxford.bsky.social
@smithschool.ox.ac.uk
🌍 geog.ox.ac.uk
PhD | Attributing Extreme Weather Events to Climate Change ⛈️
Researcher working on health impact of climate change at University of Oxford. Former postdoc at University of Lincoln and @KNMI, PhD at LSCE/IPSL, @University Paris-Saclay.
The BMJ is patient centred, evidence based, and independent. Help us improve the health of our world with the best science, journalism, education, and comment.
Climate scientist, juggler. Bikes etc. Blogging at https://www.realclimate.org - data visualization, explainers, and debunking.
Weather and climate scientist focused on extreme events like floods, droughts, & wildfires on a warming planet. www.weatherwest.com














