wrote a bit fast, that's probably not an issue if one assumes the proportional odds assumtions holds and models the data accordingly, as done in the example.
If one relaxes the assumption and models category specific effects, things are probably different.
25.08.2025 15:34 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Very cool! I'm intrigued by the treatment of ordinal variables, and I have a question. Will this approach: avg_comparisons(mod_ord, variables = "partner", hypothesis = ~ I(sum(x * 1:5))) also give a good answer when the response-distribution is unbalanced, e.g. most people responded on level 1?
25.08.2025 15:25 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 2 📌 0
Identifying Bayesian Mixture Models
If you are not discouraged by now, here is a relevant paper: Bayesian Identification and Estimation of Growth Mixture
Models (Xiao, Rabe-Heskeseth & Skrondal, 2025) www.duo.uio.no/bitstream/ha...
13.08.2025 10:54 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Identifying Bayesian Mixture Models
The question is well motivated, but there will be stumbling blocks or walls one can run into:
- degenerate classes / label switching (betanalpha.github.io/assets/case_...)
- finding # of latent classes
- non-informative class membership probs
I think very clean data are needed to have a chance.
13.08.2025 10:50 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
No worries, das Deutsch ist nicht so gut, als dass man leicht Unterhaltungen auf Deutsch führen könnte 😀. (Bin weder verwandt noch verschwägert mit dem Eigentümer...)
10.08.2025 13:39 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
I recommend this places: maps.app.goo.gl/H2QkoDjDbJr8...
The owner speaks some German 😀. More importantly, it's a friendly and quiet place with reasonably priced very good meals and nice outdoor seating in the backyard.
10.08.2025 09:46 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
I think a "rich-get-richer" effect could be stronger if one does not provide additional info. But that would in my view also be bad practice. Asking an LLM to help with a review by using a RAG system with the relevant literature could well make the effect weaker.
01.08.2025 14:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Genau für diese Art von Text, der in erster Linie für Verwaltungszwecke verfasst wird, sind m. E. LLMs nützliche und effiziente Werkzeuge, bei denen, aus meiner Sicht, die Vorteile ggü den Nachteilen der Nutzung überwiegen.
28.07.2025 09:01 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Generally agree. An neat use of ordinal regressions is to use them as a semi-parametric model for weird (multimodal) VAS data. If one splits the original scale in bins, one can with some effort calculate marginal effects on the original scale, with resolution depending on # of bins.
28.07.2025 07:25 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Typos in the post are virtue signals, indicating that no LLM was used in its writing 😀
23.07.2025 16:16 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
The last few days a couple of texts made the round here that equate using AI in the research process with doing bad research. I think these are 2 orthogonal things: Using AI can make research worse and it can make it better, depent on how it is used.
23.07.2025 16:12 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
I don't see how the post effectively criticises target population estimands. It shows that if you have a target population estimand in mind, but your study isn't designed to estimate it, you'll pay with a high variance of your estimate.
14.07.2025 16:00 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
OTH, “Our analysis should take into account that children grow around 7.5 cm per year and rarely less than 1 cm or more than 15 cm per year.” sounds entirely reasonable and illustrates that priors often reflect not just subjective beliefs but objective information that can robustify inference.
02.07.2025 14:47 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
One reason for the lack of appreciation might be that Bayesian methods are often taught in a very abstract way, just as in the book at the start of the thread. Teaching the formula “posterior = prior × likelihood” tends to focus attention on so-called subjective beliefs as priors.
02.07.2025 14:45 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
I agree that one can use Bayes for many reasons and that it is useful in relatively simple situations. However, my (admittedly limited) observation is that the ability to fit complex models attracts more people to Bayesian estimation than improved inference in simpler cases.
02.07.2025 12:49 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
It works usually well if one uses t-tests or anovas to analyse simple experiments. But one shouldn't generalise from that to the goals/usefulness of Bayesian or Frequentist methods in general.
02.07.2025 07:26 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
It seems to be a common misunderstanding that the goal of applied Bayesian inference is to let the prior influence the inference. I think a more common goal is to be able to reliably fit complex models that are hard/impossible with Frequentist methods.
02.07.2025 07:22 — 👍 18 🔁 1 💬 2 📌 0
Did they look at both parental income and education? In Norwegian data the association of child outcomes with parental education is clearly stronger than with parental income.
26.06.2025 15:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
To let LLMs produce less common and therefore likely also more creative text, one can always set the temperature parameter.
But there are trade offs. Less common might also be more likely wrong.
19.06.2025 15:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
YouTube video by 3Blue1Brown
Transformers (how LLMs work) explained visually | DL5
Understanding the transformer architecture helps explain why LLMs are so powerful—and when they’re likely to fail.
The Andrej Karpathy video goes into less detail about transformers than would be helpful. Here's a quick and accessible intro from 3Blue1Brown. www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjZo...
18.06.2025 10:53 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
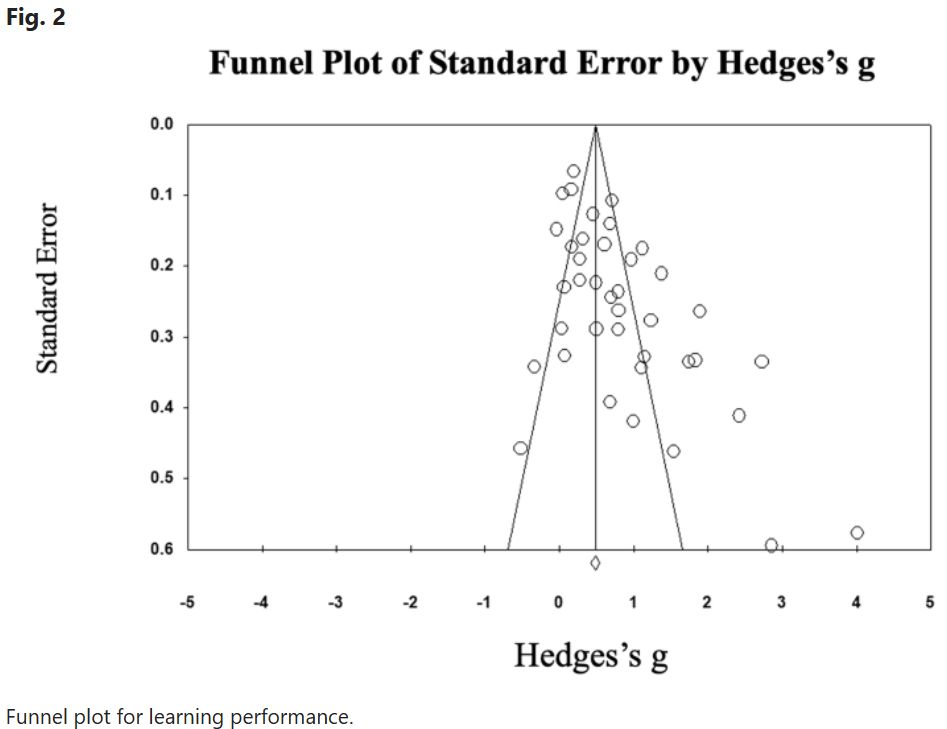
I believe large language models (LLMs) can be very useful and can be used to support learning effectively.
However, this plot from a recent study (www.nature.com/articles/s41...), which praises the impact of LLMs on learning outcomes, doesn't exactly inspire confidence.
05.06.2025 16:09 — 👍 6 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
Easily only for models with identity link function (also careful with treatment-interactions). Otherwise one might have to code up a model in e.g. Stan, omit priors on coefficients involving the treatment & put a prior on the marginal effect (calculated in the transformed parameters block).
02.06.2025 14:22 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
The article talks about non-collapsibility, but doesn't seem to use the term. I think its a helpful term, because it puts a name to a key problem with OR, which is there even if the OR is not interpreted as a RR.
26.05.2025 14:17 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Links:
documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/0...
assets-eu.researchsquare.com/files/rs-424...
arxiv.org/pdf/2409.090...
arxiv.org/pdf/2402.09809
21.05.2025 07:32 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Would be great to have that on CRAN 😀
05.05.2025 14:45 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Ist natürlich auch mit Vorsicht zu geniessen. Eine wichtige Schwäche ist, dass es alle Aussagen von Autoren unkritisch akzeptiert.
26.04.2025 11:45 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Anyhow, I am sympathetic to focusing on selection bias, because I think quasi-experimental designs, which are often possible only in selected samples, focus so much on internal validity, that it easy to overlook that they might exchange confounding bias with selection bias.
18.04.2025 20:46 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Using missingnes graphs provide an additional way to define internal and external validity: violations of internal validity are due to backdoor paths that do not involve missingness indicator nodes (or their children) and violations of external validity involve those. (Just made this up ...)
18.04.2025 20:42 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 2 📌 0
We are delighted to announce the launch of #ACAMHLearn - our innovative #OpenAccess resource, bringing together specially commissioned videos from world-leading experts in the field of #CYPMentalHealth. Visit https://bit.ly/3AV958F to learn more!
Lecturer Psych & Crim @kingscollegelondon.bsky.social | Deception Detection; Emotions; JDM | Open Science; R; Bayes | @ukrepro ReproTea & StatsTea | #statstab | 🇷🇴 🇬🇧🌍
Stats blog: https://mzloteanu.substack.com/
Primatologist lost in a Markov chain | benkawam.github.io.
Lecturer @ Göteborgs Universitet.
ed policy | teacher sorting | inequality
Professor for Applied Statistics, Freie Universität Berlin; education and health economist; table tennis player
http://janmarcus.de
Assistant Professor (Juniorprofessor) of Econometrics; FU Berlin; Interests: Causal machine learning, causality, data science, statistics, econometrics ; https://philippbach.github.io/
We rate DAGs.
(If you were hoping for dogs, try here: @weratedogs.com)
Research Associate at the Social, Genetic & Developmental Psychiatry Centre, Kings College London. Interests: developmental psychology, data science, coffee. www.bignardi.co.uk
Assistant professor at Duke-NUS medical school. Mostly interested in health economics, biostats and clinical informatics.
Laboratory of Michael J. Frank at Brown University.
Our research combines computational modeling and experimental work to understand the neural mechanisms of motivated learning, choice and cognitive control.
https://www.lnccbrown.com/
Cognitive scientist interested in social learning, morality, and preference formation. Research at Karolinska Institutet, Sweden.
Researcher University of Oslo & Oslo University Hospital ☆ PI AffectiveBrains ☆ Enthusiastic about reward behavior and experience ☆ opioids, endocannabinoids, addiction, stress, anhedonia, resilience
www.affectivebrains.com
Rotating Curator for the @rladies.org community💜
🔗 https://guide.rladies.org/rocur/
This week's curator: @ellakaye.co.uk
Complex Trait Genetics | Population Genetics | Evolutionary Genetics
https://scholar.google.nl/citations?user=hsyseKEAAAAJ&hl=en
Independent AI researcher, creator of datasette.io and llm.datasette.io, building open source tools for data journalism, writing about a lot of stuff at https://simonwillison.net/
Associate Professor of Public Policy, Politics, and Education @UVA.
I share social science.
Population and evolutionary genetics @UCDavis. Posts, grammar, & spelling are my views only. He/him. #OA popgen book https://github.com/cooplab/popgen-notes/releases
Asst. Prof. of Statistics & Political Science at Penn State. I study stats methods, gerrymandering, & elections. Bayesian. Founder of UGSDW and proud alum of HGSU-UAW L. 5118.
corymccartan.com



