Sorry I don’t know of one! If UK based I’d ask Maha Albur from Bristol who will know
01.02.2025 07:54 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Emma McGuire
@emsmcg.bsky.social
Microbiologist and ID doc at UCLH. Mum of 2 small people.
@emsmcg.bsky.social
Microbiologist and ID doc at UCLH. Mum of 2 small people.
Sorry I don’t know of one! If UK based I’d ask Maha Albur from Bristol who will know
01.02.2025 07:54 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Do Antimicrobial Stewardship ward rounds reduced use of target antibiotics?
#AMR #antimicrobials 🧪
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

Figure 1 Mechanisms of action of key antibiotics for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections Several classes of antibiotics are available for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Their mechanisms of action focus on key aspects of bacterial cell function, such as inhibiting cell wall synthesis (ie, β-lactams and fosfomycin) and function (ie, polymyxins), protein synthesis (ie, aminoglycosides and tetracyclines), folic acid synthesis (ie, trimethoprim and sulphonamides), and DNA replication (ie, fluoroquinolones). Because of increasing antimicrobial resistance, novel antibiotics have been developed to overcome some of these mechanisms; for example, by inhibiting antibiotic modification (ie, β-lactamase inhibitors) or by altering entry pathways (ie, cefiderocol, which enters via iron transporters). DHF=dihydrofolic acid. PABA=para-aminobenzoic acid. THF=tetrahydrofolate.

Figure 2 Diagnostic testing of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria Diagnosis of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections involves both species identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing. Although clinical microbiology laboratories have undergone automation of these processes and have seen the introduction of proteomic methods, such as MALDI-TOF, delays in turnaround time remain and might affect patient outcomes. New biochemical, molecular (eg, PCR), automated microscopy, and hybridisation-based rapid diagnostics now allow faster detection of antimicrobial resistance, including by testing clinical samples directly. Emerging technologies are seeking to improve both the speed of testing and provide more detailed information regarding the underlying mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance. MALDI-TOF=matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight.

Figure 3 Summary of new antibiotic agents for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections Green=antibiotic is reliably active in vitro and guideline recommended. Yellow=variable activity; antibiotic might be effective if in vitro susceptibility is shown, clinical data might be lacking to support routine use. Red=not recommended, likely absence of in vitro susceptibility. IV=intravenously. *Administered simultaneously via Y-site administration. †Administration was studied in combination with imipenem–cilastatin.
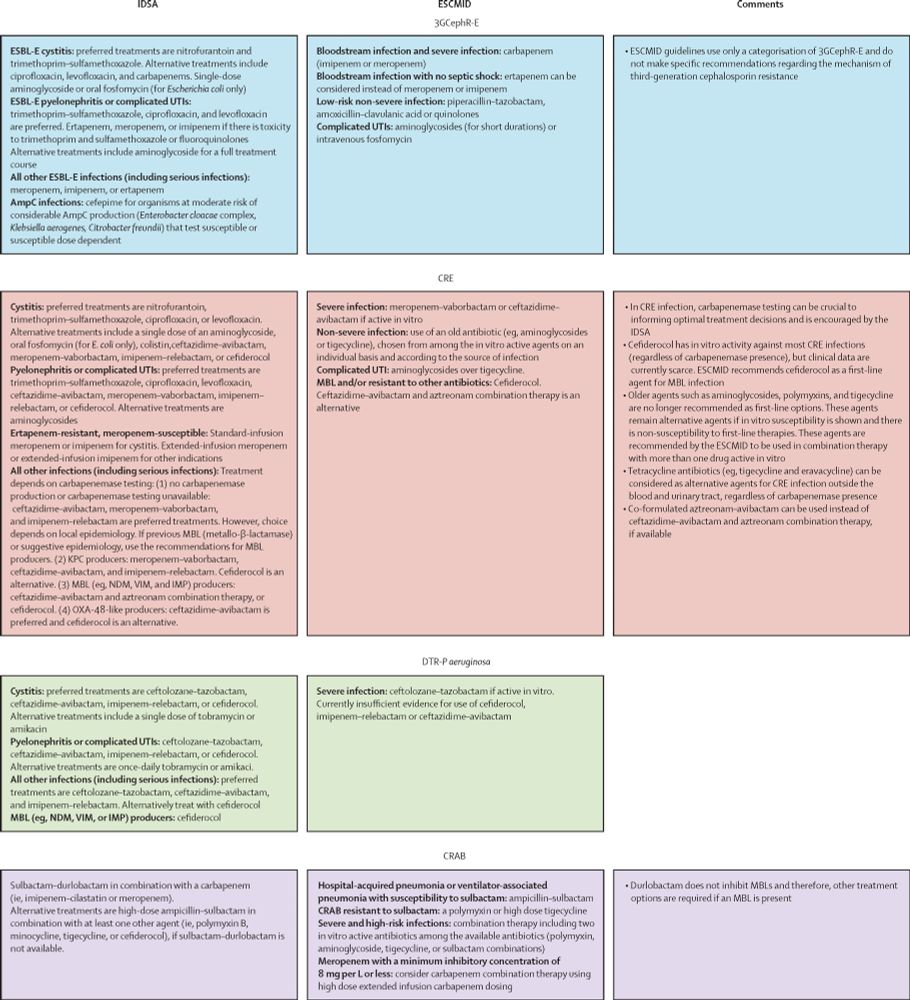
Figure 4 Summary of IDSA and ESCMID guidelines for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections 3GCephR-E=third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales. AmpC-E=β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales. CRAB=carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. CRE=carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales. DTR-P aeruginosa=difficult-to-treat resistant-Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ESBL-E=extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales. ESCMID=European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. IDSA=Infectious Diseases Society of America. MBL=metallo-β-lactamase. UTI=urinary tract infection.
#IDSky #MedSky required reading:
Multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections
Nenad Macesic, Anne-Catrin Uhlemann, Anton Peleg
Review in @thelancet.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1016/S014...
Ooh figure 4 looks especially handy thanks for sharing! 😍
17.01.2025 16:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Antibiotic use increased 16.3% since 2016, driven largely by economic growth in LMIC. Despite concerns on AMR, effective measures like stewardship programs, public awareness, improved infection prevention have helped some high-income nations limit their consumption.
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

Start smart, then focus
The UK slogan as applicable now as when first coined, in the world of antimicrobial stewardship
#AMS #AMR #IDSky #ClinMicro @rlester.bsky.social
academic.oup.com/cid/advance-...

The HPV vaccine has been recommended in the US since 2006. New study out today shows that cervical cancer deaths in young women in the years that followed have plummeted, decreasing 15% per year from 2013-2015.
jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...

academic.oup.com/jac/advance-...
Just published the first case of penicillin-resistant group B Streptococcus isolated from a patient in the UK - though of note this was from 2016 and we have not seen any further penicillin resistance since - however a salient reminder that #AMR is ever a possibility