Nascent and mature
Ribosomal RNA
Unbalanced in parts
#ChromatinHaiku #RNAsky #28S #Chromatinsky
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Chromatin Haiku
@chromatinhaiku.bsky.social
Nuclear events Narratives in chromatin By haiku, of course
@chromatinhaiku.bsky.social
Nuclear events Narratives in chromatin By haiku, of course
Nascent and mature
Ribosomal RNA
Unbalanced in parts
#ChromatinHaiku #RNAsky #28S #Chromatinsky
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
The Range Extender
For enhancers to function
At long distances
#ChromatinHaiku
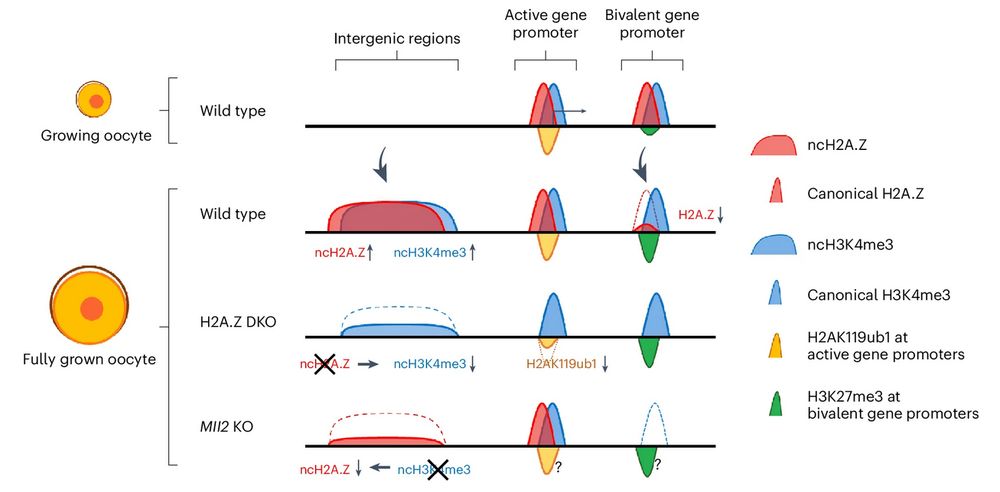
Model figure from Mei et al., Figure legend: Small growing oocytes show canonical distributions of H3K4me3 and H2A.Z at active and bivalent gene promoters. In wild-type FGOs, H3K4me3 and H2A.Z form non-canonical broad domains across intergenic regions, whereas H2A.Z is displaced at bivalent gene promoters. In H2A.Z-DKO FGOs, non-canonical H3K4me3 at intergenic regions and H2AK119ub1 at active gene promoters are partially reduced. In Mll2-KO FGOs, ncH2A.Z is partially reduced. The distributions of H3K27me3 and H2AK119ub1 were not investigated in the Mll2-KO FGOs (marked with question marks). H2AK119ub1 at bivalent gene promoters is not shown.
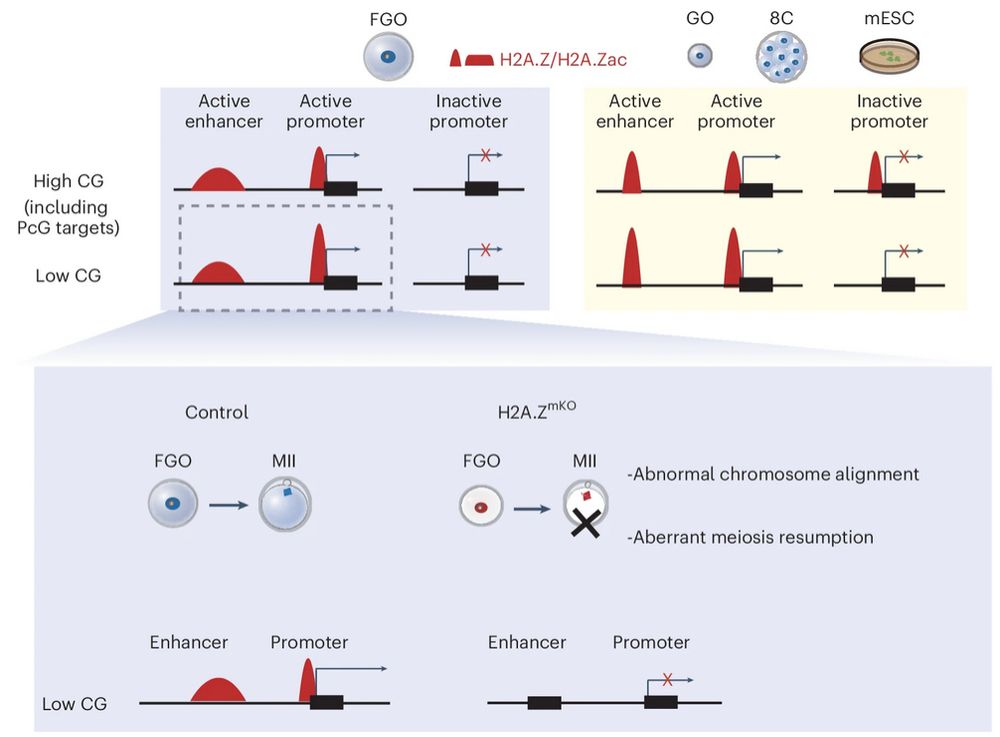
Model figure from Xu et al., Figure legend: Maternal depletion of H2A.Z results in aberrant meiosis resumption. Only a few FGOs survived to MII oocytes, with abnormal chromosome alignment. H2A.Z is acetylated (red) at active promoters and enhancers in mouse FGOs. Genes with low CG densities are preferentially downregulated in H2A.ZmKO FGOs. In mESCs, growing oocytes, and early embryos, in addition to active promoters and enhancers, H2A.Z and H2A.Zac are also present at inactive promoters with high CG densities, including Polycomb-target genes.
For mature oocytes
H2A.Z is needed
With MLL2
#ChromatinHaiku @natsmb.nature.com
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Pol2 stimulates
SETD2 methylation
Of histone H3
#ChromatinHaiku #H3K36
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Oh! I missed that it'd come out too: academic.oup.com/nar/advance-...
15.11.2024 22:01 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0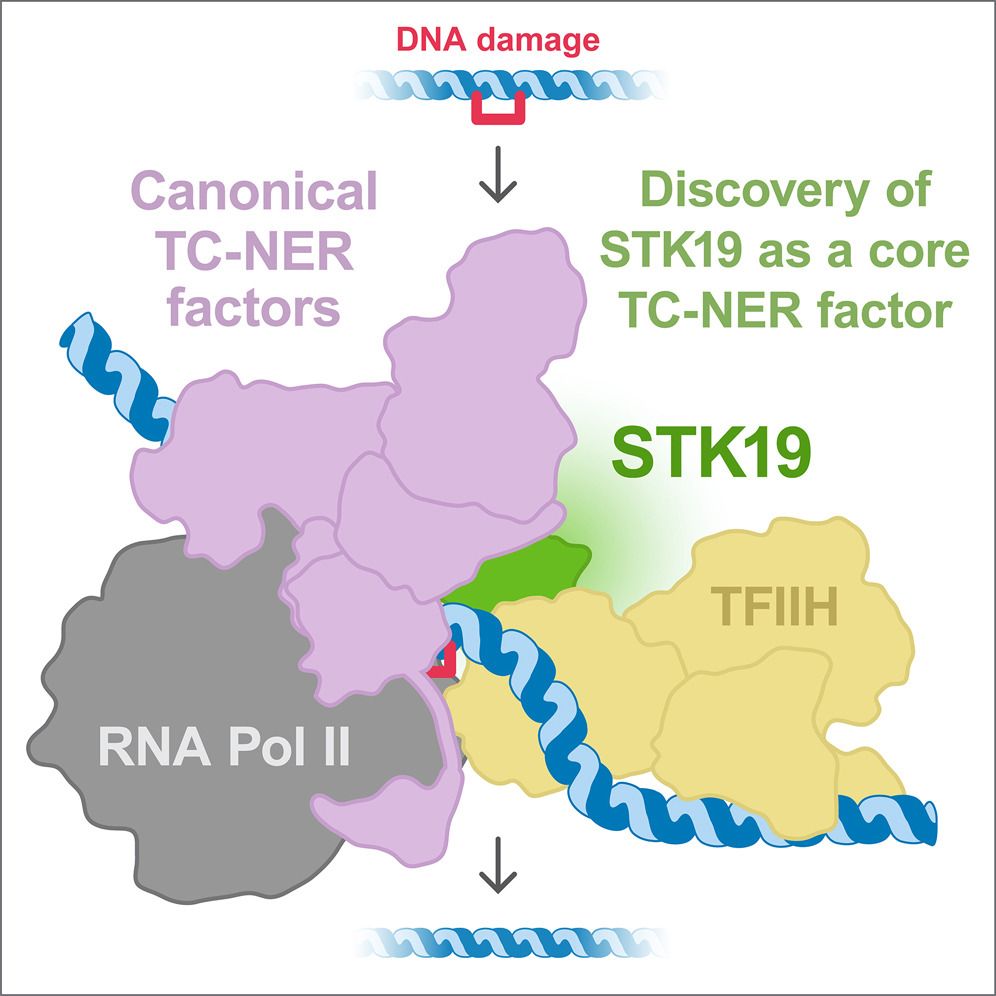
Graphical abstract for one of the papers
Graphical abstract for one of the papers
Graphical abstract for one of the papers
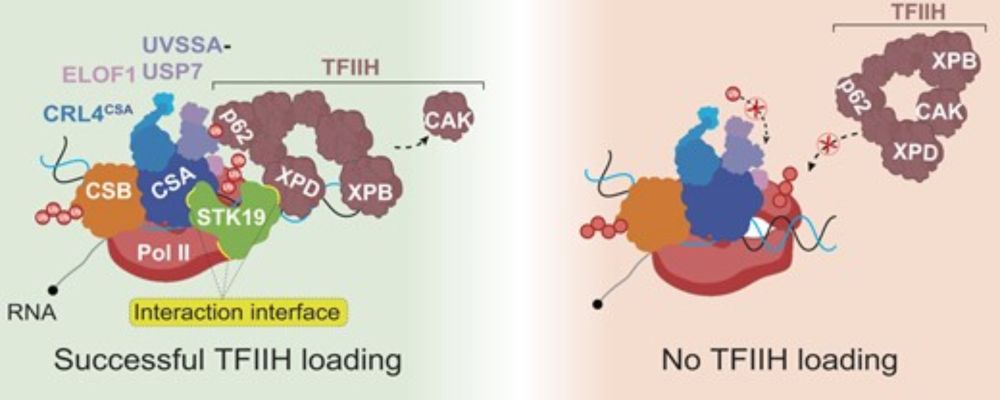
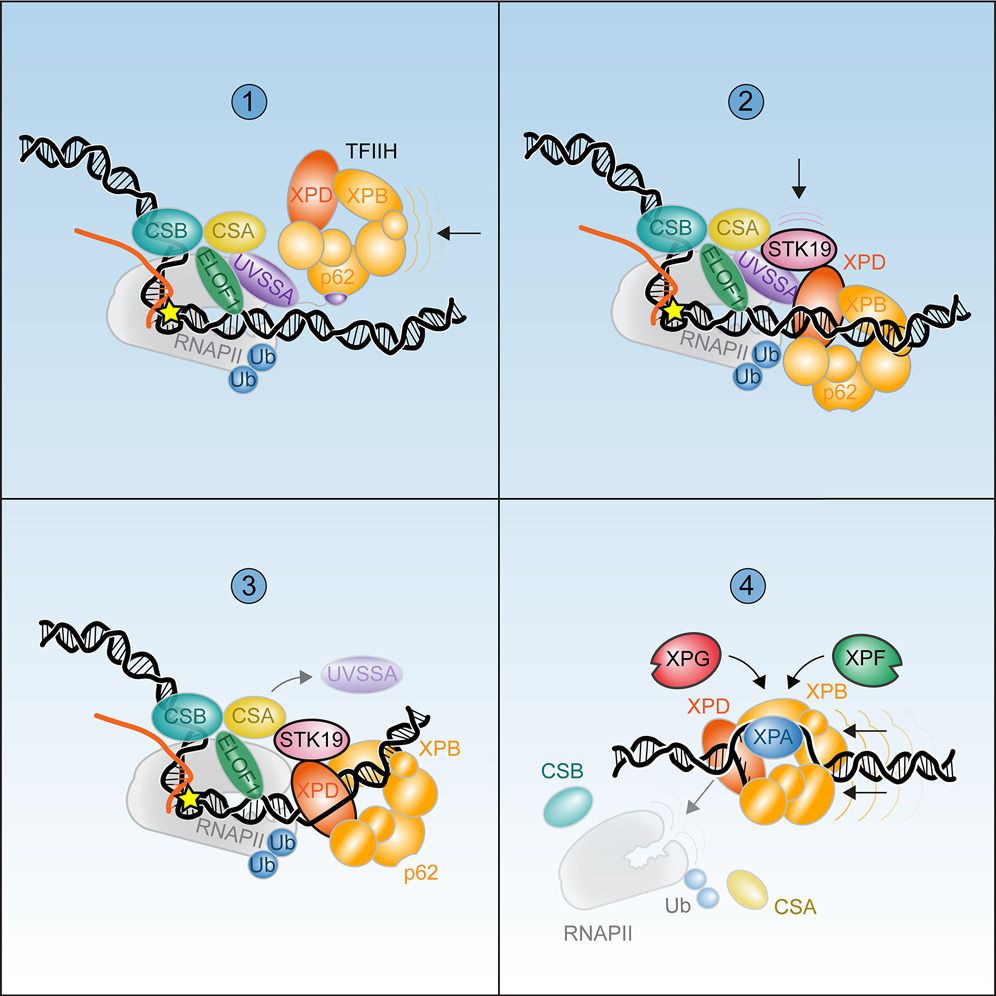
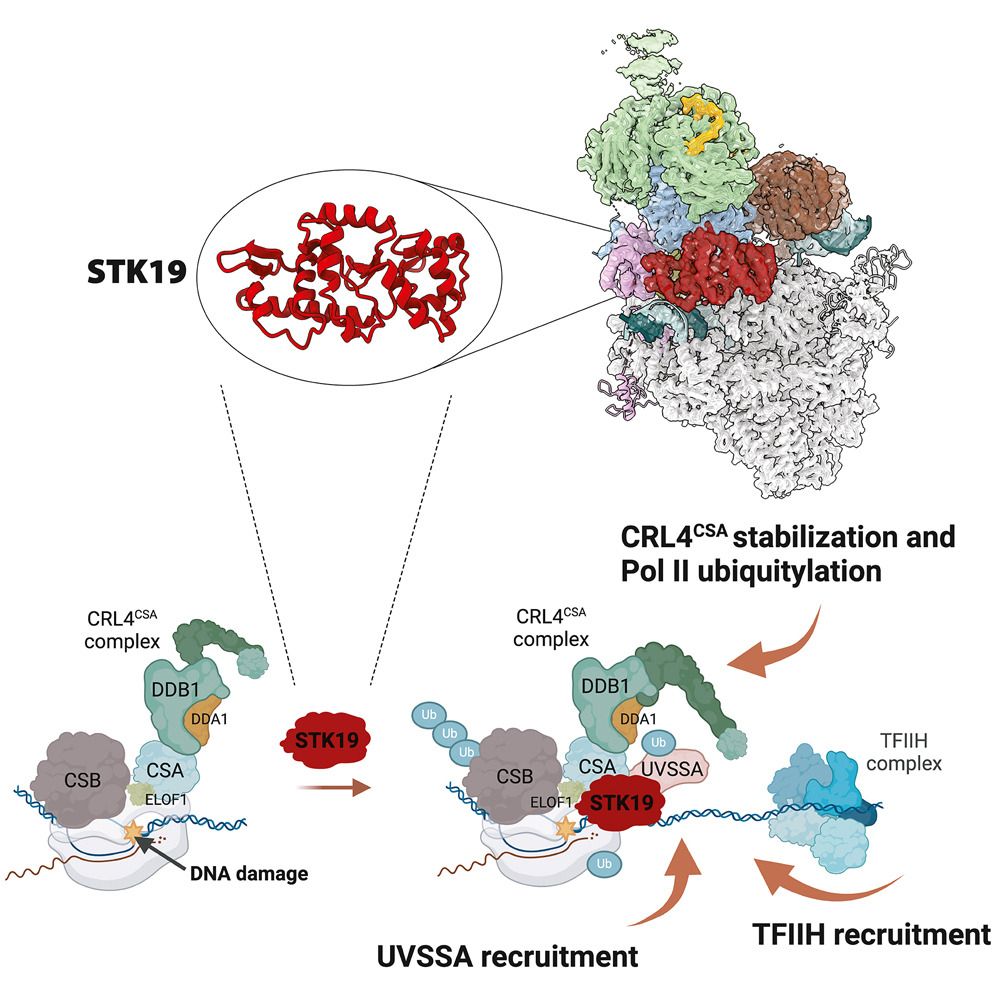
STK19
Transcription coupled repair
With TFIIH
#ChromatinHaiku
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
Polycomb restores
H2A ubiquitin
By read-write action
#ChromatinHaiku #ncPRC1-RYBP
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Being haiku-ed is an honor! You were so fast, too 🤩
12.11.2024 19:28 — 👍 38 🔁 5 💬 3 📌 0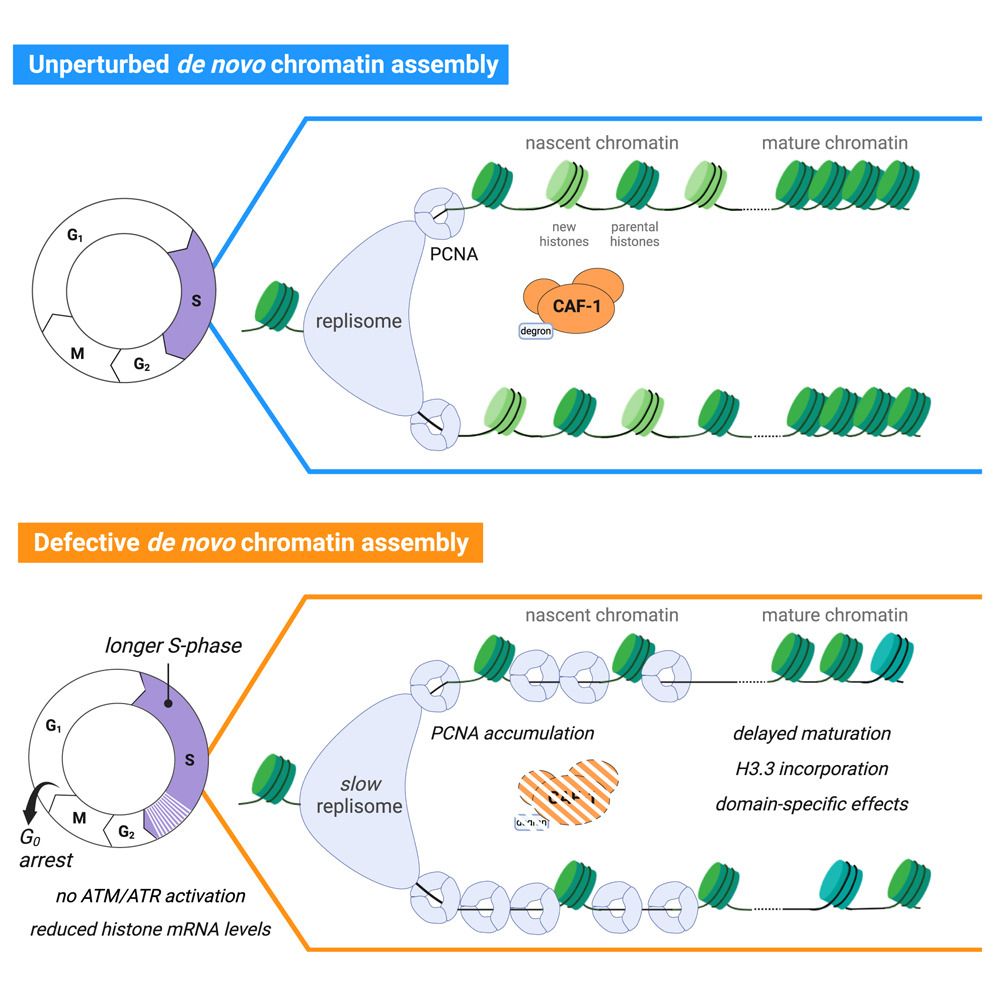
Graphical abstract for paper. Written abstract is as follows: Long-term perturbation of de novo chromatin assembly during DNA replication has profound effects on epigenome maintenance and cell fate. The early mechanistic origin of these defects is unknown. Here, we combine acute degradation of chromatin assembly factor 1 (CAF-1), a key player in de novo chromatin assembly, with single-cell genomics, quantitative proteomics, and live microscopy to uncover these initiating mechanisms in human cells. CAF-1 loss immediately slows down DNA replication speed and renders nascent DNA hyper-accessible. A rapid cellular response, distinct from canonical DNA damage signaling, is triggered and lowers histone mRNAs. In turn, histone variants’ usage and their modifications are altered, limiting transcriptional fidelity and delaying chromatin maturation within a single S-phase. This multi-level response induces a p53-dependent cell-cycle arrest after mitosis. Our work reveals the immediate consequences of defective de novo chromatin assembly during DNA replication, indicating how at later times the epigenome and cell fate can be altered.
Depleting CAF-1
Slows replisome, chromatin
G0 arrest
#ChromatinHaiku @fmattiroli.bsky.social
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...
A giant virus
With its own nucleosomes
And linker histone
#ChromatinHaiku
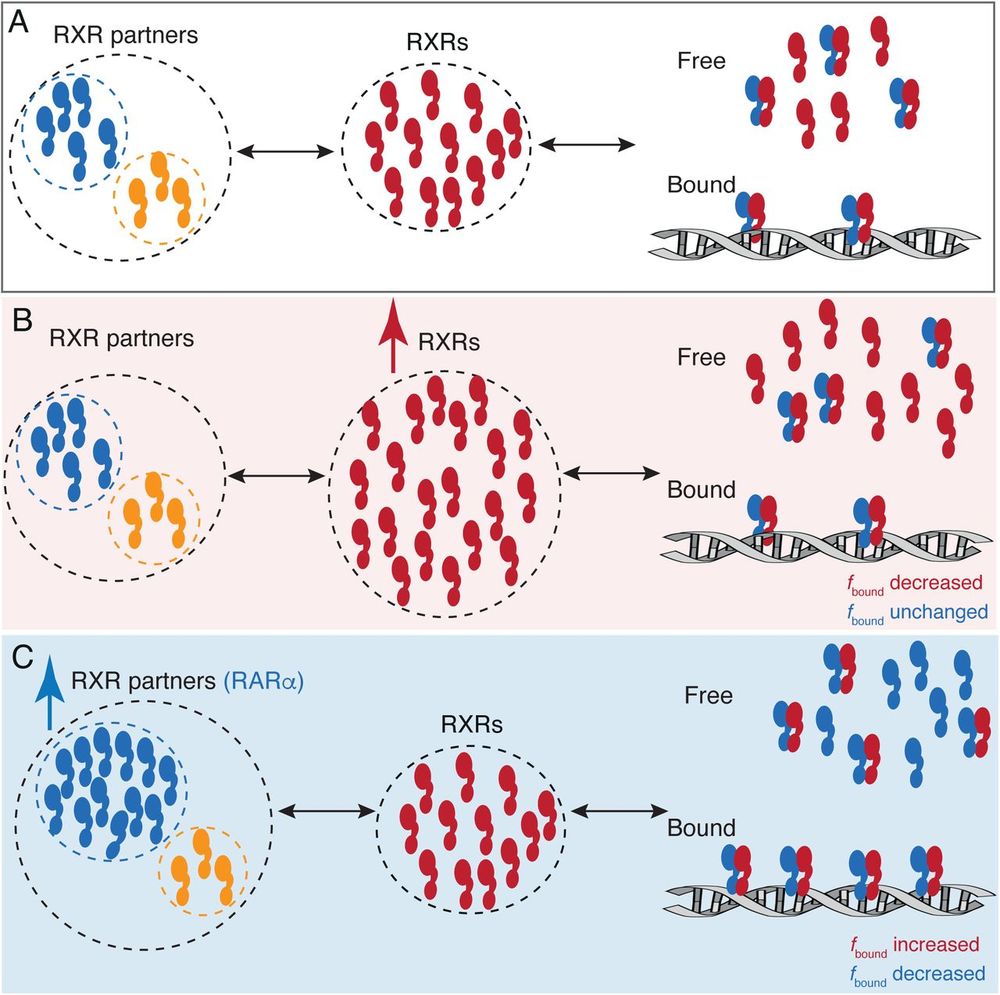
Figure 4. A model for RARα limited chromatin binding of RARα-RXRα heterodimers. (A) Pool of RXRα (red) and RXR partners (RARα – blue, other T2NRs-yellow) along with some number of chromatin bound RARα-RXRα heterodimers exist under normal conditions. (B) When the pool of free RXRα is increased, the number of chromatin bound RARα-RXRα heterodimers does not change. (C) When the pool of RARα is increased, chromatin binding RARα-RXRα heterodimers increases, until it reaches saturation. Note: For simplicity we have omitted to show heterodimerization of other T2NRs (yellow) with RXRα (red).
Limiting factors
For nuclear receptors
Live cell imaging
#ChromatinHaiku #SingleMoleculeTracking #ProximityAssistedPhotoactivation
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

DNMT3
Developmental methyl
A key role for B
#chromatinhaiku
www.youtube.com/watch?v=u2e0...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...