
🔥🔥🧠PhD positions are open in my lab, studying brain development and neurodevelopmental disorders based on neuroimaging MRI scans. Due: Dec 1, 2025. If you are interested, please DM me.
21.10.2025 19:53 — 👍 18 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 0@ethanwhitman777.bsky.social
phd student at duke with moffitt/caspi + laboratory of neurogenetics using predictive modeling to understand brain aging

🔥🔥🧠PhD positions are open in my lab, studying brain development and neurodevelopmental disorders based on neuroimaging MRI scans. Due: Dec 1, 2025. If you are interested, please DM me.
21.10.2025 19:53 — 👍 18 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 0
My second first author paper of graduate school - Sex differences in response to violence: role of salience network expansion and connectivity on depression - is now published in Translational Psychiatry! rdcu.be/eLYg6
21.10.2025 20:43 — 👍 4 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0Official job ad is up! careers.peopleclick.com/careerscp/cl...
15.10.2025 15:51 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0yes definitely!!
04.10.2025 20:11 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Congrats, Armin!!!
03.10.2025 11:25 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Our new paper is out now in Neuron! 🎉 With @vaibhavtripathi.bsky.social @maxwellelliott.bsky.social Joanna Ladopoulou, Wendy Sun, Mark Eldaief, and Randy Buckner
Paper link: www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
Delighted to see the paper describing the Reproducible Brain Charts open data resource now out in @cp-neuron.bsky.social. Paper + link to data below; huge congrats to @goliashf.bsky.social @milhammichael.bsky.social and the whole RBC team. Lots of people (>2,500 downloads) are already using RBC!
24.09.2025 13:23 — 👍 8 🔁 6 💬 0 📌 1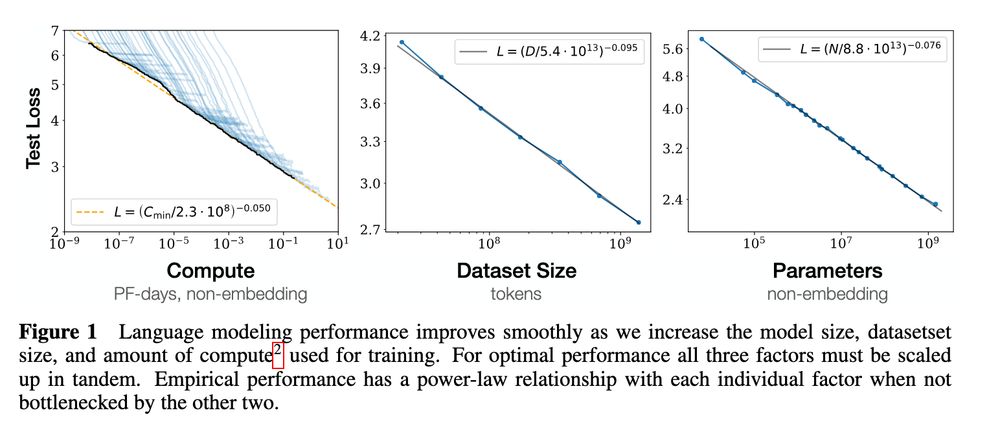
1/11 Excited to share our @Naturestudy led by @leonooi.bsky.social @csabaorban.bsky.social @shaoshiz.bsky.social
AI performance is known to scale with logarithm of sample size (Kaplan 2020), but in many domains, sample size can be # participants or # measurements...
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
thanks ted!!!
16.07.2025 17:54 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0Network analysis offers new insights into psychiatric symptoms. How can we use these tools to compare symptom patterns across groups?
⬇️🧵Thread below 🧵⬇️
doi.org/10.1017/s003...

Do you want to estimate brain aging from a single MRI scan?
Check out our latest work in Nature Aging
"DunedinPACNI estimates the longitudinal Pace of Aging from a single brain image to track health and disease"
Sex chromosome aneuploidies (varying X/Y-chrom dosage) can increase risk for psychopathology, but do these risks vary with age ? This matters for both clinical and mechanistic understanding.
A fab recent trainee - Melissa Roybal - asked these questions in a new paper. This is what she found ... ⬇️

Telltale features visible in standard brain images can reveal how quickly a person is ageing
https://go.nature.com/4kiNEPF
Many thanks to my co-first author @maxwellelliott.bsky.social, Annchen Knodt, our awesome team at Duke and Otago, and my advisors Av Caspi, Terrie Moffitt, and Ahmad Hariri!
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
We want this measure to be available to the scientific community to help uncover how aging is related to disease, exposure, and interventions.
The algorithm to estimate DunedinPACNI is publicly available at github.com/etw11/Dunedi...
DunedinPACNI is a novel, distinct approach to measuring aging from neuroimaging that can be easily estimated from simple measures from T1 MRI data.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
DunedinPACNI tended to explain a bit more variance in clinical outcomes. Notably, this variance did not overlap with brain age gap very much and DunedinPACNI and brain age gap were not very correlated.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Lastly, we wanted to test whether DunedinPACNI was distinct from brain age gap, a neuroimaging biomarker trained on chronological age.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
DunedinPACNI’s association with cognitive impairment in BrainLat was similar to that in ADNI, an initial indication of good generalization among people from Latin America.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Brain-based predictive models often fail when there are demographic differences between training and test samples – posing a hurdle for clinical translation. We tested if this was true for DunedinPACNI using the BrainLat dataset, a sample of Latin American adults with and without dementia.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
In UK Biobank, faster DunedinPACNI scores were related to frailty, number of chronic illnesses, risk of new chronic illness, and risk of death from any cause. Thus, DunedinPACNI appears to index aging across the entire body
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0So, DunedinPACNI seems like a useful predictor of cognitive and brain decline. But what about aging more broadly?
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Furthermore, faster DunedinPACNI scores at baseline predicted more rapid hippocampal atrophy in the future.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
In ADNI and UK Biobank, faster DunedinPACNI scores were correlated with worse cognition, cognitive impairment, and risk of cognitive decline
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Using Dunedin Study data, we trained an algorithm to estimate the Pace of Aging from brain structure. We call this measure “DunedinPACNI” – Pace of Aging Calculated from NeuroImaging
Then we applied this algorithm to external data to test its association with clinical outcomes.

We averaged the decline in each of these biomarkers to get a summary score of whole-body aging called “Pace of Aging”
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0First, we quantified longitudinal decline of 19 biomarkers of 6 different organ systems in members of the Dunedin Study, a cohort of 1037 people born in the same year and followed from birth until 45.
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Learning from epigenetics, we wondered if we could build a “next-generation” neuroimaging measure that estimates the rate of biological aging across the entire body
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0The best epigenetic clocks are trained using many different aging-related phenotypes. But neuroimaging clocks are almost all just trained on age
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0There are many algorithmic measures of biological aging, often called “clocks”. These are typically based on DNA methylation or brain MRI
01.07.2025 14:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0