
Can reading one article change your belief in free will? New studies say maybe—but the effect doesn’t last. Our beliefs might be more resilient than they seem
New work by @olivergenschow.bsky.social
@protzko.bsky.social @sebraem.bsky.social 💡

Can reading one article change your belief in free will? New studies say maybe—but the effect doesn’t last. Our beliefs might be more resilient than they seem
New work by @olivergenschow.bsky.social
@protzko.bsky.social @sebraem.bsky.social 💡

These findings inform current debates on what it means to become an expert (e.g., 10,000-hour rule), extending them to the domain of psychological science.
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
5/5
Knowledge about psychology was also associated with thinking that phenomena had a material basis (e.g., brain, vs. soul). This extended to intuitive responses -- which generally lean more towards dualism. Again, these effects were stronger for subjectively intense experiences.
4/5
More knowledgeable individuals believed that psychological phenomena were more explainable through science, in particular the ones that people do not consider to be explainable (i.e., with an intense subjective experience).
3/5
Importantly, we find that these shifts only happen with meaningful exposure to psychology -- that is, exposure that translates into knowledge about psychology --, not just by progressing through their degree. 🎓
2/5
New paper! 🚨
Does studying psychology change how people think about psychology (even at an intuitive level)? 🤔
We tracked students across their degree and found shifts in their beliefs about the bases of psychological phenomena and their scientific explainability.
1/5

Even if you tell people cognitive biases are good & lead to good outcomes, we still think they have the bias less than others.
Only when we see the bias as very desirable we might think we are = to others on it.
From @cruzf.bsky.social & André Mata
link.springer.com/content/pdf/...
#psych #phdsky
Visible light 🔆 or electromagnetic waves 📡: Which helps people understand better?
In a new post for Character & Context (@spspnews.bsky.social), I dive into my work with @tanialombrozo.bsky.social on how jargon shapes scientific understanding. Check it out here!
spsp.org/news/charact...
🇬🇧
I recently had a conversation with @tiagoramalho.bsky.social about the research I've been conducting.
💡We talked about topics I'm passionate about: Overconfidence and science learning, how this is impacted by artificial intelligence, and more.
🇵🇹
Recentemente, estive à conversa com o @tiagoramalho.bsky.social a respeito da investigação que tenho conduzido.
💡 Falámos sobre temas que me entusiasmam: Sobreconfiança e aprendizagem de ciência, como isto é impactado pela inteligência artificial, etc.
Para os interessados👇


So grateful for the chance to attend the EASP Summer School organized by @jimaceverett.bsky.social. Huge thanks to @jimaceverett.bsky.social and @mgreinecke.bsky.social for your mentorship in the Moral Psych of AI workstream, and to all of the other amazing students I had the chance to learn from!
01.08.2025 12:39 — 👍 12 🔁 5 💬 2 📌 2
🚨Check out our new paper with @boissinesther.bsky.social, Alexandra Delmas & @wimdeneys.bsky.social in Acta Psych!
📹 We show that video debiasing training can boost reasoning accuracy - not just deliberation, but intuition too!
🔓 Open access: www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
Quick summary👇

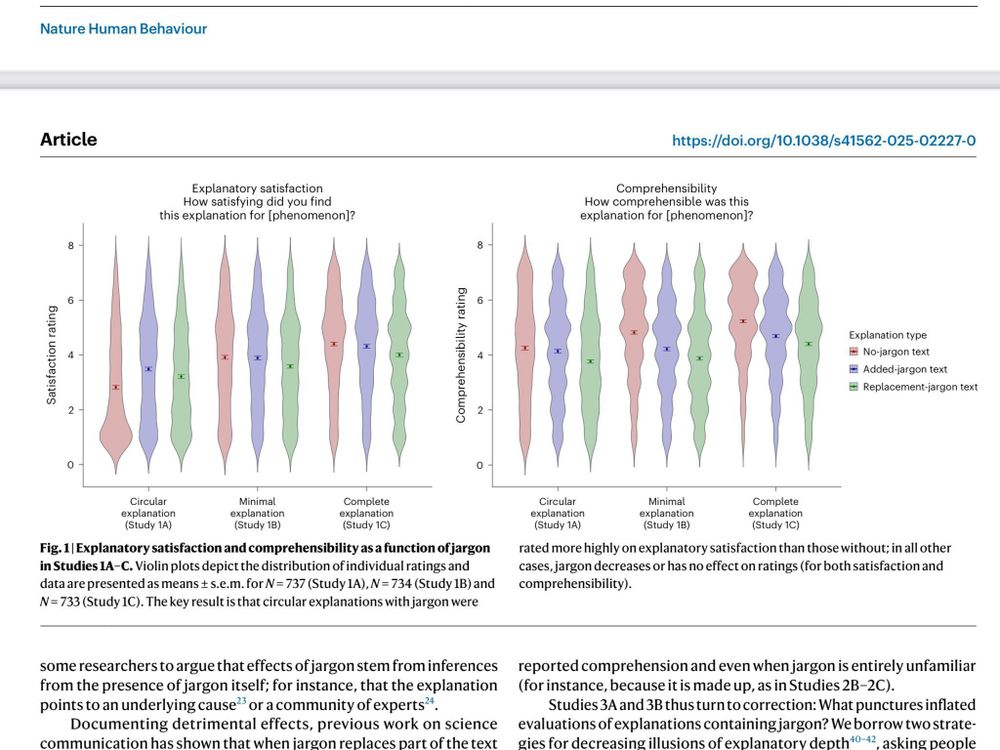
Research by @cruzf.bsky.social & @tanialombrozo.bsky.social suggests laypeople may find explanations containing jargon more satisfying despite understanding them less well because they assume the jargon fills gaps in explanations that are otherwise incomplete:
buff.ly/FWgSBaZ
Thank you, @rafmbatista.bsky.social! Let us know if you have any thoughts or questions!
12.06.2025 13:36 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
A special thanks to @tanialombrozo.bsky.social, my advisor, without whom this wouldn't be possible, for all the guidance and all she taught me!
And shout-out to my lab mates @keremoktar.bsky.social @caseylewry.bsky.social
Read more here: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
9/9
This work has implications for the present epistemic landscape, which is becoming increasingly complex. We discuss downstream consequences for conceptualizing overconfidence, delivering science communication, and thinking about human-AI alignment!
8/9
✅ We find that people are poorly calibrated in the perceptions they have about the quality of their own explanations. In particular, miscalibration emerges for those that are exposed to explanations but fail to reproduce it in their own (S4).
7/9
✅ Effects of jargon even when they are misguided (i.e., for made-up jargon) and for naturalistic stimuli (e.g., tweets, S2B-S2C);
✅ We can correct people's biased responses by showing them that gaps persist (e.g., asking them to generate their own explanations, S3A-S3B);
6/9
💡 Main findings 💡
✅ Jargon increases explanatory satisfaction (for circular explanations, Studies 1A-4 [S1A-S4]), but decreases comprehensibility (S1A-S1C);
✅ Jargon increases perceptions of explanations by filling explanatory gaps (S2A-S3B);
5/9
We identified how to reduce this bias as well: Asking people to e.g., generate explanations impacted more their ratings of explanations with jargon. We also observed overconfidence, which we found the most for those that read explanations with jargon, but fail to reproduce them.
4/9
We then tested an explanatory account for this dissociation: People assume the jargon is doing important work, filling in conceptual gaps. So, this boost in quality for explanations with jargon is punctured for more complete explanations, since there are less gaps to fill.
3/9
Across 9 experiments (+6600 participants), we explored a paradox: How do non-experts judge scientific explanations they can’t fully understand? We found that scientific jargon can increase people’s satisfaction with explanations, even though it makes them less comprehensible.
2/9
🚨 I’m incredibly excited to share this one: Latest paper out in Nature Human Behaviour!
Publishing in Nature has always been a goal of mine, and I’m so happy I got there with work developed at Princeton, where I learned so much and grew as a researcher.
1/9
🔬 How did we test this?
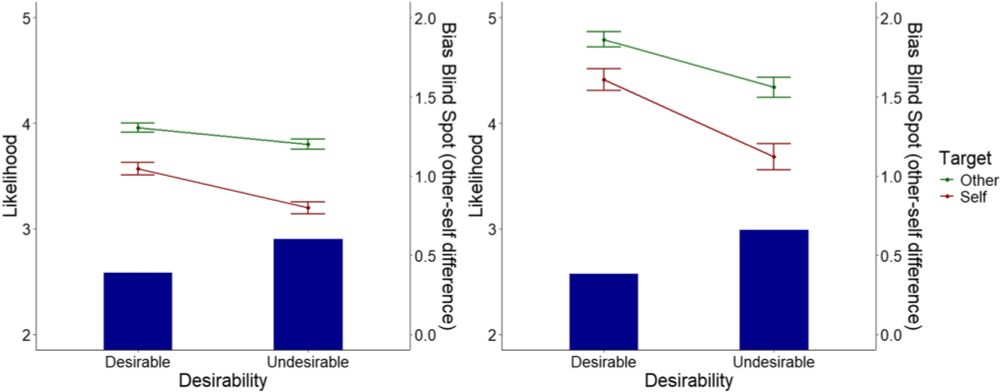
We manipulated bias desirability. Biases were framed as desirable (e.g., beneficial to the individual) or undesirable (e.g., harmful). We tested this both within the same bias and across different biases.
5/5
💡 What did we find?
Our study shows that the bias blind spot is smaller when the bias is considered desirable (e.g., being overly positive about close others). The more someone sees a bias as desirable, the smaller their blind spot for that bias.
4/5
🧠 What was our objective?
We aimed to reframe the bias blind spot. While it's often thought to be due to introspection, we tested whether it’s driven by motivations to maintain a positive self-image. People deny their biases but may accept those they see as desirable.
3/5
🔍 What is the Bias Blind Spot?
The Bias Blind Spot is when people recognize biases in others but not in themselves. Despite being subject to the same biases, we often see ourselves as less biased than others.
2/5
🚨 New Research Published! 🚨
"Motivated Bias Blind Spot: People confess to more or less bias depending on its desirability"
link.springer.com/article/10.1...
1/5

5/end
This is highly consequential: If we want the public to better understand and accept psychological science, we should match our explanations to appeal to their intuitions (or alternatively reframe these intuitions gently).
Paper link: www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....
4/
This suggests people default to “prototype” (brain-based) explanations, aligned with their views of low-subjectivity phenomena (but not high-subjectivity ones).
When you give people the right kind of explanation, even these subjective phenomena become more explainable.