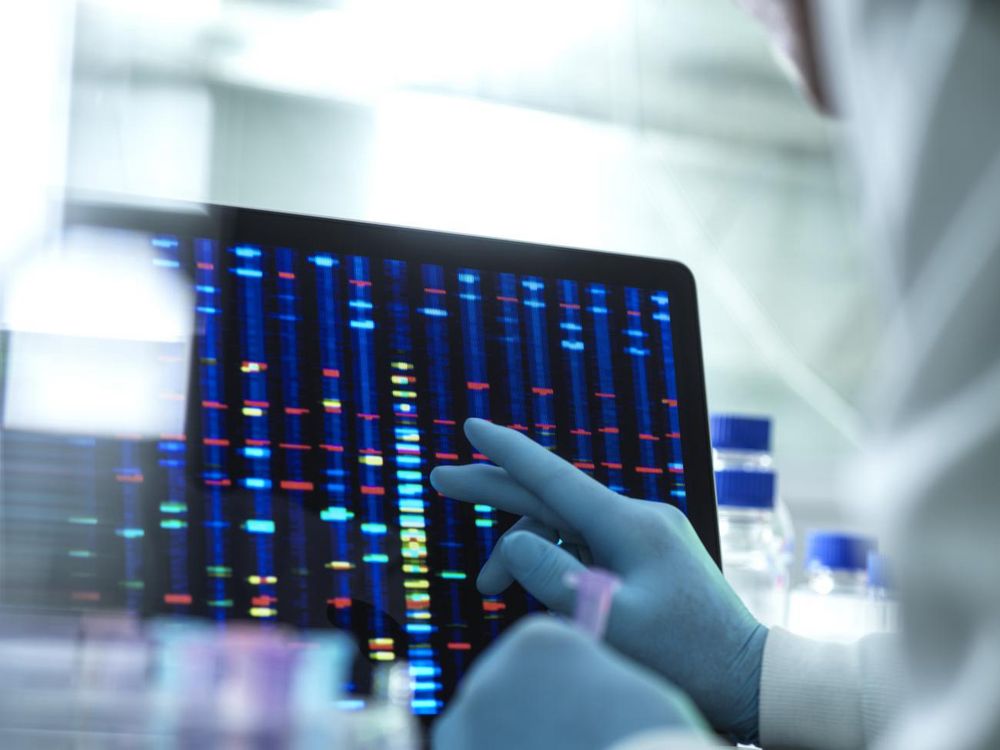
A review of the functions of human #CyclinDependentKinases, highlighting their roles in #cellcycle control, disease progression, & the therapeutic potential of #CDKInhibitors in #cancer & other diseases. @gusbald.bsky.social
#STTT: doi.org/10.1038/s413...
11.10.2025 16:30 — 👍 4 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0

Great presentation at #CRO_Aviano_IRCCS by @biancastellac.bsky.social on genetic and #epigenetic alterations in #breast tissue. Thank you Biancastella, it was wonderful have you in Aviano!
10.09.2025 18:07 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 1

This review summarizes the functions of #CyclinDependentKinases (CDKs), discusses their potential roles and deregulation in human pathologies and underscores the role of CDK inhibitors as standard therapies in #cancer. #medsky @gusbald.bsky.social @gustavo_baldassarre
#OpenAccess: buff.ly/NA2B1Fs
13.08.2025 16:30 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Sunset from #Monte_Faito #Campania #Italy. From right to left you can admire the Vesuvius Vulcan, Monte di Procida, the islands Procida, Ischia and Capri and the peninsula Sorrentina. This is the magnificent #gulf_of_Napoli
10.08.2025 01:52 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Sunrise at #Scilla #Calabria Italy! Just beautiful!!
10.08.2025 01:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Death-ision: the link between cellular resilience and cancer resistance to treatments
Just out in #Molecular_Cancer a beautiful journey with Ivana de la Serna and Francois Vallette discussing #cancer_cells #clonal_evolution and #resistance to treatments from 3 different and complementary points of view. Hope you will enjoy read this review as we enjoyed writing it.
rdcu.be/emfur
16.05.2025 13:29 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0


Free registration open for BIG2025.
Limited on site places. All info on: 👇
ecm.meetingsrl.eu/BIG2025/defa...
Registration for ITALIAN PARTICIPANT 👇
ecm.meetingsrl.eu/BIG2025/defa...
Registration forFOREIGN PARTICIPANT 👇
www.meetingsrl.eu/registration...
Meet the speakers
See you in Venice
10.05.2025 17:51 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Here we are!
Registration for BIG 2025 is now open. All info on: 👇
ecm.meetingsrl.eu/BIG2025/defa...
Registration for ITALIAN PARTICIPANT 👇
ecm.meetingsrl.eu/BIG2025/defa...
Registration forFOREIGN PARTICIPANT 👇
www.meetingsrl.eu/registration...
See you in Venice
09.05.2025 17:30 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

The 4th edition of BIG is approaching. An exceptional panel of speakers discussing the novelties in #translational and #clinical #gynecology_oncology. Free registration but limited places. Below, you can see the venue and meet the organizers. Stay tuned for updates. See you in #Venice
26.04.2025 10:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 1
A Vaccine For Pancreatic Cancer Continues To Show Promise
In a small trial, nearly half of pancreatic cancer patients who received an mRNA vaccine for the disease had no relapse three years later.
90% of people diagnosed with pancreatic cancer die from the disease. That's why the medical community is excited about the results of a small trial in which nearly half of the pancreatic cancer patients who received an mRNA vaccine for the disease remained relapse-free three years later.
16.03.2025 14:09 — 👍 32831 🔁 7721 💬 831 📌 836

The 4th edition of BIG is approaching. Don’t miss the opportunity to joining us and meet an exceptional panel of speakers in the wonderful city of Venice. Stay tuned for further updates
06.03.2025 10:12 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Right now, I can't open:
www.nlm.nih.gov
ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
01.03.2025 21:50 — 👍 18 🔁 11 💬 12 📌 5
Europe PMCHome - Europe PMC
Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.
As we can expect PubMed dysfunction more and more or to be swamped with fake journals I suggest you get acquainted to this nice alternative: europepmc.org
02.03.2025 07:54 — 👍 433 🔁 156 💬 11 📌 8
Europe PMCHome - Europe PMC
Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.
Remember, EuropePMC is actually better than #PubMed because it includes ALL preprints in search results, not just those including NIH-funded research.
europepmc.org
02.03.2025 08:28 — 👍 483 🔁 178 💬 12 📌 9

Enjoying skiing on Dolomiti alps in a sunny, cold Saturday with old friends! What a day!
15.02.2025 18:24 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0


Positano and Capri from Monte Faito, Italy
09.02.2025 13:03 — 👍 6 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Cyclin-dependent protein kinases and cell cycle regulation in biology and disease
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy - Cyclin-dependent protein kinases and cell cycle regulation in biology and disease
What a great start to 2025 having our review on the role of hashtag#CDKs in human physiology and diseases just published in #Signal_Transduction_Targeted_Therapies!
Here is the link to the open access article 👇
rdcu.be/d6a4g
A big effort of the lab but we learnt a lot!
I hope you will enjoy it
14.01.2025 20:33 — 👍 10 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0

Cyclin-dependent protein kinases and cell cycle regulation in biology and disease
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy - Cyclin-dependent protein kinases and cell cycle regulation in biology and disease
What a great start to 2025 having our review on the role of hashtag#CDKs in human physiology and diseases just published in #Signal_Transduction_Targeted_Therapies!
Here is the link to the open access article 👇
rdcu.be/d6a4g
A big effort of the lab but we learnt a lot!
I hope you will enjoy it
14.01.2025 20:33 — 👍 10 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases and cell cycle regulation in biology and disease.
Published in Signal transduction and targeted therapy
Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs) are crucial for cell division and exist in 20 variations, each with unique roles. Their malfunction is linked to diseases like cancer and Alzheimer's. CDK inhibitors are now cancer treatments, and exploring their use in other diseases could help improve patient care.
13.01.2025 08:00 — 👍 1 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
This paper is the result of an incredibly fun collaboration with Sandro Santagata and Peter Sorger. Led by an amazing postdoc @tanjinakader.bsky.social and JiaRen Lin, we provide a pre-cancer atlas of Fallopian tube precursors to High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. The data is also on cbioportal!
24.12.2024 17:40 — 👍 24 🔁 5 💬 0 📌 0
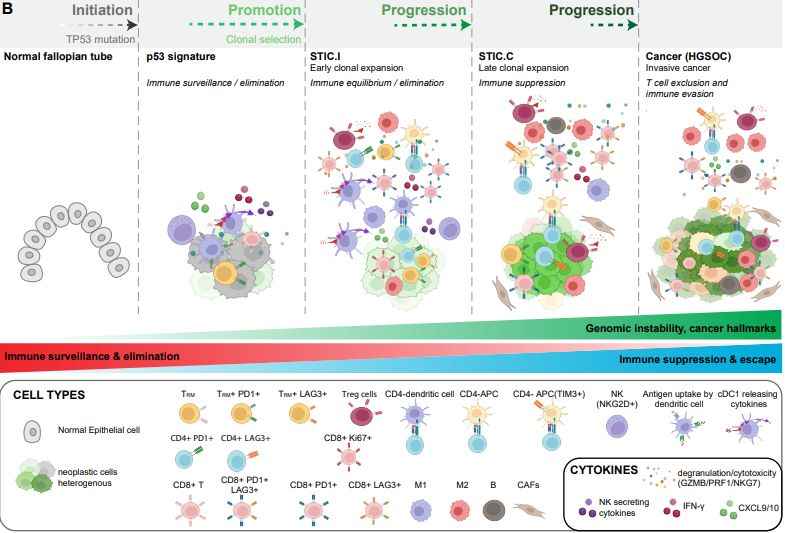
Schematic representation of HGSCO progression, emphasizing the temporal development of hallmark cancer features and the dynamic interplay and interactions between immune cells and precancer/cancer
cells. Cancer often starts with oncogenic changes (mutations, aneuploidy, and other cancer hallmarks), under selective pressure. These cells may remain latent for decades. Only a subset of these
“phenotypically normal” but mutated clones undergo clonal expansion and acquire additional mutations, ultimately developing into cancer. Early on, despite limited genomic instability, innate immune responses, including the NK-cDC1-CTL axis and tissue-resident memory T cells (TRM), help contain p53 signature cells. Increasing aneuploidy or extrinsic factors can enhance immune surveillance, potentially eliminating precancer clones before significant proliferation occurs. During early STIC expansion, there is pronounced IFN response activation, with activated cDC1 and APCs, and NK cell-secreted chemokines, further attracting cDC1. This environment suggests active immune surveillance and is accompanied by interactions among APCs, activated CD4+, and CD8+ T cells. However, immunosuppressive cells, such as M2-like macrophages and Tregs, also emerge, indicating a complex equilibrium where cytotoxic and suppressive forces coexist. As STIC lesions advance, there is a reduction in CD8+ T cells and the interactions between APCs and CD4 T cells, along with an increase in exhausted CD8+ CTL and CD4+ cells expressing LAG3, almost no NK and cDC1 cells, and more suppressive APCs. The transition from STIC to overt cancer involves hallmark mechanisms such as TGF-β signaling, which excludes CTLs, changes in cytokine and fibroblast profiles, and induction of EMT and migratory programs. Dotted arrows indicate the hypothetical timing of these events, suggesting a prolonged interval from p53 signature to early STIC, followed by a more rapid progression from early to late STIC.
Now online in Cancer Discovery: Multimodal Spatial Profiling Reveals Immune Suppression and Microenvironment Remodeling in Fallopian Tube Precursors to High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma - by Tanjina Kader, Jia-Ren Lin, Clemens Hug, Ronny Drapkin, Sandro Santagata, et al. doi.org/10.1158/2159...
20.12.2024 15:54 — 👍 34 🔁 6 💬 2 📌 2

Il mondo novax ha costruito una intera narrazione sull'efficacia e utilità dell'idrossiclorochina e azitromicina contro COVID-19. Ora lo studio "Principe" è stato ritirato.
17.12.2024 18:56 — 👍 321 🔁 94 💬 14 📌 5
Cancer genetics at Imperial College London
- working on #breastcancer and #coloncancer, and a mix and match of cool side projects
Global Healthcare Services Manager @ Hyland | Passionate about healthcare, digital health, AI & cloud | BSc, PRINCE2, MSP, L6σ Green Belt | Opinions are my own | https://linktr.ee/paulcochrane
COR2ED develops high-quality Independent Medical Education programmes for HCPs globally.
Visit our website: https://cor2ed.com/
Read the Community Guidelines: https://t.co/KZbQi7TR4U
#MedEd #IME #MedicalEducation
A career network featuring science jobs in academia and industry.
Visit our platform at www.science.hr
Executive Editor/Team Leader Open Access Science Journals Sage Publishing
Opinions = mine
http://linkedin.com/in/jlovick-editor
#oncology #cancerresearch #medicine #biology #cardiology #neurology #microbiology #publichealth #healthcare #technology
A platform for life sciences. Publications, research protocols, news, events, jobs and more. Sign up at https://www.lifescience.net.
Exploring cool places with cool minds
University of Colorado Anschutz gynecologic oncologists and researchers committed to advancing the future of women’s health. Focused on innovating early detection, prevention, and treatment through cutting-edge research. #GynOncology #CUAnschutz
FGB promotes therapeutic innovation from the earliest phases of research and the education of new generations of physician-scientists in Oncology
Dad, husband, President, citizen. barackobama.com
Assistant Professor @OSUCCC
#CancerInformatics, #ncRNAs, #Epitranscriptomics, #HERVs, #LungCancer, #ML #AI
EMBO is the organization of more than 2,100 leading researchers that promotes excellence in life sciences in Europe and beyond.
https://www.embo.org/
scientist, structural biologist, poet, reader, gardener, cat lover
🧪🧬💎✒️📚🎨🌿🐾🏳️🌈
she/her
all views my own
https://www.unimedizin-mainz.de/medizinische-mikrobiologie-und-hygiene/
#DGfI #DGHM #EFIS #IUIS / 🦖☄️🦠🔬🧫🐁🧍/ #immunometabolism / #host-pathogen interaction / 🇪🇺 / #UM #JGU: excellence in basic research and health care / own views only
Medicinal chemistry lab @IKCU, Faculty of Pharmacy, Izmir.
Drug discovery studies; design and synthesis new compounds as antileishmanial, antibacterial, anticancer, antiparasitic, FABPi, TYK2i
@istanbulluh.bsky.social
@huseyinkosker.bsky.social
Assistant Professor, ovarian cancer genetics & epigenetics, mom of 2, cooking and gardening
Opinions are my own, and not representative of my employer.
jessicalanglab.github.io
European Research Council, set up by the EU, funds top researchers of any nationality, helping them pursue great ideas at the frontiers of knowledge. #HorizonEU


























