Grateful to have been included in this interesting and sure to be very impactful work!
23.09.2025 08:39 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0@brianfclarke.bsky.social
@brianfclarke.bsky.social
Grateful to have been included in this interesting and sure to be very impactful work!
23.09.2025 08:39 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
📢 Recruitment for the EMBL International PhD Programme is officially open!
At EMBL, we train young scientists to become skilled and creative future leaders in academia and other sectors. Join us and get a head start on your career in life sciences!
bit.ly/47mmiFF
Deadline in 9 days - apply now!
04.07.2025 09:36 — 👍 1 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Job alert: Join us for a postdoc in AI in genetics at @EMBL Heidelberg! Great collaboration with @Adrian Cortes @GSK, aiming to develop new tools to elucidate genetic effects using population-scale cohorts and single-cell readouts. Please share!
embl.wd103.myworkdayjobs.com/de-DE/EMBL/d...

We're hiring!
Want use deep learning to discover genetic disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets? Like the sound of applying Bayesian deep learning, DNA language models and federated learning to this exciting problem? Then this position in our group is for you!
An insightful thread for the second study by the one and only @manusaraswat.bsky.social that spearheaded this superstar team effort together with @lauraruedag.bsky.social and Elisa Heinzelmann in the labs of @oliverstegle.bsky.social and me:
bsky.app/profile/manu...
How does tumour heterogeneity arise? How can we predict cancer cell plasticity? In 2 new studies, we trace #glioblastoma heterogeneity to a spatial cancer cell trajectory w. multimodal cell atlassing bit.ly/4mkrWgs & predict plasticity w. snRNA/ATAC+deep learning bit.ly/3FbI6Ic 🧵
16.05.2025 11:42 — 👍 73 🔁 31 💬 6 📌 5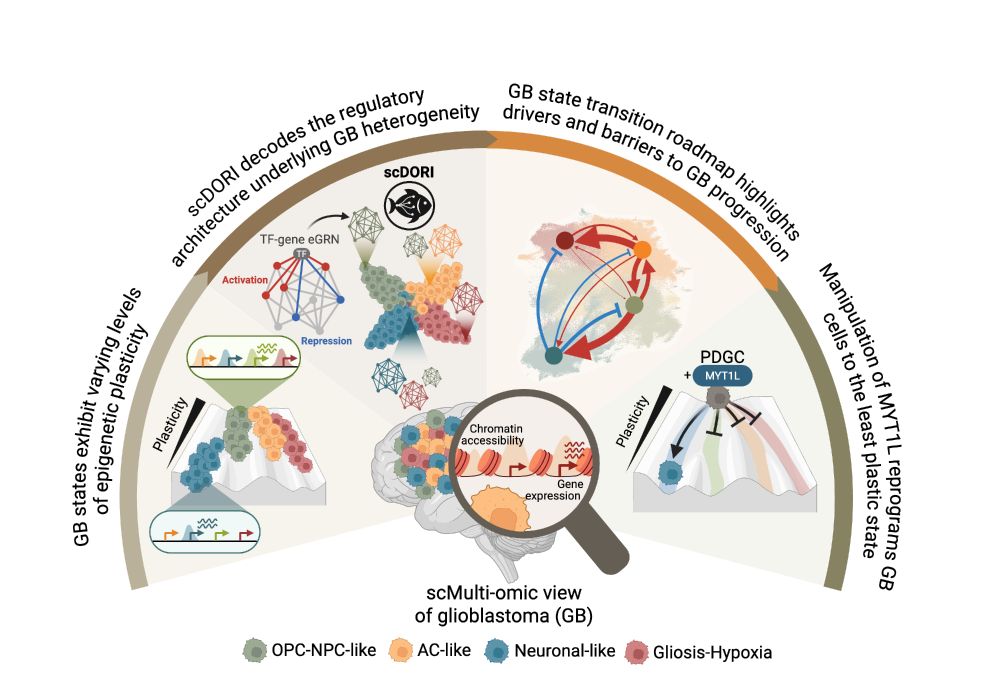
🧠 Excited to share my main PhD project! We mapped the regulatory rules governing Glioblastoma plasticity using single-cell multi-omics and deep learning. This work is part of a two-paper series with @bayraktarlab.bsky.social @oliverstegle.bsky.social and @moritzmall.bsky.social, Preprint at end🧵👇
16.05.2025 10:04 — 👍 76 🔁 29 💬 1 📌 6
PHD POSITIONS IN COMPUTATIONAL RESEARCH, DATA SCIENCE AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Are you interested in solving fascinating biological or medical questions computationally? At the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Germany’s largest biomedical research institute with its core site in Heidelberg, computational scientists work at the forefront of artificial intelligence and cancer research. They combine inter disciplinary approaches from computer science, medical informatics, physics, biology, bioinformatics and statistics to analyze and understand complex biological and medical data. Main activities at the DKFZ involving big data: • Development and application of machine learning and computa tional methods for multi-modal data integration, including integrative analysis of genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, meta bolomic and radiomic imaging data • Development of methods for modeling and simulation of biological and medical processes • Medical Informatics • • • • DNA mutation analysis and machine learning to decipher cancer genome variation Application and development of state-of-the-art technologies for single-cell omics and life cell imaging Computer-assisted radiology and surgery Biostatistical evaluation of experimental and clinical data More information at www.dkfz.de/datascience. Full funding is provided for the duration of the PhD. To apply online to the International PhD Program visit To apply online to the International PhD Program visit www.dkfz.de/phd Application deadline 24 April 2025 We support and value diversity and encourage applications from individuals from underrepresented groups. If you require assistance during the application process, please contact phd@dkfz.de.
The next selection round for the DKFZ International PhD Program has started. Please consider applying to this really excellent program! I'll be proposing projects, as will many other outstanding PIs.
18.03.2025 14:56 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Segger logo
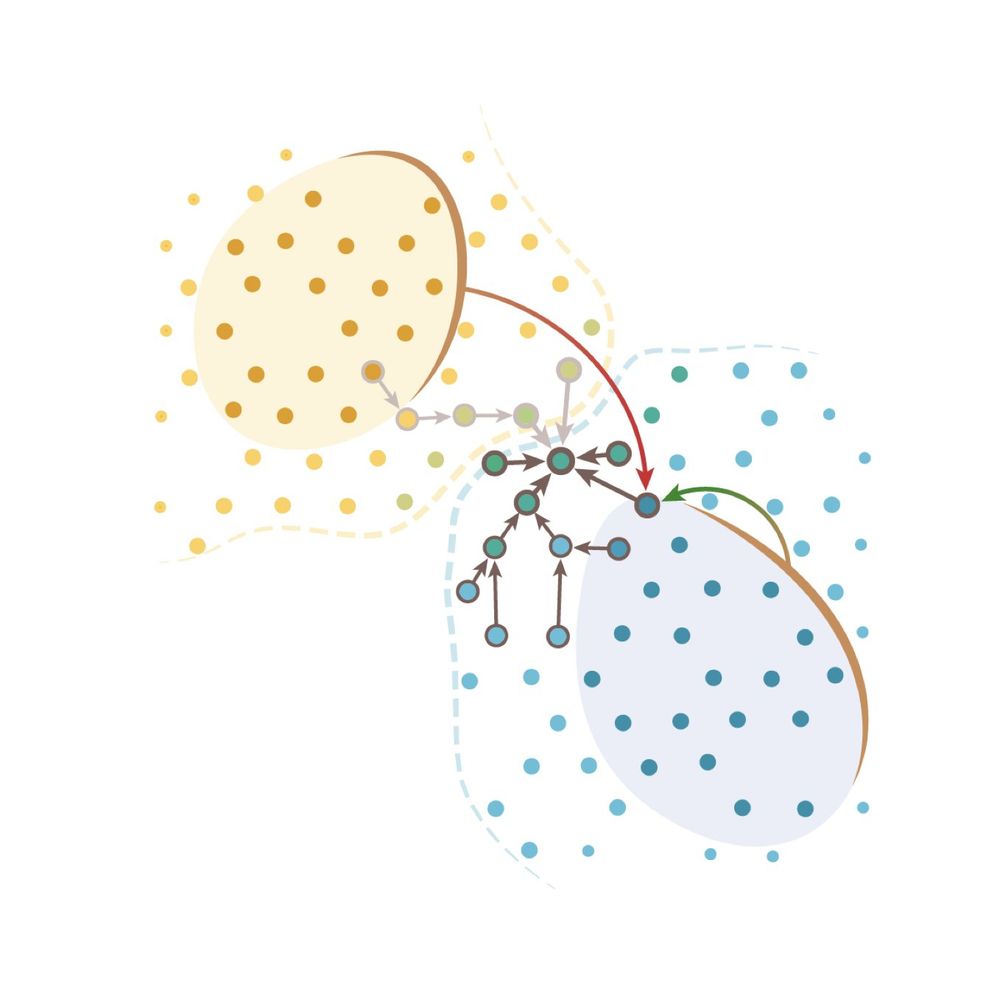
Message passing intuition behind the segger’s link-prediction model and the network architecture
1/ New preprint! 🍳
@elihei.bsky.social and our team at @embl.org , @dkfz.bsky.social, and @mskcancercenter.bsky.social built #segger - a fast, accurate cell segmentation tool for spatial transcriptomics that assigns transcripts to their cell origins!
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

Fig 4.
Cell2fate learns which genes have co-regulated transcription rates => spatially mapping velocity modules & improved robustness. Bayesian modelling => easier to add biological realism.
Exciting collab with Alexander Aivasidis in Bayraktar & @steglelab.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Exciting job opportunity!👇
A great chance to work on an application of machine learning in human genetics which will make an impact on our understanding of disease and has real potential for future translation to the clinic.