Thrilled to share our story in its final form! nature.com/articles/s41... 💥 After ~10 years, we show that BMAL1 represses transposons via chromatin regulation in embryonic stem cells—rather than circadian rhythms as in adult tissues.
10.09.2025 14:26 — 👍 18 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 1

Computational image analyst (m/f/d)
The Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster, Germany, has an opening for a
My lab @mpi-muenster.bsky.social is looking for a computational biologist with a passion for imaging and spatial biology. A staff scientist position with long-term perspective! Apply and spread the word 🙏 jobs.mpi-muenster.mpg.de/jobposting/0...
12.09.2025 06:17 — 👍 87 🔁 86 💬 1 📌 1
Thanks a lot, Maria!
25.04.2025 17:21 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Thanks for all the support and discussions, Sara!
23.04.2025 20:44 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
20/ Biostatistics/Bioinformatics IRB facility scientists from @irbbarcelona.org + best colleagues and friends Paloma Solá @guiomarsolanas.bsky.social @circatom.bsky.social @aznarbenitahlab.bsky.social
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 5 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
19/ Thanks for making it until the end! Last but not least, most special thanks go to all the people who helped this project finally make it to a written article, including our mechanobiology expert collaborators @sarawickstrom.bsky.social @katemiro.bsky.social +
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
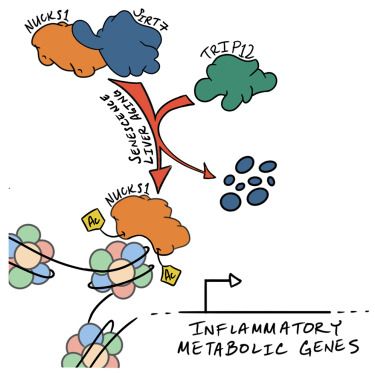
18/ During ageing, following YAP activation, BMAL1-YAP complex is directed to enhancers of inflammation genes, many of which are regulated by p65. All this leads to an increase in expression of these genes, contributing to the transcriptional rewiring of epid cells during ageing.
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
17/ Finally, based on all the above-mentioned results, we propose the following molecular mechanism:
In adult epidermis, during homeostatic conditions, BMAL1 and YAP coordinately bind to enhancers of identity and maintenance genes.➕
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
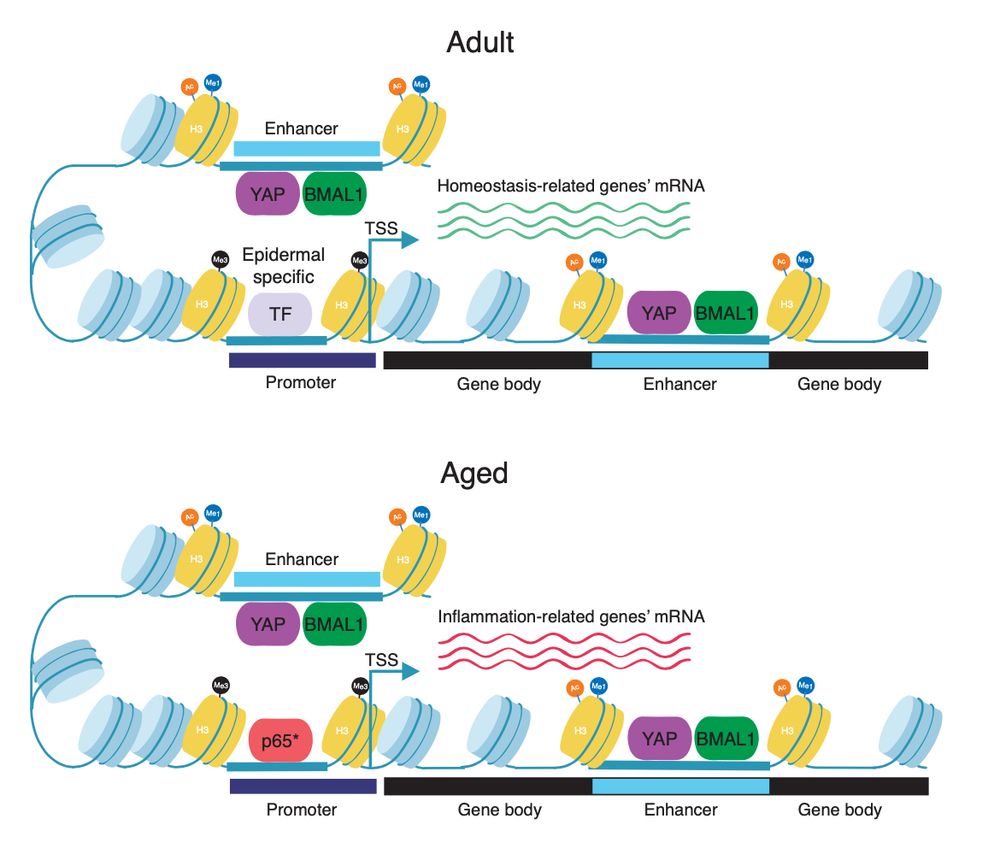
16/ Now, a more detailed p65 genomic occupancy analysis revealed the presence of p65 in promoters and TSSs of up-regulated inflammation-related genes, some of which present BMAL1-YAP bound enhancers.
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
15/ We consistently found p65-NF-kB binding sites enriched in active enhancers bound by BMAL1 and YAP in aged epidermis.
Actually, we have already shown in a previous study that p65 plays a key role in controlling the expression of inflammation genes during epidermal ageing!👀
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
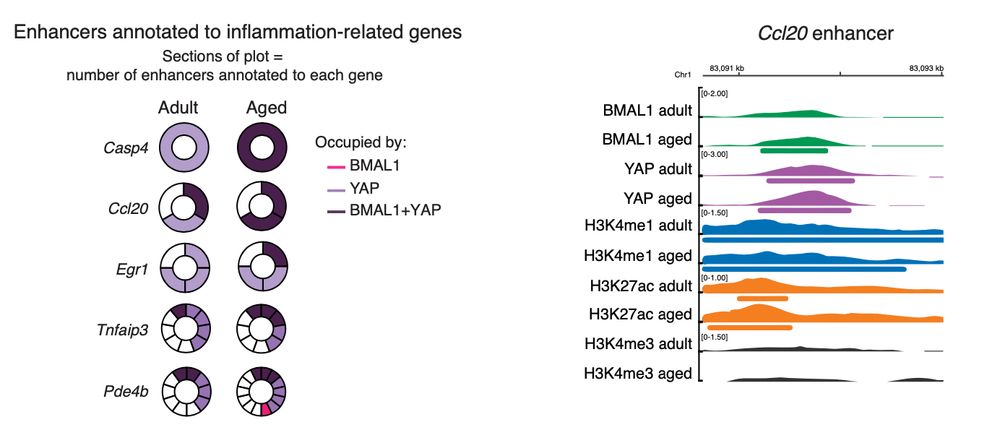
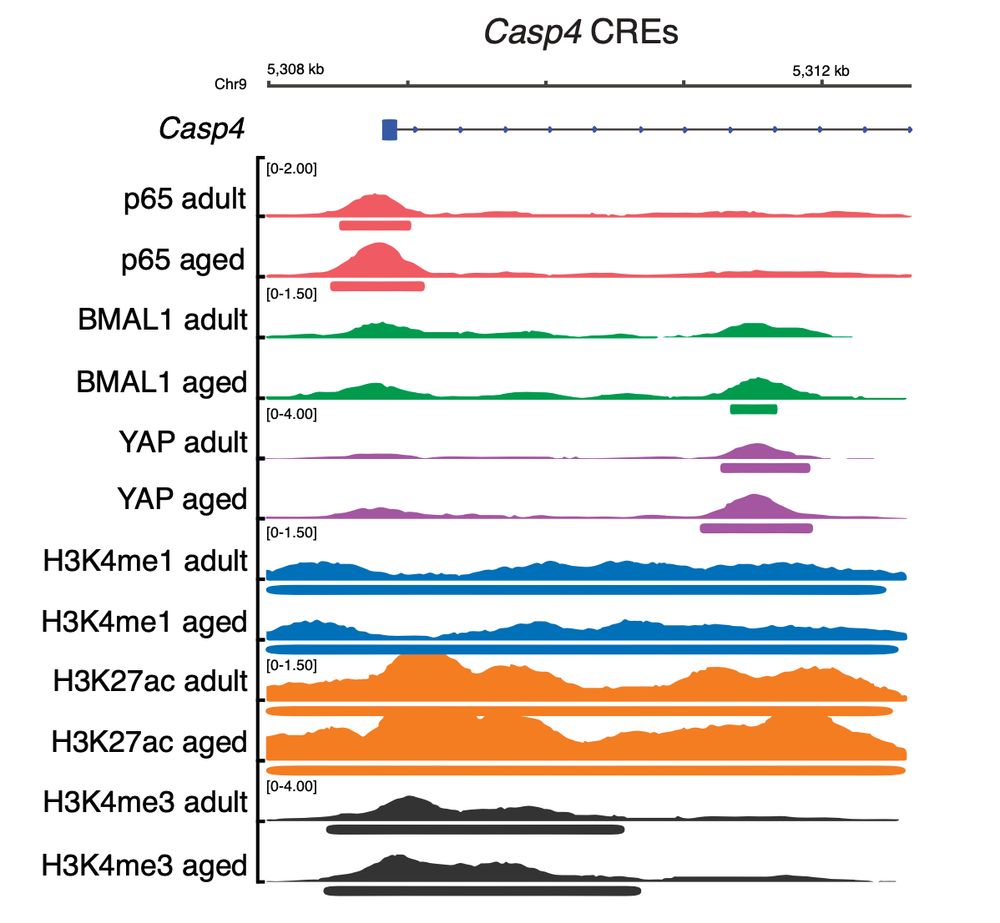
14/ What’s more, some of the up-regulated inflammation-related genes that were BMAL1 or YAP targets in adult epidermis, gain BMAL1-YAP binding in their enhancers with age.
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
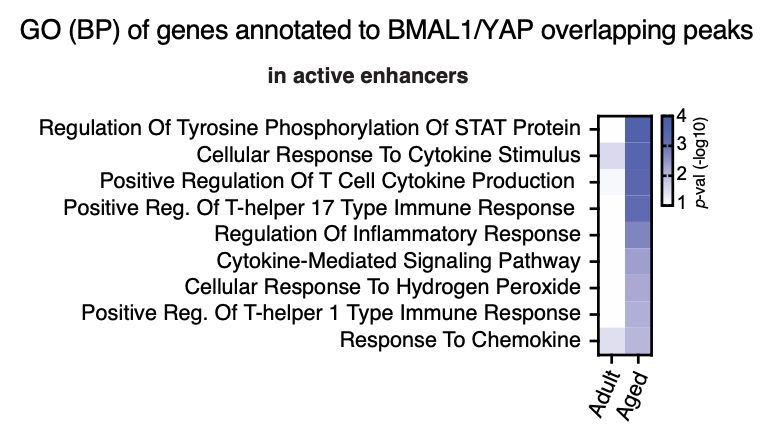
13/ What about BMAL1-YAP complex? Indeed, when we compare both TFs ChIP-seq data, we observe a stat significant genomic overlap between the two TFs.
+ Notably, during ageing, this happens in active enhancers of inflammation genes, some of which expression is up-regulated.
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
12/ These suggest that, in addition to mechanical changes of the skin, pro-inflammatory cues act as a second signalling layer that leads to ageing-associated YAP activation. 👯
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
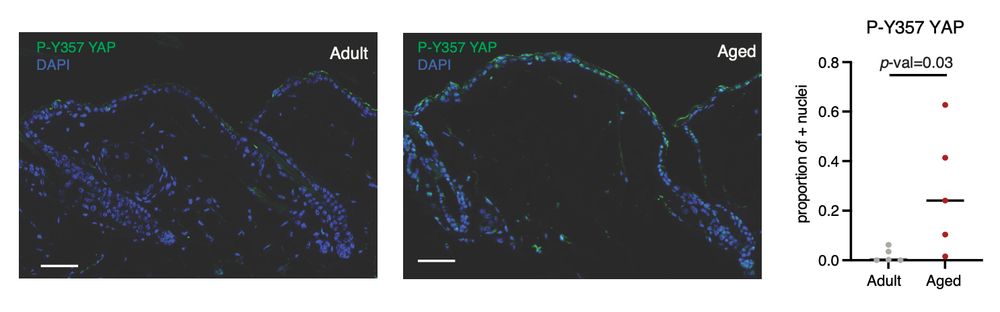
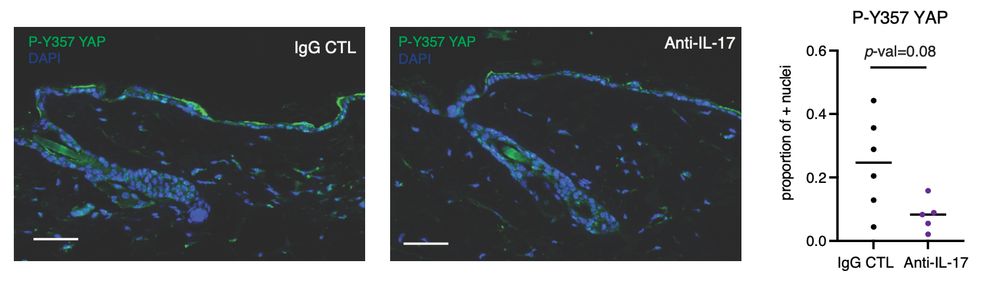
11/ Yes! We show that a non-canonical YAP activation through phosphorylation of Tyr357 is increased in the aged epidermis, and that this activation is reduced upon anti-inflammatory treatment with anti-IL17 blocking antibodies.
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
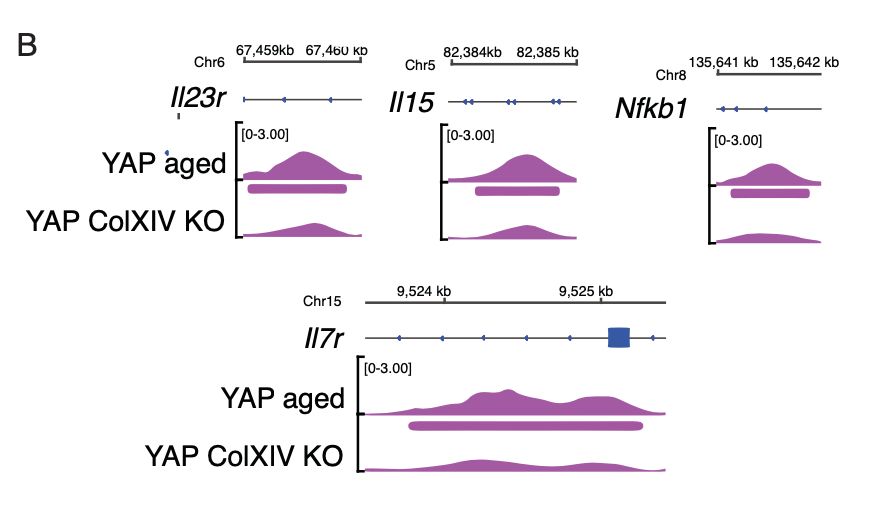
10/ Using a Col14KO mouse to model skin ageing mechanics, we unveiled that YAP activation through mechanotransduction signalling alone is not enough to recapitulate YAP aged binding to inflammation genes.
So, are there other triggers that can boost YAP activation during ageing?
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
9/ Could YAP activation be involved in BMAL1 genomic location rewiring to inflammation-related genes we observe during ageing?
To tackle that, we first needed to gain a little insight into how YAP activation happens during ageing. ⤵️
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
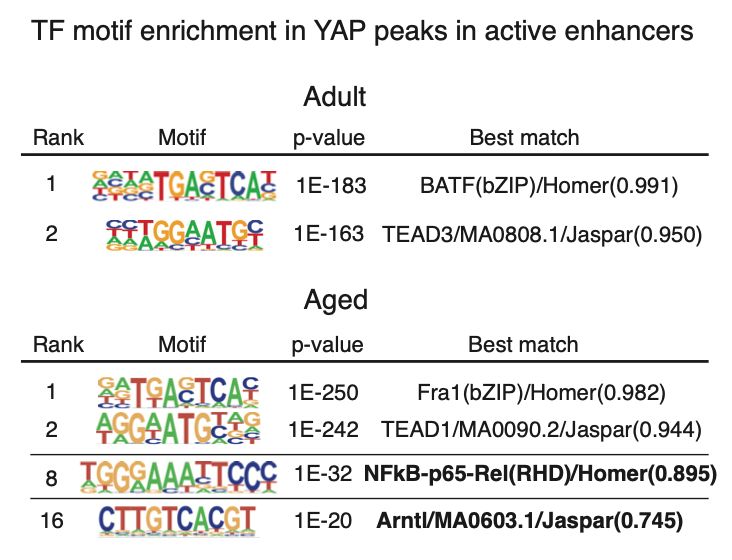
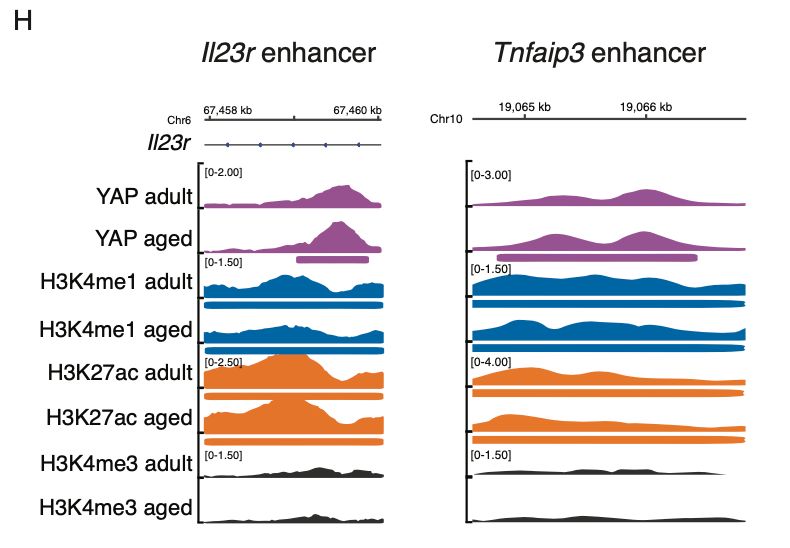
8/ However, during ageing, YAP gains binding to inflammation-related genes, similar to what we see for BMAL1. In fact, BMAL1 binding sites are enriched exclusively in aged YAP peaks located in active enhancers.😮
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
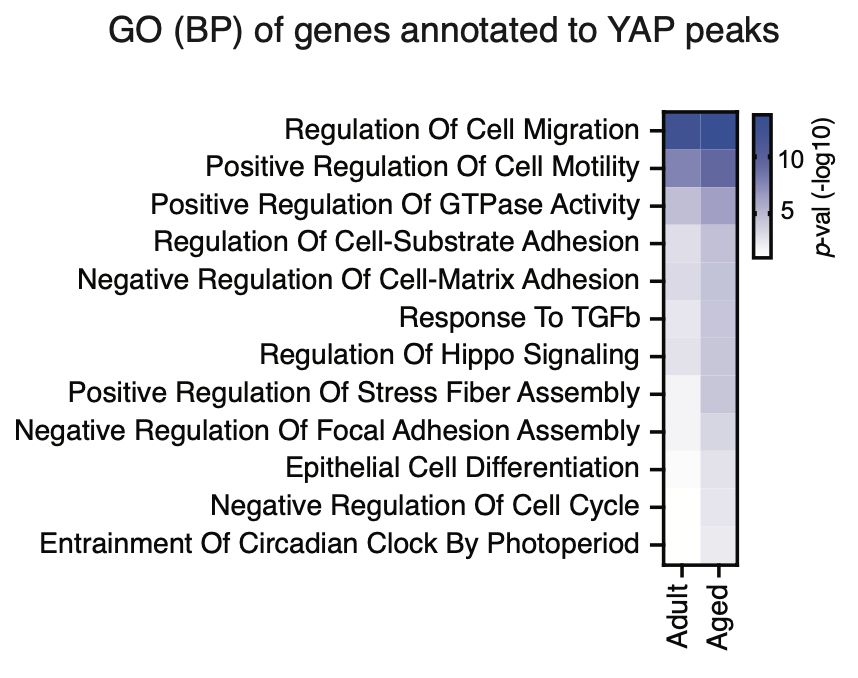
7/ In vivo ChIP-seq analysis of YAP in the epidermis confirmed its well-known role as a mechanotransduction TF, as its genomic occupancy is enriched in mechanics- and Hippo-related genes.🦛
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
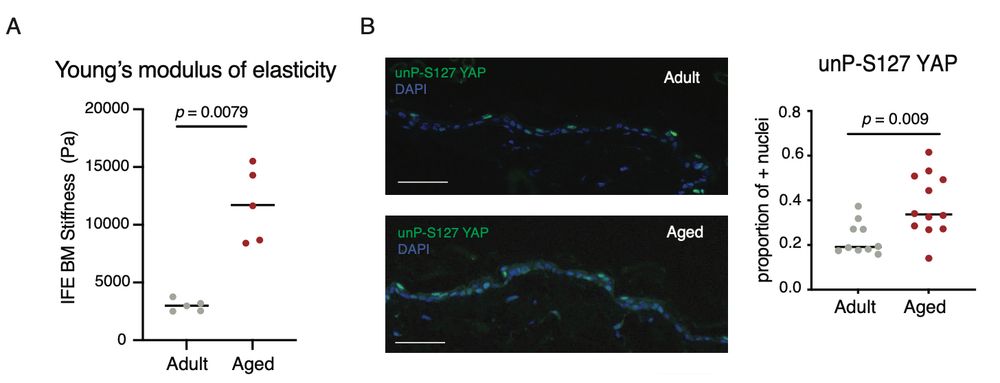
6/ Other groups have underscored that changes in tissue mechanics occur during ageing. In the IFE, we observed an increased stiffness of the BM during ageing, and this correlates with an increased proportion of epidermal cells positive for the Hippo-dependent active YAP.❗️
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
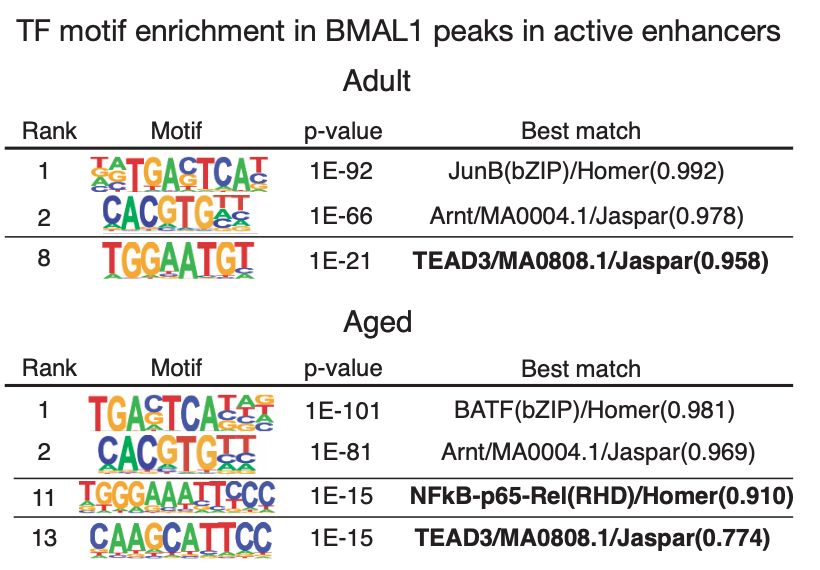
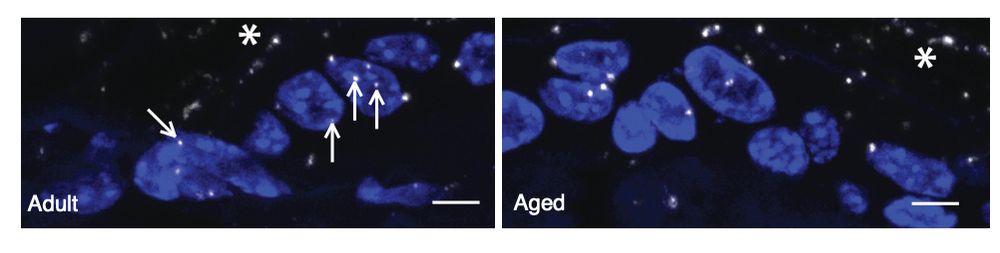
5/ TF motif enrichment analysis of BMAL1 peaks in active enhancers revealed TEAD binding sites.
PLA assay on skin sections shows BMAL1-YAP interactions in the nucleus of epidermal cells, suggesting a possible BMAL1 and YAP functional interaction in the epidermis chromatin.🧐
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
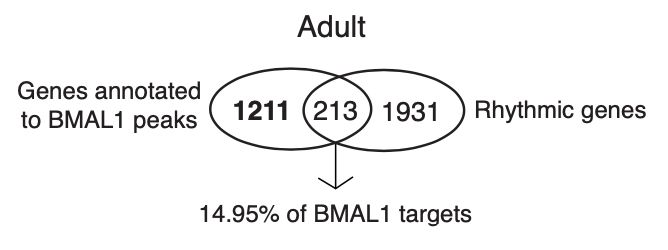
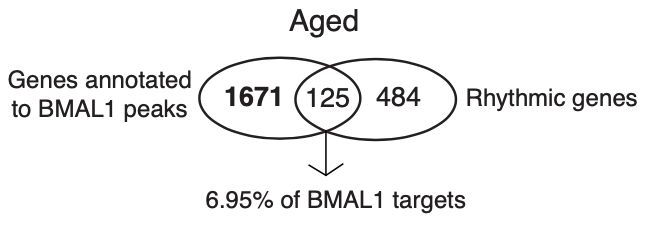
4/ In addition, we also see that BMAL1 binding is not restricted to rhythmically expressed genes, supporting a non-canonical BMAL1 function as a transcription factor beyond its role in the circadian clock.😈
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
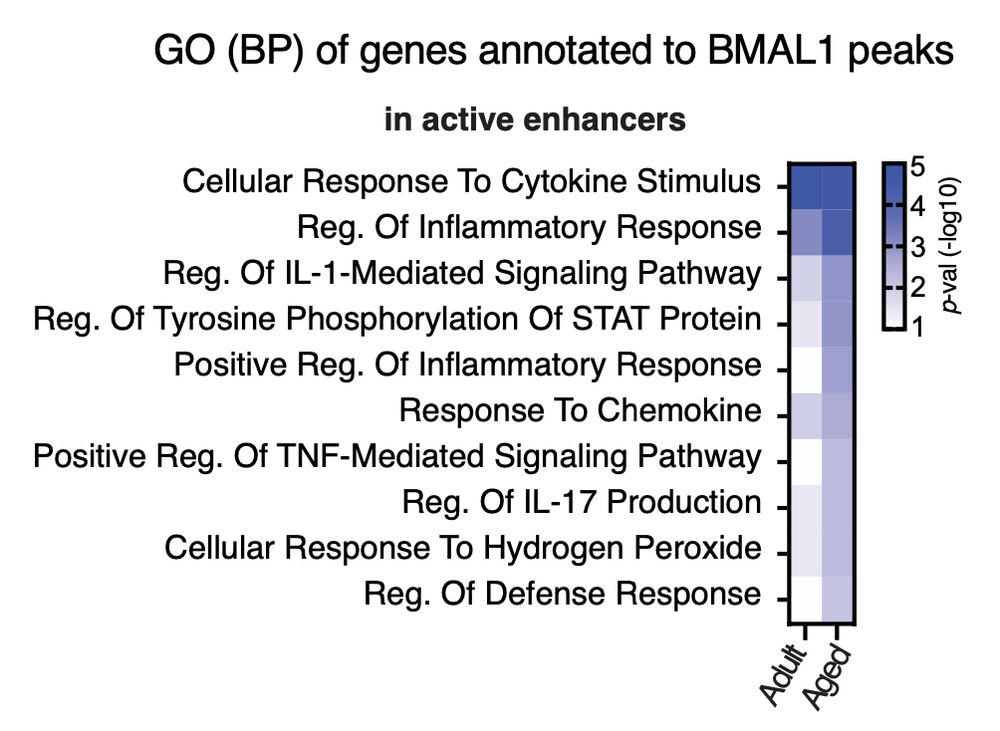
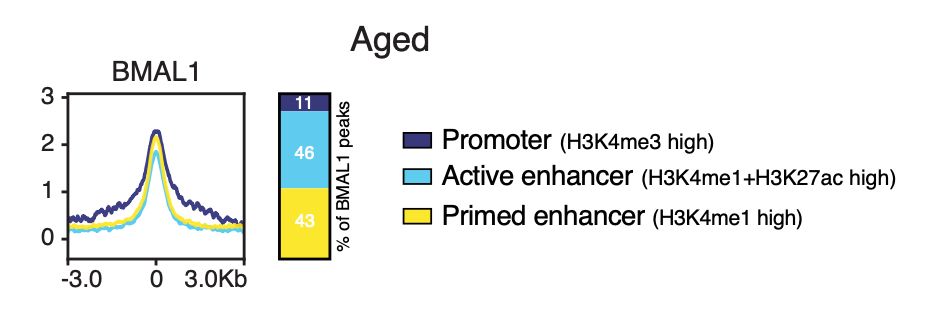
3/ In vivo ChIP-seq revealed BMAL1 binding to be enriched in inflammation genes in the aged epidermis, while during adulthood, this binding is more restricted to homeostatic genes.
Moreover, this binding occurs in enhancers, emphasising BMAL1 role in enhancer regulation.
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
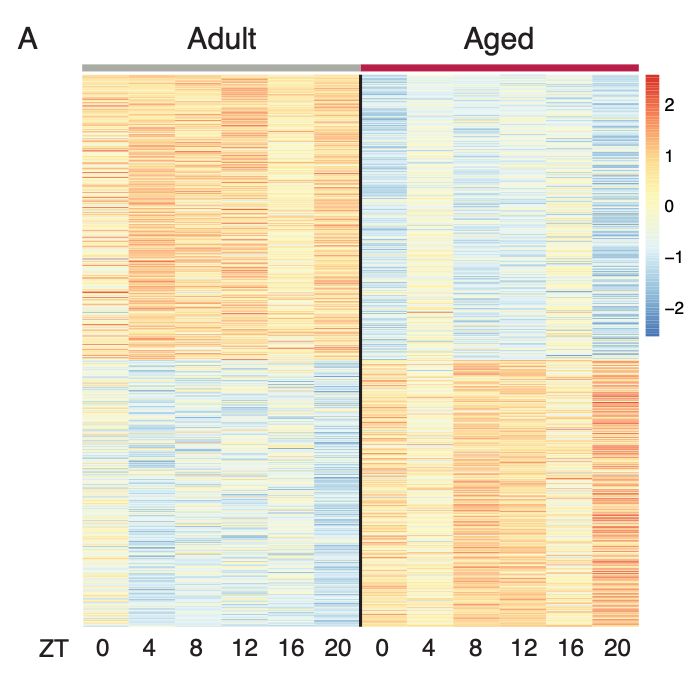
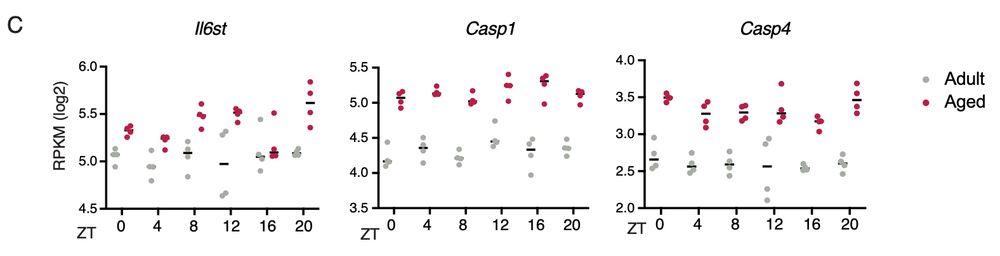
2/ By performing a comprehensive analysis of DEGs throughout 24 hours in adult and aged murine epidermis, we reveal a list of more than 100 up-regulated genes during ageing associated with inflammation functions.
But who promotes such an expression program?
23.04.2025 14:49 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
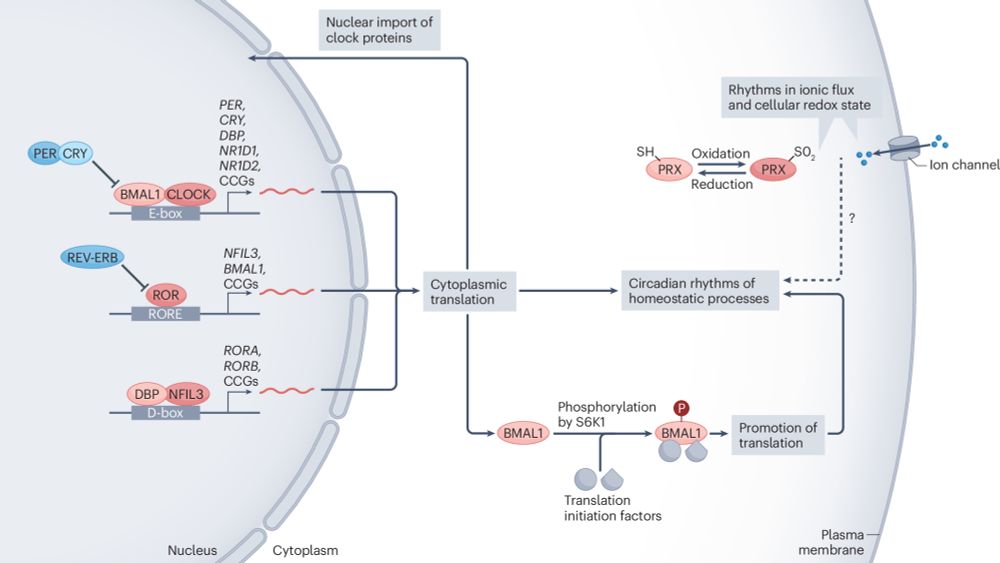
Circadian clock communication during homeostasis and ageing
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology - Communication between the circadian clocks of different cell and tissue types supports the daily rhythms of homeostatic processes that maintain bodily...
🧪 ✍️ Please check out our new review on intercellular and interorgan communication between circadian clocks ⏰🧬 out today in Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 🎉
@natrevmcb.bsky.social
! Here is the SharedIt link for free access: rdcu.be/d5ppE
03.01.2025 12:00 — 👍 26 🔁 9 💬 3 📌 1
PhD student in @SendoelLab interested in stems cells and their translational landscape during aging
Bioinformatics Scientist / Next Generation Sequencing, Single Cell and Spatial Biology, Next Generation Proteomics, Liquid Biopsy, SynBio, AI/ML in biotech // http://albertvilella.substack.com
Learning how cells remember and forget, and how can we restore their memories @GENYO University of Granada, Spain. www.landeiralab.ugr.es
Marie Skłodowska-Curie fellow at ISEM Montpellier. Physicist studying complex biological systems - ecosystems, cancer, immune networks and microbial communities.
We study the cell nucleus and the tissue microenvironment, driving dynamic cell mechanics. Multiscale Bioengineering Lab at College of Engineering & Mathematical Sciences at the University of Vermont. mccreerylab.com
We are the Hospital de Mar Research Institute. An institution dedicated to biomedical research. We are Hospital del Mar, #iCerca and located at the PRBB.
Cancer researcher at Hunter College of the City University of New York & Weill Cornell Medicine. Views are my own.
Group of Adrien Hallou @kiroxford.bsky.social @ox.ac.uk
Biophysics & spatial biology of cell fate decisions & tissue dynamics
Alumnus @cam.ac.uk & @normalesup.bsky.social
Franco-British Young Leader 2024 🇨🇵🇬🇧
L'Hospital Sant Joan de Déu Barcelona és un centre d'alta especialització en el tractament d'infants i dones embarassades.
El Hospital Sant Joan de Déu Barcelona es un centro de alta especialización en el tratamiento de niños y mujeres embarazadas.
🧬Genetics geek, 🤖AI enthusiast. PI @GenomeDataLab studying DNA repair, mutations, epigenome & NMD. 2xERC, professor @bric-ucph.bsky.social, GL @irbbarcelona.org. 🎲Chaotic good.
PostDoc @ Vignjevic lab, Institut Curie~ Matrix - cells - basement membrane interactions ~ intestine biology ~ Tissue development & homeostasis 🔬 Hiker, baker, lithops gardner 🌵 a mom
Postdoc at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York | Fascinated by cancer cell plasticity, tumor microenvironment, immunology and therapy resistance
Science news from the medical university Karolinska Institutet (KI) in Sweden. Our vision is to advance knowledge about life and strive towards better health for all. https://ki.se/
Physician Scientist at DKFZ & NCT Heidelberg
studying 🩸🧬 #epigenomics #DNAmethylation #singleCell #precisiononcology #JMML
www.translational-cancer-epigenomics.de
A journal dedicated to publishing the latest advances across all areas of cell biology. Part of @natureportfolio.nature.com
nature.com/ncb/index.html
We study how micro-environmental and epigenetic mechanisms drive cancer cells into dormancy. We seek to control this biology to prevent and treat metastasis. https://einsteinmed.edu/faculty/16974/julio-aguirre-ghiso
We are the largest biomedical science hub in the south of Europe, by the beach in Barcelona.
Recerca biomèdica amb vistes |
@researchmar.bsky.social @crg.eu @melisupf.bsky.social @embl.org @isglobal.org @ibe-barcelona.bsky.social @fpmaragall.bsky.social
Postdoc in Sonnen Lab (@_Hubrecht Institute). Organoids + Microfab enthusiast. Alumni: Schwille Lab @MPI_Biochem
Biotech investor & board member | Covering biotech, drug development, venture capital, startups and pharma |📍New York
https://www.linkedin.com/in/rubensebastianperez/