Thanks for the question! I think this result is consistent with the previous result (figure 3) where we found response eQTLs share more similar genomic features with disease-associated locus.
27.05.2025 15:24 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Heading to Minneapolis next week to share this work at STATGEN2025!
17.05.2025 21:23 — 👍 5 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0
Thank you!
06.05.2025 15:09 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

This is such an exciting project! Huge thanks to Wenhe Lin, @jmpopp.bsky.social, @radster95.bsky.social, Olivia Allen, Jonathan Burnett, and to @alexisbattle.bsky.social, @ygilad.bsky.social, and Matthew Stephens for their mentorships! Check out our preprint for more!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 10 🔁 1 💬 2 📌 0
9/n We expect that by continuing to broaden the contexts to include a wider range of cell types, time points, and environmental exposures, we will uncover more context-dependent and functionally relevant loci, which will enhance our ability to explain disease risk.🌐🧬
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
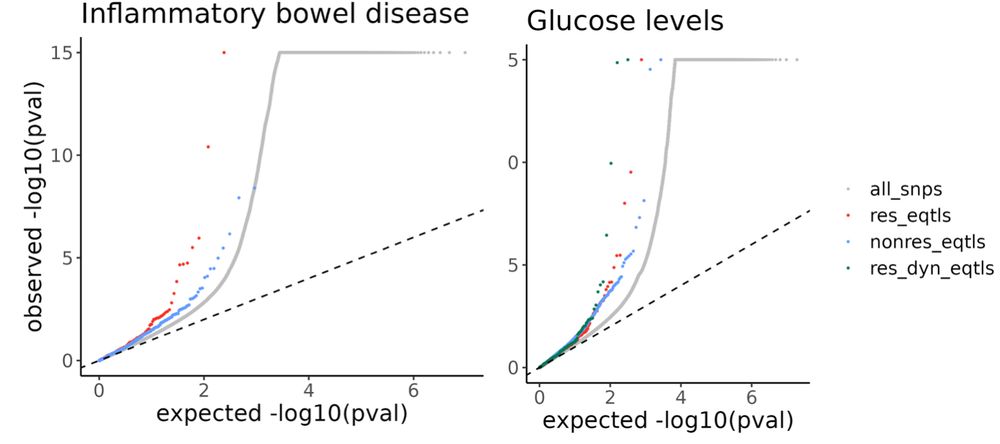
8/n We found that incorporating more context-specificity enabled us to identify regulatory effects that may enhance the functional understanding of GWAS associations. These effects would have been missed had we only explored a single tissue type or not accounted for GxE.
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
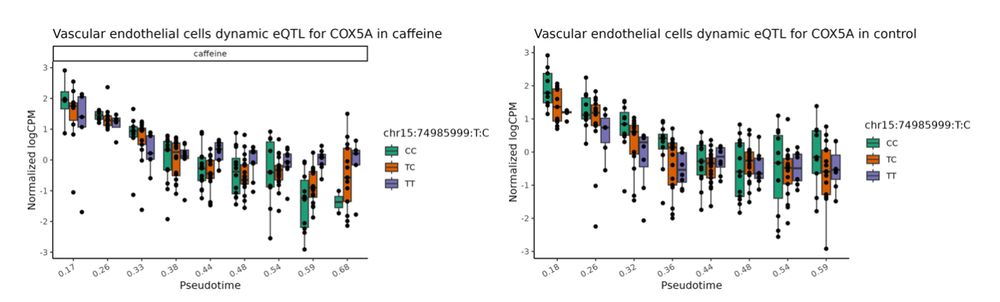
7/n We also mapped dynamic response eQTLs that vary their regulatory effects throughout cellular differentiation. Example: A caffeine-response dynamic eQTL affecting COX5A emerged exclusively in late-stage vascular differentiation. ☕️🩸✨
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 1
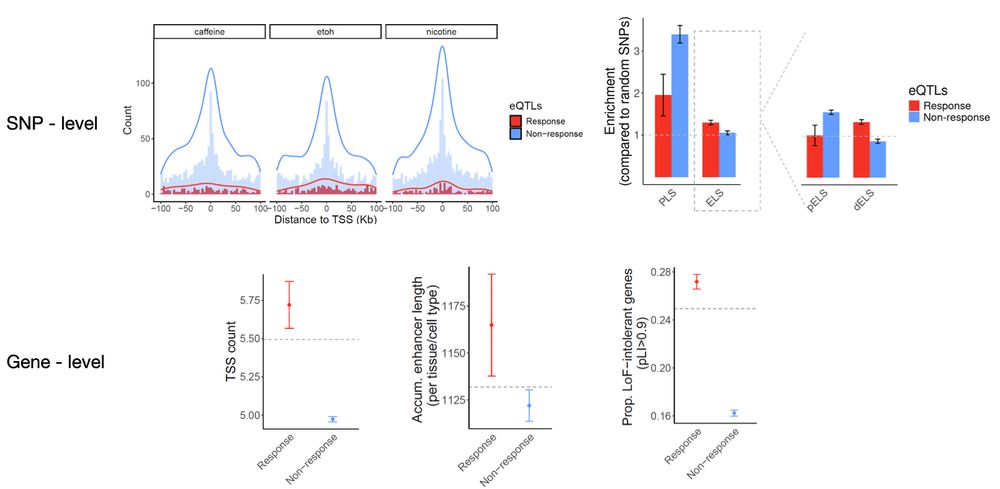
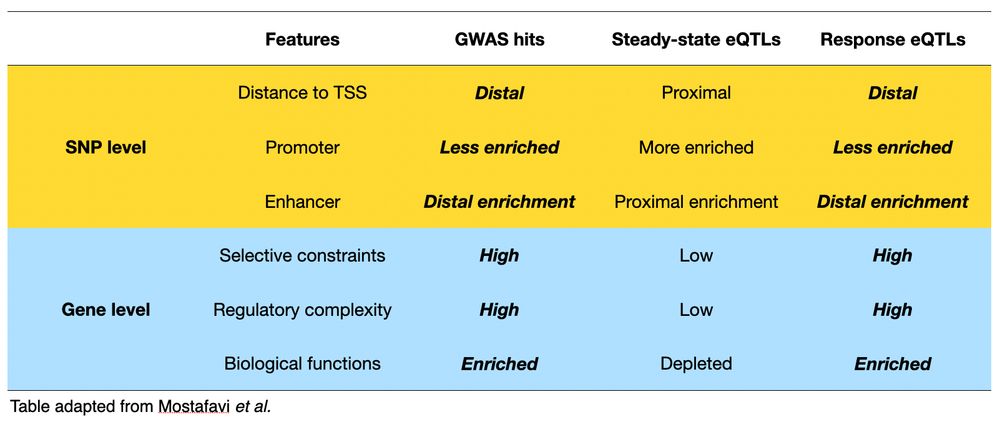
6/n Importantly, we found that response eQTLs share important properties with disease-associated GWAS loci, including similar regulatory landscapes, gene-level constraint, and functional enrichments.📍🔍
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 5 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
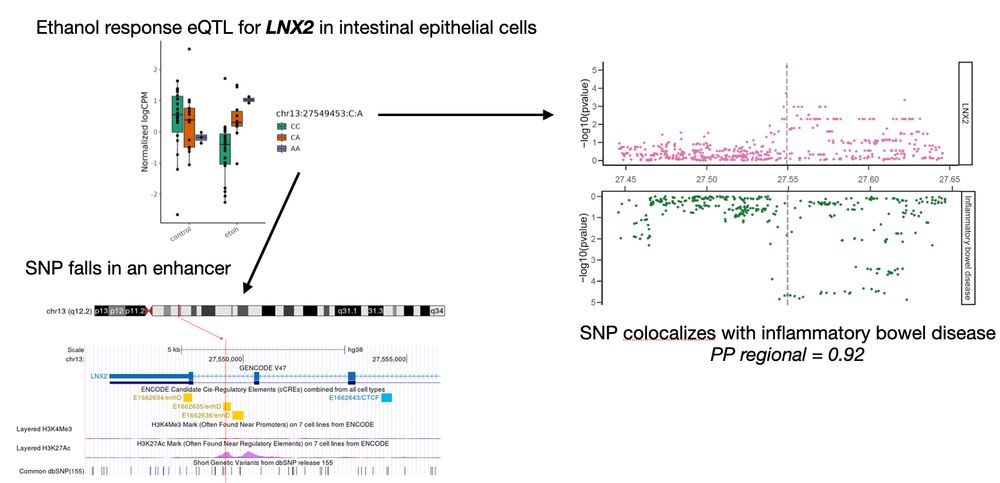
5/n suggesting a functional mechanistic connection between a gene regulatory variant, ethanol exposure, LNX2 expression in the intestinal epithelium, and IBD. 🍷➡️🩺
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
4/n For example, an ethanol-specific eQTL for LNX2 found only in intestinal epithelial cells is located in an enhancer element and aligns closely with a genetic risk locus for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
3/n We identified hundreds of response eQTLs, effects change in response to exposure of common environmental factors. These context-dependent eQTLs are often missed in conventional eQTL assays using untreated samples.🌡️🧬
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
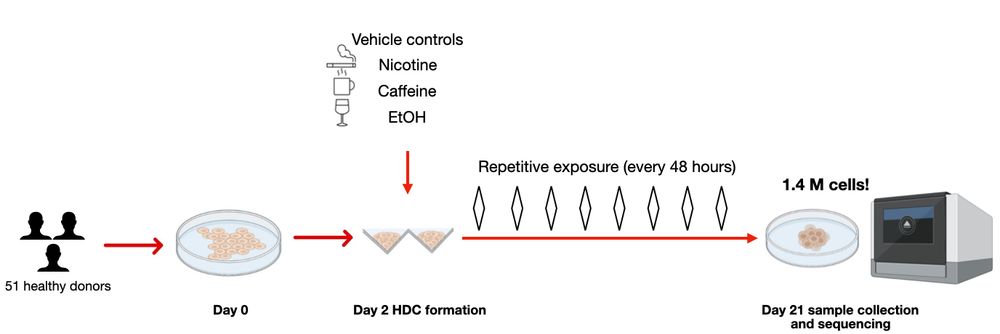
2/n Here, we utilized heterogeneous differentiating cultures (HDCs) to do this. Using single-cell RNA-seq data from 1.4 MILLION cells across 51 genetically diverse individuals, we studied eQTLs under environmental exposures: caffeine, ethanol, and nicotine. ☕️🍷🚬
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
1/n 🚨Very excited to share our recent work!🚨
To understand gene regulation across diverse environmental conditions and cellular contexts, we treated a broad array of human cell types with three environmental exposures in vitro.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
05.05.2025 19:07 — 👍 36 🔁 15 💬 3 📌 4
Ph.D student @ Harvard BIG
Chair, Computational BIology and Medicine Program, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network.
Associate Professor, Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto.
Disclosures: https://github.com/michaelmhoffman/disclosure/
Associate Professor of Biostatistics and Biomedical Engineering at Johns Hopkins. stephaniehicks.com
Origins and consequences of genome mutation; software for genomic discovery.
Prof. and Chair of Human Genetics at U. of Utah.
https://www.genetics.utah.edu/
http://quinlanlab.org
Associate prof @JHUBME. Doing #spatialtranscriptomics #compbio #dataviz #rstats. Founder @cuSTEMized. Editor @PLOSCompBio. Alum @HarvardDBMI @mbhsmagnet.
EMBO Postdoctoral fellow at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney, Australia.
Previously EMBL-EBI, Wellcome Sanger Institute and University of Cambridge in Cambridge, UK.
All things single-cell, genetics & genomics.
CS PhD student in the Battle Lab at JHU
Bloomberg Distinguished Professor at Johns Hopkins University. http://schatz-lab.org
Population & Human Genetics
Physician-scientist @stanford medicine, AHFTC, genomics of rare disease, cardiovascular genetics, exercise multiomics, cardiomyopathy, novel therapeutics and data. #motrpac #UDN #Gregor #CFDE . Husband, kids and cats, mountains and snow. Resist hate.
Professor @ JHU, statistical genomics, www.hansenlab.org
VP for Research, T.H. Smoot Professor
Depts Chemical and Biomolecular Engn, Pathology, Oncology, INBT
Johns Hopkins University
3D multi-omic, CAR T therapy, cell migration and mechanics
Lab: https://wirtzlab.johnshopkins.edu
A leading peer-reviewed genomics journal. https://genome.cshlp.org
Submit: http://submit.genome.org
Professor of Computer Science @ JHU. https://www.langmead-lab.org/ https://www.youtube.com/BenLangmead
Finished a human genome, working on a few more 👨💻
Lab: https://genomeinformatics.github.io
Posts are my own
Genomics, Machine Learning, Statistics, Big Data and Football (Soccer, GGMU)
AI4Science researcher. Associate Professor @CSHL. My lab advances AI for genomics and healthcare!
http://koo-lab.github.io
Chief AI Officer @ UHN; Assistant Prof. @ U of Toronto; CIFAR AI Chair @ Vector Institute; AI & Biology






