Delighted to see our work on the impact of drought on the oak microbiome featured on the cover of @cp-cellhostmicrobe.bsky.social
Link to the article below this post 👇🏻
11.02.2026 17:35 — 👍 31 🔁 10 💬 4 📌 4
Anyone know where you can buy acrolein for electron microscopy? Apparently it must be stabilised with either hydrochinon or hydroquinon-monomethylether 🫠
03.02.2026 13:47 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
I would caution this since GTDB placement isn't enough taxonomic evidence to propose a new species, multiple lines of evidence should be obtained to corroborate the proposed taxonomy.
02.02.2026 04:50 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Hmmm I would probably go with "many are proposed species in GTDB, represented by only MAGs and for which no cultured representative exists". Although GTDB also contains SAGs so genomes instead of MAGs might be better
01.02.2026 17:01 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We do GENUS sp. as Paul suggests, it highlights it's an unknown species and gives the taxonomic assignment
01.02.2026 16:42 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

This Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) program is funded by the National Science Foundation to create "points of entry" for students interested in research. Students apply from across the country to spend 10 weeks in Bozeman, Montana this summer (May 26, 2026 - August 1, 2026). Admitted students are paired with a faculty mentor, who serves as an advisor for a student's summer project. Each student receives a stipend ($7000 for 10 wks). Travel compensation, room, and board are also provided.
Our program leverages MSU’s unique microbiology expertise, focusing specifically on microbes living with little or no oxygen (like those in the hot springs of nearby Yellowstone). Low oxygen microbes are essential to human and ecosystem health. They influence (or control) such processes as the breakdown of food in the GI tract, removal of toxins from our bodies and the environment, and production of greenhouse gases. They are also models for understanding the origins of life on this planet, and the potential for life on other planets.
A key goal of our program is to recruit students from schools with limited research infrastructure. Being in Montana, a state with a vibrant Native American community, we are particularly interested in applications from students at tribal colleges. However, ANYONE with an interest in microbiology - or biology/science in general - can and should apply.
If willing and able, please share/tweet/spread the word far and wide. Applications are due February 14, 2026. Full details can be found through our website http://www.montana.edu/mbi/reu/



Friends, please help spread the word about our microbiology REU program at Montana State University.
www.montana.edu/mbi/reu/
Each student receives a stipend ($7000 for 10 wks). Travel compensation, room, and board are also provided.
Details in the attached pic--Feb 14 deadline
🧫🧪🦠#microsky
28.01.2026 19:45 — 👍 62 🔁 84 💬 3 📌 0
Ok, then I think BacDive is probably your best bet. I think they have an API and also link to alternative strain IDs that have been used along with genomes for the strains. Lorenz who heads it is also super helpful 😁 good luck!
28.01.2026 20:02 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Microbes in total or just bacteria? DSMZ have done the best job I know off for creating resources like BacDive or StrainInfo, but I'm pretty sure they are bacteria specific and might lack strains that weren't ever deposited in a culture collection
28.01.2026 19:41 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
The pre print of my PhD research is out! 📣 Check it out for some cool results on high-throuhput microbial isolation, #SynComs and #Tree #Microbiome 🌳🧫
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
#PhDone 💯
19.11.2025 20:39 — 👍 11 🔁 6 💬 0 📌 0
Come and do a PhD with me! Are you looking for a PhD project at the intersection of #microbiome and #food science? This project, in collaboration with ADM milling, will explore novel microbiome targeted food ingredients
14.10.2025 16:01 — 👍 2 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0
Bakta generally, but not tried with funkier genomes
05.10.2025 05:59 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

New article on equitable reuse of public sequencing data, published in @natmicrobiol.nature.com!
Led by the Data reuse core team @lhug.bsky.social @environmicrobio.bsky.social Cristina Moraru, @geomicrosoares.bsky.social, @folker.bsky.social and with Anke Heyer and The Data Reuse Consotrium!
26.09.2025 19:34 — 👍 35 🔁 20 💬 0 📌 4

Next we wanted to create SynComs that allow mechanistic studies of a disease, so we chose IBD. By comparing healthy and IBD metaGs we selected a SynCom for each. In germ-free mice we showed the IBD SynCom caused increased inflammation. 6/7
24.09.2025 13:22 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
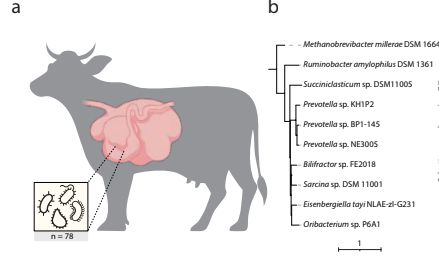
Using MiMiC2 we were able to create SynComs for a range of ecosystems, including the rumen of cows! We wondered our function-based approach would select a methanogen, since they are sub-dominant, but critical members. It did, along with diverse other members! 5/7
24.09.2025 13:22 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

This comparison is done against ALL input metaGs, not a single metaG, allowing the SynComs to capture the variability within an ecosystem. Strains are also selected together, reducing functional redundancy between each other. 4/7
24.09.2025 13:22 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

MiMiC2 addresses this by reducing both metaGs and isolate genomes down to the protein families they encode. Next, we can select strains that functional match our metaGs of interest. 3/7
24.09.2025 13:22 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
SynComs are usually put together based on expert curation, but microbiota are functionally complex, and capturing that complexity in only a few strains is hard. Hence the idea "what if we used metagenomes (metaGs) to select the correct strains?" 2/7
24.09.2025 13:22 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Professor at UC Davis
Work: evolution, ecology, function & phylogenomics of host-microbiome systems; #openscience;
Other: #birds; baseball; T1D
Lab phylogenomics.me
Pics jonathaneisen.smugmug.com
Links linktr.ee/jonathaneisen
TED go.ted.com/6WPm
🦠🌱Aiming to structure the European research community on beneficial root-associated microorganism interactions 🇪🇺👩🏻🌾
Metabolomics Specialist at the @ZimmermannLab.
📍Heidelberg, Germany
🇧🇷
Group Leader @University of Bern
Associate Editor in Frontiers for Young Minds
Gut microbiota researcher
Microbiome 🦠 data science 📈 computational biology 💻 and other crazy stuff at the amazing Maier Lab in Tübingen. He/Him.
Junior Professor @RWTH Aachen, Germany.
Biophysics of host-microbe interactions 🦠🔬👩🔬 through the lens of bacterial motility
Bioinformatician & web software developer 🇫🇮
Microbiology x population genetic
Post-doctoral fellow in the Genome Institute of Singapore.
Nucleic Acids Research (NAR), from Oxford University Press, publishes the results of leading-edge research into physical, chemical, biochemical and biological aspects of nucleic acids and proteins involved in nucleic acid metabolism and/or interactions
Microbiologist & Plant physiologist. Symbiosis, Mycorrhizae, Genomics, Plant-microbe interactions, Microbial ecology. Views are my own
https://mycor.nancy.inra.fr/IAM/?page_id=10523
Ecologist studying plant microbiota assembly and microbiome engineering / Seeds / SynComs 🦠/ Sustainable agriculture 🌾
Researcher at INRAE, France
http://mariesimonin.com/
Marie Skłodowska-Curie fellow at ISEM Montpellier. Physicist studying complex biological systems - ecosystems, cancer, immune networks and microbial communities.
30+ scientists from 8 leading research institutions in Austria with one vision: unlock the microbiome's potential for planetary health. 🌍🧫🦠
Follow us for exciting updates on environmental🌳, medical 🩺, and methodological 🔬 microbiome research.
Developing data intensive computational methods • PI @ Seoul National University 🇰🇷 • #FirstGen • he/him • Hauptschüler
synthetic/engineering biology, computational biology group leader @UCL. Microbial communities, control, self-organisation, patterning, and bio-computation. You might know me as Sandy. #newPI he/him
The International Society for Microbial Ecology is a non-profit association and owner of the ISME Journal and ISME Communications.
Next symposium #ISME20 in Auckland, New Zealand in August 2026.
Associate Professor www.thibaultlab.com at Nanyang Technological University Singapore 🇸🇬. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in health and diseases • Co-PI Mechanobiology Institute • MBoC Assoc Editor • University of Toronto alumni
A microbiologist 🦠& bioinformatician 🧬 uncovering diverse microbial mechanisms via AI ✨. A rising assistant professor @NTU Singapore. With data in the cloud, the sky is the limit! Check out our lab website :) https://genomiverse.net/