can I code fast? no. but can I code well? also no. but does my code work? alas, no
30.11.2024 21:39 — 👍 18328 🔁 2135 💬 408 📌 153can I code fast? no. but can I code well? also no. but does my code work? alas, no
30.11.2024 21:39 — 👍 18328 🔁 2135 💬 408 📌 153
From Szeliski's "Computer Vision – Algorithms and Applications."
29.11.2024 12:03 — 👍 26 🔁 2 💬 3 📌 0That account is doing AMA about research at deepmind 🤣
26.11.2024 05:28 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Trying to build a "books you must read" list for my lab that everyone gets when they enter. Right now its:
- Sutton and Barto
- The Structure of Scientific Revolutions
- Strunk and White
- Maybe "Prediction, Learning, and Games", TBD
Kinda curious what's missing in an RL / science curriculum



Want to learn / teach RL?
Check out new book draft:
Reinforcement Learning - Foundations
sites.google.com/view/rlfound...
W/ Shie Mannor & Yishay Mansour
This is a rigorous first course in RL, based on our teaching at TAU CS and Technion ECE.
Big fan of this essay by @abeba.bsky.social
25.11.2024 20:22 — 👍 25 🔁 3 💬 1 📌 0+100 to this recommendation
26.11.2024 01:03 — 👍 31 🔁 2 💬 2 📌 0
Nadav Cohen and I recently uploaded lecture notes on the theory (and surprising practical applications) of linear neural networks.
Hope that it can be useful, especially to those entering the field as it highlights distinctions between DL and "classical" ML theory
arxiv.org/abs/2408.13767
Your blog makes up for it... Equally balanced 😄😄
24.11.2024 19:02 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0Games are reasonable stepping stones as testbeds for AI progress. NetHack and text adventure games hit on modern AI weaknesses. I literally just gave a talk on why we should take Dungeons and Dragons and other role-playing games seriously as AI challenges.
23.11.2024 13:36 — 👍 71 🔁 11 💬 7 📌 1
Book outline
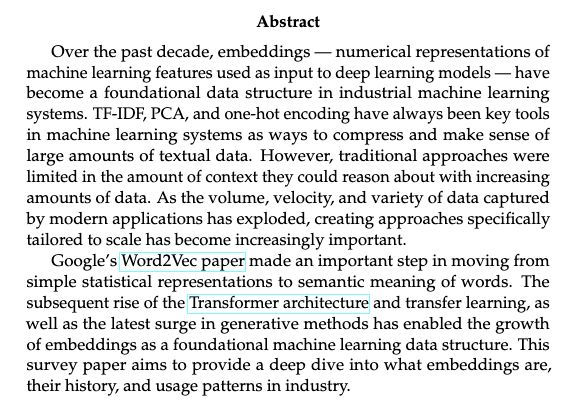
Over the past decade, embeddings — numerical representations of machine learning features used as input to deep learning models — have become a foundational data structure in industrial machine learning systems. TF-IDF, PCA, and one-hot encoding have always been key tools in machine learning systems as ways to compress and make sense of large amounts of textual data. However, traditional approaches were limited in the amount of context they could reason about with increasing amounts of data. As the volume, velocity, and variety of data captured by modern applications has exploded, creating approaches specifically tailored to scale has become increasingly important. Google’s Word2Vec paper made an important step in moving from simple statistical representations to semantic meaning of words. The subsequent rise of the Transformer architecture and transfer learning, as well as the latest surge in generative methods has enabled the growth of embeddings as a foundational machine learning data structure. This survey paper aims to provide a deep dive into what embeddings are, their history, and usage patterns in industry.

Cover image
Just realized BlueSky allows sharing valuable stuff cause it doesn't punish links. 🤩
Let's start with "What are embeddings" by @vickiboykis.com
The book is a great summary of embeddings, from history to modern approaches.
The best part: it's free.
Link: vickiboykis.com/what_are_emb...
Cohere's studies have shown that LLMs tend to rely on documents that contain procedural knowledge, such as code or mathematical formulas, when performing reasoning tasks.
This suggests that LLMs learn to reason by synthesizing procedural knowledge from examples of similar reasoning processes.
New here? Interested in AI/ML? Check out these great starter packs!
AI: go.bsky.app/SipA7it
RL: go.bsky.app/3WPHcHg
Women in AI: go.bsky.app/LaGDpqg
NLP: go.bsky.app/SngwGeS
AI and news: go.bsky.app/5sFqVNS
You can also search all starter packs here: blueskydirectory.com/starter-pack...
Is there any evidence for "pure" memory of space and time? All spatial and temporal memory tasks I can think of query memory of particular events/objects embedded in space and time. I conjecture that it's impossible for us to recall a location or time in the absence of events or objects.
20.11.2024 10:38 — 👍 52 🔁 8 💬 10 📌 1
The Llama 3.2 1B and 3B models are my favorite LLMs -- small but very capable.
If you want to understand how the architectures look like under the hood, I implemented them from scratch (one of the best ways to learn): github.com/rasbt/LLMs-f...