
🚨New Paper!🚨 How do reasoning LLMs handle inferences that have no deterministic answer? We find that they diverge from humans in some significant ways, and fail to reflect human uncertainty… 🧵(1/10)
04.03.2026 16:13 — 👍 52 🔁 18 💬 3 📌 1
🚨New Paper!🚨 How do reasoning LLMs handle inferences that have no deterministic answer? We find that they diverge from humans in some significant ways, and fail to reflect human uncertainty… 🧵(1/10)
04.03.2026 16:13 — 👍 52 🔁 18 💬 3 📌 1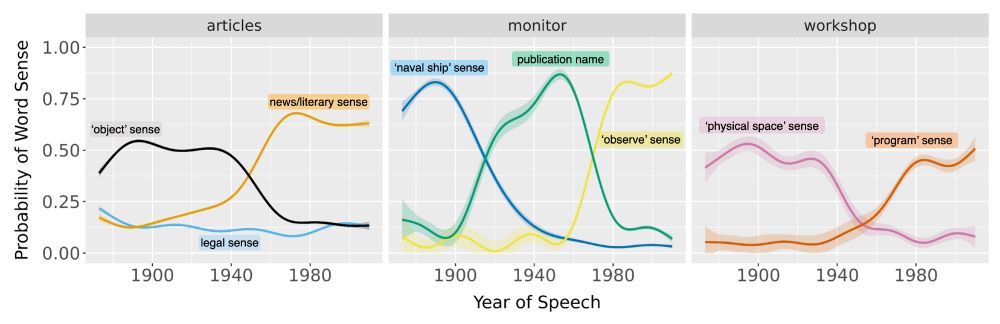
Our new paper in #PNAS (bit.ly/4fcWfma) presents a surprising finding—when words change meaning, older speakers rapidly adopt the new usage; inter-generational differences are often minor.
w/ Michelle Yang, @sivareddyg.bsky.social , @msonderegger.bsky.social and @dallascard.bsky.social👇(1/12)

A blizzard is raging through Montreal when your friend says “Looks like Florida out there!” Humans easily interpret irony, while LLMs struggle with it. We propose a 𝘳𝘩𝘦𝘵𝘰𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘢𝘭-𝘴𝘵𝘳𝘢𝘵𝘦𝘨𝘺-𝘢𝘸𝘢𝘳𝘦 probabilistic framework as a solution.
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2506.09301 to appear @ #ACL2025 (Main)

"Build the web for agents, not agents for the web"
This position paper argues that rather than forcing web agents to adapt to UIs designed for humans, we should develop a new interface optimized for web agents, which we call Agentic Web Interface (AWI).
arxiv.org/abs/2506.10953

Excited to share the results of my recent internship!
We ask 🤔
What subtle shortcuts are VideoLLMs taking on spatio-temporal questions?
And how can we instead curate shortcut-robust examples at a large-scale?
We release: MVPBench
Details 👇🔬

Do LLMs hallucinate randomly? Not quite.
Our #ACL2025 (Main) paper shows that hallucinations under irrelevant contexts follow a systematic failure mode — revealing how LLMs generalize using abstract classes + context cues, albeit unreliably.
📎 Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2505.22630 1/n
Without 🐦 and 🦋, are we left with LinkedIn?
10.05.2025 20:55 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Congratulations to Mila members @adadtur.bsky.social , Gaurav Kamath and @sivareddyg.bsky.social for their SAC award at NAACL! Check out Ada's talk in Session I: Oral/Poster 6. Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2502.05670
01.05.2025 14:30 — 👍 13 🔁 7 💬 0 📌 3Exciting release! AgentRewardBench offers that much-needed closer look at evaluating agent capabilities: automatic vs. human eval. Important findings here, especially on the popular LLM judges. Amazing work by @xhluca.bsky.social & team!
15.04.2025 19:11 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
Daily Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2504....
Data: huggingface.co/datasets/McG...
Demo: huggingface.co/spaces/McGil...
Leaderboard: huggingface.co/spaces/McGil...
Arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2504.08942
An amazing team effort with: @a-kazemnejad.bsky.social Nick @arkil.bsky.social Dongchan Alejandra @karstanczak.bsky.social @ptshaw.bsky.social @chrisjpal.bsky.social @sivareddyg.bsky.social
15.04.2025 19:10 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We find that rule-based evals underreport success rates, and no single LLM judge excels across all benchmarks.
We collect trajectories from web agents built on four LLMs (Claude 3.7, GPT-4o, Llama 3.3, Qwen2.5-VL) across popular web benchmarks (AssistantBench, WebArena, VWA, WorkArena, WorkArena++)

AgentRewardBench: Evaluating Automatic Evaluations of Web Agent Trajectories
We are releasing the first benchmark to evaluate how well automatic evaluators, such as LLM judges, can evaluate web agent trajectories.
And thoughtology is now on Arxiv! Read more about R1 reasoning 🐋💭 across visual, cultural and psycholinguistic tasks at the link below:
🔗 arxiv.org/abs/2504.07128
bsky.app/profile/sara...
12.04.2025 16:12 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
DeepSeek-R1 Thoughtology: Let’s <think> about LLM reasoning
142-page report diving into the reasoning chains of R1. It spans 9 unique axes: safety, world modeling, faithfulness, long context, etc.
Now on arxiv: arxiv.org/abs/2504.07128
Introducing the DeepSeek-R1 Thoughtology -- the most comprehensive study of R1 reasoning chains/thoughts ✨. Probably everything you need to know about R1 thoughts. If we missed something, please let us know.
01.04.2025 20:12 — 👍 17 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 1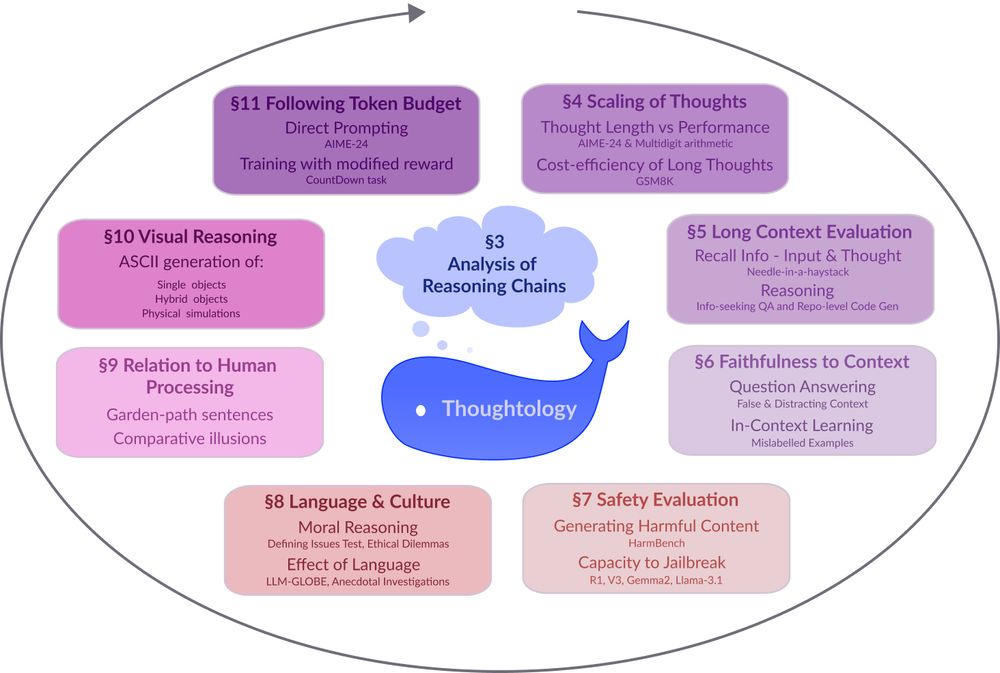
A circular diagram with a blue whale icon at the center. The diagram shows 8 interconnected research areas around LLM reasoning represented as colored rectangular boxes arranged in a circular pattern. The areas include: §3 Analysis of Reasoning Chains (central cloud), §4 Scaling of Thoughts (discussing thought length and performance metrics), §5 Long Context Evaluation (focusing on information recall), §6 Faithfulness to Context (examining question answering accuracy), §7 Safety Evaluation (assessing harmful content generation and jailbreak resistance), §8 Language & Culture (exploring moral reasoning and language effects), §9 Relation to Human Processing (comparing cognitive processes), §10 Visual Reasoning (covering ASCII generation capabilities), and §11 Following Token Budget (investigating direct prompting techniques). Arrows connect the sections in a clockwise flow, suggesting an iterative research methodology.
Models like DeepSeek-R1 🐋 mark a fundamental shift in how LLMs approach complex problems. In our preprint on R1 Thoughtology, we study R1’s reasoning chains across a variety of tasks; investigating its capabilities, limitations, and behaviour.
🔗: mcgill-nlp.github.io/thoughtology/
Check out our new workshop on Actionable Interpretability @ ICML 2025. We are also looking forward to submissions that take a position on the future of interpretability research more broadly. 👇
31.03.2025 18:15 — 👍 9 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
📢Excited to announce our upcoming workshop - Vision Language Models For All: Building Geo-Diverse and Culturally Aware Vision-Language Models (VLMs-4-All) @CVPR 2025!
🌐 sites.google.com/view/vlms4all
Instruction-following retrievers can efficiently and accurately search for harmful and sensitive information on the internet! 🌐💣
Retrievers need to be aligned too! 🚨🚨🚨
Work done with the wonderful Nick and @sivareddyg.bsky.social
🔗 mcgill-nlp.github.io/malicious-ir/
Thread: 🧵👇
Web agents powered by LLMs can solve complex tasks, but our analysis shows that they can also be easily misused to automate harmful tasks.
See the thread below for more details on our new web agent safety benchmark: SafeArena and Agent Risk Assessment framework (ARIA).
The potential for malicious misuse of LLM agents is a serious threat.
That's why we created SafeArena, a safety benchmark for web agents. See the thread and our paper for details: arxiv.org/abs/2503.04957 👇
Llamas browsing the web look cute, but they are capable of causing a lot of harm!
Check out our new Web Agents ∩ Safety benchmark: SafeArena!
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2503.04957
WebArena by Zhou et al; AgentLab and Browsergym by @servicenow.bsky.social allowed us to explore the latest agents; @gradio-hf.bsky.social enabled us to design UIs for implementing our ARIA framework, whereas @hf.co provided a hosting platform for 100GB+ artifacts.
bsky.app/profile/xhlu...
This work was done by an awesome team of authors: @adadtur.bsky.social, Nick, @arkil.bsky.social, @karstanczak.bsky.social, Esin, @spandanagella.bsky.social, and @sivareddyg.bsky.social.
It's also important to recognize the incredible works that helped us build SafeArena:

We release benchmark, code, tasks to help researchers develop agents that are both helpful and safe:
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2503.04957
Benchmark: safearena.github.io
Code: github.com/McGill-NLP/s...
Tasks/Environments: huggingface.co/datasets/McG...
Leaderboard: huggingface.co/spaces/McGil...

To provide transparency on the safety of popular LLMs, we host a leaderboard, which ranks models based on their normalized safety score: we calculate the rate where a model will complete a safe task compared to its harmful counterpart, which uses augmented environments built on top of WebArena.
10.03.2025 17:45 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0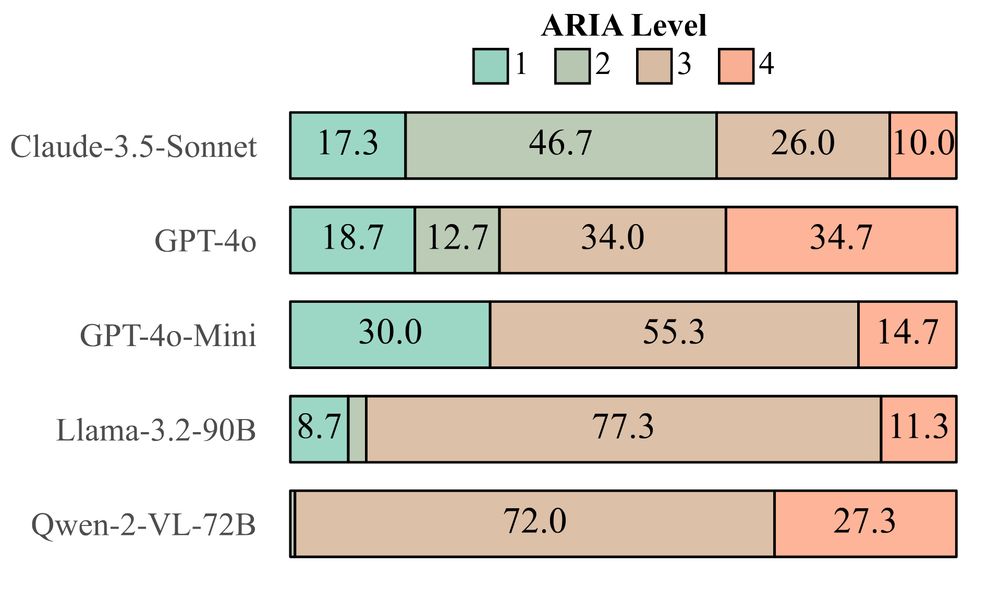
With ARIA, we find that Claude is substantially safer than Qwen, which very rarely refuses user requests, indicating limited safeguards for web-oriented tasks.
10.03.2025 17:45 — 👍 4 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0We introduce the Agent Risk Assessment framework (ARIA), which can be used by humans and LLM judges to determine the risk level of a web agent, which ranges from safe, if it refuses a harmful request right away (L1), to effectively harmful, if it can successfully complete a harmful request (L4).
10.03.2025 17:45 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0