A table showing profit margins of major publishers. A snippet of text related to this table is below.
1. The four-fold drain
1.1 Money
Currently, academic publishing is dominated by profit-oriented, multinational companies for
whom scientific knowledge is a commodity to be sold back to the academic community who
created it. The dominant four are Elsevier, Springer Nature, Wiley and Taylor & Francis,
which collectively generated over US$7.1 billion in revenue from journal publishing in 2024
alone, and over US$12 billion in profits between 2019 and 2024 (Table 1A). Their profit
margins have always been over 30% in the last five years, and for the largest publisher
(Elsevier) always over 37%.
Against many comparators, across many sectors, scientific publishing is one of the most
consistently profitable industries (Table S1). These financial arrangements make a substantial
difference to science budgets. In 2024, 46% of Elsevier revenues and 53% of Taylor &
Francis revenues were generated in North America, meaning that North American
researchers were charged over US$2.27 billion by just two for-profit publishers. The
Canadian research councils and the US National Science Foundation were allocated US$9.3
billion in that year.

A figure detailing the drain on researcher time.
1. The four-fold drain
1.2 Time
The number of papers published each year is growing faster than the scientific workforce,
with the number of papers per researcher almost doubling between 1996 and 2022 (Figure
1A). This reflects the fact that publishers’ commercial desire to publish (sell) more material
has aligned well with the competitive prestige culture in which publications help secure jobs,
grants, promotions, and awards. To the extent that this growth is driven by a pressure for
profit, rather than scholarly imperatives, it distorts the way researchers spend their time.
The publishing system depends on unpaid reviewer labour, estimated to be over 130 million
unpaid hours annually in 2020 alone (9). Researchers have complained about the demands of
peer-review for decades, but the scale of the problem is now worse, with editors reporting
widespread difficulties recruiting reviewers. The growth in publications involves not only the
authors’ time, but that of academic editors and reviewers who are dealing with so many
review demands.
Even more seriously, the imperative to produce ever more articles reshapes the nature of
scientific inquiry. Evidence across multiple fields shows that more papers result in
‘ossification’, not new ideas (10). It may seem paradoxical that more papers can slow
progress until one considers how it affects researchers’ time. While rewards remain tied to
volume, prestige, and impact of publications, researchers will be nudged away from riskier,
local, interdisciplinary, and long-term work. The result is a treadmill of constant activity with
limited progress whereas core scholarly practices – such as reading, reflecting and engaging
with others’ contributions – is de-prioritized. What looks like productivity often masks
intellectual exhaustion built on a demoralizing, narrowing scientific vision.

A table of profit margins across industries. The section of text related to this table is below:
1. The four-fold drain
1.1 Money
Currently, academic publishing is dominated by profit-oriented, multinational companies for
whom scientific knowledge is a commodity to be sold back to the academic community who
created it. The dominant four are Elsevier, Springer Nature, Wiley and Taylor & Francis,
which collectively generated over US$7.1 billion in revenue from journal publishing in 2024
alone, and over US$12 billion in profits between 2019 and 2024 (Table 1A). Their profit
margins have always been over 30% in the last five years, and for the largest publisher
(Elsevier) always over 37%.
Against many comparators, across many sectors, scientific publishing is one of the most
consistently profitable industries (Table S1). These financial arrangements make a substantial
difference to science budgets. In 2024, 46% of Elsevier revenues and 53% of Taylor &
Francis revenues were generated in North America, meaning that North American
researchers were charged over US$2.27 billion by just two for-profit publishers. The
Canadian research councils and the US National Science Foundation were allocated US$9.3
billion in that year.

The costs of inaction are plain: wasted public funds, lost researcher time, compromised
scientific integrity and eroded public trust. Today, the system rewards commercial publishers
first, and science second. Without bold action from the funders we risk continuing to pour
resources into a system that prioritizes profit over the advancement of scientific knowledge.
We wrote the Strain on scientific publishing to highlight the problems of time & trust. With a fantastic group of co-authors, we present The Drain of Scientific Publishing:
a 🧵 1/n
Drain: arxiv.org/abs/2511.04820
Strain: direct.mit.edu/qss/article/...
Oligopoly: direct.mit.edu/qss/article/...
11.11.2025 11:52 — 👍 569 🔁 414 💬 7 📌 54

A joke scientific paper with the title "Over 90% of children diagnosed with autism consumed breast milk and/or formula mileL a comprehensive cross-sectional analysis of the obvious"
Who did this?!
01.11.2025 20:38 — 👍 1202 🔁 313 💬 69 📌 41
Index zone by BenLangmead
October 2025 batch of Kraken 2 indexes, including core_nt and many others, available: benlangmead.github.io/aws-indexes/k2
Coming soon to K2: a feature for querying many K2 indexes as though they're a single index. Highly useful if the index you want to query is too big to build and/or fit in RAM.
30.10.2025 18:11 — 👍 21 🔁 8 💬 2 📌 0

Napoleon's retreat from Moscow CREDIT Barbieri et al., Current Biology
DNA from Napoleon’s 1812 army identifies the pathogens likely responsible for the army’s demise during their Russian retreat. www.cell.com/current-biol...
Nicolás Rascovan & colleagues
@currentbiology.bsky.social
24.10.2025 15:00 — 👍 65 🔁 22 💬 4 📌 7
Around 10% of your Nanopore reads (SQK-RBK114) are incorrectly trimmed. Here is why, and how our new tool Barbell solves it:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Want to get started? github.com/rickbeeloo/b...
23.10.2025 20:16 — 👍 49 🔁 30 💬 3 📌 4
Really exciting that the preprint on Barbell, a new demultiplexer, is finally out!
It's the first tool that builds on Sassy, the approximate-DNA-searching tool that @rickbitloo.bsky.social and myself developed earlier this year, specifically with this application in mind.
23.10.2025 21:28 — 👍 20 🔁 15 💬 2 📌 0

GTDB release 10: a complete and systematic taxonomy for 715 230 bacterial and 17 245 archaeal genomes
Abstract. The Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB; https://gtdb.ecogenomic.org) provides a phylogenetically consistent and rank normalized genome-based taxonomy
Our @narjournal.bsky.social manuscript is out! It explores the growth of the GTDB (gtdb.ecogenomic.org) since its inception, as well as updates to the website, methodology, policies, and major taxonomic and nomenclatural changes over the past three years.
academic.oup.com/nar/advance-...
22.10.2025 14:20 — 👍 68 🔁 47 💬 0 📌 2
A randomized phase 1 study investigating gut microbiome changes with moxifloxacin vs. oral vancomycin: Implications for Clostridioides difficile risk
AbstractBackground. The epidemic, hypervirulent Clostridioides difficile ribotype (RT) 027 strain is associated with bacterial virulence traits, including
At first seems like comparing apples and oranges: moxifloxacin vs vancomycin?!
Results a bit surprising ("narrow spectrum" vancomycin change microbiome more), but this is just helicopter view.
More broadly, 👏 to these experimental medicine approaches for discovery science
#IDSky #ClinMicro #AMR
19.10.2025 14:18 — 👍 5 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0

Aftonbladet
Greta Thunberg: “Israeli soldiers hit, kicked, starved, and tortured me”
• They placed a flag next to me, and anytime the flag touched me, they kicked me
• Whenever I raised my head to look at Ben-Gvir, I was kicked
• She was filmed while stripped naked
Aftonbladet: tinyurl.com/a33vxatc
15.10.2025 16:44 — 👍 3075 🔁 1692 💬 60 📌 175
#EuropeanResearchersNight is starting early in some countries!
Today, from 11:00 to 16:00, Randi Bertelsen's team will be at the Research Square at Festplassen in Bergen.
Her stand is called ''Puss, puss for friske lunger'' 🦷 🫁 🪥 🔬 🦠
More info: bit.ly/46uUi0v
20.09.2025 07:01 — 👍 8 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0
Annual Norwegian NORM/NORM-VET report released.
Norway’s strict antibiotic policies pay off. Record-low use in humans & animals, and some of Europe’s lowest #AMR rates. But ESBL & VRE are on the rise, so vigilance is vital.
www.unn.no/4a675d/sitea...
16.09.2025 17:34 — 👍 34 🔁 12 💬 0 📌 1
X-Mapper 🦠🧬🧪 - a sequence aligner developed for microbes, now on Bioconda! 🚀
• 11–24× fewer suboptimal alignments (same for human genome)
• 3–579× lower inconsistency
• improves on ~30% of reads aligned to non-target species
github.com/mathjeff/map...
bioconda.github.io/recipes/x-ma...
#microsky
15.09.2025 02:32 — 👍 47 🔁 23 💬 4 📌 0
Beautiful work 🎉 that resolved a long standing question: tumor microbiome, do they exist?🦠🧪 #microbesky
13.09.2025 16:19 — 👍 58 🔁 13 💬 3 📌 0
When using ARG databases, it is much better to have a low number of false positives, then to identify every gene under the Sun as a potential ARG.
My preferred options are ResFinder and CARD (with the latter having some entries that are probably better considered housekeeping genes)
20.08.2025 10:29 — 👍 26 🔁 3 💬 3 📌 1

GitHub - bluenote-1577/skani: Fast, robust ANI and aligned fraction for (metagenomic) genomes and contigs.
Fast, robust ANI and aligned fraction for (metagenomic) genomes and contigs. - bluenote-1577/skani
skani v0.3.0 is released. github.com/bluenote-157...
- 30-40% potential reduction in memory with approximately the same runtime.
- Breaking changes to indexing and searching databases
Calculate ANI for contigs, genomes -- even search > 140k genomes. Pre-indexed GTDB-R226 available for download.
13.08.2025 14:19 — 👍 42 🔁 18 💬 0 📌 0
Genome assemblies for a respiratory metagenomics positive control | ARTIC network - pathogen genomics from sample to response
Interested in respiratory metagenomics? We assembled nearly all of the virus genomes in a respiratory verification panel manufactured by ZeptoMetrix.
Blog: artic.network/2025-07-26_p...
Assemblies: github.com/bede/zmrp
@scalene.bsky.social @pathogenomenick.bsky.social @articnetwork.bsky.social
12.08.2025 08:14 — 👍 11 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Likewise! Optimal collaboration environment! A banger!
06.08.2025 07:28 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
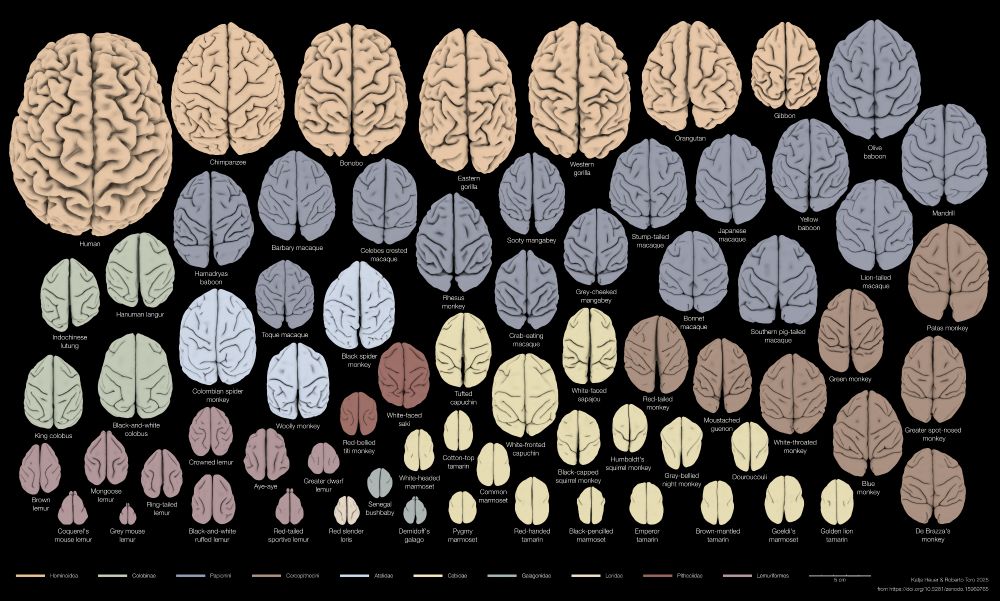
Brain Surfaces of 70 primate species
1
To predict the behaviour of a primate, would you rather base your guess on a closely related species or one with a similar brain shape? We looked at brains & behaviours of 70 species, you’ll be surprised!
🧵Thread on our new preprint with @r3rt0.bsky.social , doi.org/10.1101/2025...
27.07.2025 17:26 — 👍 497 🔁 225 💬 15 📌 26
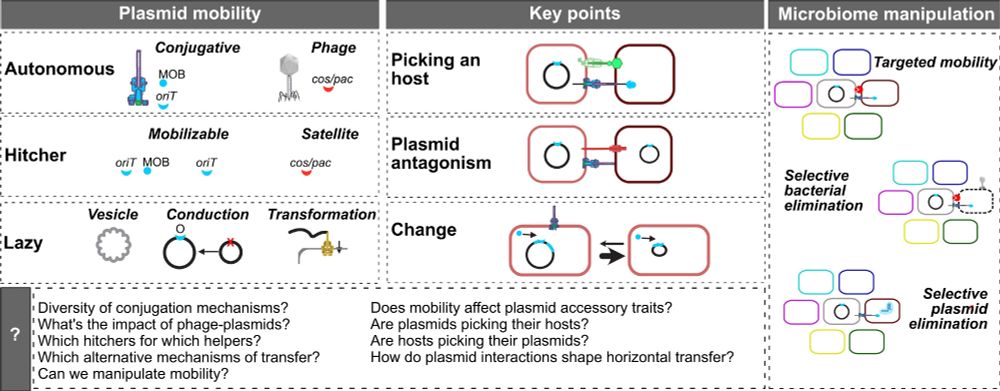
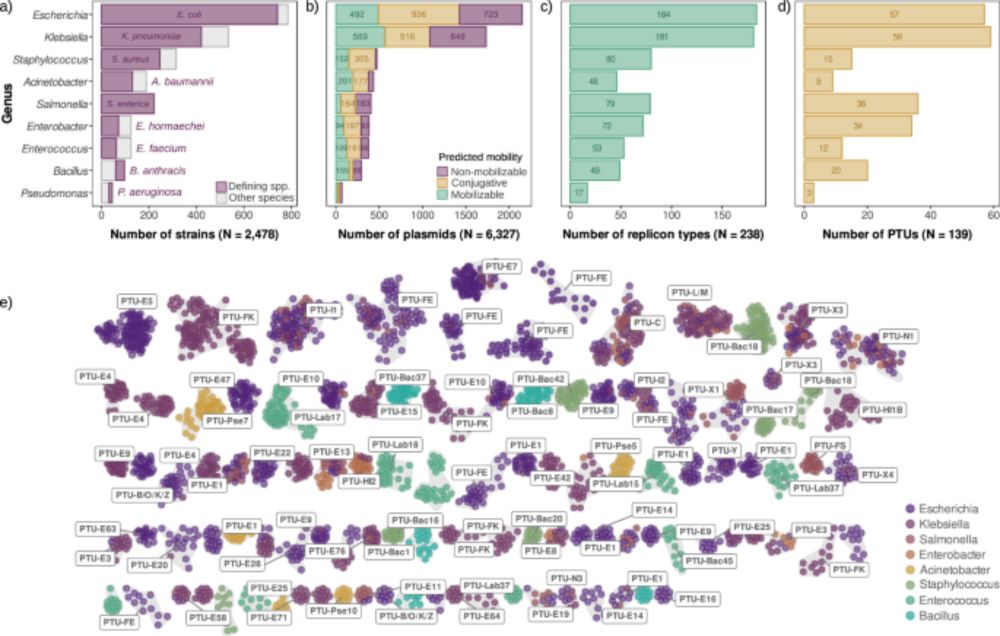
graphical abstract of the article the extended mobility of plasmids
Here's our new broad review on the extended mobility of plasmids, about all mechanisms driving and limiting their transfer. From conjugation to conduction, phage-plasmids to hitchers, molecular to evolutionary dynamics, ecology to biotech. The state of affairs. 1/9 academic.oup.com/nar/article/...
23.07.2025 07:35 — 👍 184 🔁 93 💬 4 📌 9

No, AlphaFold has not completely solved protein folding
Biology is hard. Yes, even for AI.
Interesting overview of the limitations of AlphaFold. As with all AI tools, try not to get hit by the hype-train. open.substack.com/pub/clauswil... (h/t @steveroyle.bsky.social)
14.07.2025 13:43 — 👍 18 🔁 8 💬 0 📌 0
Deacon: fast sequence filtering and contaminant depletion https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.06.09.658732v1
13.06.2025 01:46 — 👍 7 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 1
Physician-scientist at UC San Diego, Microbiology, Immunology, Novel Drug and Vaccine Discovery, #IDSky, Mentoring and Supporting STEM Career Development.
Enjoy exploring the outdoors, world cultures, sports, comedy, community.
http://nizetlab.ucsd.edu
Temerty Professor of Modern European History, Munk School, University of Toronto; Permanent Fellow, IWM Vienna; Emeritus Levin Professor, Yale. Author of "On Freedom," "On Tyranny," "Our Malady," "Road to Unfreedom," "Black Earth," and "Bloodlands"
A microbiologist 🦠& bioinformatician 🧬 uncovering diverse microbial mechanisms via AI ✨. A rising assistant professor @NTU Singapore. With data in the cloud, the sky is the limit! Check out our lab website :) https://genomiverse.net/
microbial ecology, metagenomics, science policy and funding.
Ph.D. in systems & computational biology (2024)
Predoctoral researcher at evodynamics lab in Madrid.
Bacterial and plasmid evolution 🫧🧬💻
We study Antibiotic Resistance Ecology and Evolution · Ramón y Cajal University Hospital · Madrid · www.evodynamicslab.com
Macrobe qui aime les microbes
http://www.shapirolab.ca/
Computational biology lab focusing on microbiomes in the human gut and the environment
Homepage: https://www.bork.embl.de/
Mastodon: https://mstdn.science/@BorkLab
Forfatter og stortingsrepresentant for Rødt (Rogaland). Siste bok: «Pabbi» (2024).
Located at the University of California-Berkeley at the Innovative Genomics Institute.
Purveyors of Microbial Ecology, Bioinformatics, & Nanogeoscience.
Reposts or likes≠endorsements.
https://www.banfieldlab.com/
Research fellow in clinical metagenomics at University College London
Virology with a side-order of human evolution. Currently on maternity leave.
Semi-informed molecular biologist & recovering football coach / Research Professor / Microbial Genomics / Evolution / AMR /
/ https://www.fhi.no / www.haploid.no
Waitress turned Congresswoman for the Bronx and Queens. Grassroots elected, small-dollar supported. A better world is possible.
ocasiocortez.com
Infectious Diseases doctor (at UCLH) and academic (at UCL). Research focuses on immune responses to TB and leprosy, but I'm also involved in too many other projects I probably shouldn't be...
Assistant Professor, Department of Microbiology, UT Southwestern. Posts are my own.
Lab Website: forsberglab.org
Banner Art: Tamanash Bhattacharya