This work could not have been possible without many people, including Trevor Bedford, Amanda Perofsky and @paredesmig.bsky.social, and all the hard work at @doh.wa.gov, @brotmanbaty.bsky.social and UW Virology to build a genomic sentinel SARS-CoV-2 surveillance with detailed linked metadata! 7/
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Finally, building on the expectation that infectors should tend to be observed first within pairs of identical sequences, we use the timing of sequence collection to understand the groups driving transmission. 6/
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Patterns of occurrence of identical sequences between age groups show assortativity in age mixing and transmission between generations. Jointly analyzing the ages & geographies of pairs of identical sequences, we find that age transmission patterns vary across spatial scales. 5/
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

The location of pairs of identical sequences is in line with expectations from cell phone derived mobility data. Outliers in the relationship between genetic and mobility data can be explained by large clusters of identical sequences shared between male prisons' postal codes. 4/
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
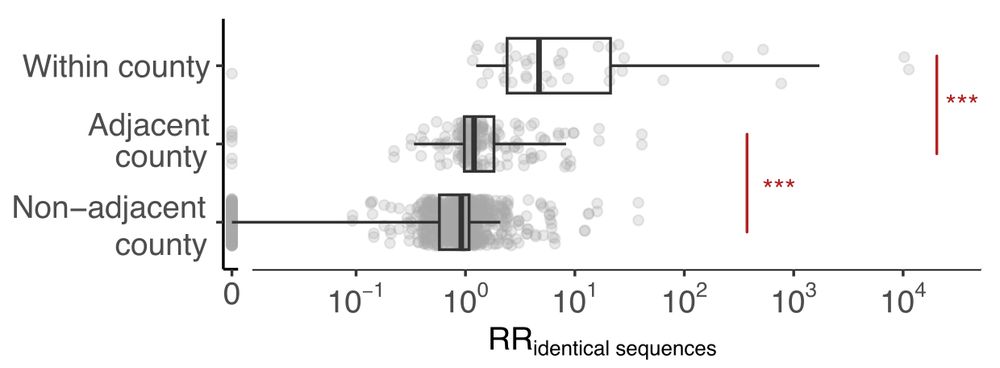
Applying the framework to more than 114,000 SARS-CoV-2 sequences collected through genomic sentinel surveillance in WA, USA between Mar 2021 & Dec 2022, we find a strong signal for local spread, with identical sequences having an increased risk of being observed between nearby counties. 3/
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
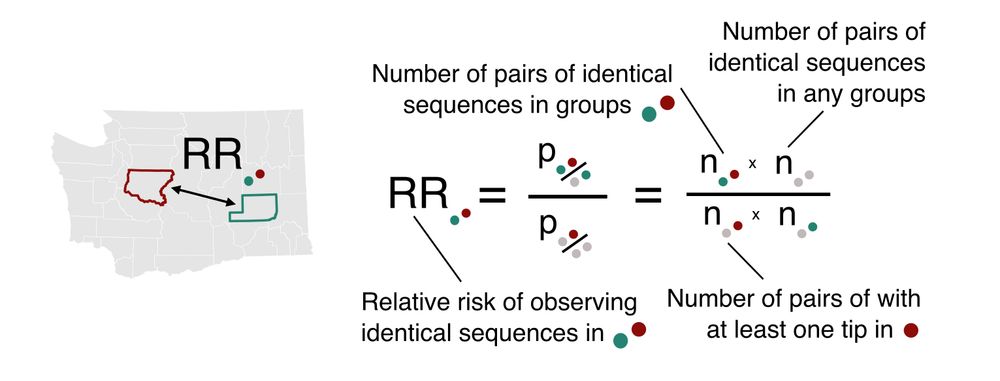
Genetic proximity between infecting viruses indicates epidemiological linkage. Here, we introduce a relative risk (RR) metric that quantifies how the number of pairs of identical sequences in two groups differs from what we expect from the sequencing effort. 2/
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Fine-scale patterns of SARS-CoV-2 spread from identical pathogen sequences - Nature
The analysis of pairs of identical SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences enables characterization of transmission patterns between geographies and age groups.
Pathogen genomes can provide insights into underlying disease transmission patterns but new methods are needed to analyze large genome datasets. Our work using identical pathogen sequences to characterize fine scale SARS-CoV-2 transmission was just published in @nature.com tinyurl.com/bdzk9xjj 🥳
05.03.2025 16:48 — 👍 41 🔁 17 💬 2 📌 2
PhD candidate at UW Seattle. I study how interactions between viruses shapes their evolution. Also 📷, 🎹, 📽️, 🐦
Assistant Professor, University of Washington, Genome Sciences.
Previous: JSMF Fellow, Berkeley EECS
♡: Computational biology, evolutionary dynamics, quantitative immunology
https://dewitt-lab.github.io/
[disclaimer: opinions mine] 🇺🇸🚫👑
Scientist.
Infectious disease dynamics · outbreak response · control measures · host mobility and contacts · digital epidemiology.
www.epicx-lab.com
Molecular evolution of pathogens | Wellcome Trust Fellow @biology.ox.ac.uk | Independent Investigator Data Analytics & Epi Group @psioxford.bsky.social | MedSci Fellow @lincoln.ox.ac.uk | Oxford DTP & Zoology alum | https://users.ox.ac.uk/~univ4613/
Bioinformatics, viral evolution, math models | UW / Fred Hutch | Loves science, gizmos, silly jokes, dogs | 🇮🇳→🇳🇬→🇬🇭→🇸🇬→🇺🇸
professor at Institut Pasteur. Bacterial genomics, vaccine-preventable diseases, antimicrobial resistance, bioinformatics and public heath applications. International capacity building and teaching. Klebsiella diphtheria whooping cough genomic librairies
Postdoc | Infectious disease modeling | Stanford School of Medicine
Views are my own
A research group at @mpiib.bsky.social, led by Matthieu Domenech de Cellès, focused on vaccines, interactions, and the seasonality of infectious diseases.
Website: https://www.mpiib-berlin.mpg.de/1953092/Infectious-Disease-Epidemiology
Full professor for Computational Evolution at ETH Zürich
PhD Student in AMR modelling at Institut Pasteur / UVSQ / Inserm 🦠 & Running addict 🏃🏻♀️
Assoc Prof at Imperial College London and at LSHTM
Respiratory viruses, bayesian inference, evidence synthesis, vaccines, outbreak analysis, photographer, urban gardener.
Stanford physician-scientist | Infectious diseases, epidemiology, modeling, and public health | Views mine | Lo Lab: http://profiles.stanford.edu/nathan-lo
Infectious Disease Research Unit at the University of Cambridge working on the emergence, spread, and control of pathogens. See more at: www.pdu.gen.cam.ac.uk Member starter pack: https://go.bsky.app/7PFMyLu
Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution
#ClimateChange, #Health #CoBenefits of #Climate actions, #Epidemiology, #PublicHealth, #Environment, academic activism.
Junior Pr. @ENS-PSL, formerly @Le Cnam (Paris) & Imperial College London.
Other interrests: infectious disease, occupational health.
Lead of GEEP at NIH/FIC | Phylodynamics | Bayesian inference | Viral evolution | Disease ecology | Views are my own





