
Narrative surprise is a core element of storytelling for engaging audiences, and yet it remains underexplored in the context of large language models (LLMs) and narrative generation. While surprise arises from events that deviate from expectations while maintaining retrospective coherence, current computational approaches lack comprehensive frameworks to evaluate this phenomenon. This paper presents a novel framework for assessing narrative surprise, drawing on psychological theories of narrative comprehension and surprise intensity. We operationalize six criteria—initiatoriness, immutability violation, predictability, post-dictability, importance, and valence—to measure narrative surprise in story endings. Our study evaluates 120 story endings, generated by both human authors and LLMs, across 30 mystery narratives. Through a ranked-choice voting methodology, we identify significant correlations between reader preferences and four of the six criteria. Results underscore the continuing advantage of human-authored endings in achieving compelling narrative surprise, while also revealing significant progress in LLM-generated narratives.
LLMs may allow computational studies of literature to get beyond word-counting and model things readers value, like surprise. But — what exactly is "surprise"? New work by Annaliese Bissell, Ella Paulin, and @andrewpiper.bsky.social. aclanthology.org/2025.wnu-1.7/
10.05.2025 14:29 —
👍 35
🔁 4
💬 1
📌 0
Another one of those little shocking AI moments: this sound clip was generated in 46 seconds on my home PC from the script below. Just the text
Nari Lab's Dia does some of the best expressive AI voice I have seen and it is open weights & created by two undergrads with no funding
22.04.2025 21:12 —
👍 66
🔁 6
💬 2
📌 0
Magi-1: The Autoregressive Diffusion Video Generation Model
🥇 The first autoregressive video model with top-tier quality output
🔓 100% open-source & tech report
📊 Exceptional performance on major benchmarks
22.04.2025 06:10 —
👍 13
🔁 3
💬 3
📌 0

Comparing Human versus LLM Judges
TREC, which is a community of researchers in information retrieval and natural language processing convened by the NIST, found that an independent human judge correlates better with GPT-4o than a human judge.
22.04.2025 19:17 —
👍 10
🔁 1
💬 2
📌 0
Lvmin Zhang launched FramePack, a novel approach for next - frame prediction models in video generation.
Project: lllyasviel.github.io/frame_pack_g...
Image-to-5-Seconds (30fps, 150 frames)
21.04.2025 02:39 —
👍 3
🔁 1
💬 2
📌 0

Microsoft's BitNet b1.58 2B4T — the first large-scale, native 1-bit LLM🚀🚀
BitNet achieves performance on par with leading full-precision LLMs — and it’s blazingly fast⚡️⚡️uses much lower memory🎉
Everything is open-sourced, per them.
16.04.2025 04:18 —
👍 63
🔁 9
💬 2
📌 6

Don't lie to your friends: Learning what you know from collaborative self-play
Jacob Eisenstein, Reza Aghajani, Adam Fisch, Dheeru Dua, Fantine Huot, Mirella Lapata, Vicky Zayats, Jonathan Berant
To be helpful assistants, AI agents must be aware of their own capabilities and limitations. This includes knowing when to answer from parametric knowledge versus using tools, when to trust tool outputs, and when to abstain or hedge. Such capabilities are hard to teach through supervised fine-tuning because they require constructing examples that reflect the agent's specific capabilities. We therefore propose a radically new approach to teaching agents what they know: \emph{collaborative self-play}. We construct multi-agent collaborations in which the group is rewarded for collectively arriving at correct answers. The desired meta-knowledge emerges from the incentives built into the structure of the interaction. We focus on small societies of agents that have access to heterogeneous tools (corpus-specific retrieval), and therefore must collaborate to maximize their success while minimizing their effort. Experiments show that group-level rewards for multi-agent communities can induce policies that \emph{transfer} to improve tool use and selective prediction in settings where individual agents are deployed in isolation.
A way to help models "be aware of their own capabilities and limitations" from @jacobeisenstein.bsky.social et al: arxiv.org/abs/2503.14481 #MLSky
22.03.2025 16:09 —
👍 40
🔁 9
💬 3
📌 0
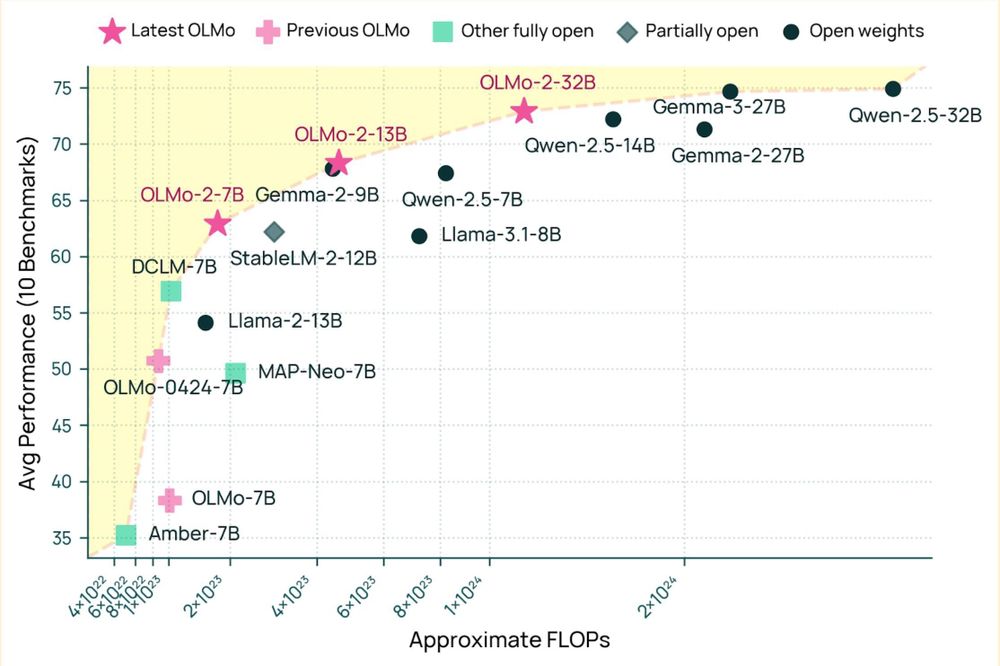
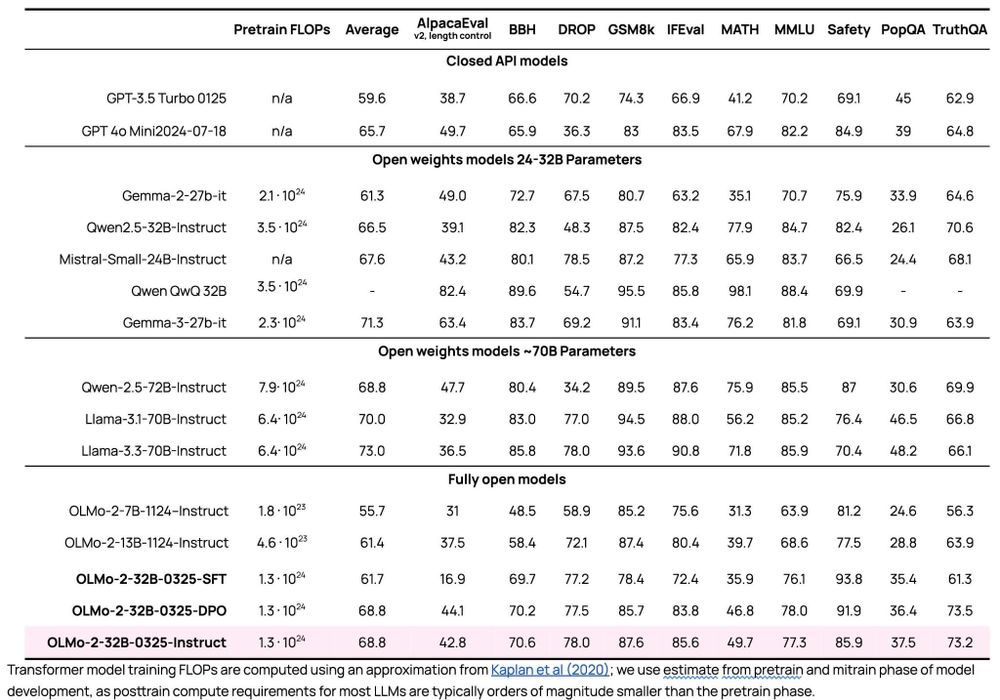
A very exciting day for open-source AI! We're releasing our biggest open source model yet -- OLMo 2 32B -- and it beats the latest GPT 3.5, GPT 4o mini, and leading open weight models like Qwen and Mistral. As usual, all data, weights, code, etc. are available.
13.03.2025 18:16 —
👍 140
🔁 37
💬 5
📌 3
Google has released Gemma 3, the latest open model. Being the most capable and advanced version in the open - source model family, it adds highly requested features like longer context and multimodality.
13.03.2025 05:35 —
👍 6
🔁 1
💬 1
📌 0

Introducing Gemma 3: The most capable model you can run on a single GPU or TPU
Today, we're introducing Gemma 3, our most capable, portable and responsible open model yet.
Introducing our Gemma 3 open models, the most capable models that you can run on a single GPU or TPU. Multimodal, multilingual, 128k context length, and exceeds quality of other open models that are an order of magnitude larger in terms of hardware footprint. 🎉
blog.google/technology/d...
13.03.2025 14:55 —
👍 139
🔁 21
💬 2
📌 3

PapersChat – Chat with Research Papers
PapersChat provides an agentic AI interface for querying papers, retrieving insights from ArXiv & PubMed, and structuring responses efficiently.
github.com/AstraBert/Pa...
10.03.2025 04:47 —
👍 35
🔁 4
💬 0
📌 1


Mistral has just released a new OCR model, Mistral-OCR. Yet still the usual VLM curse: with challenging manuscripts, it hallucinates completely.
06.03.2025 19:02 —
👍 50
🔁 10
💬 1
📌 1
Mercury is the first commercial-scale Diffusion LLM.
01.03.2025 16:42 —
👍 16
🔁 5
💬 3
📌 0

The Blue Report
The top links on Bluesky, updated hourly
The Blue Report is amazing. The most clicked on articles are right here
theblue.report
01.03.2025 21:21 —
👍 19918
🔁 4635
💬 580
📌 263

An Overview of Large Language Models for Statisticians
- Stat for LLM: How statistical methods can improve LLM uncertainty quantification, interpretability, trustworthiness & more.
27.02.2025 04:09 —
👍 32
🔁 7
💬 2
📌 1
I asked Claude “Make an interactive artifact that will illustrate to me why I should not start Civ VII right now.”
This is what it came up with on its own.
08.02.2025 22:34 —
👍 183
🔁 18
💬 11
📌 1

Why do LLMs trained on over 90% English text perform so well in non-English languages?
They find that they learn to share highly abstract grammatical concept representations, even across unrelated languages!
06.02.2025 07:18 —
👍 37
🔁 9
💬 2
📌 0
Fellow journos covering "AI": Please don't do their PR for them! "Virtual employees" is a harmful anthropomorphism in that it (a) is false; (b) confuses readers about the emerging technology and inaccurately lends human attributes like agency, accountability, etc.; and (c) harms humans in real jobs.
06.01.2025 17:07 —
👍 304
🔁 109
💬 9
📌 2
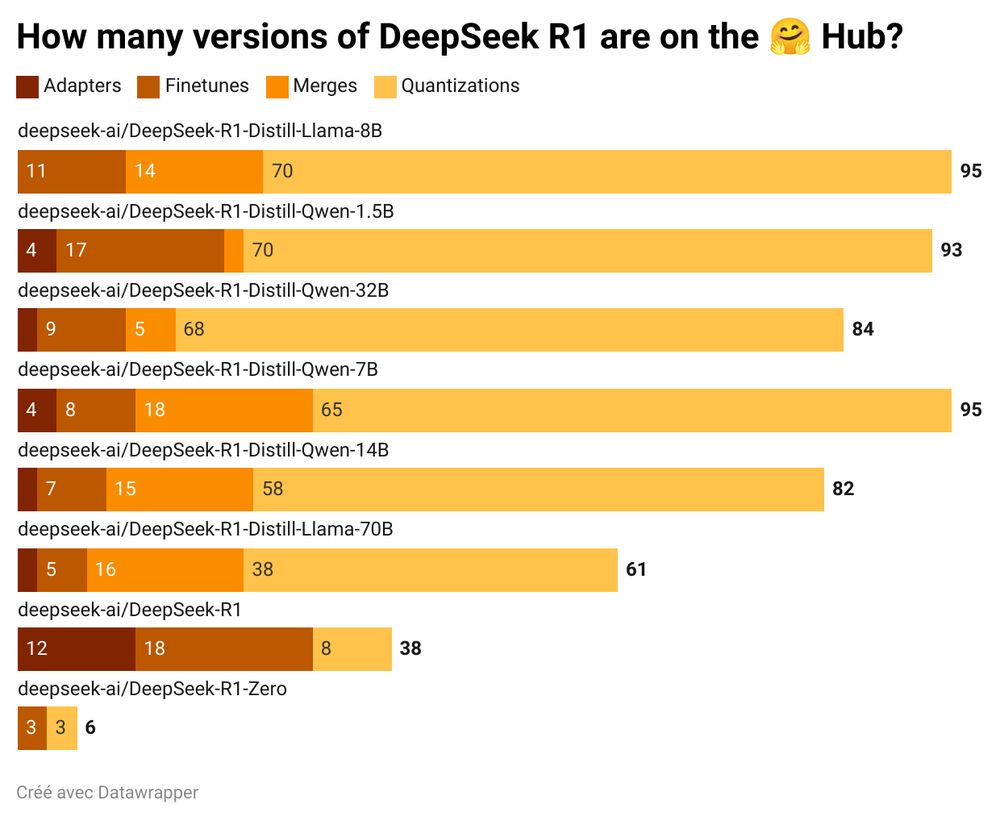
Yes, DeepSeek R1's release is impressive. But the real story is what happened in just 7 days after:
Original release: 8 models, 540K downloads. Just the beginning...
The community turned those open-weight models into +550 NEW models on @huggingface. Total downloads? 2.5M—nearly 5X the originals.
27.01.2025 16:24 —
👍 75
🔁 22
💬 3
📌 4
We’re excited to introduce Transformer², a machine learning system that dynamically adjusts its weights for various tasks!
sakana.ai/transformer-...
Adaptation is a remarkable natural phenomenon, like how the octopus blends into its environment, or how the brain rewires itself after injury.
🧵 1/N
15.01.2025 05:49 —
👍 38
🔁 9
💬 1
📌 2
Yet more interesting research by sakana.ai
26.01.2025 10:57 —
👍 2
🔁 0
💬 0
📌 0

ByteDance Doubao-1.5-pro
- Includes a "Deep Thinking" mode, surpassing O1-preview and O1 models on the AIME benchmark.
- Outperforms deepseek-v3, gpt4o, and llama3.1-405B on popular benchmarks.
team.doubao.com/en/special/d...
24.01.2025 21:43 —
👍 16
🔁 4
💬 2
📌 2

Full Moon is a model client that makes great use of the MLX framework, running the Llama 3 1b or 3b model. 1b model operates at lightning speed locally on the iPhone, so if you're interested, feel free to check it out 🌕🧵1/3
Testflight: fullmoon.app
22.12.2024 04:30 —
👍 14
🔁 4
💬 2
📌 2
FCVG
Generative Inbetweening through Frame-wise Conditions-Driven Video Generation
In extensive evaluations across various scenarios, including natural landscapes, complex human poses, camera movements, and animations, existing methods often exhibit incoherent transitions between frames. fcvg-inbetween.github.io
25.12.2024 13:38 —
👍 2
🔁 1
💬 1
📌 0




























