Chatbots — LLMs — do not know facts and are not designed to be able to accurately answer factual questions. They are designed to find and mimic patterns of words, probabilistically. When they’re “right” it’s because correct things are often written down, so those patterns are frequent. That’s all.
19.06.2025 11:21 — 👍 36896 🔁 11374 💬 634 📌 961
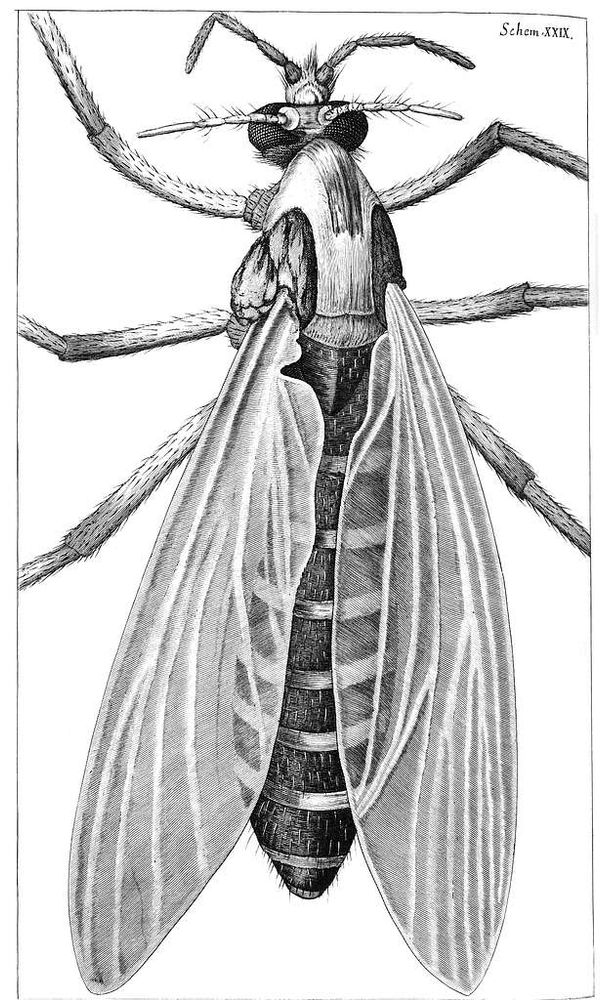
Drawing of gnat
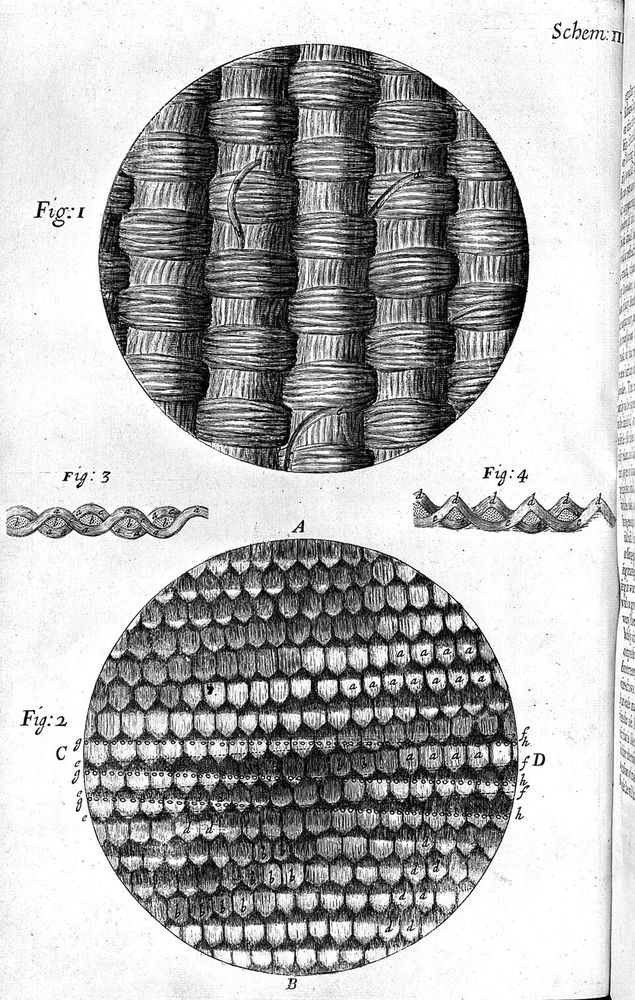
Drawing of silk
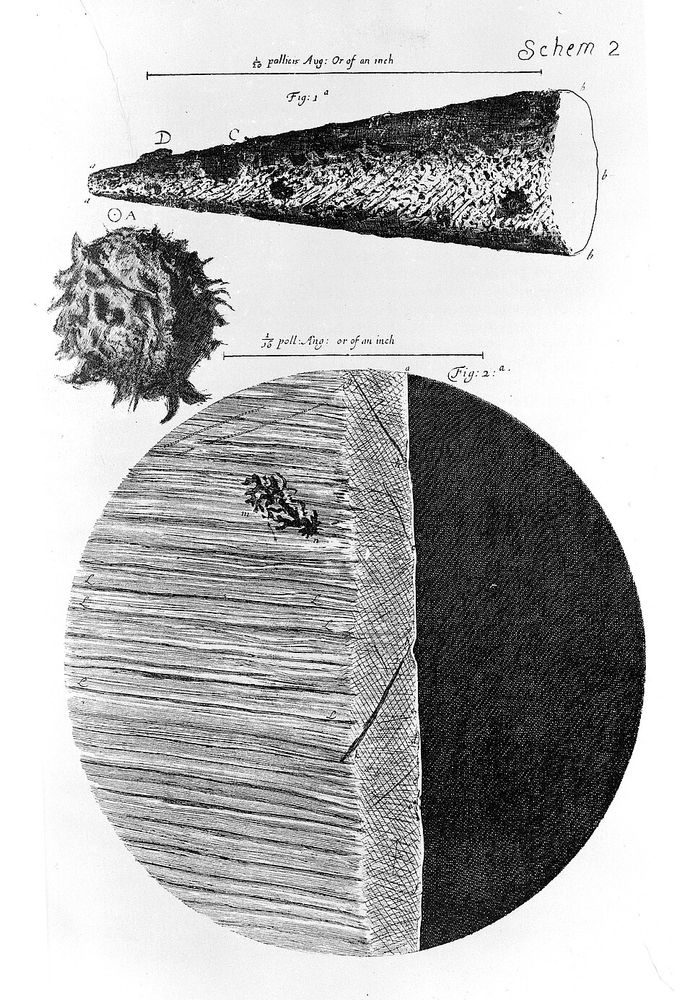
Drawing of a needle's point
Robert Hooke's drawings of objects under the microscope were so beautiful. These are from "Micrographia" in 1665
09.09.2025 12:25 — 👍 102 🔁 18 💬 5 📌 0

How many people died of COVID?
We likely undercounted, not overcounted COVID deaths
Persistent minimizing of the COVID death toll hits me especially hard in the #demography feels. To be clear:
➡️ Over one million Americans died of COVID-19.
➡️ Official COVID deaths were likely undercounted, not overcounted.
jenndowd.substack.com/p/how-many-p...
09.09.2025 11:02 — 👍 63 🔁 32 💬 4 📌 4
The psych job market may not be dead... but it is gravely injured 😬 So far it's looking like the Trump administration's attacks on higher ed/research are going to have more than 2x the impact on the job market as the covid-19 pandemic. #psychjobs #neurojobs #academicjobs
03.09.2025 18:27 — 👍 165 🔁 73 💬 14 📌 10
The AI and Education discourse is maddening. "Does AI improve learning?" is a dumb question. What form of "AI" and in what context? What do you mean by learning? Improving on a test or knowledge for use?
If you're asking that question, you don't actually care about a real answer.
02.09.2025 13:21 — 👍 14 🔁 5 💬 1 📌 2

Screenshot of title page of article published in the Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition titled "Expert Thinking With Generative Chatbots."
Great article with one of the best brief layperson introductions to AI v. LLMs that I’ve seen. And I love the exploration of whether and how LLMs’ are useful depends on the user’s level of expertise. #PsychSciSky #AcademicSky #EduSky
doi.org/10.1037/mac0...
25.08.2025 12:02 — 👍 30 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 2

Models as Prediction Machines: How to Convert Confusing Coefficients into Clear Quantities
Abstract
Psychological researchers usually make sense of regression models by interpreting coefficient estimates directly. This works well enough for simple linear models, but is more challenging for more complex models with, for example, categorical variables, interactions, non-linearities, and hierarchical structures. Here, we introduce an alternative approach to making sense of statistical models. The central idea is to abstract away from the mechanics of estimation, and to treat models as “counterfactual prediction machines,” which are subsequently queried to estimate quantities and conduct tests that matter substantively. This workflow is model-agnostic; it can be applied in a consistent fashion to draw causal or descriptive inference from a wide range of models. We illustrate how to implement this workflow with the marginaleffects package, which supports over 100 different classes of models in R and Python, and present two worked examples. These examples show how the workflow can be applied across designs (e.g., observational study, randomized experiment) to answer different research questions (e.g., associations, causal effects, effect heterogeneity) while facing various challenges (e.g., controlling for confounders in a flexible manner, modelling ordinal outcomes, and interpreting non-linear models).

Figure illustrating model predictions. On the X-axis the predictor, annual gross income in Euro. On the Y-axis the outcome, predicted life satisfaction. A solid line marks the curve of predictions on which individual data points are marked as model-implied outcomes at incomes of interest. Comparing two such predictions gives us a comparison. We can also fit a tangent to the line of predictions, which illustrates the slope at any given point of the curve.

A figure illustrating various ways to include age as a predictor in a model. On the x-axis age (predictor), on the y-axis the outcome (model-implied importance of friends, including confidence intervals).
Illustrated are
1. age as a categorical predictor, resultings in the predictions bouncing around a lot with wide confidence intervals
2. age as a linear predictor, which forces a straight line through the data points that has a very tight confidence band and
3. age splines, which lies somewhere in between as it smoothly follows the data but has more uncertainty than the straight line.
Ever stared at a table of regression coefficients & wondered what you're doing with your life?
Very excited to share this gentle introduction to another way of making sense of statistical models (w @vincentab.bsky.social)
Preprint: doi.org/10.31234/osf...
Website: j-rohrer.github.io/marginal-psy...
25.08.2025 11:49 — 👍 1009 🔁 288 💬 47 📌 22
It's so weird how LLMs know so much about things I don't know anything about, and yet make fundamental and basic errors about things I do know anything about. Oh well, I'm sure that's a coincidence.
11.08.2025 19:56 — 👍 439 🔁 108 💬 9 📌 3
All of Statistics is secret linear algebra.
We often don't do the linear algebra or don't know we are doing it because of assumptions.
Here is a more accessible resource for what you're really doing when you analyze human subjects data.
18.08.2025 11:57 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

The cover of Bayesian Data Analysis book

The cover of Regression and Other Stories book

The cover of Active Statistics book
All three books I've co-authored are freely available online for non-commercial use:
- #Bayesian Data Analysis, 3rd ed (aka BDA3) at stat.columbia.edu/~gelman/book/
- #Regression and Other Stories at avehtari.github.io/ROS-Examples/
- Active Statistics at avehtari.github.io/ActiveStatis...
02.08.2024 13:35 — 👍 327 🔁 134 💬 6 📌 4
Reminder that all three books I've co-authored are freely available online for non-commercial use (and the fourth will be, too)
11.08.2025 17:44 — 👍 153 🔁 50 💬 4 📌 1
Today I’ll be sharing some of my favorite Quarto learning resources 💻✨
Most of what I know, I learned thanks to the amazing work of others. So this thread is a small tribute to open educational content and the people behind it.
Let’s go! 👇
#QuartoPub #RLadies #RStats
16.07.2025 13:13 — 👍 42 🔁 17 💬 3 📌 0
At this point, I might as well --
Here's an infographic showing different ways to include age as a predictor. The top shows two extremes, just as a plain old numerical predictor (imposes linear trajectory) vs. categorical predictor (imposes nothing whatsoever). And then three solutions in between!
16.07.2025 12:33 — 👍 211 🔁 47 💬 22 📌 1
#statstab #386 {bayestestR} Evaluating Evidence and Making Decisions using Bayesian Statistics by @mattansb.msbstats.info
Thoughts: Want to start using Bayesian stats? Here is a quick but comprehensive guide in #R
#bayesian #bayes #mcmc #easystats #guide
mattansb.github.io/bayesian-evi...
14.07.2025 22:14 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 1 📌 0
Sometimes authors summarize their responses to 3-6 major points raised by the reviewers in their resub cover letters or at the top of their rebuttal letters. This is so super helpful to editors, because it brings us right up to speed after not having read the paper/reviews for months. THANKS!!
09.07.2025 16:15 — 👍 189 🔁 35 💬 8 📌 4
Hey #rstats,
What's your rule for splitting R scripts that form part of a wider analysis pipeline / project?
I usually write a single script which includes sections for each step from data cleaning to the final results, but it can become unwieldy when the script becomes long.
...
01.07.2025 21:57 — 👍 25 🔁 7 💬 11 📌 3

Experimentology cover: title and curves for distributions.
Experimentology is out today!!! A group of us wrote a free online textbook for experimental methods, available at experimentology.io - the idea was to integrate open science into all aspects of the experimental workflow from planning to design, analysis, and writing.
01.07.2025 18:25 — 👍 533 🔁 228 💬 9 📌 15

Positron with a chat panel open with a question about fixing a ggplot plot
Positron now supports a chat panel with Claude and it's pretty neat
04.06.2025 04:41 — 👍 90 🔁 15 💬 6 📌 1

I read *a lot* of scientific abstracts that are missing key elements.
Here are the 5 things an abstract needs:
1. Introduce the topic,
2. State the unknown,
3. Outline the method used to answer the question,
4. Preview the findings, and
5. Tell us what your work teaches us.
05.06.2025 13:36 — 👍 132 🔁 30 💬 11 📌 6

"Even when explicitly prompted for accuracy, most LLMs produced broader generalizations of scientific results than those in the original texts."
20.05.2025 00:37 — 👍 116 🔁 52 💬 3 📌 8
Say it after me: Chat GPT is not a search engine. It does not scan the web for information, it just generates statistically likely sentences. You cannot use it a search engine, or as a substitute for searching.
Now. Please never use an LLM for information searches ever again.
30.04.2025 23:31 — 👍 18566 🔁 6446 💬 44 📌 35

Why The Learning Styles Myth Persists And How It Damages Learning
New paper shows that learning style labels create harmful educational hierarchies
"The most troubling implication of the learning styles myth is that it invites low expectations. Labelling a student a “kinesthetic learner” or a “visual learner” easily becomes shorthand for what they can’t do."
24.04.2025 11:03 — 👍 6 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0

Three box plot/density plot/rainfall plots showing body weight for three penguin species, with Gentoo significantly higher. Colours also show density, and species. Background is light with dark text.

Three box plot/density plot/rainfall plots showing body weight for three penguin species, with Gentoo significantly higher. Colours also show density, and species. Background is dark with light text.
A quick plot for #TidyTuesday this week - celebrating the addition of the penguins data into base R 🐧 I used {ggdist} to plot the distribution of body weights with four different chart types in one! 📊
I couldn't quite decide whether I prefer the light or dark version💡
#RStats #DataViz #ggplot2
16.04.2025 15:18 — 👍 50 🔁 9 💬 4 📌 0

Increasing the playback speed of video lectures is popular amongst students as a time saving strategy, but does this negatively impact test performance? Here, we conducted a meta-analysis to examine the effect of increasing video lecture playback speed on content test performance. A meta-regression with robust variance estimation was used to aggregate data from 110 effect sizes, stemming from 24 studies of learning from lecture videos. The results demonstrated that increasing the playback speed of lectures can negatively impact content test performance, but this cost is small (and often non-significant) for speeds 1.5 x and slower. In addition, we found no evidence of moderation of this cost by a number of theoretically important variables (e.g., test type, lecture duration). These results contribute important insights into a popular study strategy and one that is likely to be a mainstay in educational settings for years to come.
Extremely useful and timely meta-analysis on the impact of increasing the speed of lecture recordings - 1.25x and 1.5x no/low cost that is probably balanced by increased engagement but 2x and 2.5x impairs learning.
#AcademicSky
link.springer.com/article/10.1...
13.04.2025 11:25 — 👍 47 🔁 19 💬 1 📌 1
#statsmeme
24.12.2024 07:20 — 👍 83 🔁 13 💬 6 📌 7
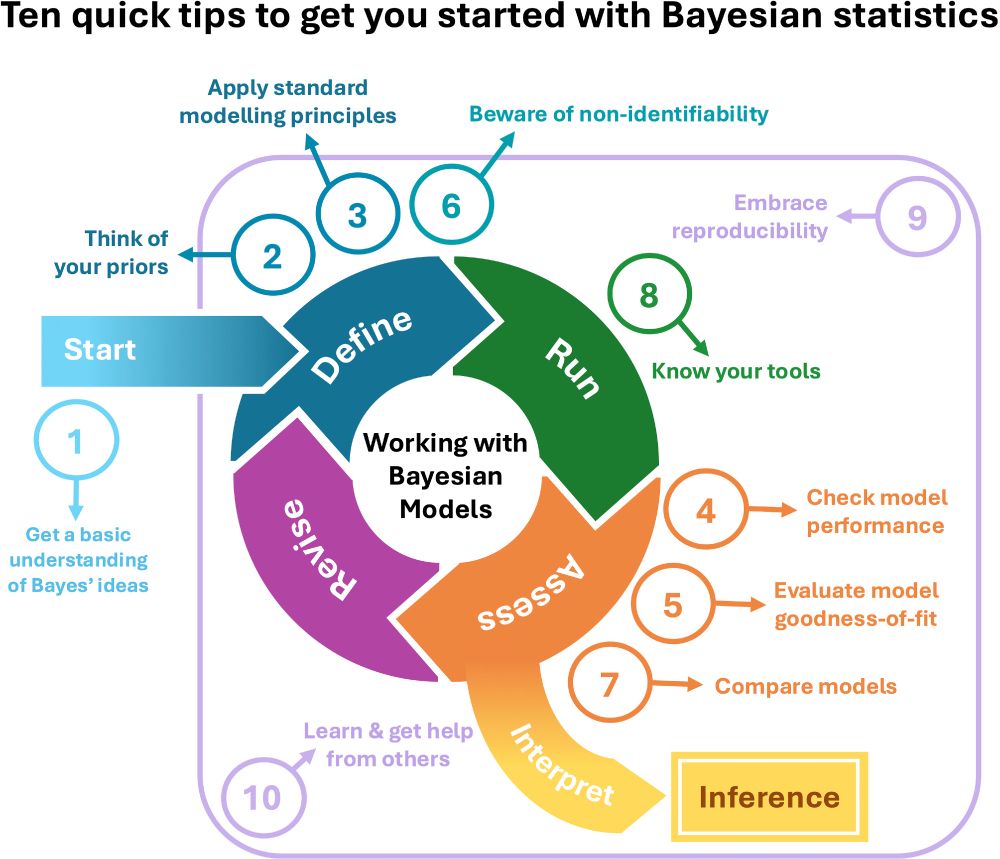
Graphical summary of 10 quick tips to get started with Bayesian statistics and how they fit into a larger view of an analytical workflow with Bayesian models.
🚨🎉 New paper "Ten quick tips to get you started with Bayesian statistics", hope you'll like it 😇🤗
✍🏽 w/ Andy Royle, Marc Kéry and Chloé Nater
🔗 dx.plos.org/10.1371/jour...
@plos.org @cnrsecologie.bsky.social @cnrsoccitanieest.bsky.social @umontpellier.bsky.social
11.04.2025 04:23 — 👍 162 🔁 69 💬 3 📌 3
Learned Society based in the UK.
We organise three scientific meetings + four funding rounds per year.
More information on our website - https://eps.ac.uk/
Assistant Professor in quantitative methods @mghinstitute, speech-language pathologist by training. Enthusiastic about quantitative methods in rehabilitation research and health services research for aphasia. 🥾🏔️🦮🍕
PREreview is a free and open platform for the crowdsourcing of #preprint reviews, a resource center, and a convener. Working to make science and scholarship more equitable, transparent, and collaborative.
To learn more, visit: https://linktr.ee/prereview
Posts about #rstats. Weekly newsletter digest at https://rstats.blaze.email. Maintained by @alastairrushworth.com.
Peer Community In Psychology is a free and fully transparent preprint recommendation service in the field of Psychology.
https://psych.peercommunityin.org/
Meta-scientist and psychologist. Senior lecturer @unibe.ch. Chief recommender @error.reviews. "Jumped up punk who hasn't earned his stripes." All views a product of my learning history. If behaviorism did not exist, it would be necessary to invent it.
Association for Interdisciplinary Metaresearch & Open Science. Our mission is to improve the quality of scientific research.
https://aimos.community/
#metasci #openscience #aimos
Professor at Temple University, PA. Interested in Psychological Assessment, Psychometrics, Statistics, Psychotherapy, R
The fastest growing independent news network in the world. We cover breaking news, politics, law and more. We are unapologetically pro-democracy.
Assistant professor @alleghenycol, memory and brain networks researcher | Former Postdoc with Eric Wassermann @NIH | @NuinComm and @smithcollege alum | She/her
Raising two kids, co-PI-lot of the Natural and Artificial Intelligence Lab & trying to do some funky research on the intersection of neuroscience, psychology and AI. Estonian
nail.cs.ut.ee
https://scholar.google.de/citations?user=FvFOzS8AAAAJ&hl=en&oi=a
🇨🇦 Associate Professor Learning Sciences; Faculty of Education; McGill University (he/him). Educational tech/games + math cog
mcgill.ca/tlc
Full Professor @ FLACSO Mexico. I study comparative public policy, water governance, waste management, public administration, environmental politics, homelessness, eldercare and care work, mixed/experimental methods.
MetaROR is a community initiative led jointly by RoRI and AIMOS. It provides a platform that leverages the publish–review-curate model to improve the dissemination and evaluation of metaresearch.
Academy Professor in computational Bayesian modeling at Aalto University, Finland. Bayesian Data Analysis 3rd ed, Regression and Other Stories, and Active Statistics co-author. #mcmc_stan and #arviz developer.
Web page https://users.aalto.fi/~ave/
🧮 Statistics & data science
💊 Clinical trials & R&D & Epidemiology
💻 R enthusiast
👩💻 Stats @ loyal.com
https://jesslgraves.github.io
Instats is a mission-driven organization devoted to improving research practices through expert-led training for PhD and post-PhD researchers across a broad range of fields, methods, and theoretical orientations across the globe.
Curating #altac jobs for advanced degrees | Primarily Humanities & Social Sciences | majority US, some UK | https://altacjobs.com/
The Strategic Education Research Partnership generates innovative, scalable solutions to our schools’ most pressing problems through sustained collaborations among education researchers, practitioners, and designers.
Virtual conference to bring together a multidisciplinary group of researchers and stakeholders to discuss advancements, challenges, and future opportunities related to Big Team Science
bigteamscienceconference.github.io