Genetic regulation of cell type-specific chromatin accessibility shapes immune function and disease risk
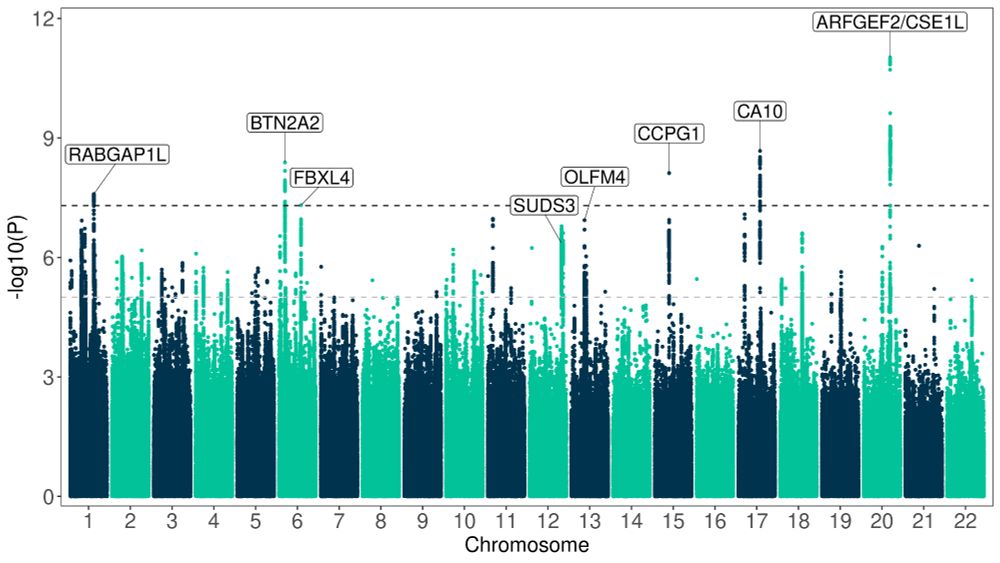
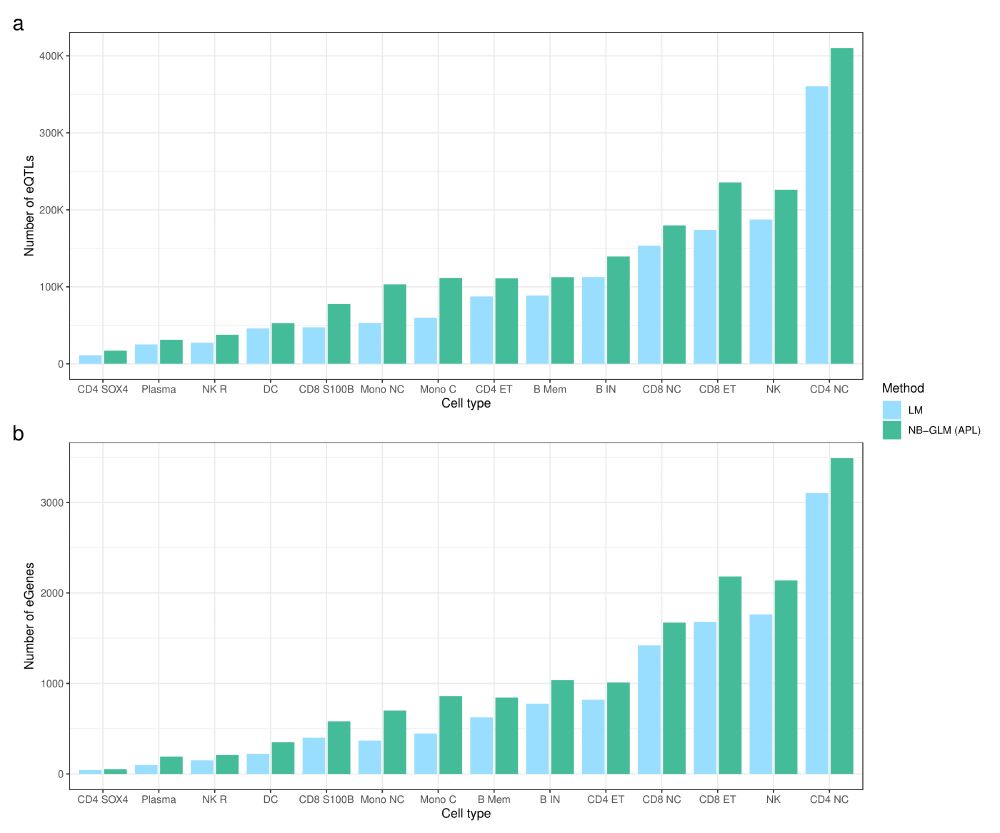
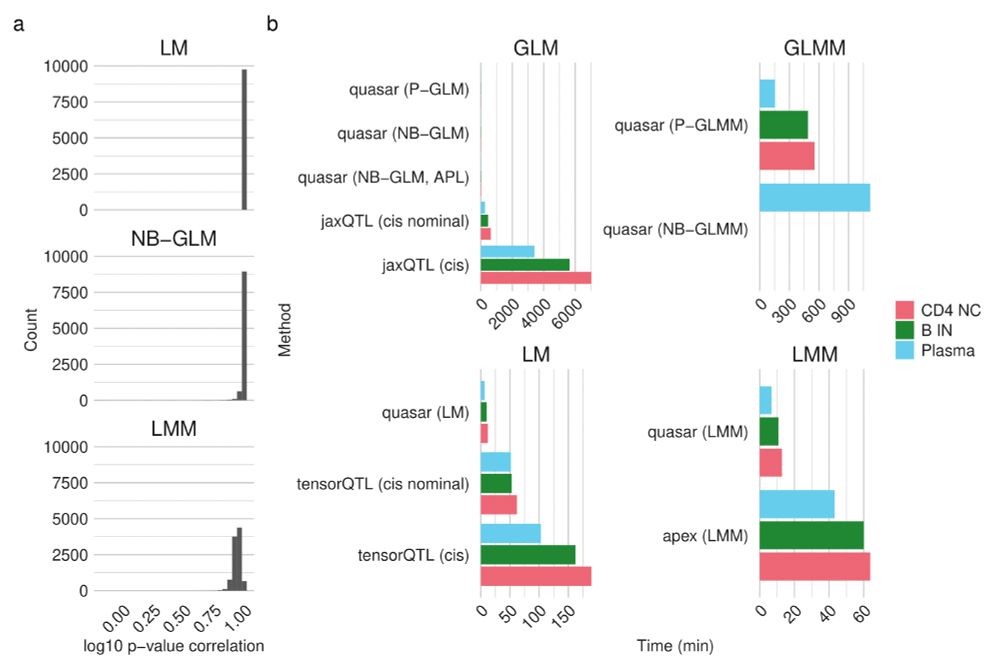
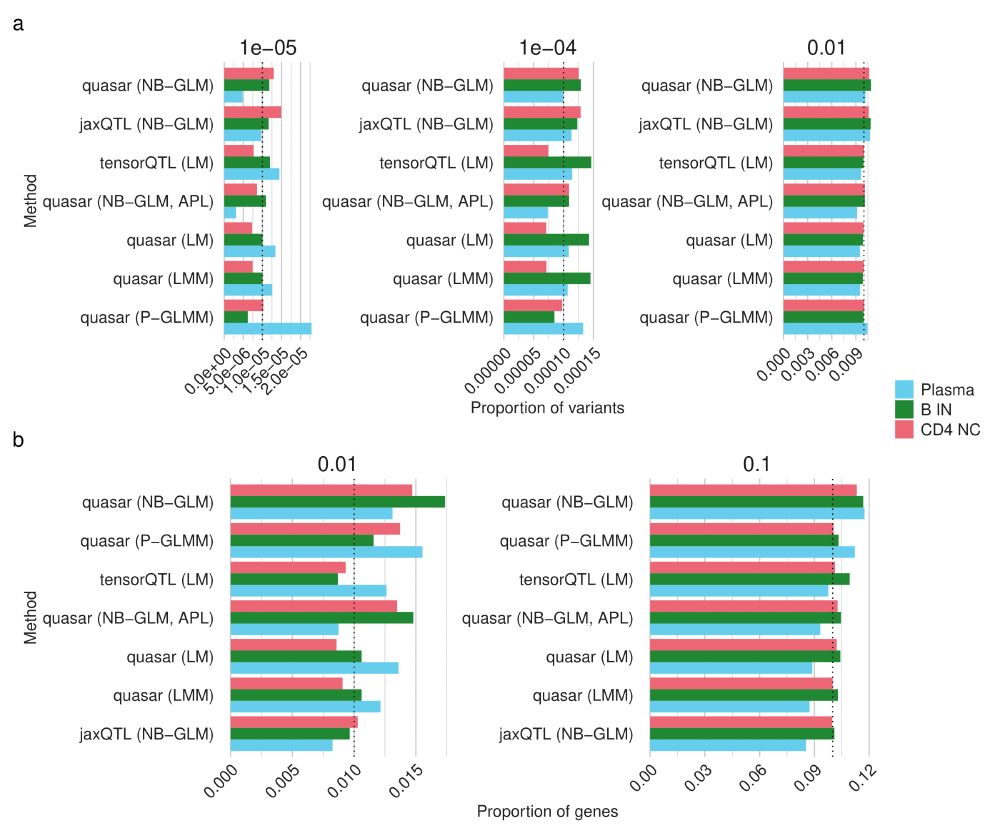
Understanding how genetic variation influences gene regulation at the single-cell level is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms underlying complex diseases. However, limited large-scale single-cell multi-omics data have constrained our understanding of the regulatory pathways that link variants to cell type-specific gene expression. Here we present chromatin accessibility profiles from 3.5 million peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) across 1,042 donors, generated using single-cell ATAC-seq and multiome (RNA+ATAC) sequencing, with matched whole-genome sequencing, generated as part of the TenK10K program. We characterized 440,996 chromatin peaks across 28 immune cell types and mapped 243,273 chromatin accessibility quantitative trait loci (caQTLs), 60% of which are cell type-specific. Integration with TenK10K scRNA-seq data (5.4 million PBMCs) identified 31,688 candidate cis-regulatory elements colocalized with eQTLs; over half (52.5%) show evidence of causal effects mediated via chromatin accessibility. Integrating caQTLs with GWAS summary statistics for 16 diseases and 44 blood traits uncovered 9.8% - 30.0% more colocalized signals compared with using eQTLs alone, many of which have not been reported in prior studies. We demonstrate cell type-specific mechanisms, such as a regulatory effect on IRGM acting through altered promoter chromatin accessibility in CD8 effector memory T cells but not in naive cells. Using a graph neural network, we inferred peak-to-gene relationships from unpaired multiome data by incorporating caQTL and eQTL signals, achieving up to 80% higher accuracy compared to using paired multiome data without QTL information. This improvement further enhanced gene regulatory network inference, leading to the identification of 128 additional transcription factor (TF)-target gene pairs (a 22% increase). These findings provide an unprecedented single-cell map of chromatin accessibility and genetic variation in human circulating immune cells, establishing a powerful resource for dissecting cell type-specific regulation and advancing our understanding of genetic risk for complex diseases. ### Competing Interest Statement L.C., E.B.D., and K.K.H.F. are employed at Illumina Inc. D.G.M. is a paid advisor to Insitro and GSK, and receives research funding from Google and Microsoft, unrelated to the work described in this manuscript. G.A.F reports grants from National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia), grants from Abbott Diagnostic, Sanofi, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and NSW Health. G.A.F reports honorarium from CSL, CPC Clinical Research, Sanofi, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Heart Foundation, and Abbott. G.A.F serves as Board Director for the Australian Cardiovascular Alliance (past President), Executive Committee Member for CPC Clinical Research, Founding Director and CMO for Prokardia and Kardiomics, and Executive Committee member for the CAD Frontiers A2D2 Consortium. In addition, G.A.F serves as CMO for the non-profit, CAD Frontiers, with industry partners including, Novartis, Amgen, Siemens Healthineers, ELUCID, Foresite Labs LLC, HeartFlow, Canon, Cleerly, Caristo, Genentech, Artyra, and Bitterroot Bio, Novo Nordisk and Allelica. In addition, G.A.F has the following patents: "Patent Biomarkers and Oxidative Stress" awarded USA May 2017 (US9638699B2) issued to Northern Sydney Local Health District, "Use of P2X7R antagonists in cardiovascular disease" PCT/AU2018/050905 licensed to Prokardia, "Methods for treatment and prevention of vascular disease" PCT/AU2015/000548 issued to The University of Sydney/Northern Sydney Local Health District, "Methods for predicting coronary artery disease" AU202290266 issued to The University of Sydney, and the patent "Novel P2X7 Receptor Antagonists" PCT/AU2022/051400 (23.11.2022), International App No: WO/2023/092175 (01.06.2023), issued to The University of Sydney. ### Funding Statement A.X. is supported by NHMRC Investigator grant 2033018. J.E.P. is supported by NHMRC Investigator grant 2034556, and a Fok Family Fellowship; D.G.M. is supported by an NHMRC investigator grant (2009982). G.A.F. and the BioHEART Study have been supported by NHMRC Investigator Grant, NSW Health Office of Health and Medical Research, and the NSW Health Statewide Biobank scheme. ### Author Declarations I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained. Yes The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below: The Human Research Ethics Committee of St Vincent's Hospital gave ethical approval for this work. The National Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research of the National Health and Medical Research Council gave ethical approval for this work. I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals. Yes I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance). Yes I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable. Yes Raw caQTL summary statistics will be available at Zenodo website prior to acceptance. [https://github.com/powellgenomicslab/tenk10k\_phase1\_multiome][1] [1]: https://github.com/powellgenomicslab/tenk10k_phase1_multiome